Smart IDE for working with databases
On-the-fly coding assistance
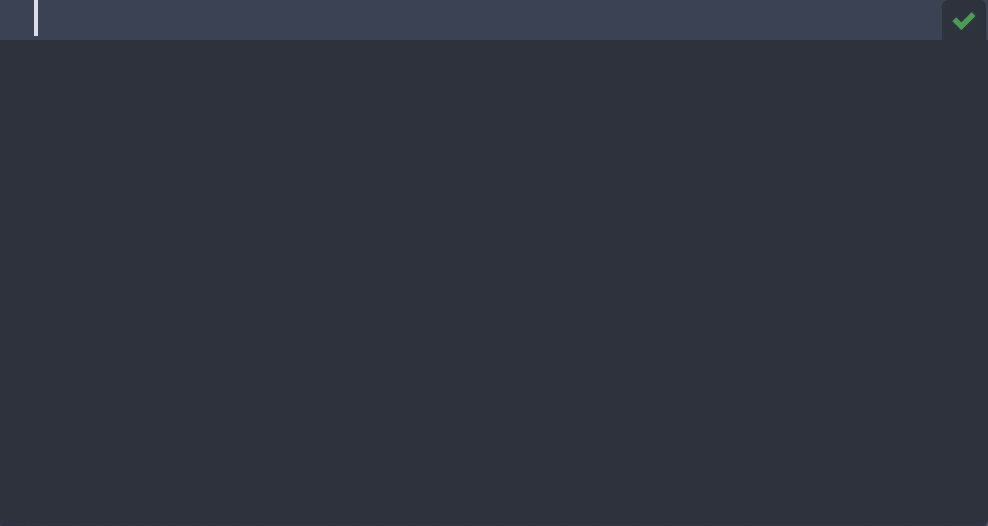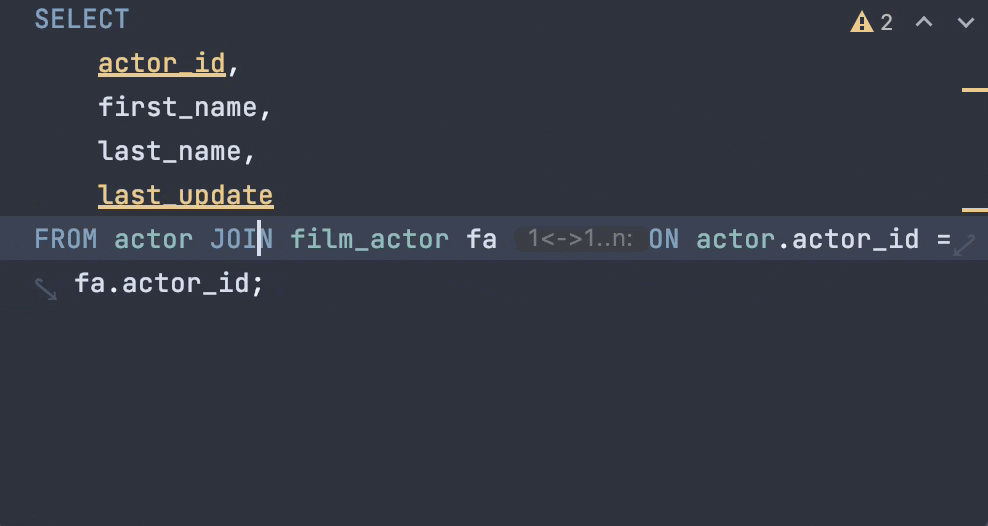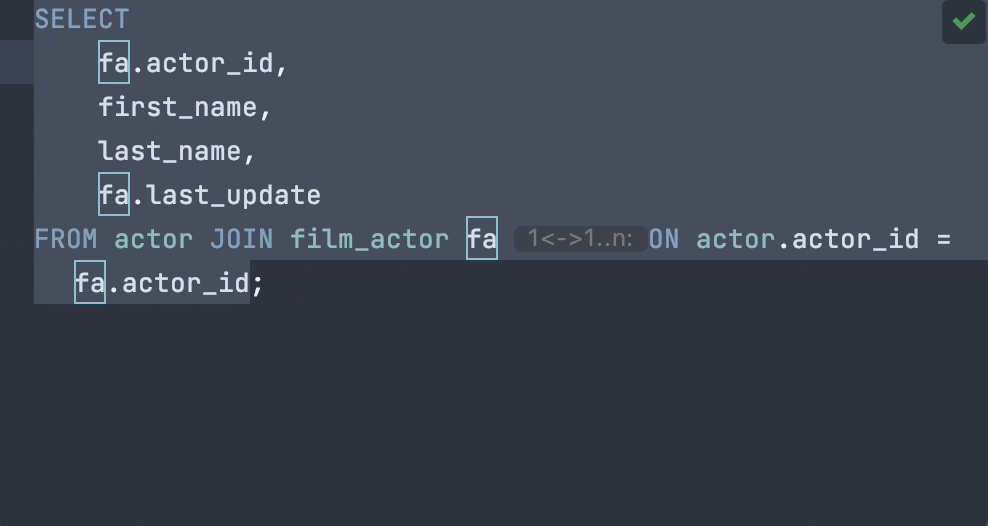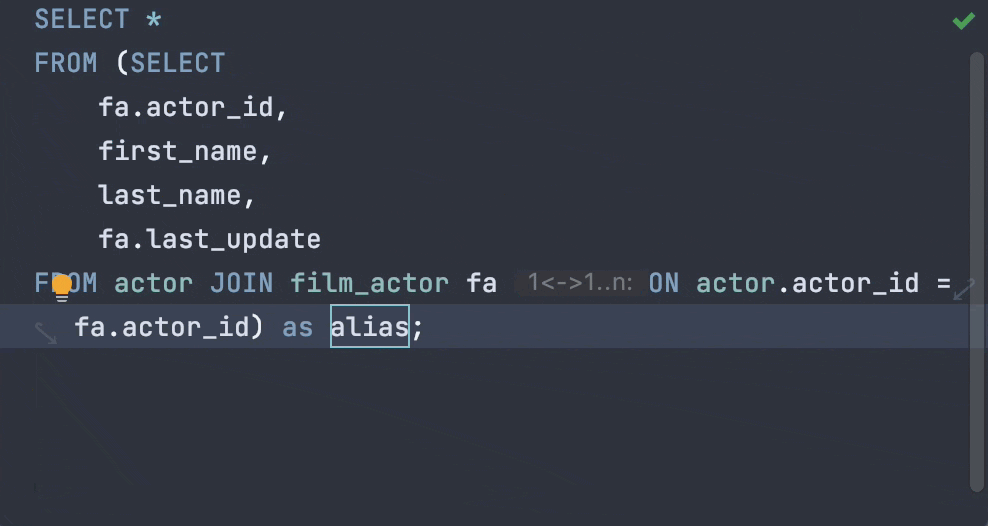
Coding is what most developers spend the bulk of their time doing in an IDE. DataGrip’s smart features like auto-completion, code snippets, formatter, refactorings, and various intention actions help you code faster. Concentrate on the logic, not on what you need to type!
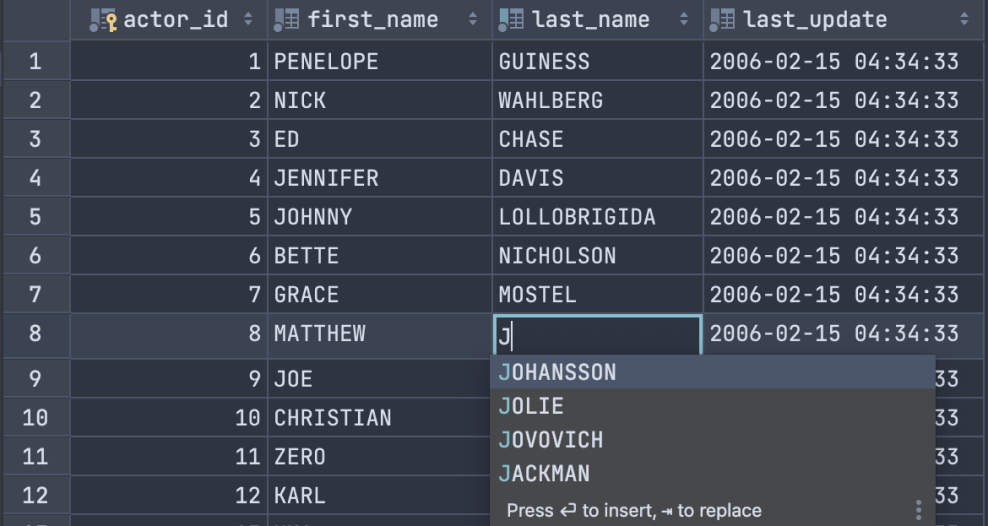
Smart data editor
DataGrip provides a smart data editor with the ability to add, delete, and change data. All of the queries DataGrip runs during data updates can later be found in its SQL log so you can perform the same changes against another database.
DataGrip’s data extractor supports many formats including SQL INSERTS, SQL UPDATES, CSV, JSON, XML, and others. The mechanism is customizable so you can create your own formats, such as Markdown or just plaintext.
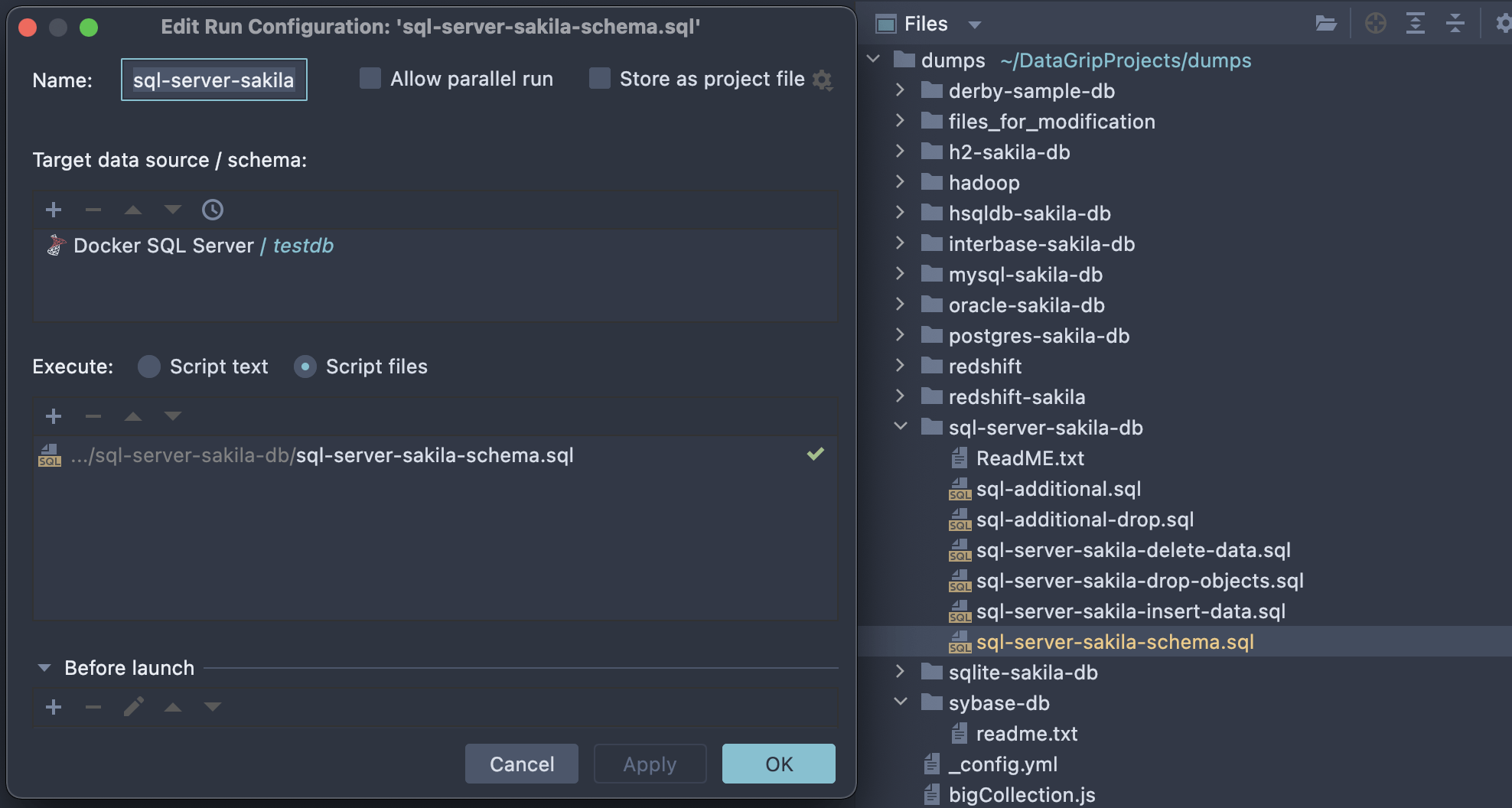
Convenience when working with files
If you work with SQL files stored on your computer, then you might already have a working directory with tons of scripts. DataGrip provides a handy interface for that. Attach folders from your computer, associate them with data sources, run scripts against several databases, or even use built-in Git integration!

Fully customizable
The DataGrip interface can be customized in many ways. You can choose from any of the default color schemes or create your own, mark data sources with different colors, and even customize or set up your own keyboard scheme.
DataGrip for MS SQL Server developers
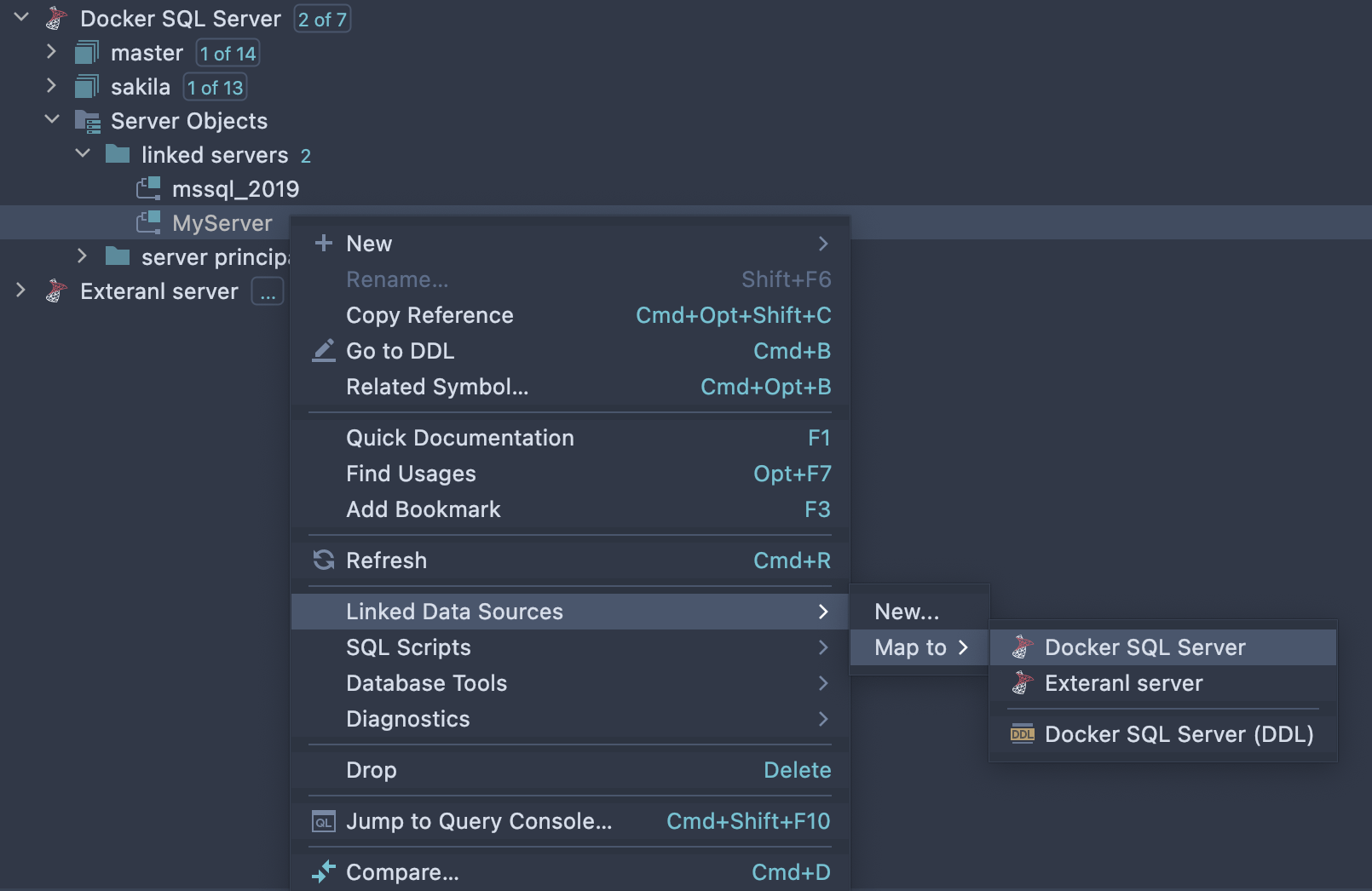
Linked Servers
DataGrip displays Linked Servers in the Database Explorer. You can map your linked server in an SQL Server to any existing data source so that code completion and resolution will work for queries using those external objects.

tSQLt support
tSQLt is a framework for unit testing on Microsoft SQL Server. You can use it to test stored procedures, functions, views, and triggers for a database.
After installation, the tSQLt script creates the tSQLt schema, from which you can run one or more tests and explore the results.
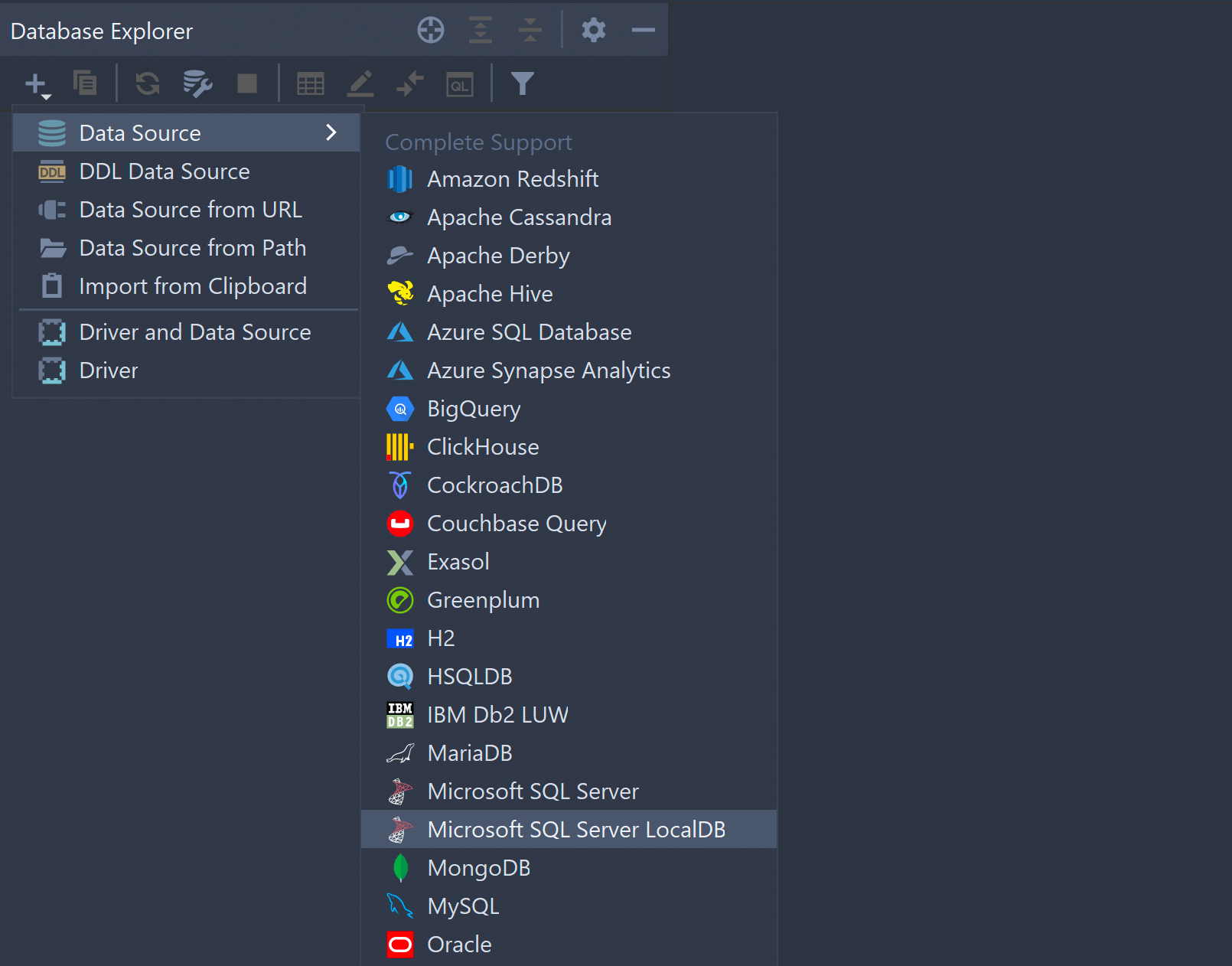
LocalDB support
SQL Server LocalDB has its own dedicated data source type for LocalDB. You only need to set the path for the executable once, in the driver options, and it will be applied for all data sources.
Getting started with DataGrip for MS SQL Server
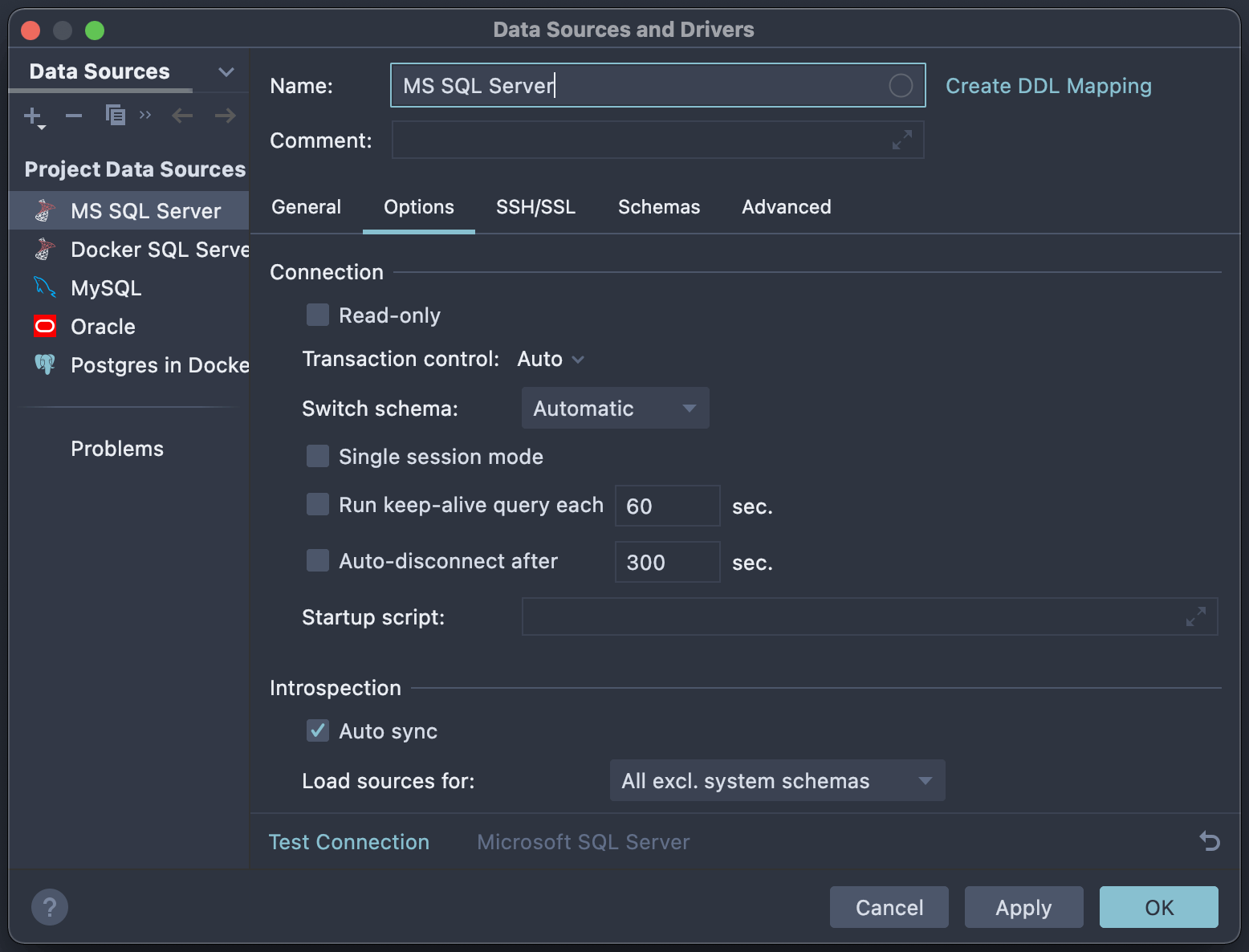
Step 1. Connect to the database
DataGrip uses a JDBC driver to connect to your MS SQL Server database, which will be downloaded automatically when testing the connection. In addition to the main credentials you’ll need in order to connect (such as port, user, and password), you can set several options for the new MS SQL Server data source:
- Mark the data source as read-only. In this mode, every DDL or DML query will be underlined. If you execute it, you will receive a warning notifying you of possible side effects.
- Transaction control is an option that lets you decide whether you want all transactions to be committed automatically or not.
- Run a keep-alive query and auto-disconnect to help you manage connection behavior.
- The startup script is an SQL query which will be run each time you establish a connection.
- Auto-sync determines if the database tree should be updated automatically after running DDL queries.
- SSH/SSL options are also available if needed.
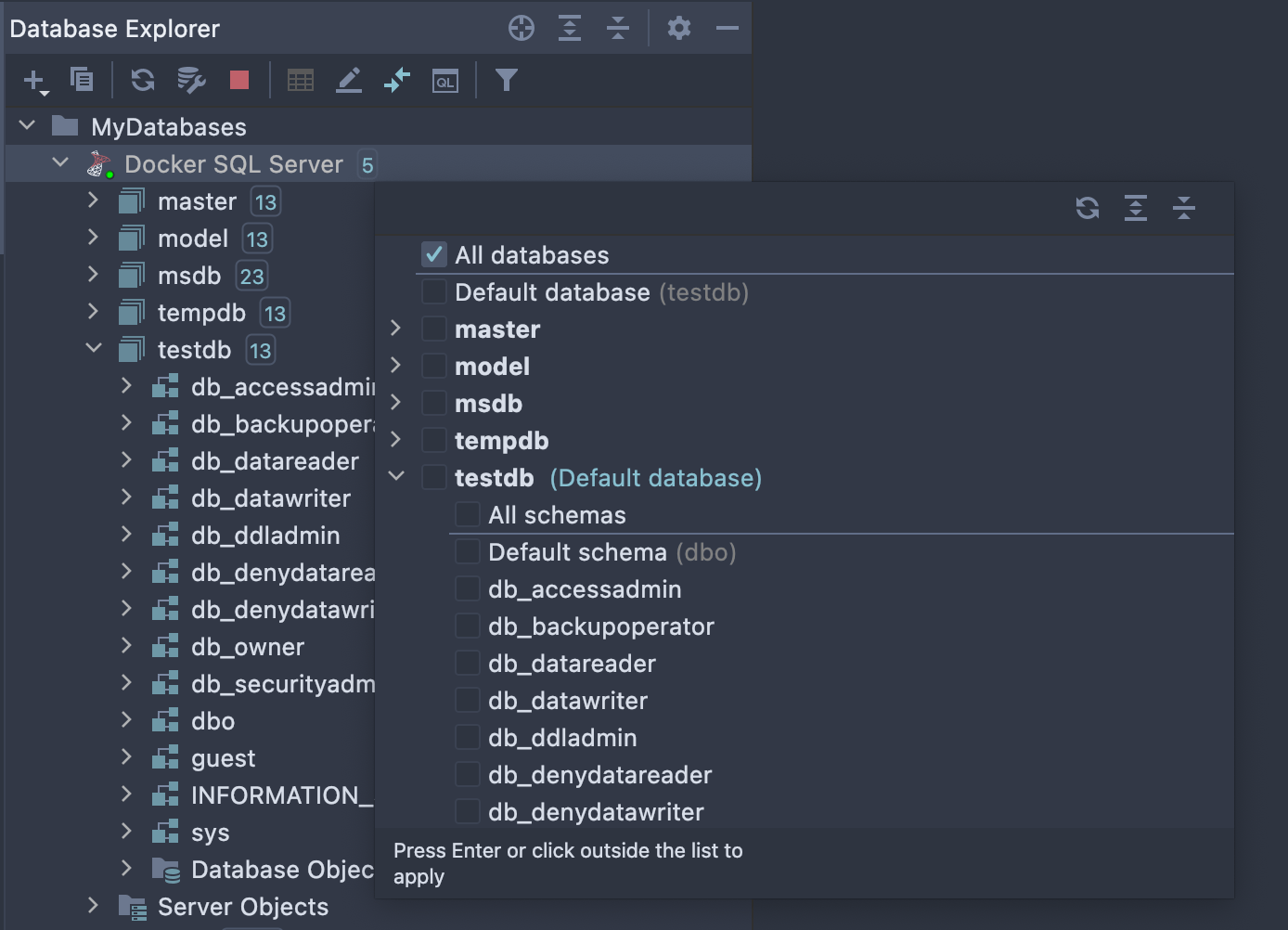
Step 2. Explore database objects
Once you’re connected to your MS SQL Server database, you’ll see the list of objects in the left-hand pane, called the Database Explorer. Here you can filter objects and choose which schemas should be shown.
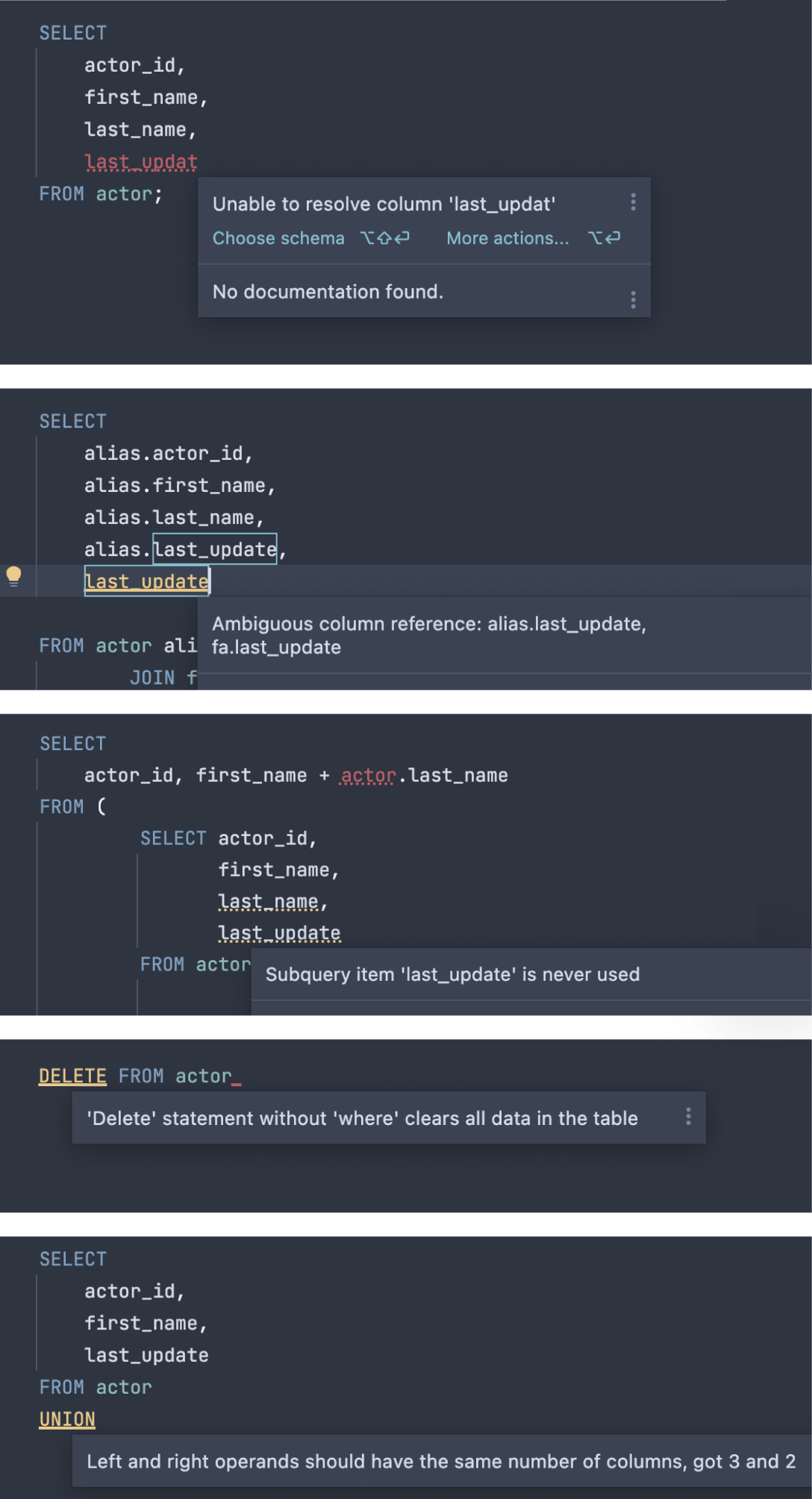
Step 3. Write SQL
DataGrip can help you detect bugs and problems that are likely to arise in your SQL code before you compile and run it. Here are just a few examples of DataGrip coming to the rescue by catching mistakes and bringing them to your attention.