Data connections
Whether you work with CSV files, S3 buckets, or SQL databases, Datalore offers you easy ways to access and query your data from multiple data sources in one notebook.
Watch the Data connections video overview below:
Internal storage
Datalore comes with persistent internal storage for fast access to your notebooks and other work artifacts.

Notebook files
Whether you upload local files and folders or import data by link or download files from code, all the data will be stored in notebook files. When sharing a notebook with collaborators, notebook files will be shared automatically.
Workspace files
Share datasets among multiple notebooks via Workspace files. When working in a shared workspace, you can upload a dataset once and it will become available for every workspace editor.
Database connections from UI
Connect your notebooks to databases right from the editor with a few clicks, and query your data with native SQL cells without passing your credentials to the environment.
Datalore supports user and password authentication for Amazon Redshift, Azure SQL Database, MariaDB, MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, Snowflake, and more. Please contact us via datalore-support@jetbrains.com if you have specific questions about database connectivity.
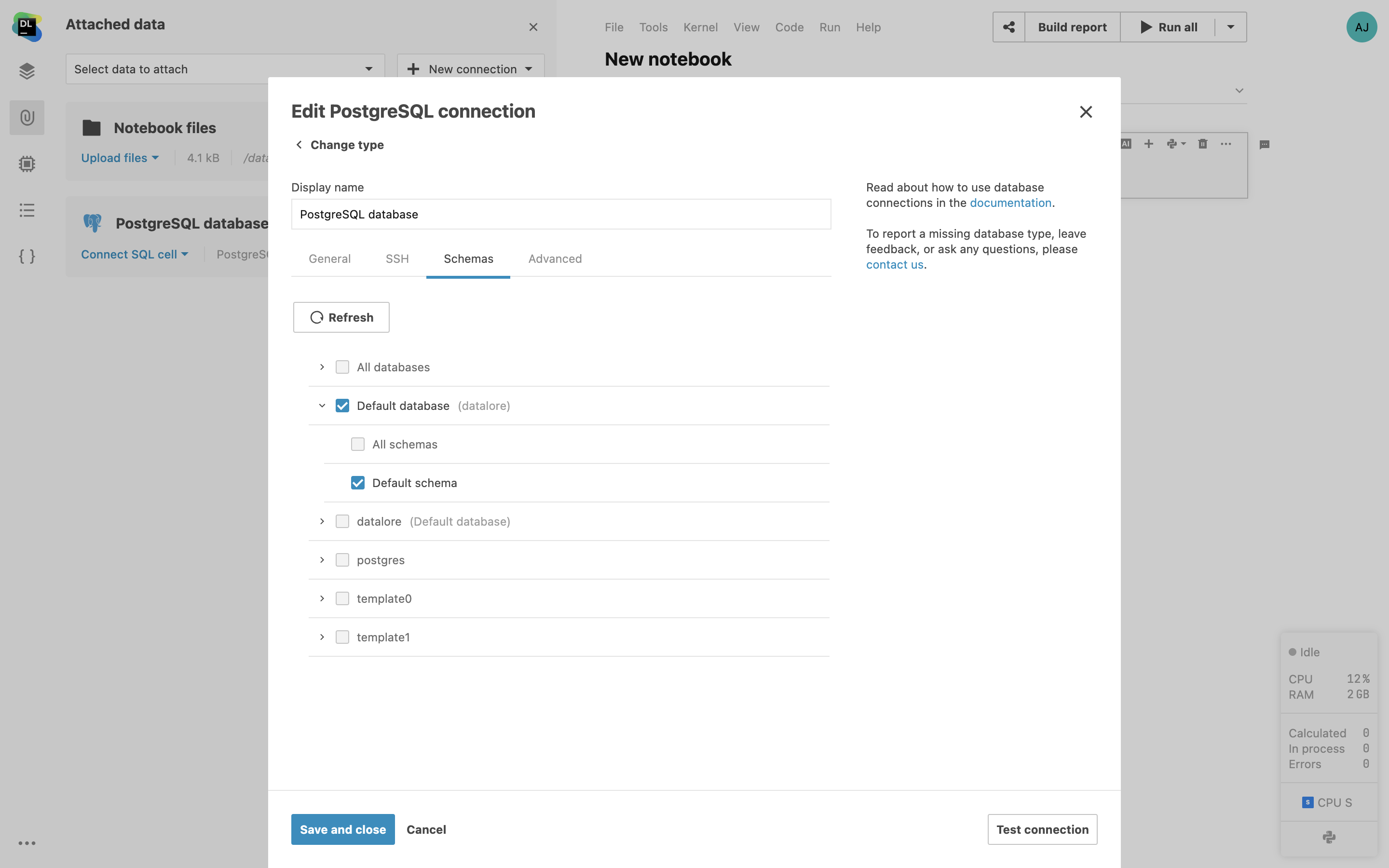
Limiting DB's schema for introspection
Enterprise
Team
Professional
Choose specific database schemas and tables for introspections when creating a database connection in Datalore. This will help speed up the initial introspection and make schema navigation easier.
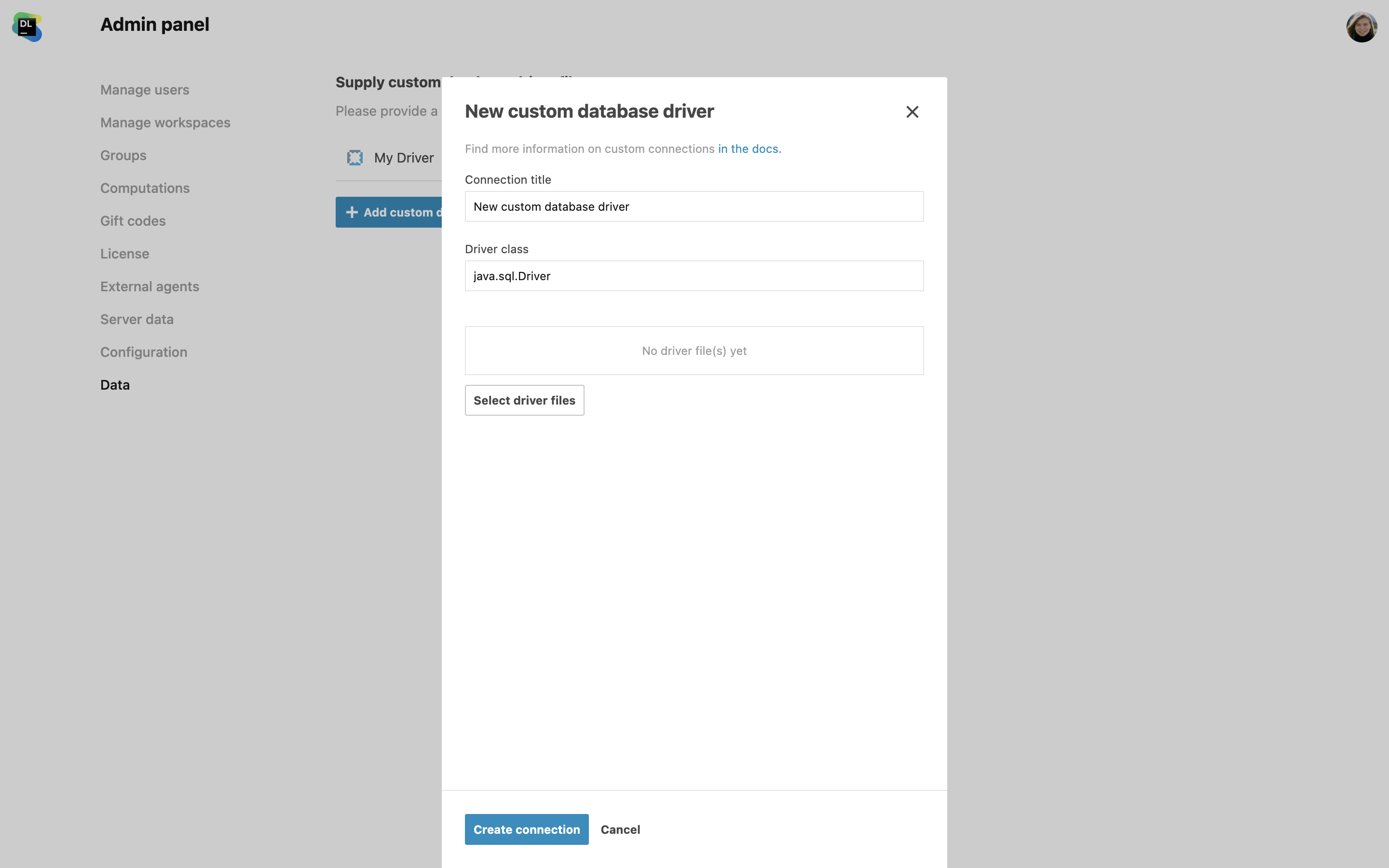
Custom JDBC driver support
Enterprise
Admins can now add custom JDBC drivers to connect to databases that are not natively supported in Datalore Enterprise. Go to Admin panel | Miscellaneous and use the New custom database driver dialog to select and upload driver files from your local system.
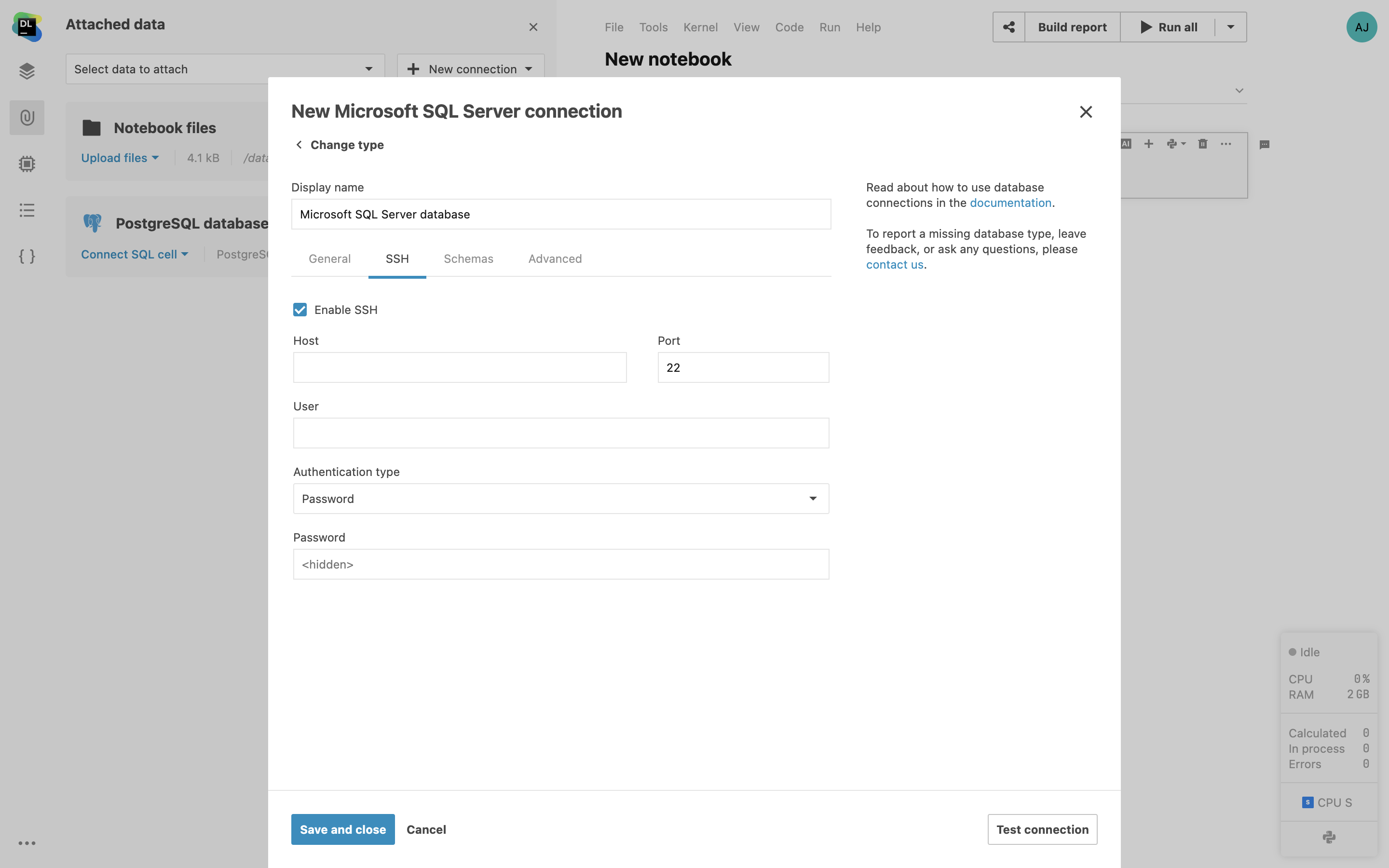
SSH tunneling support
Connect to your remote databases using SSH tunneling in Datalore. This will create an encrypted SSH connection between Datalore and your gateway server. Connecting via SSH tunnels makes it possible to connect to databases that are not exposed to a public network.
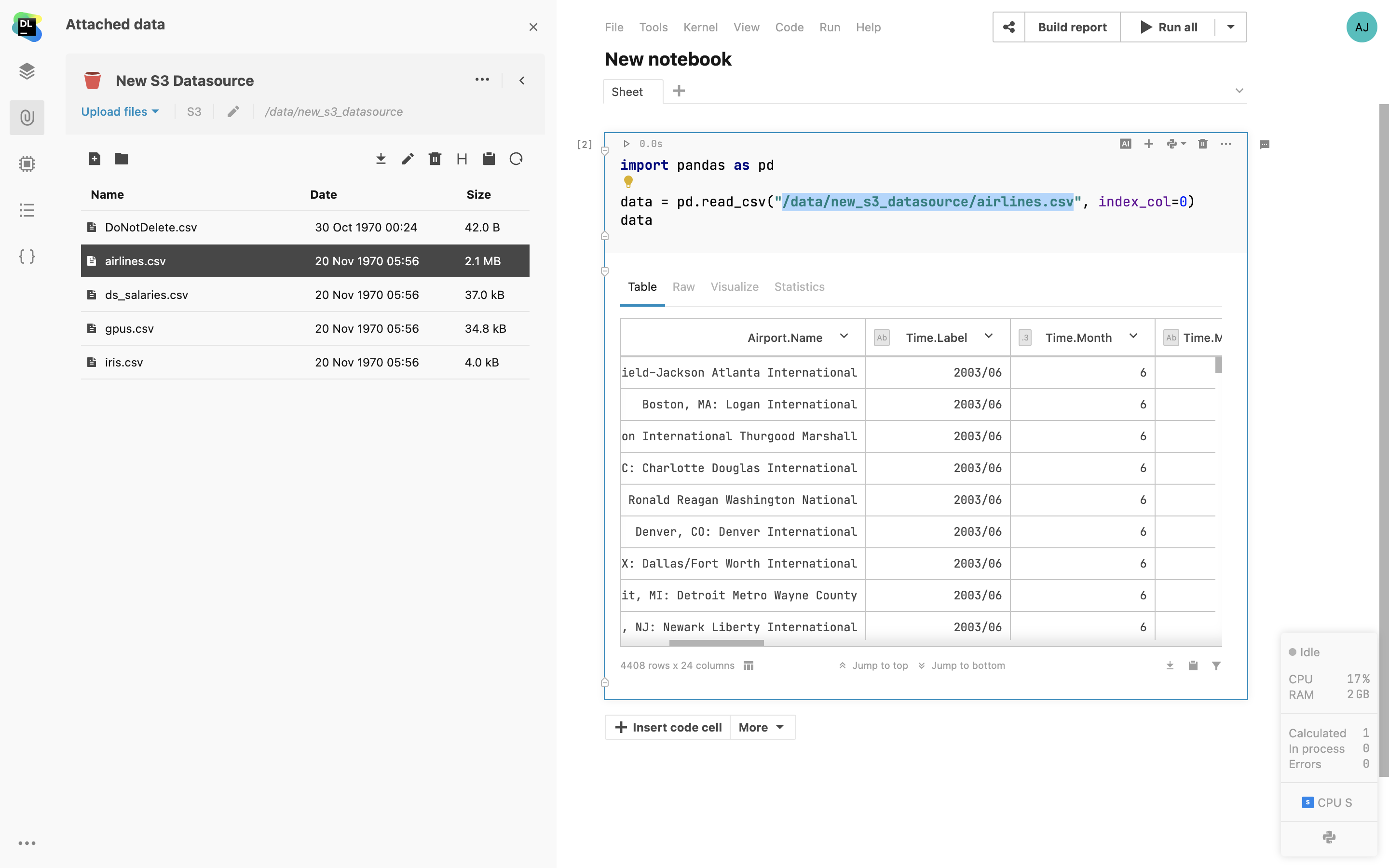
S3 bucket mounting
Mount AWS S3 and GCS buckets as folders directly to the notebook without passing your credentials to the environment.
Data connections from code
Apart from the supported data source connections via the user interface, you can connect any bucket, database, or data storage from code as you would normally with a Jupyter notebook.
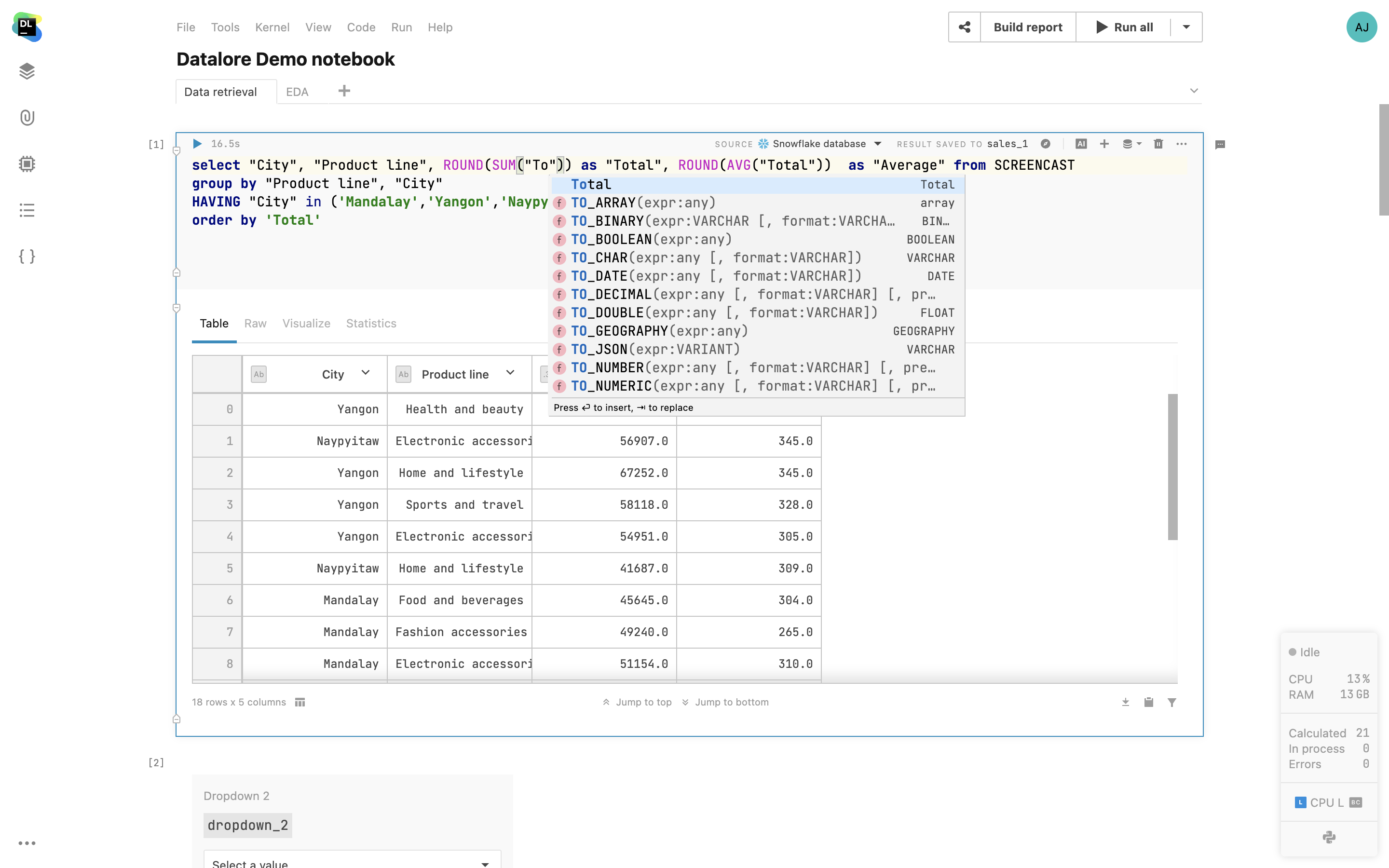
SQL cells
Add native SQL cells to query your database connections. In addition to SQL syntax-highlighting, you get code completion based on the introspected database tables. The query result is automatically transferred to a pandas DataFrame and you can continue working on the dataset in Python.
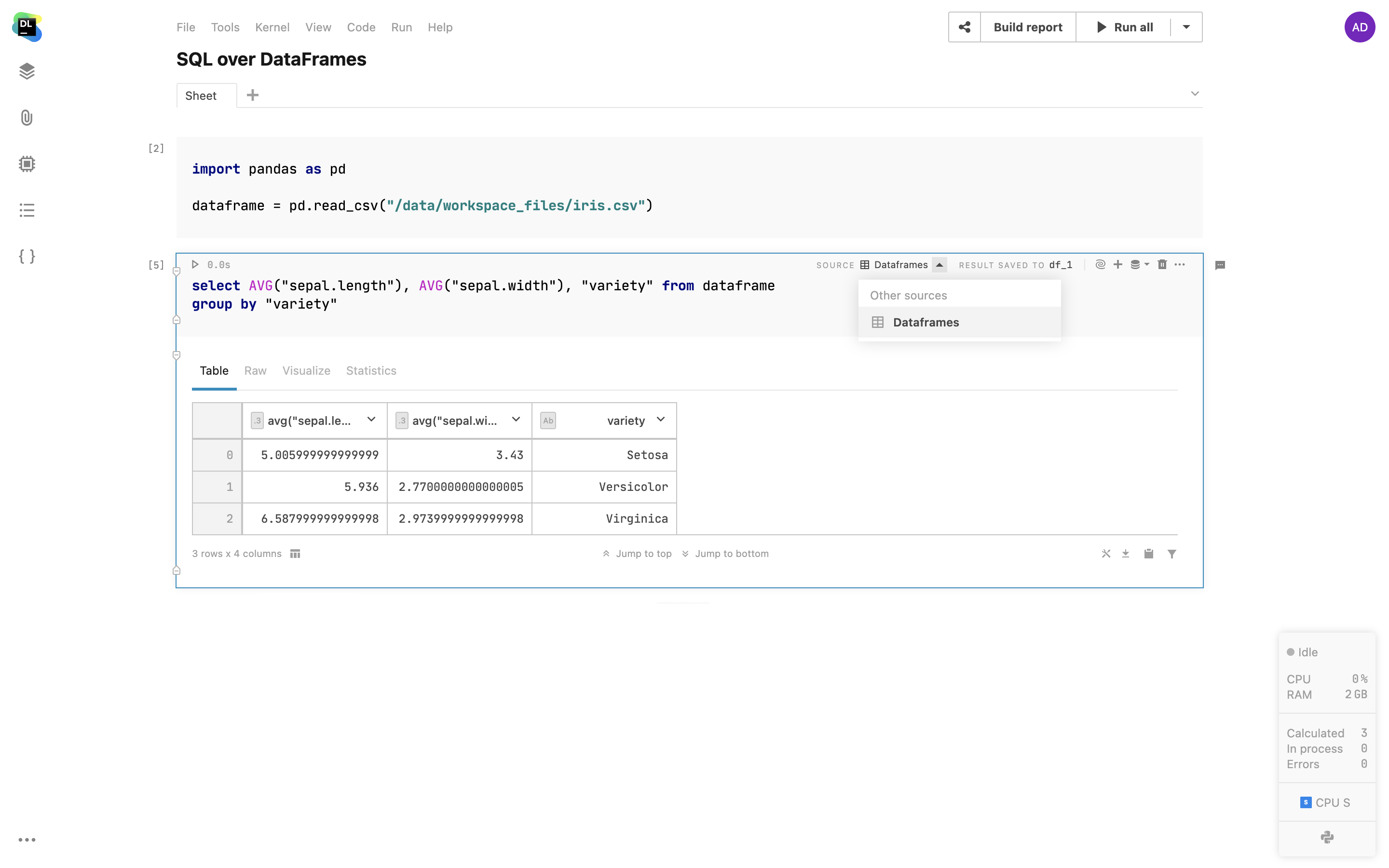
Query DataFrames via SQL cells
Use SQL cells to easily query 2D DataFrames and CSV files from attached documents, just like you would with databases. Simply browse through your notebook’s DataFrames, pick one, and use it as your source for SQL cells. With this feature, you can merge data from various sources into a single DataFrame using SQL or break down complex queries into a sequence of SQL cells.
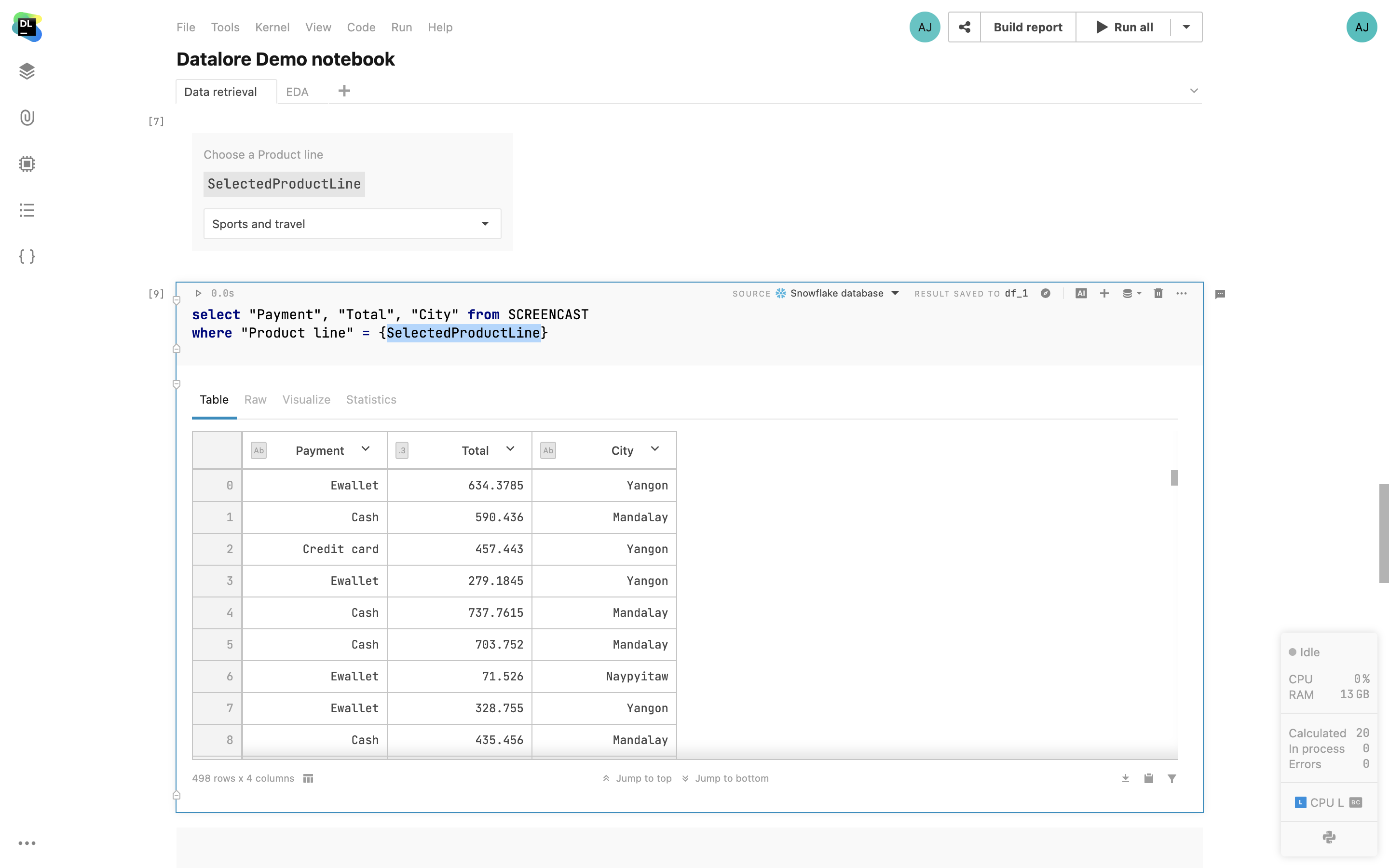
Parameterized SQL queries
Enterprise
Team
Professional
In Datalore, it is now possible to use variables (strings, numbers, booleans, lists) defined in Python code inside the SQL cells. This allows you to build interactive reports with parameterized queries, helps minimize the SQL code written, and presents a better UI for report users.
Work with databases in isolated environments
With this feature, you can work with databases even in isolated environments. Run SQL code without an internet connection, ensuring that the information exchanged between your notebook and the database remains accurate and consistent and minimizing the chances of data corruption or loss.
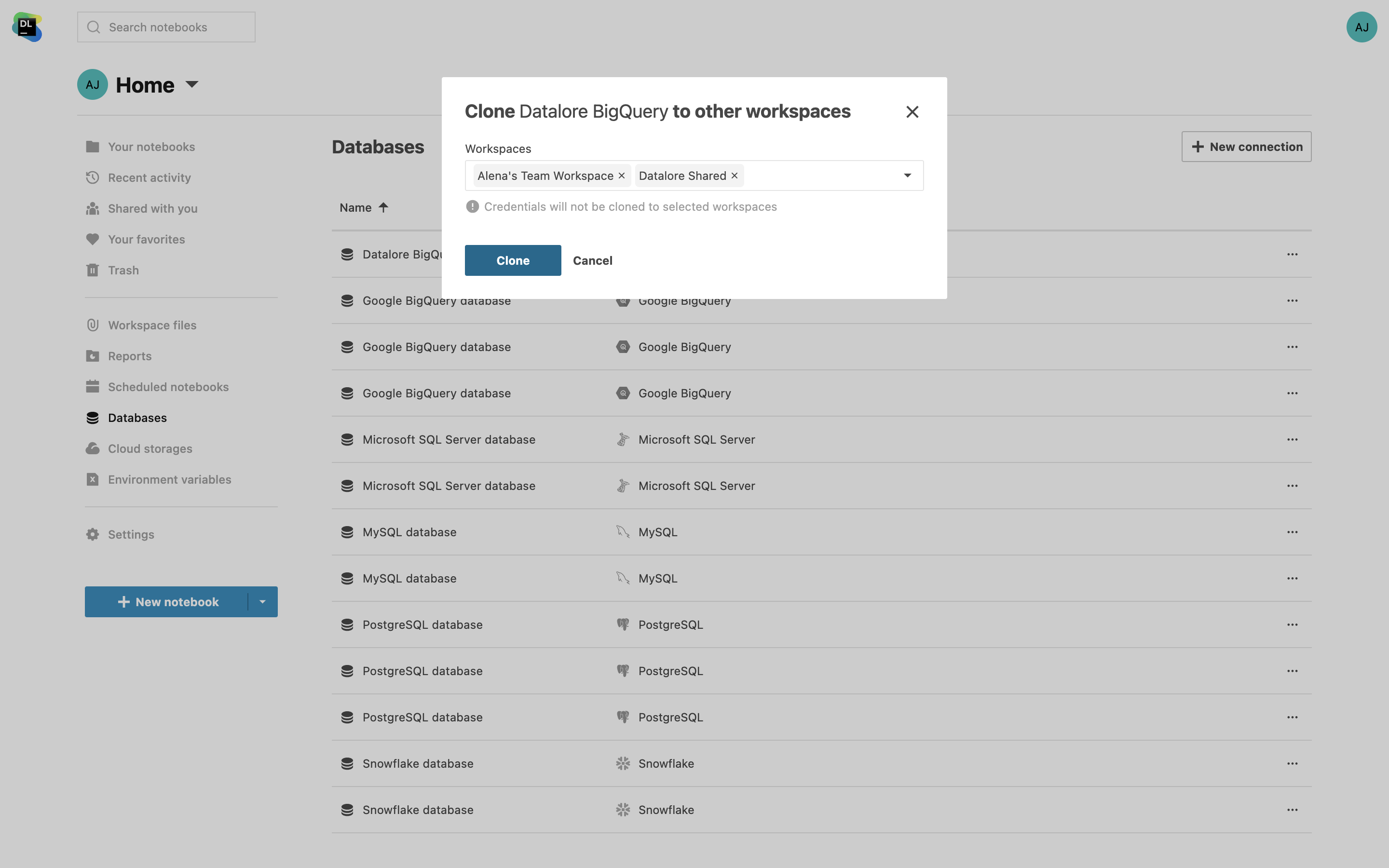
Clone data connections across workspaces
You can now clone database connections from one workspace to another, eliminating the need for repetitive setups. Save time by just copying settings, excluding credentials. You also have the option to select multiple workspaces at once.
SMB/CIFS Storage
Add SMB/CIFS storage to your workspace via the File system view or directly from the notebook interface. Access and modify SMB folder content without leaving the notebook environment.