Quick start: your first task in JetBrains Air
JetBrains Air is an agentic development environment (ADE) that helps developers delegate coding tasks to AI agents while keeping full control of the work. It is designed for developers who work in hybrid human–agent teams.
The user interface is built around two key parts of this workflow: defining a task and reviewing the result.
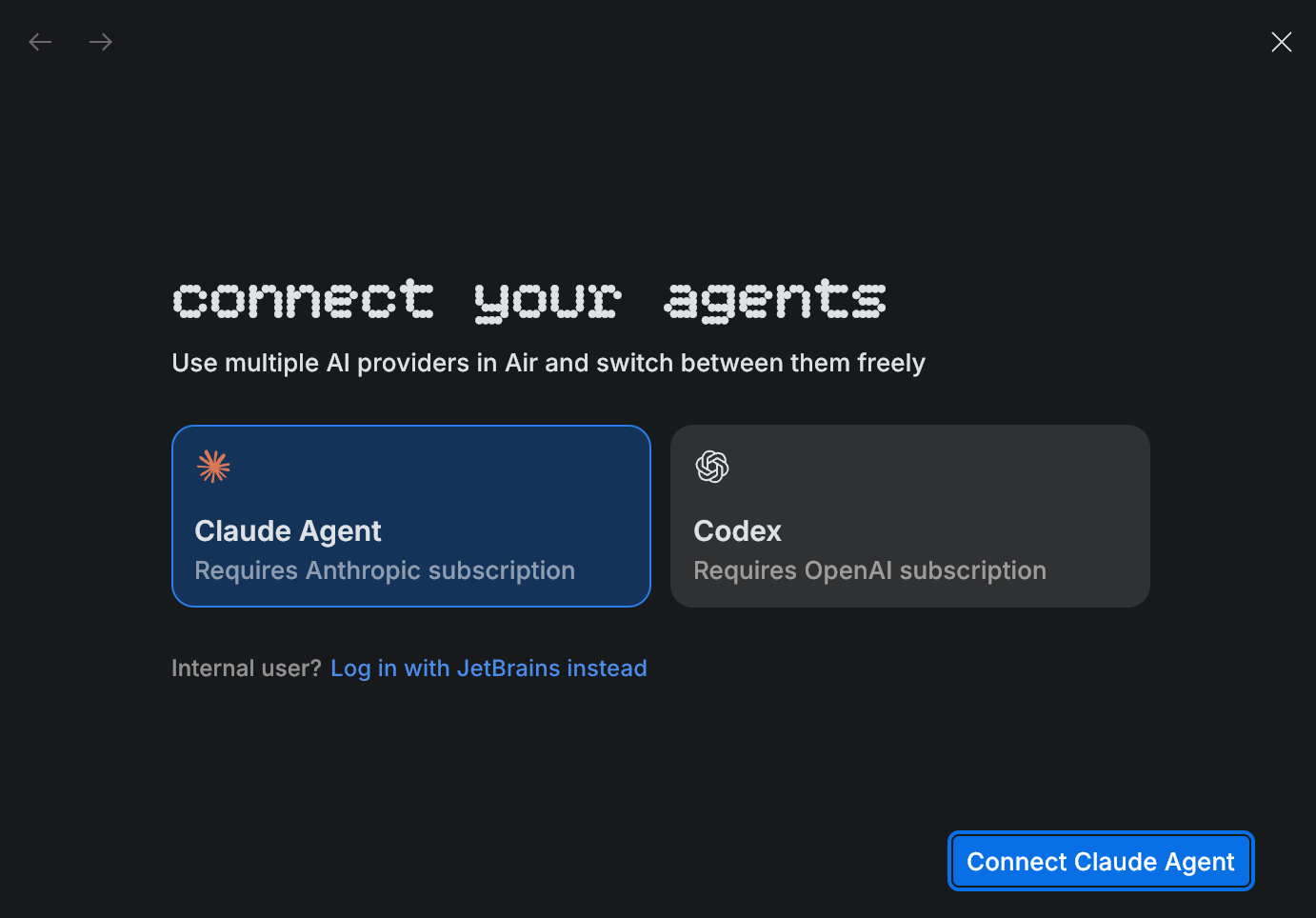
JetBrains Air is available as part of the Preview program and currently supports Claude Agent and OpenAI Codex. It requires an active Anthropic or OpenAI ChatGPT subscription.
How to try JetBrains Air
You can download JetBrains Air for macOS from the official page at air.dev. Support for Windows and Linux is planned for 2026.
First run
When you first run JetBrains Air, you will be prompted to log in to your Claude or OpenAI account.
Open a project
To open an existing local project, click Open and navigate to the project folder on your computer.
To clone a project from Git:
Click Clone from Git.
In the Source URL field, enter the URL of the Git repository.
In the Location field, specify the path where you want to store the cloned repository.

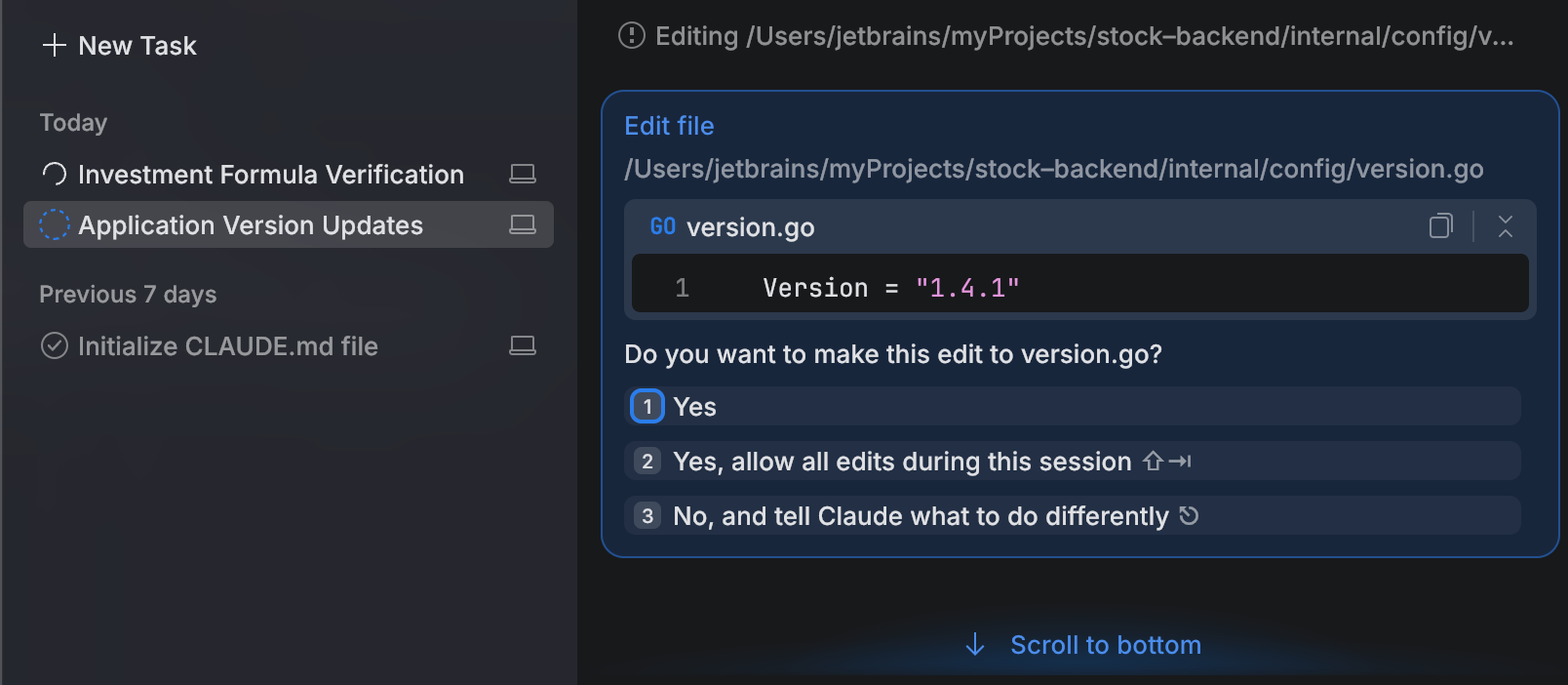
When the workspace opens, JetBrains Air will ask whether you trust the code in the folder. If you click Preview, JetBrains Air functionality will be limited.
For all features to work, JetBrains Air may need to execute project code. Actions like importing the project, running scripts, and executing Git commands can run malicious code if the source is untrusted. Only trust the project if you trust the code authors.

If you trust the code in the folder, click Trust.
You can now start working.
Define a new task
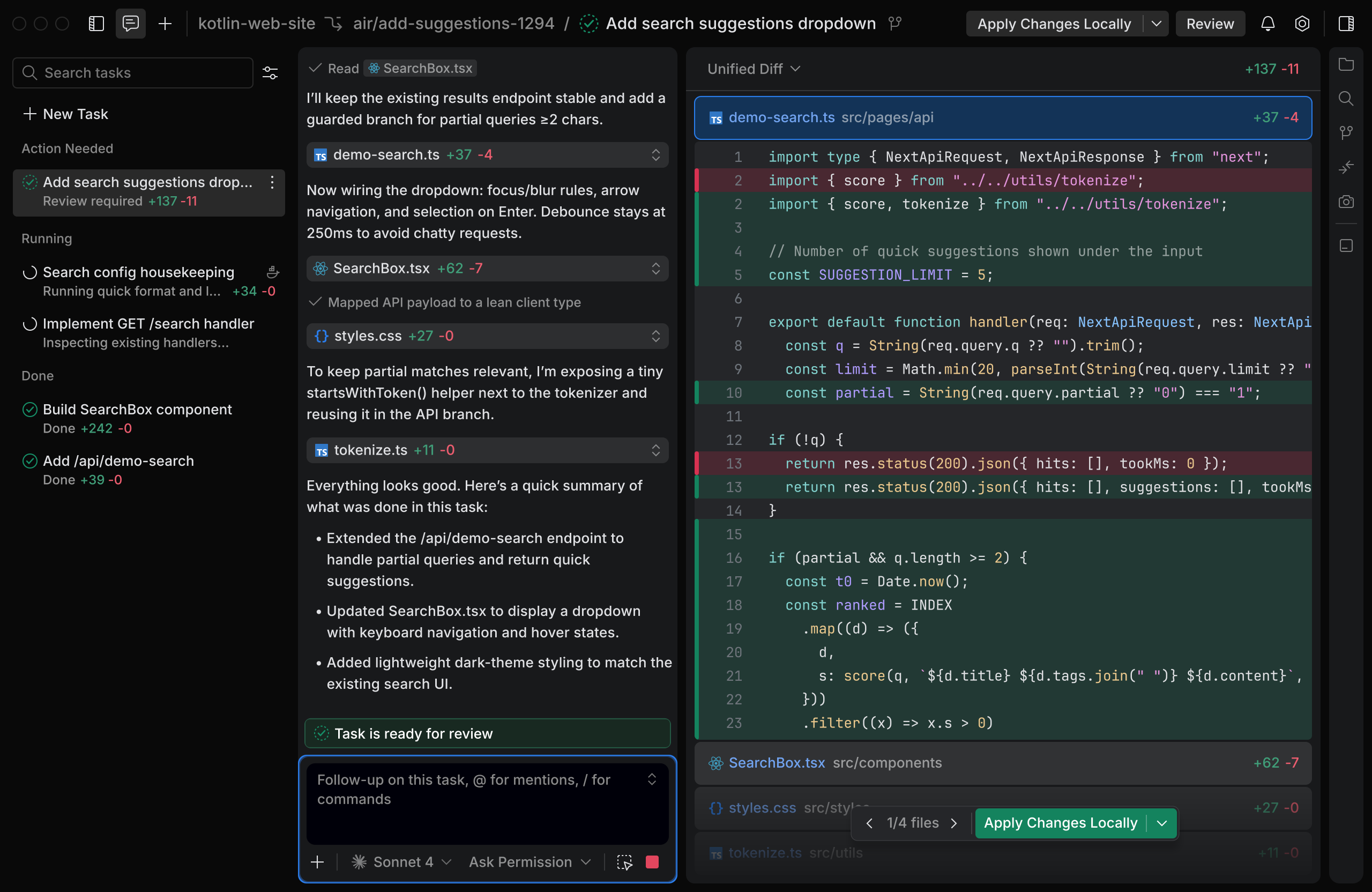
Defining a task involves writing a clear prompt and providing all necessary context. When you work with complex tasks, specific instructions help produce accurate results. In JetBrains Air, you define the task through an interactive chat mode. This is not a single-shot request. You can refine the task step by step.
You can use the interactive plan mode to ask the agent to create a detailed execution plan. You can also guide the agent by asking questions, adding context, and clarifying requirements during the conversation. This helps the agent understand your intent and produce better results.
JetBrains Air currently works with Claude Agent and OpenAI Codex. Make sure you have an active Anthropic or OpenAI ChatGPT subscription.
Configure task settings
Before running the task, you can configure the execution environment, AI model, and permissions.
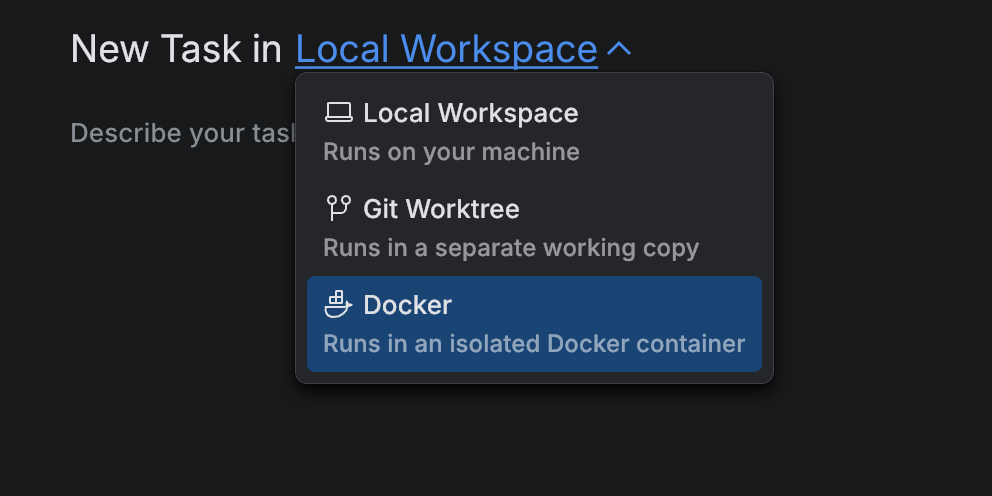
Select the execution environment:
Git Worktree: creates a separate working branch of the repository. This mode provides isolation from your main branch while still using your local environment. Note that you may need to reinstall project dependencies or repeat location-specific setup for every new task.
Docker: runs in an isolated container. You must have Docker Desktop installed and a valid license to use it. This mode offers complete isolation for code changes and tools. Isolation means that all edits, commands, and dependencies stay inside the container and do not affect your local workspace or system environment.
Local Workspace: runs directly in your current workspace. This mode has the fastest startup and uses your existing environment, but changes are applied to your project folder. It does not provide isolation.
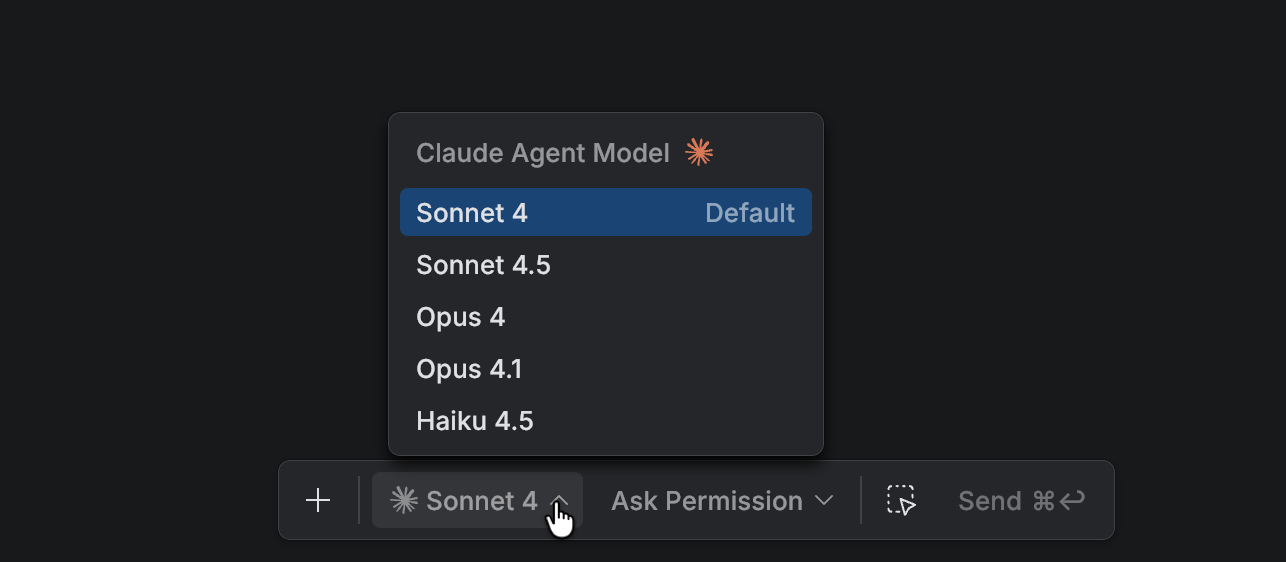
Click the Agent and Model drop-down menu and select the AI model you want to use.
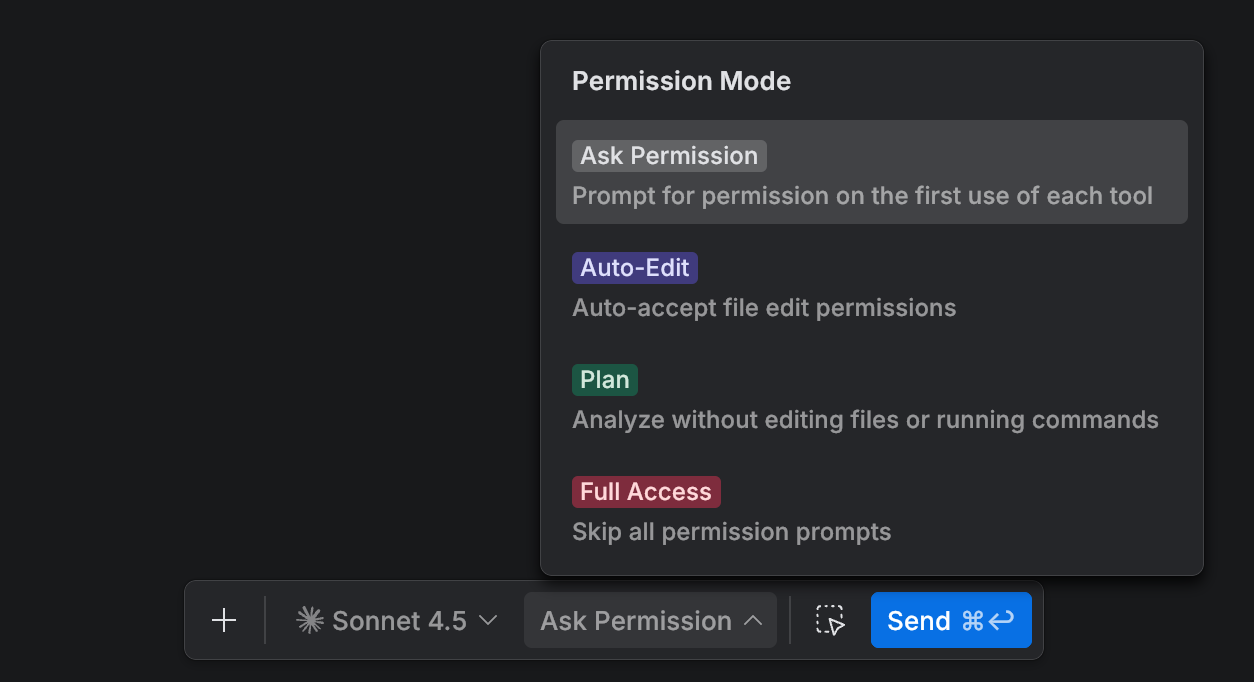
Select a Permission Mode to control how the agent asks for approval before editing files or running commands.
Ask Permission: prompts for permission on the first use of each tool.
Auto-Edit: automatically accepts file edit permissions.
Plan: analyzes code without editing files or running commands.
Full Access: skips all permission prompts.
Add context to the task
You can add context to the task prompt in several ways:
Click the Add context button to attach specific items. You can add:
Files and Folders: reference files and folders from your workspace.
Git Branches: reference a specific branch.
Git Commits: reference a specific commit.
Local Changes: reference changed files from the Git tool window.
MCP Server: connect an MCP server to provide extra tools.
Terminals: reference a specific terminal tab.
Upload from Computer: upload files from your computer.
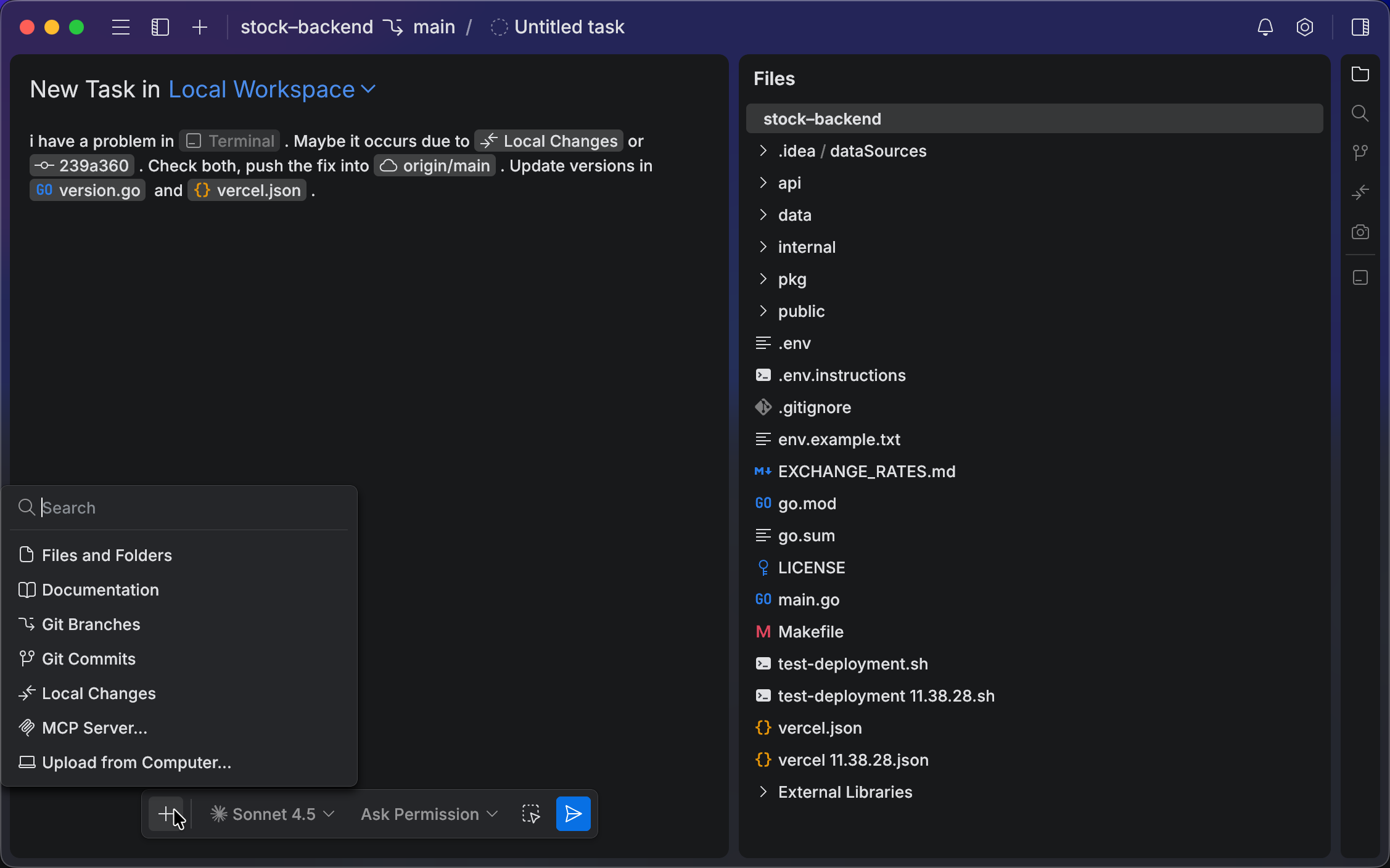
Add symbol mentions through the @ menu. Use the Symbols submenu to reference symbols from the current file or from the project.
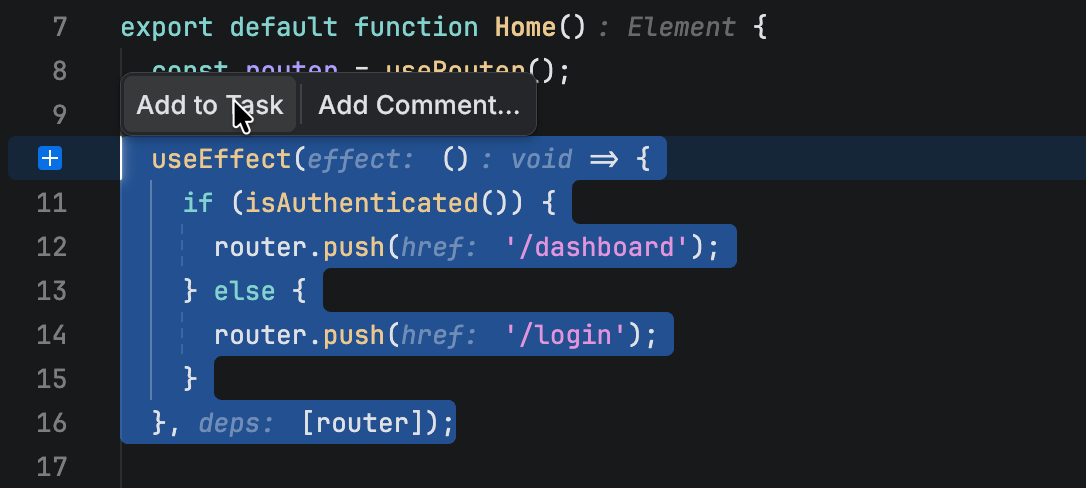
Select code in the editor and click Add to Task on the floating toolbar to attach the selected code.
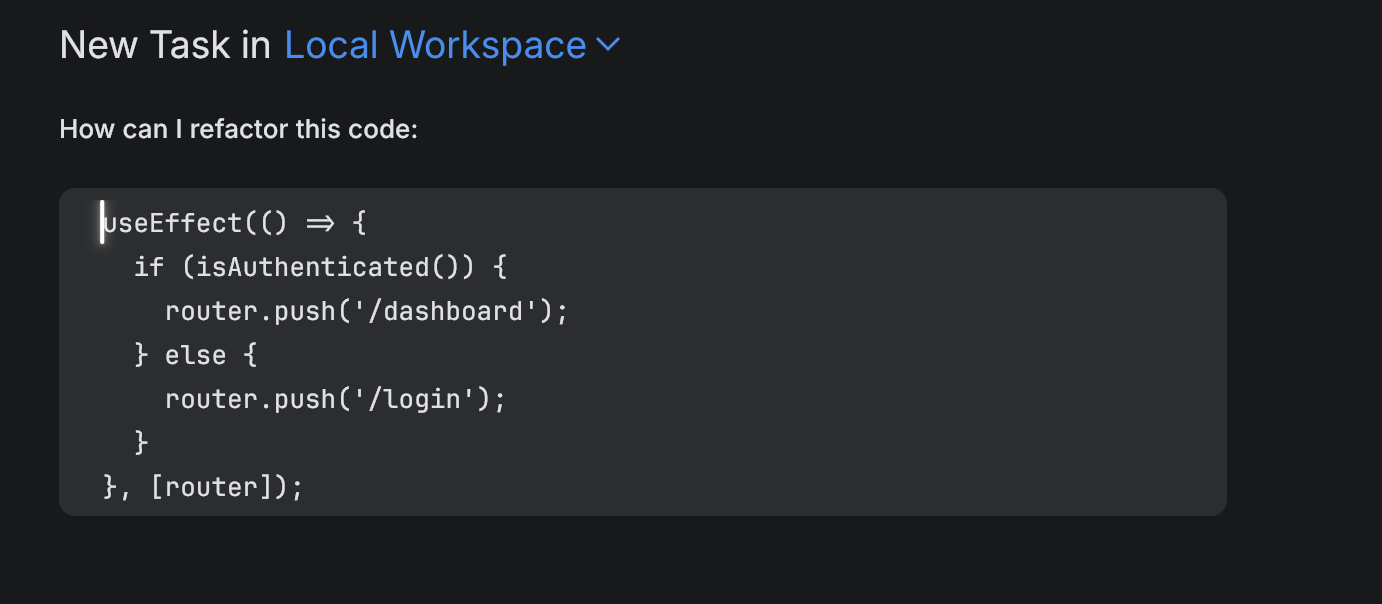
Add a code snippet manually by typing it inside triple backticks (
```).
Turn on Instant mode in the chat toolbar to automatically reference code as you select it in the editor.

Run and manage async agents
JetBrains Air can run multiple tasks asynchronously. For example, you can start one task adding new tests and an agent fixes a bug in another task. You can continue to work on a new feature at the same time.
View the list of tasks
To view the list of tasks in your current project, press ⌘ 1. You can also click the Tasks menu icon.
Add a new task
Press ⌘ \ and click the New Task button.
Click the New Task icon (
).
A task might have the following states:
Running: the agent is working on the task. You can follow the task progress and provide additional input at any moment.
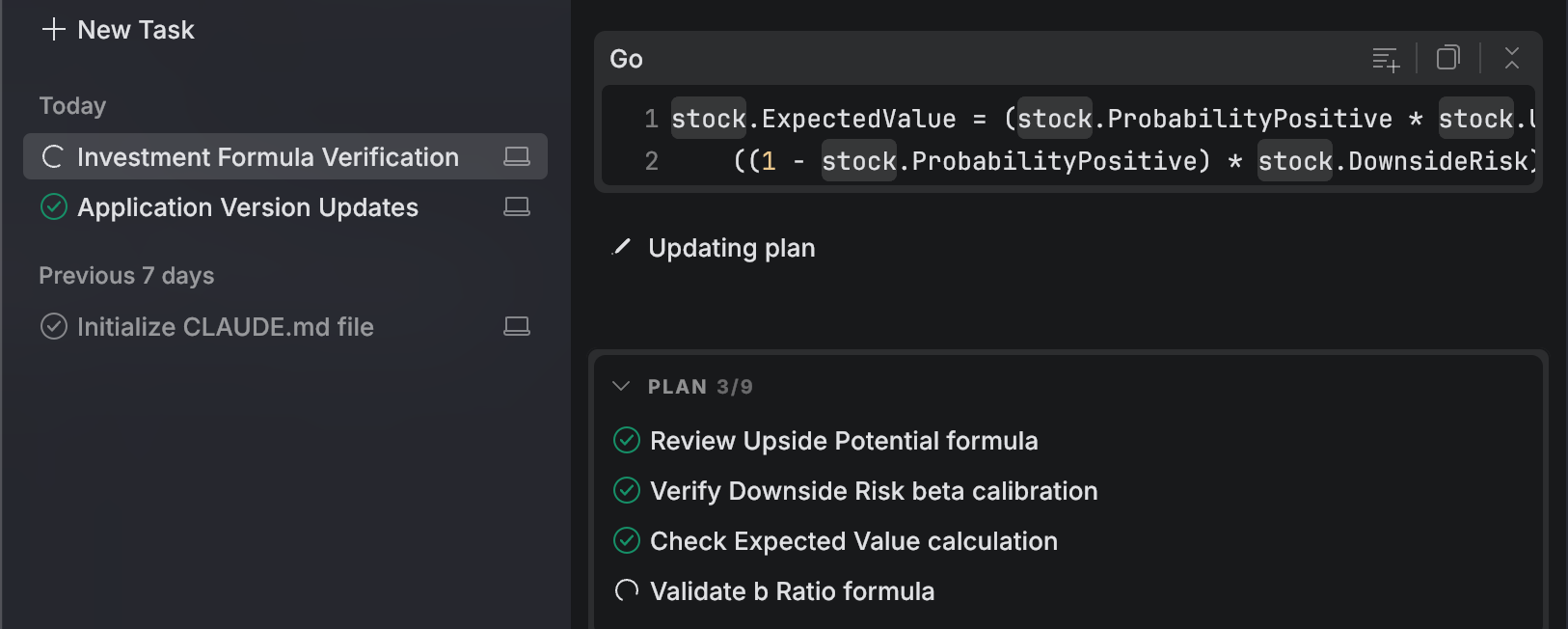
Input required: the agent has paused and needs information or a decision from you.
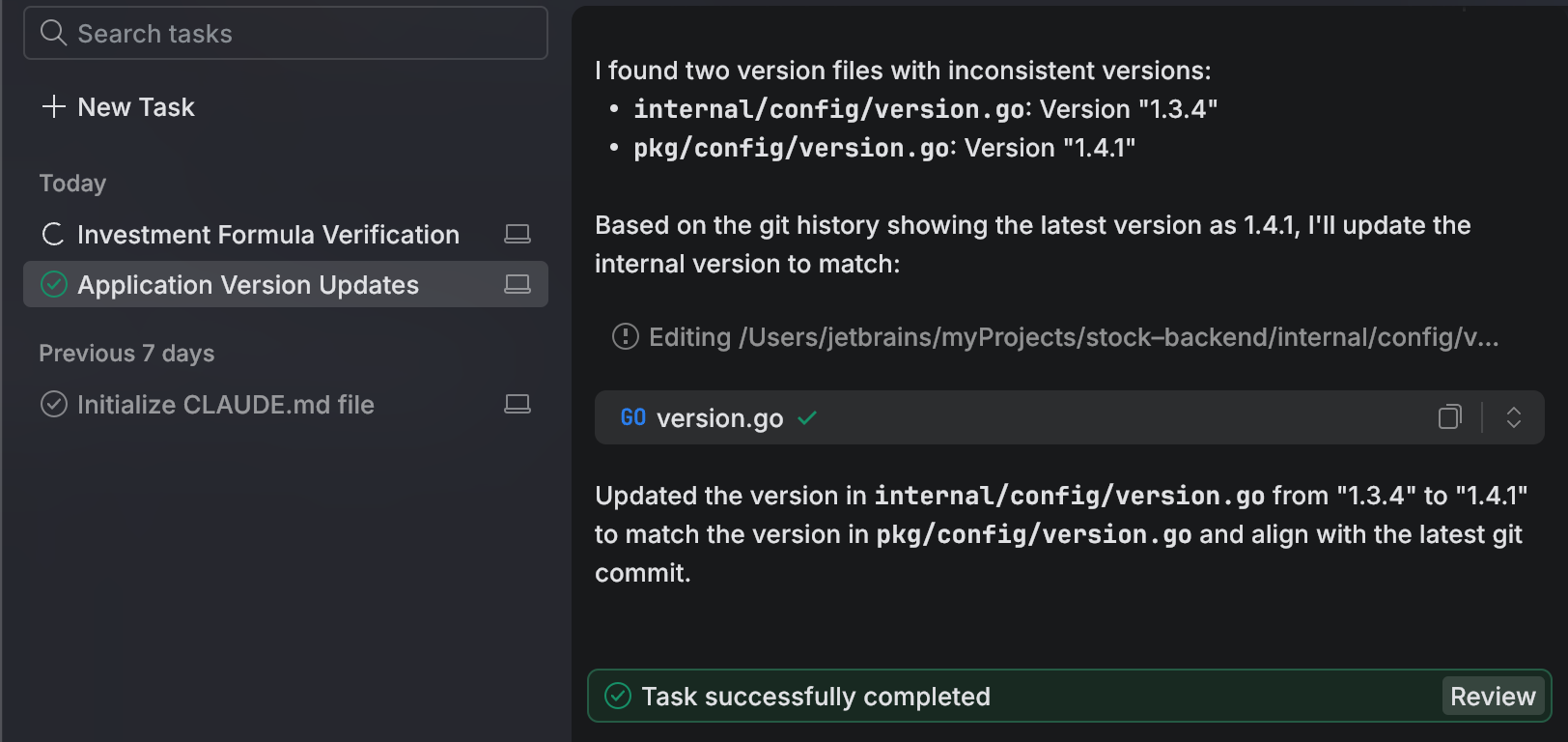
Done: the agent has completed the task. You can review and commit the changes.
Canceled: you stopped the task before the agent completed it.
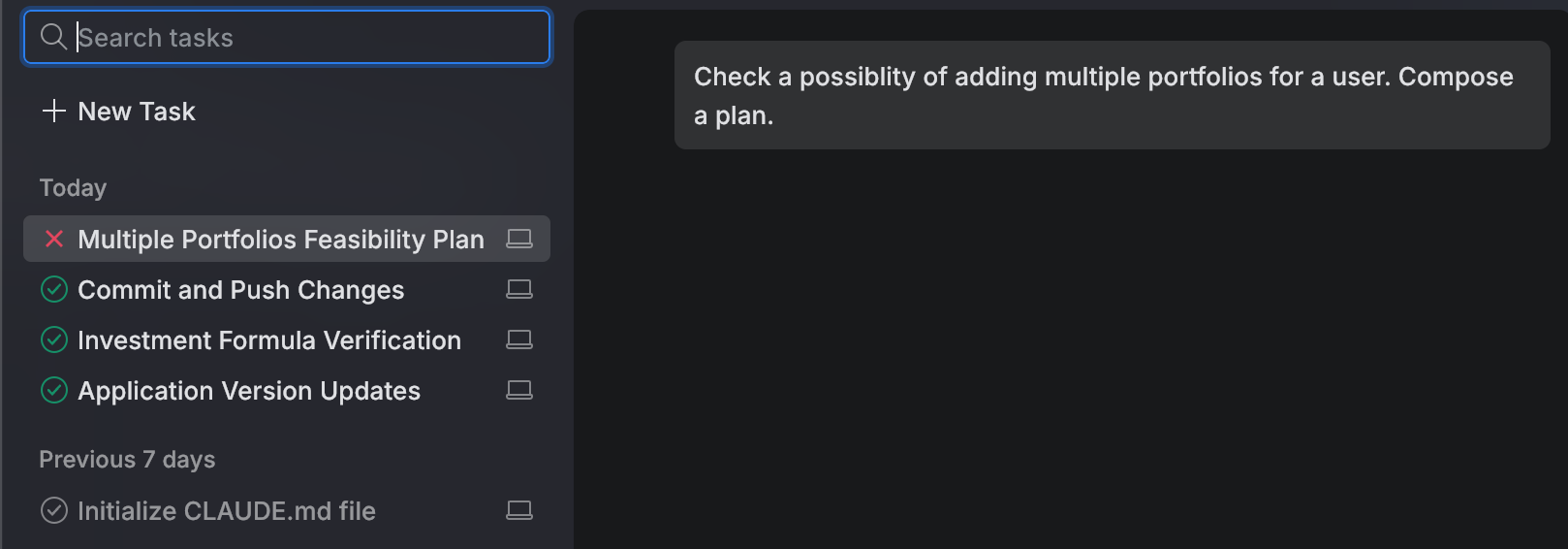
Tasks completed before today are moved to a dedicated section.
Review changes
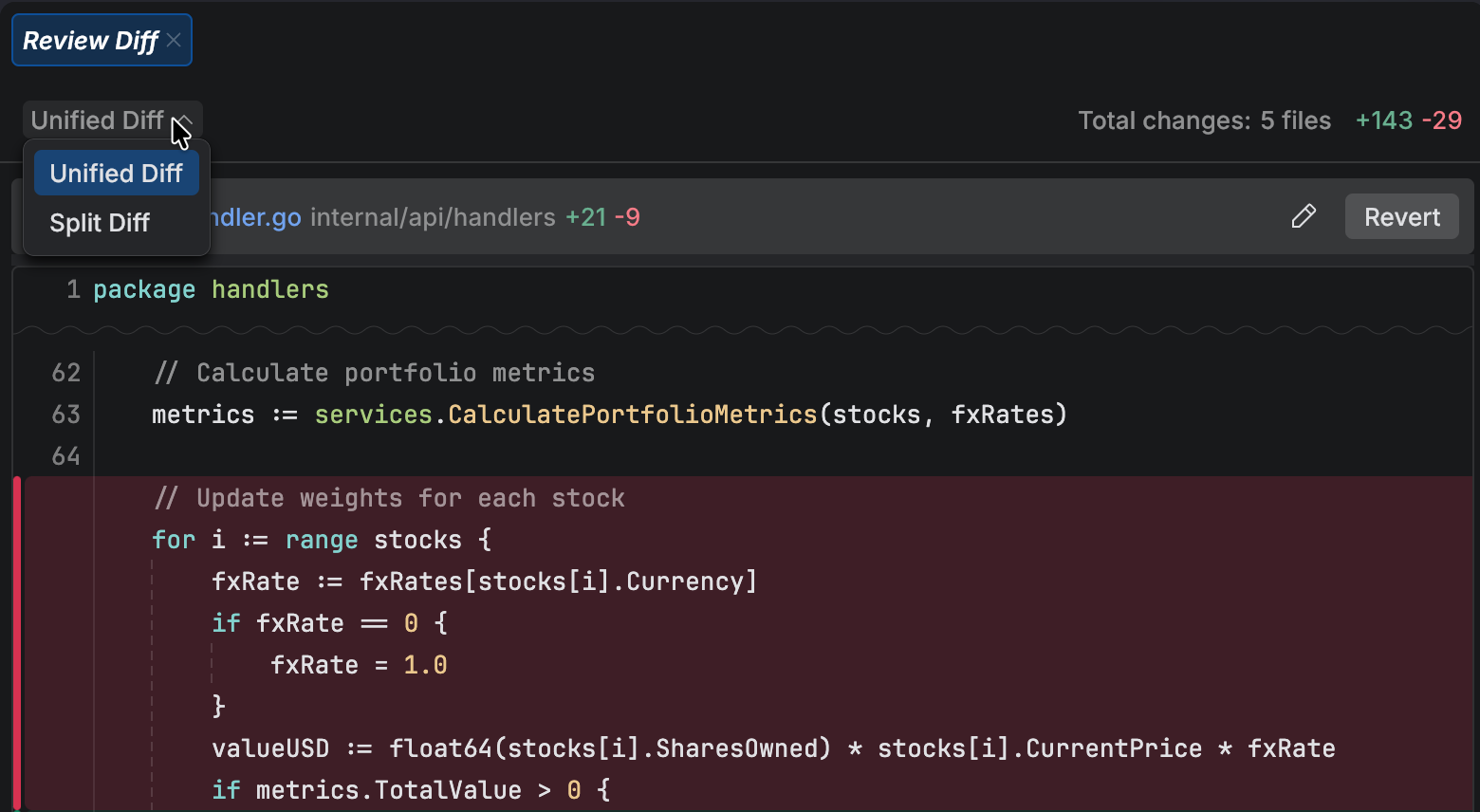
When a task is finished, switch to the Review tab to review the changes in the files. The diff panel shows the changes made by the agent.
You can provide feedback to the agent directly in the diff panel, similar to a regular code review. Use the icon in the gutter to comment on a specific line or selection.
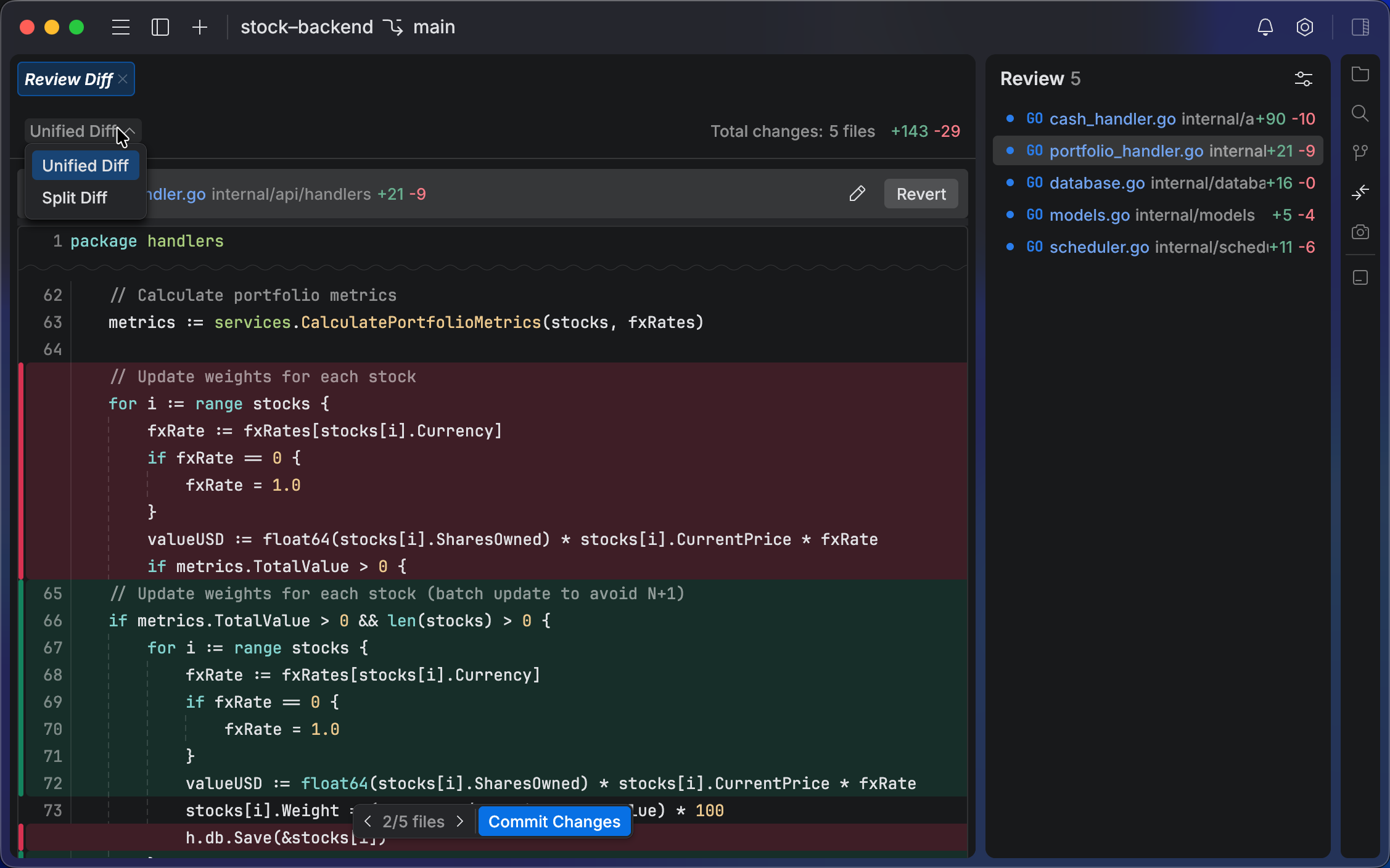
Provide feedback to an agent
Navigate to .
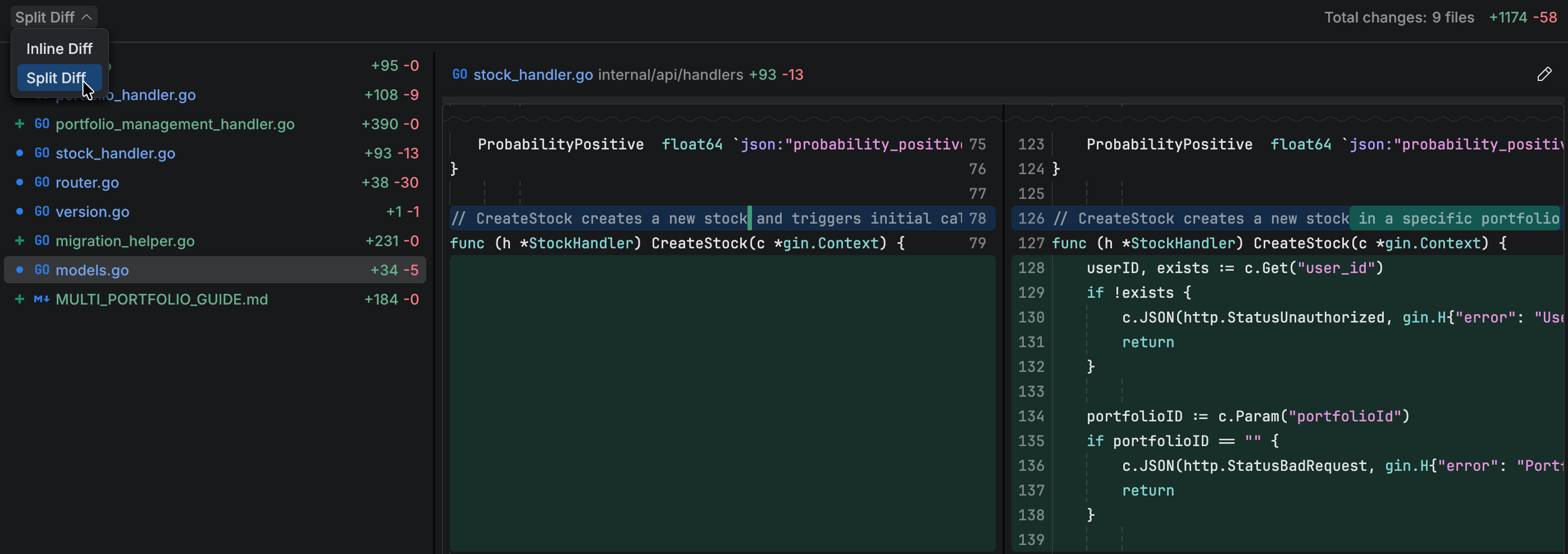
Select the type of diff to display. You can choose between:
Select the code that you want to change and click Add comment in the popup.
Type your prompt for the agent. The comment is added to the chat as part of a future task.
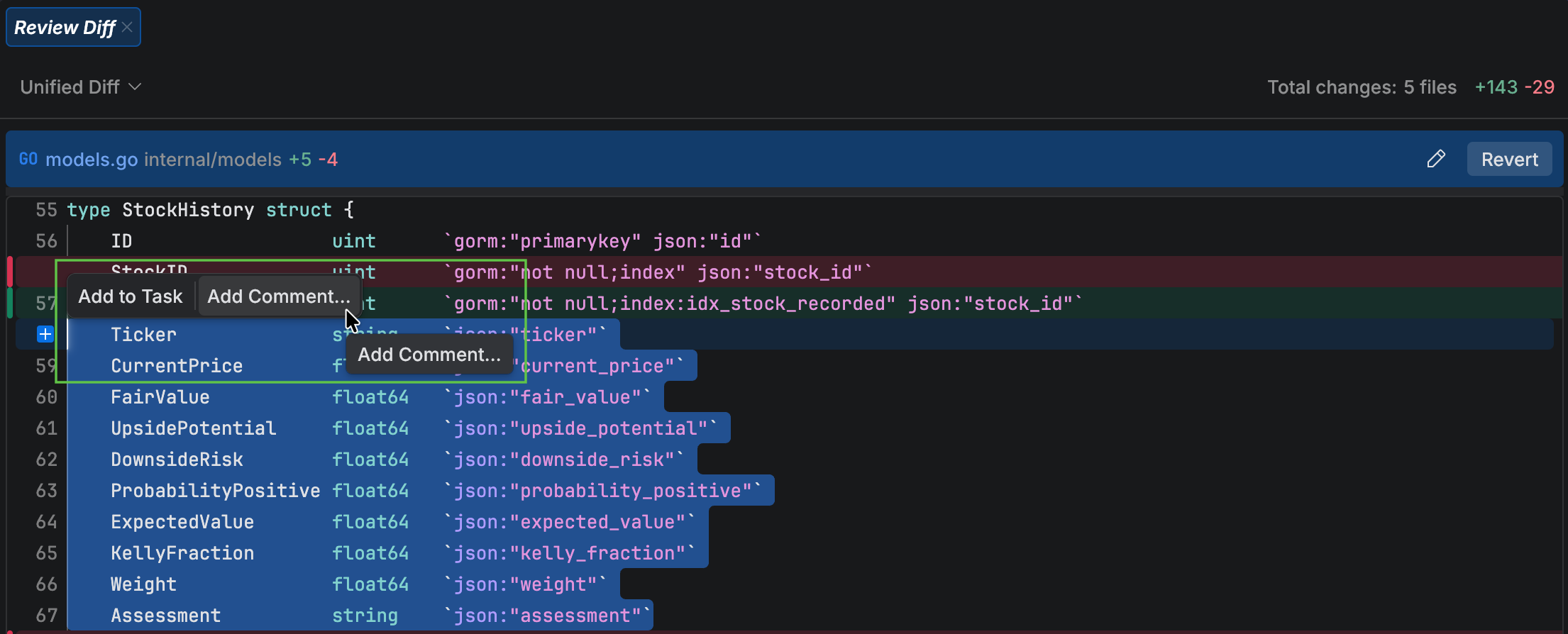
Push your changes
After your review, JetBrains Air helps you bring your changes back to the local workspace, and you can then push the changes to the remote repository.
Commit and push your changes
Navigate to .
In the Git view, select the files that you want to commit.
In the commit message field, type a description of the changes. You can also click Generate Commit Message with AI to generate a commit message based on the diff.
If you worked with two repositories in your workspace, select the remote repository where you want to push your changes.
Click Push. If this is your first push, JetBrains Air may ask for a GitHub token. Click the Generate link to create a token on GitHub. The minimum required permissions are set automatically, and you do not need to change them.
Other features
JetBrains Air includes other features that help you work with agents:
Built-in web preview for verifying results in web applications.
Project snapshots to roll back changes made by the agent.
MCP server integration
JetBrains Air can interact with external tools and data sources via the Model Context Protocol (MCP). By connecting to MCP servers, JetBrains Air gains access to a range of tools that significantly extend its capabilities.
Configure an MCP server
Press ⌘ , to open settings and select .
Click Add MCP Server and paste your server configuration in JSON format. Example:
{ "mcpServers": { "alphavantage": { "command": "uvx", "args": ["av-mcp", "YOUR_API_KEY"] } } }The server appears in the list.
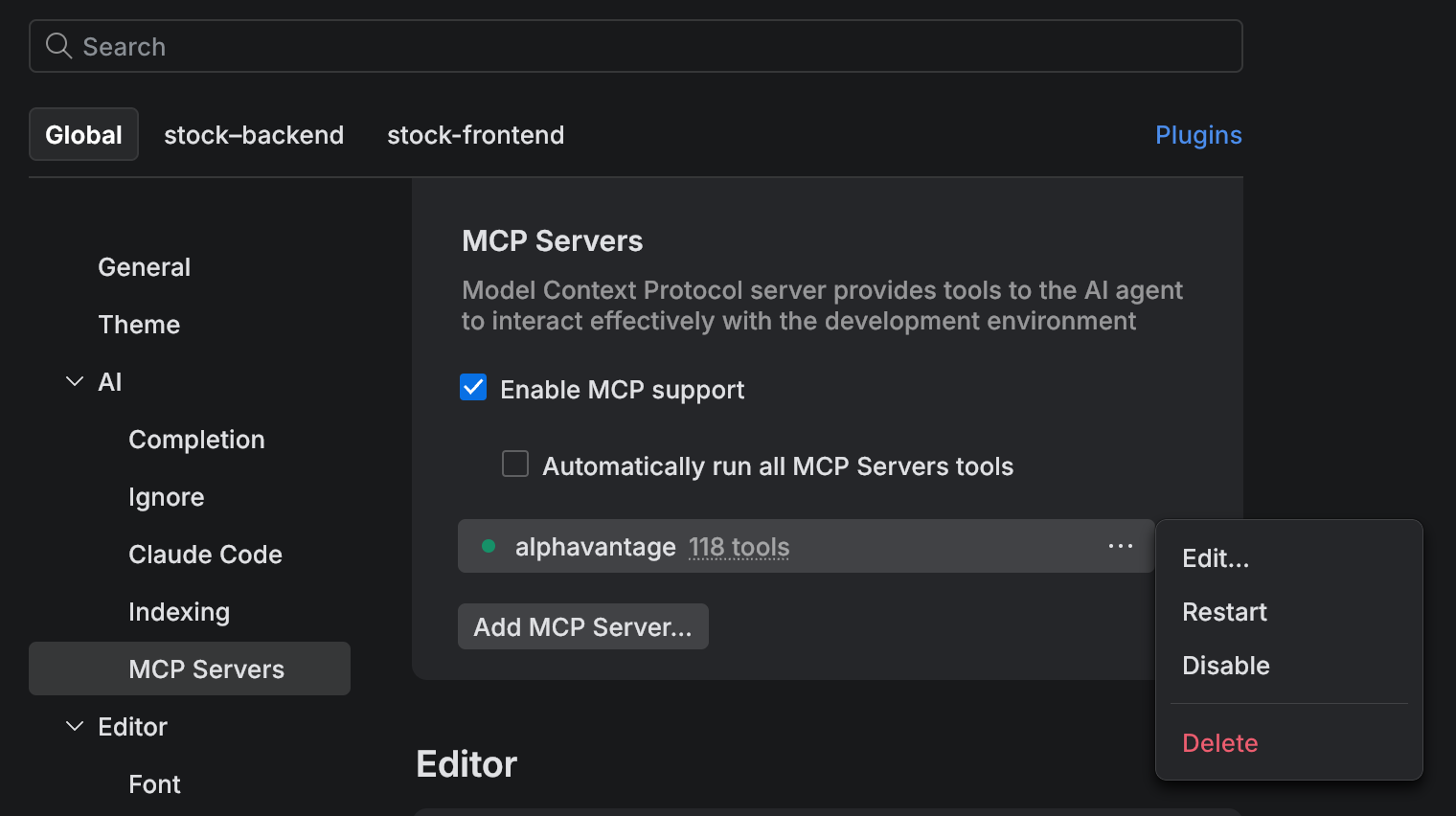
Manage MCP server connections
Press ⌘ , to open settings and select .
When your server appears in the list, click the … button to Edit, Restart, Disable, or Delete the server connection.
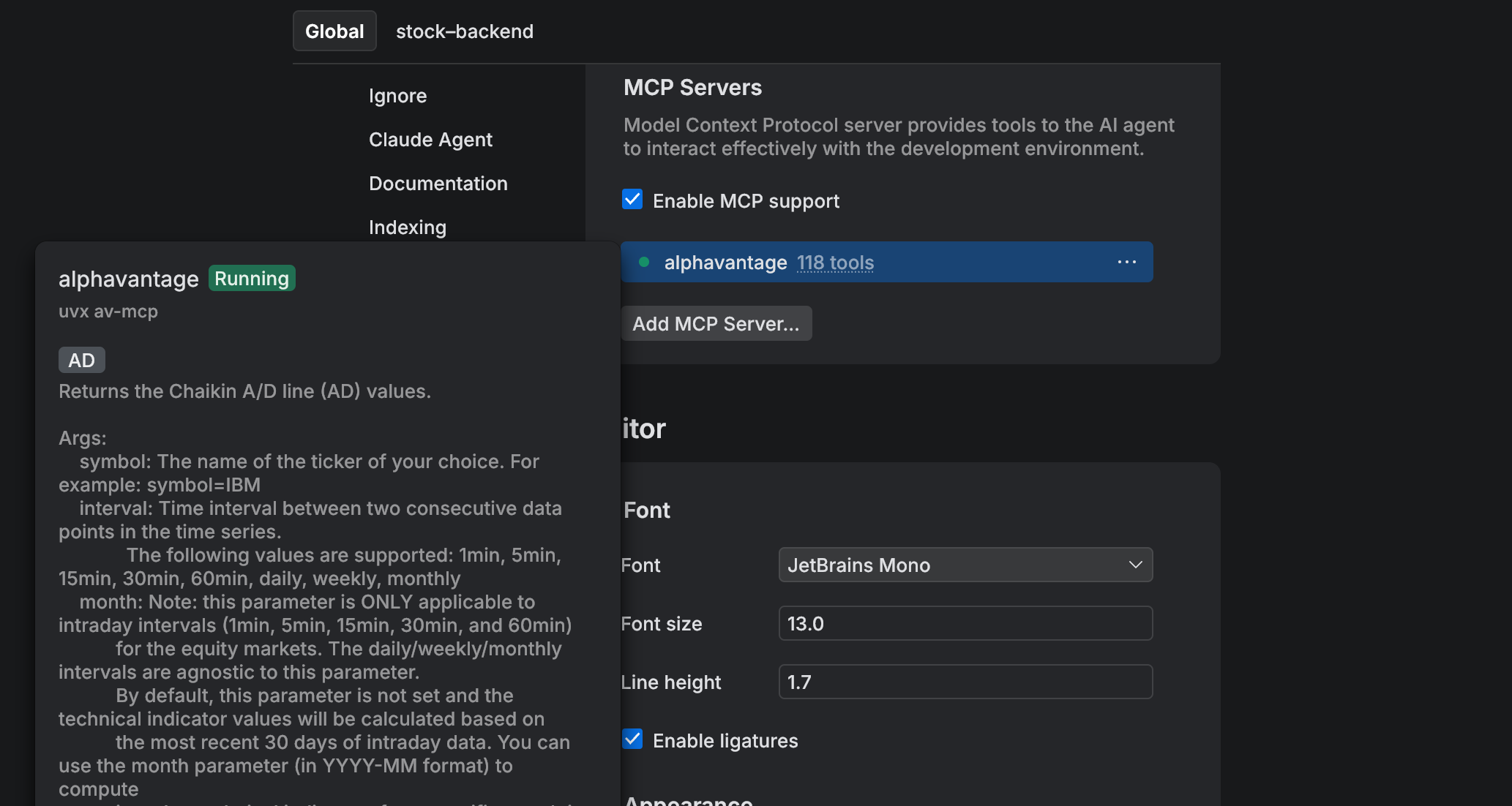
View available MCP server tools
Click the tool link next to your server name to see the list of available tools.
Configuration of Claude Agent
Currently, JetBrains Air uses Claude Agent as the primary agent. JetBrains Air supports Claude Agent built-in commands and custom commands that you can trigger by typing / in a task prompt.
Configure Claude Agent
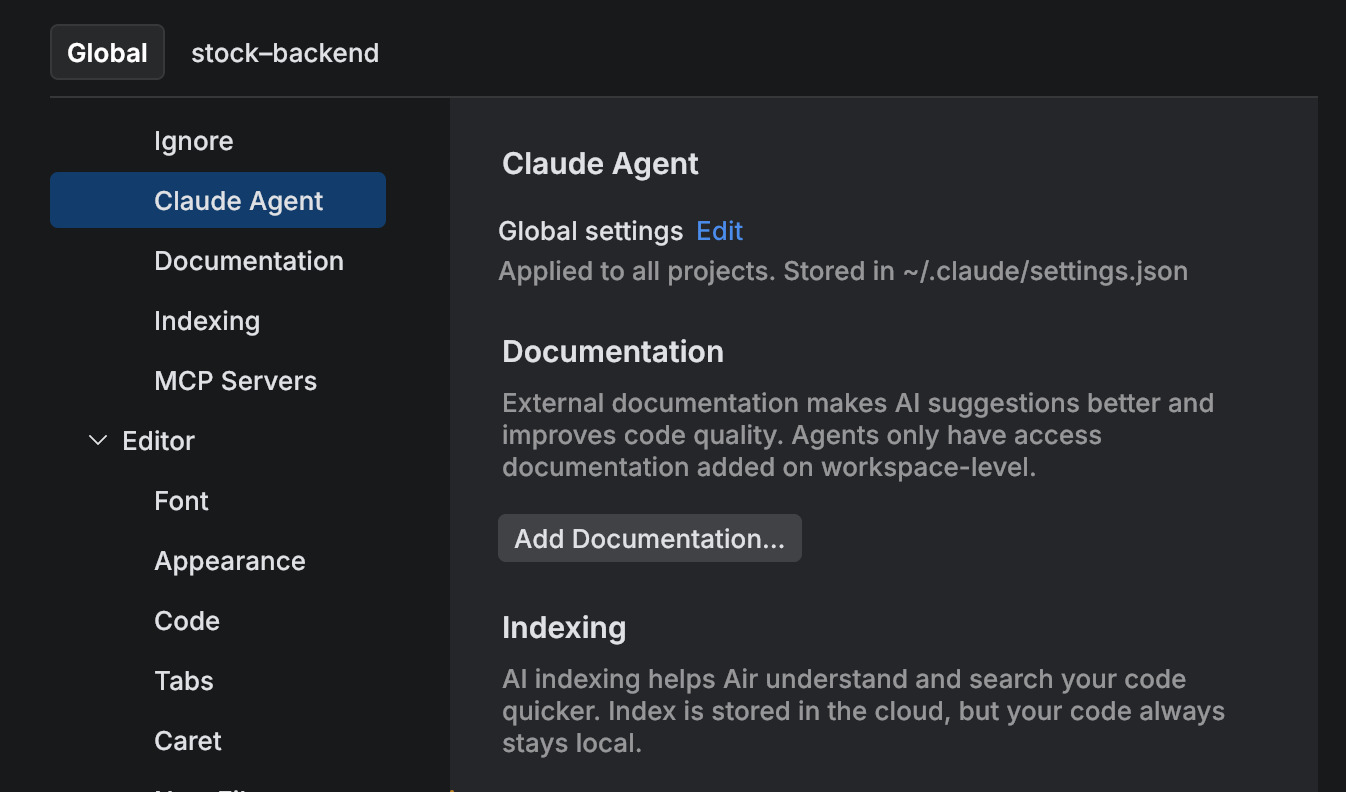
Press ⌘ , to open settings and select .
You can configure the following Claude Agent settings:
To configure global settings, click Edit next to the Global Settings menu option. Enter the settings for your Claude Agent instance in JSON format. For more information, see Claude Agent settings.
To configure indexing, select the necessary checkboxes in the indexing section.
Adding OpenAI Codex models
JetBrains Air supports OpenAI Codex models for running agentic tasks. You can connect your OpenAI account and select a Codex model directly from the JetBrains Air interface.
JetBrains Air supports two types of OpenAI accounts:
ChatGPT account (Plus, Pro, or Team), which uses your existing ChatGPT subscription.
OpenAI Platform account, which uses API billing.
Connect an OpenAI account
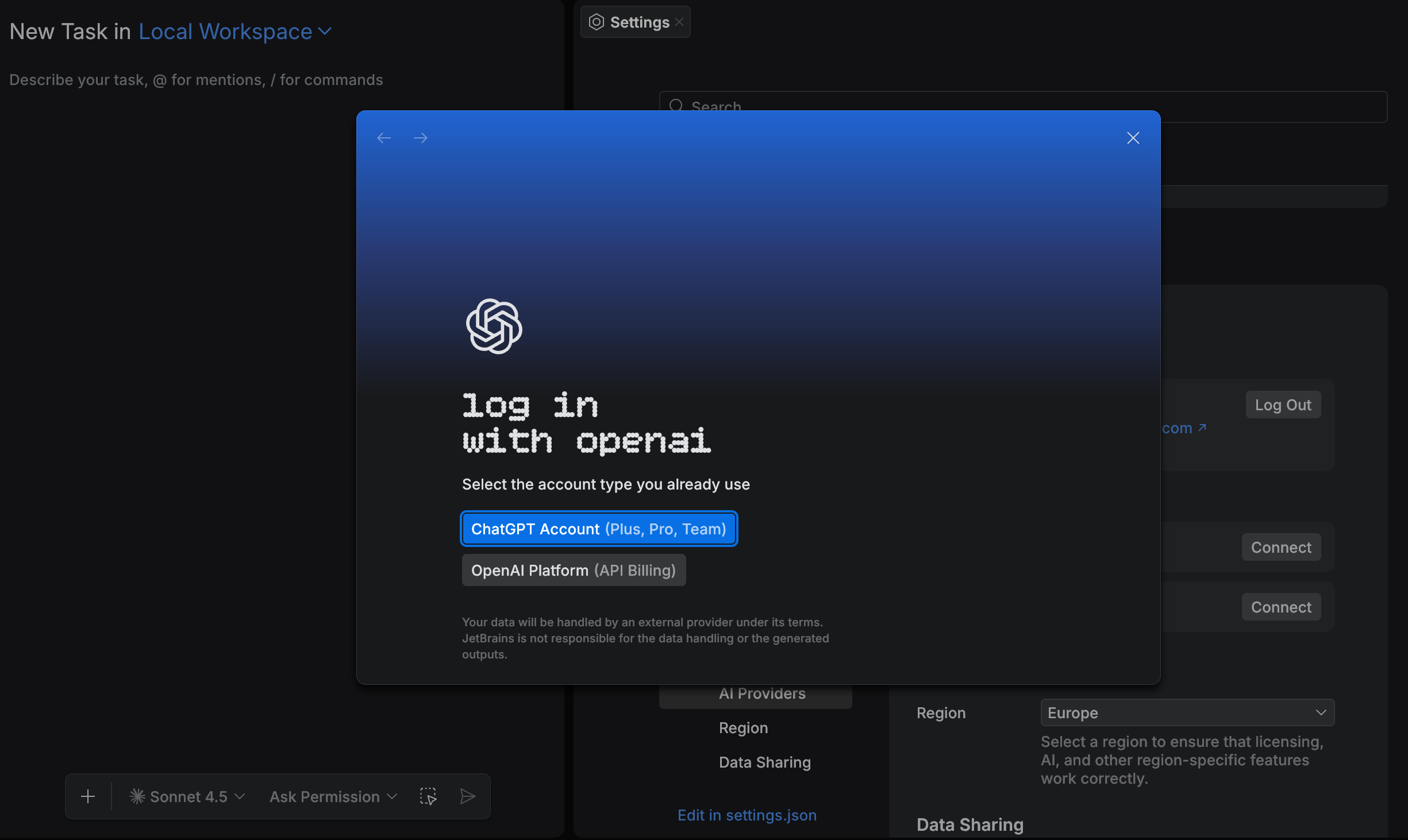
Log in with OpenAI
Press ⌘ , to open settings and select .
Click Connect next to OpenAI.
In the login dialog, select the account type you already use:
ChatGPT Account (Plus, Pro, Team)
OpenAI Platform (API Billing)
Complete authentication in the browser window that opens. After successful login, OpenAI appears in the list of connected providers.
Select an OpenAI Codex model
After connecting your OpenAI account, you can select an OpenAI Codex model, which JetBrains Air will use for tasks.
Choose a Codex model
Open a new task. For more information about defining a task, refer to Define a new task.
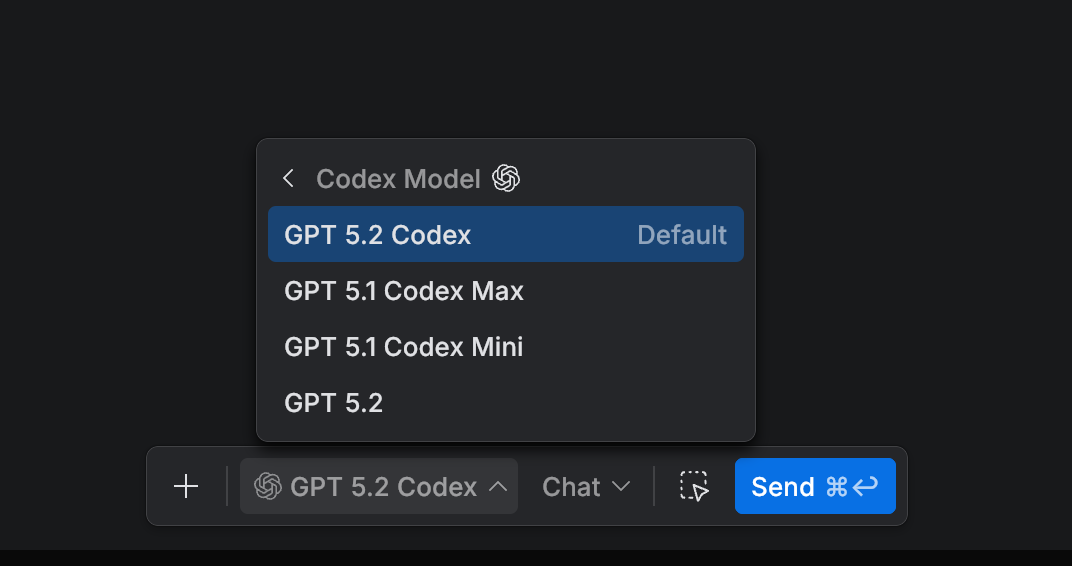
Click the Agent and Model selector in the task toolbar.
From the list, select one of the available OpenAI Codex models, for example:
GPT-5.1 Codex Max
GPT-5.2 Codex
GPT-5.1 Codex Mini
GPT-5.2
Web preview
The preview feature in JetBrains Air lets you instantly preview your web application.
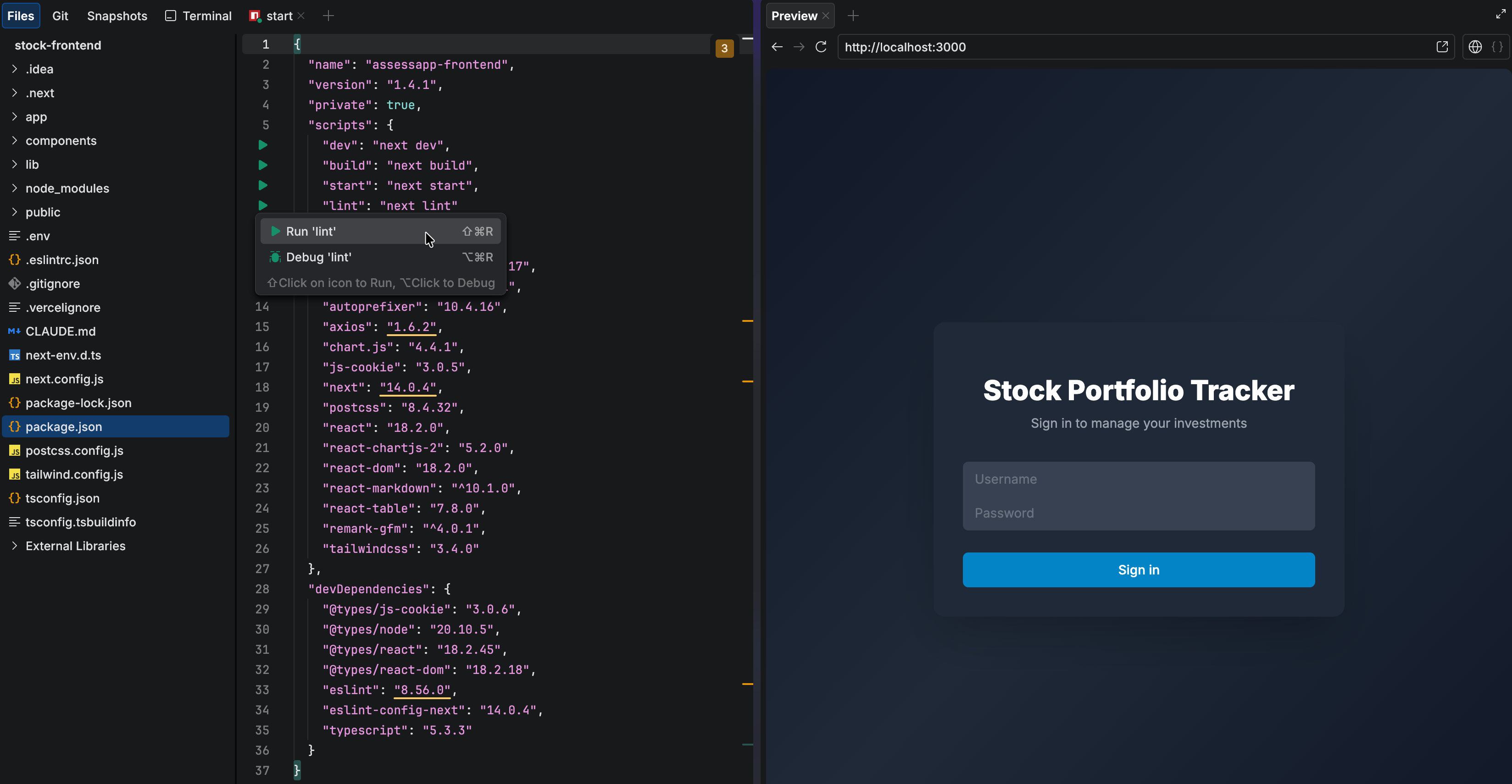
The preview opens automatically for web-based projects when your server starts, or for static projects that contain an HTML file. By default, the preview pane opens in preview mode, indicated by the toolbar in the upper-right corner.
If the preview does not appear, try running it manually.
Run the preview manually
Press ⌘ ⇧ K and start typing New Preview Tool. Select New Preview Tool.
You can switch from the preview to the source code view to inspect the underlying HTML source. The code is read-only, indicated by a lock icon. You cannot edit the code in this mode.
Switch between preview and source code modes
Click the web or code mode icon in the upper-right corner of the Preview tool window.
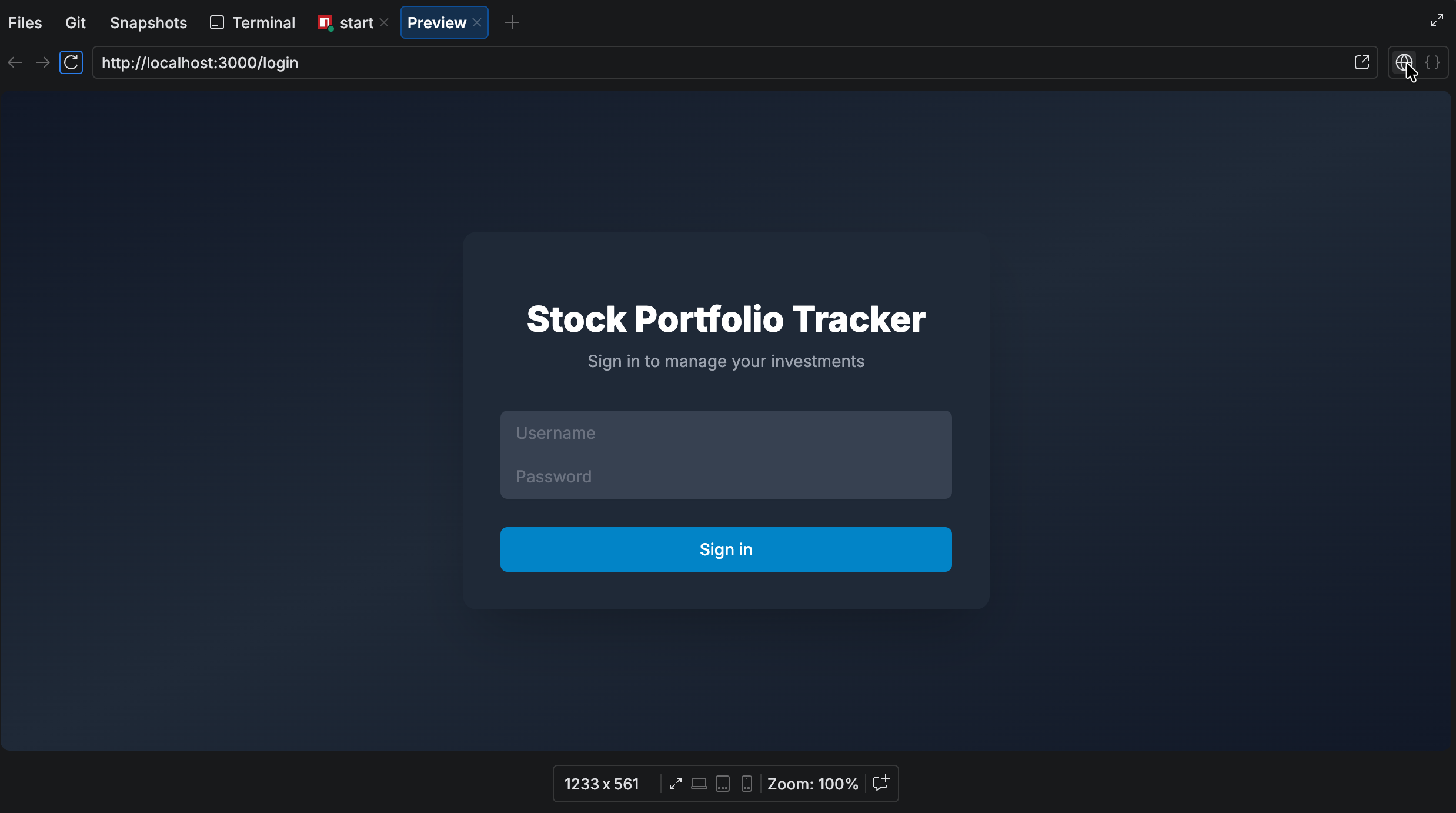
If the page does not open or shows an error, you can ask the chat to summarize the problem and suggest possible fixes. You can also use the Reload Page button in the toolbar to refresh the preview and load the latest changes.
By default, the preview is in responsive mode, shown by the Expand icon in the Devices toolbar. Responsive mode uses the full width and height of the editor and adjusts automatically as you resize the window.
Local history snapshots
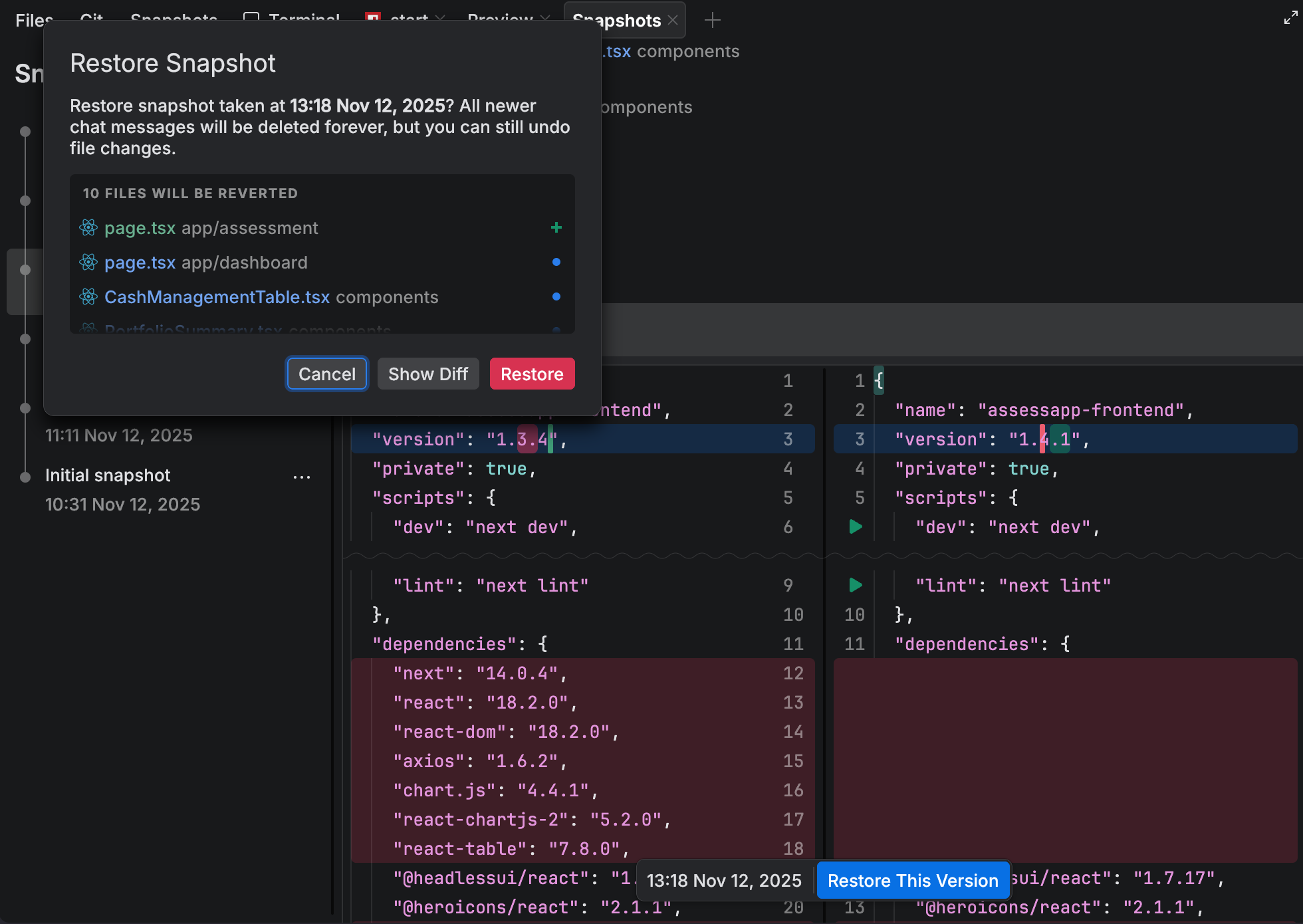
The local history snapshots feature in JetBrains Air lets you revert your entire workspace to the state it had before a specific chat prompt. Each time you interact with the chat, a snapshot is created. This allows you to restore your code to the exact state it had before a change or experiment.
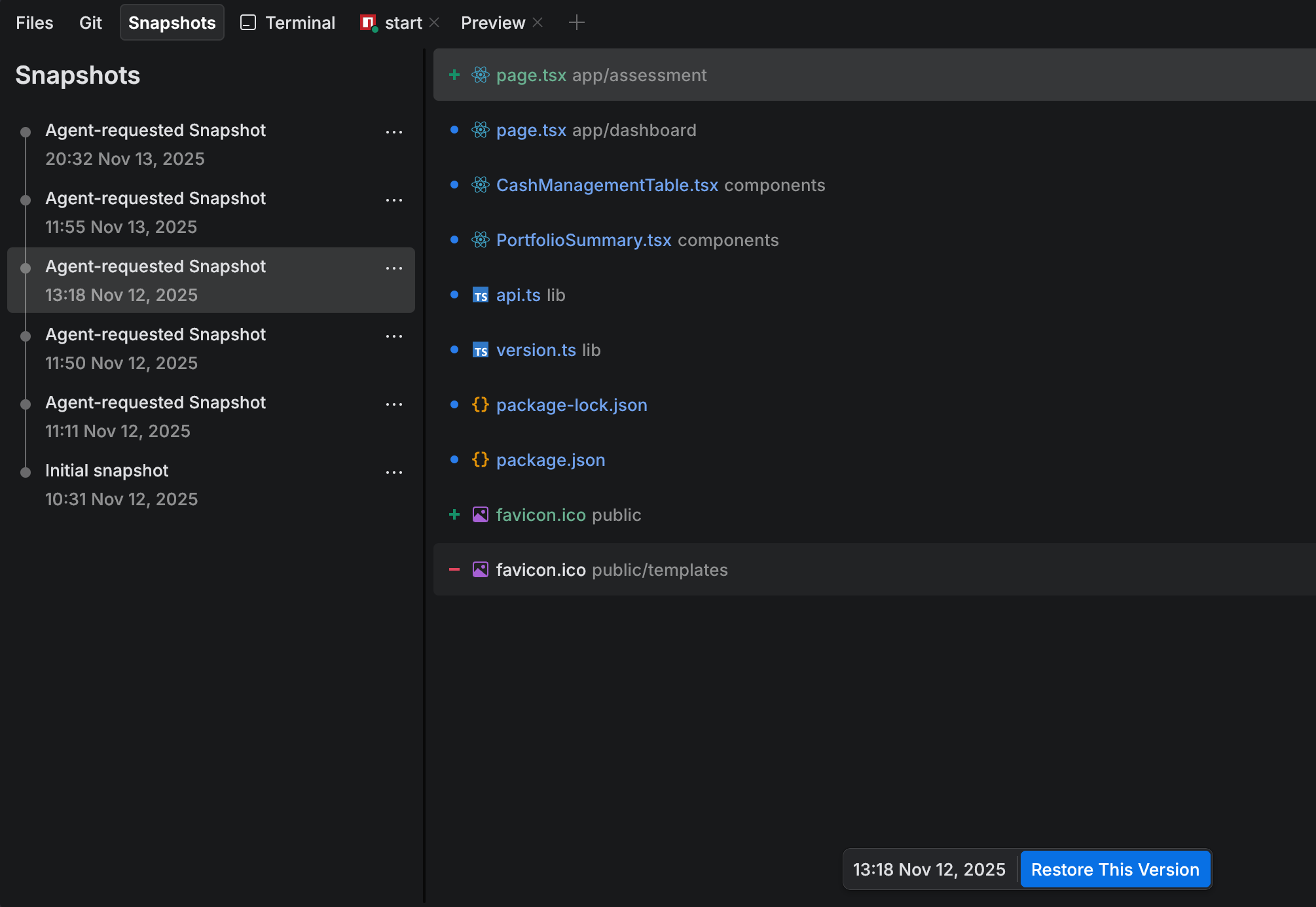
Restore a snapshot
Press ⌘ ⇧ K and start typing
New Snapshots Tool. Select New Snapshots Tool.In the pane with files, review the list of files that will be reverted. You can click a file to compare the current and previous versions.
Click Restore This Version.
In the Restore Snapshot dialog, click Restore to confirm the action.