File template variables
A file template can contain variables, which are replaced by their values when the template is applied. A variable is a string that starts with a dollar sign $ followed by the variable name. The variable name may optionally be enclosed in curly braces. For example: $MyVariable and ${MyVariable} are different notations of the same variable.
Predefined and custom variables are available in the template body and in the filename. For example, if you type MyFile_${MONTH_NAME_FULL} in the File name field of your template, the resulting file will be named MyFile_April if you create it in April. Here, ${MONTH_NAME_FULL} is a predefined variable. If you use a custom variable instead, CLion will prompt you to enter the variable value when you create a file based on this template.
Predefined template variables
The following predefined variables can be used in file templates:
Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Base function call signature during the override generation |
| Current system date |
| Current day of the month |
| Default return value of the function |
| Path to the directory of the new file (relative to the project root) |
| Dollar sign |
| Name of the new C or C++ file |
| Always returns |
| Name of the header file generated for a class or a source file |
| Current hour |
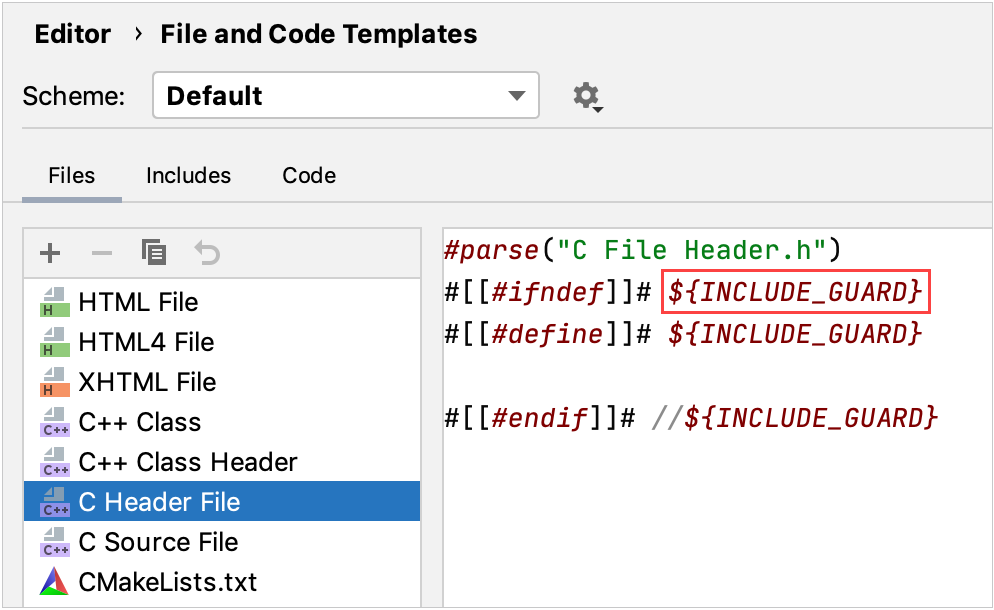
| Prevents repeated include of a particular header file |
| Current minute |
| Current second |
| Current month |
| Full name of the current month (January, February, and so on) |
| First three letters of the current month name (Jan, Feb, and so on) |
| Name of the new entity (file, class, interface, and so on) |
| End of a namespace block created during refactoring |
| Beginning of a namespace block created during refactoring |
| Name of the IDE (for example, CLion) |
| Name of the current project |
| Type of the function's return value (used for generating new functions) |
| Google test suite name |
| Google test name |
| Current system time |
| Login name of the current user (all platforms) |
| For Windows and Linux: login name of the current user For macOS: registered full name of the user |
| Current year |
The following variables are available in CMakeLists.txt file templates:
${CMAKE_DEFAULT_PROJECT_FILE} | the main.cpp/main.c/libary.cpp/library.c file of the project. |
${CMAKE_LANGUAGE_VERSION} | the selected language standard. |
${CMAKE_MAJOR_VERSION} | the major number of the minimum supported CMake version. For example, if the version if |
${CMAKE_MINOR_VERSION} | the minor number of the minimum supported CMake version. For example, if the version if |
${CMAKE_LIBRARY_TYPE} |
|
${QT_VERSION} | the selected Qt version. |
${REQUIRED_LIBS} | the Qt libraries required for the selected project type. By default, they are |
Variable methods
Because CLion uses Velocity as a template engine for file templates, variables in file templates can use Java String methods. For example, the following is possible:
${NAME.toUpperCase()}: convert the name of the new entity (file) to upper case letters.${PROJECT_NAME.length()}: print the length of the project name.${PRODUCT_NAME.substring(0,5)}: print the first five characters of the name of the IDE you are using.
Custom template variables
Besides predefined template variables, it is possible to specify custom variables. If necessary, you can define the values of custom variables right in the template using the #set directive. Write the directive before the corresponding variable is used.
For example, if you want to use your full name instead of your login name defined through the predefined variable ${USER}, add the following construct before your custom variable:
If the value of a variable is not defined in the template, CLion will ask you to specify it when the template is applied.