Running and Debugging Node.js
The following is only valid when Node.js Plugin is installed and enabled!
On this page:
- Before you start
- Local and remote modes of running or debugging Node.js applications
- Running a Node.js application
- Debugging a Node.js application locally
- Debugging a Node.js application running on a Docker container
- Node.js multiprocess debugging
Before you start
Install and enable the NodeJS plugin. The plugin is not bundled with CLion, but it can be installed from the JetBrains plugin repository as described in Installing, Updating and Uninstalling Repository Plugins and Enabling and Disabling Plugins.
Local and remote modes of running or debugging Node.js applications
Running a Node.js application in CLion is supported only in the local mode. This means that CLion itself starts the Node.js engine and the target application according to a run configuration and gets full control over the session.
Debugging can be performed in two modes:
- Locally, with the Node.js engine started from CLion.
- Remotely, when CLion connects to an already running Node.js application. This approach gives you the possibility to re-start a debugging session without re-starting the Node.js server.
You can also configure the behaviour of the browser and enable debugging the client-side code of the application. This functionality is provided through a JavaScript Debug run configuration, so technically, CLion creates separate run configurations for the server-side and the client-side code, but you specify all your settings in one dedicated Node.js run configuration.
Running a Node.js application
- Create a Node.js run configuration.
- To launch the application, select the run configuration from the list on the main tool bar and then choose on the main menu or click the Run toolbar button
 . The Run tool window opens.
. The Run tool window opens. - Open the browser of your choice and open the page with the URL address generated through the server.listen function based on the
portandhostparameters. The page shows the result of executing your Node.js application.
Debugging a Node.js application locally
- Set the breakpoints in the Node.js code, where necessary. If you want the debugging tool to stop at the first line of your code, set a breakpoint at the first line.
- Create a Node.js run/debug configuration.
- To start a debugging session, select the required debug configuration from the list on the main tool bar and then choose on the main menu or click the Debug toolbar button
 .
. - Open the browser of your choice and open the starting page of your application. Control over the debugging session returns to CLion.
- Switch to CLion, where the controls of the Debug tool window are now enabled. Proceed with the debugging session — step through the breakpoints, switch between frames, change values on-the-fly, examine a suspended program, evaluate expressions, and set watches.
Debugging a Node.js application running on a Docker container
- Set the breakpoints in the Node.js code, where necessary. If you want the debugging tool to stop at the first line of your code, set a breakpoint at the first line.
- On the main menu, choose . In the Edit Configuration dialog box that opens, click the Add New Configuration toolbar button
 , and choose Node.js on the context menu. In the Run/Debug Configuration: Node.js dialog that opens, choose the relevant Node.js interpreter running in a Docker container. Choose one of the existing interpreters from the Node Interpreter drp-down list or configure a new one as described in .
, and choose Node.js on the context menu. In the Run/Debug Configuration: Node.js dialog that opens, choose the relevant Node.js interpreter running in a Docker container. Choose one of the existing interpreters from the Node Interpreter drp-down list or configure a new one as described in . - Specify the Docker container settings. Type the settings manually, or click
 next to the field and specify the settings in the Edit Docker Container Settings dialog that opens, or select the Auto configure checkbox to have CLion do it automatically.
next to the field and specify the settings in the Edit Docker Container Settings dialog that opens, or select the Auto configure checkbox to have CLion do it automatically. To invoke the automatic configuration mode for a Docker container, select the Auto configure check box in the Run/Debug Configuration: Node.js dialog. In the Automatic Configuration mode:
- CLion creates a new image and installs the
npmmodules in it.CLion copies
package.jsonto the/tmp/project_modulesfolder in the image, runsnpm install, and then copies the modules to the project folder in the container. Consequently, changingpackage.jsonin the project results in re-building the image. - CLion runs the container with the new image, binds your project folder to
/opt/projectfolder in the container to ensure synchronization on update, and maps/opt/project/node_modulesto the OS temporary directory.
With automatic configuration, you still need to bind the port that your application is running on with the port of the container. Those exposed ports are available on the Docker host’s IP address (by default 192.168.99.100). Such binding is required when you debug the client side of a Node.js Express application so you need to open the browser from your computer and access the application at the host of the container through the port specified in the application.
- Click
 next to the Docker Container Settings field.
next to the Docker Container Settings field. - In the Edit Docker Container Settings dialog that opens, expand the Port bindings area.
- Click
 . The Port bindings dialog box opens. In this dialog box, map the ports as follows:
. The Port bindings dialog box opens. In this dialog box, map the ports as follows: - In the Container port text box, type the port specified in your application.
- In the Host port text box, type the port through which you want to open the application in the browser from your computer.
- In the Host IP text box, type the IP address of the Docker's host, the default IP is 192.168.99.100. The host is specified in the API URL field on the Docker page of the Settings / Preferences Dialog.
- Click OK to return to the Edit Docker Container Settings dialog where the new port mapping is added to the list.
- Click OK to return to the Run/Debug Configuration: Node.js dialog.
- CLion creates a new image and installs the
- Save the run configuration.
- Proceed as as during a local debugging session, as described above.
Node.js multiprocess debugging
CLion supports debugging additional Node.js processes that are launched by the child_process.fork() method or by the cluster module. Such processes are shown as threads in the Frame pane on the Debugger tab of the Debug Tool Window.
- Set the breakpoints in the processes to debug.
- Create a Node.js run/debug configuration.
- Choose the newly created configuration in the Select run/debug configuration drop-down list on the tool bar and click the Debug toolbar button
 .
. The Debug Tool Window opens and the Frames drop-down list shows the additional processes as threads as soon as they are launched:
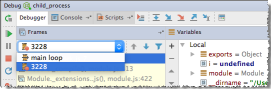
To examine the data (variables, watches, etc.) for a process, select its thread in the list and view its data in the Variables and Watches panes. When you select another process, the contents of the panes are updated accordingly.