Advanced configuration
Besides the standard options available in the IDE settings, CLion enables you to perform low-level configuration of the underlying platform and the Java runtime.
JVM options
CLion runs on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which has various options that control its performance.
The default options used to run CLion are specified in the IDE installation directory:
<IDE_HOME>\bin\clion64.exe.vmoptions
CLion.app/Contents/bin/clion.vmoptions
<IDE_HOME>/bin/clion64.vmoptions
Configure JVM options
Do one of the following to create a copy of the default file with JVM options in the configuration directory that will override the original file:
In the main menu, go to .
If you do not have any project open, on the Welcome screen, click Configure and then Edit Custom VM Options.
If you cannot start CLion, manually copy the default file with JVM options to the CLion configuration directory.
If you do not have write access to the CLion configuration directory, you can add the CLION_VM_OPTIONS (CLION64_VM_OPTIONS on Windows) environment variable to specify the location of the file with your preferred JVM options. This file will override both the original default file and the copy located in the CLion configuration directory.
Locate the JVM options file
If you are not sure where CLion is getting its JVM options, check the following:
The location specified by the
CLION_VM_OPTIONS(CLION64_VM_OPTIONSon Windows) environment variable. If the specified file exists, it will override all other JVM options files.If the Toolbox App manages your current CLion instance, open the Toolbox App, click
 next to the relevant IDE instance, and select Settings. Under Configuration, find Java Virtual Machine options and click Edit.
next to the relevant IDE instance, and select Settings. Under Configuration, find Java Virtual Machine options and click Edit.If you are running a standalone CLion instance, check the configuration directory.
If there are no JVM options files defined in the previous locations, CLion will use the default JVM options file. Do not modify it. Use it only to check what are the default options that CLion uses.
Common options
The default values of the JVM options should be optimal in most cases. The following are the most commonly modified ones:
-XmxLimits the maximum memory heap size that the JVM can allocate for running CLion. The default value depends on the platform. If you are experiencing slowdowns, you may want to increase this value, for example, to set the value to 2048 megabytes, change this option to
-Xmx2048m.For more information, refer to Increase the memory heap of the IDE.
-XmsSpecifies the initial memory allocated by the JVM for running CLion. The default value depends on the platform. It is usually set to about half of the maximum allowed memory (see -Xmx), for example,
-Xms1024m.-XX:NewRatioSpecifies the ratio between the size of the young and old generation in the heap. In most cases, a ratio between 2 and 4 is recommended. This will set the size of the young generation to be 1/2 to 1/4 of the old generation correspondingly, which is good when you are often working on one project and only a few files at a time. However, if you are constantly opening new files and switching between several projects, you may need to increase the young generation. In this case, try setting
-XX:NewRatio=1, which will make the young generation as large as the old generation, allowing objects to remain in the young generation for longer.For more information, see Java Garbage Collection Basics.
Specify each option on a separate line. Example JVM options file:
For more information about the available JVM options, refer to the java command reference.
Platform properties
CLion enables you to customize various platform-specific properties, such as the path to user-installed plugins and the maximum supported file size. The default properties used to run CLion are specified in the IDE installation directory:
<IDE_HOME>\bin\idea.properties
CLion.app/Contents/bin/idea.properties
<IDE_HOME>/bin/idea.properties
Configure platform properties:
Do one of the following to create an empty idea.properties file in the configuration directory that will override the values from the original file:
Go to .
If you do not have any project open, on the Welcome screen, click Configure and then select Edit Custom Properties.
If you cannot start CLion, manually create an empty idea.properties file in the CLion configuration directory.
If you do not have write access to the CLion configuration directory, you can add the CLION_PROPERTIES environment variable to specify the location of the idea.properties file. The properties in this file will override the corresponding properties in both the original default file and the one located in the CLion configuration directory.
Common properties
Users often change the location of the default IDE directories. For more information, refer to Change the location of IDE directories.
Limits that can affect performance:
idea.max.content.load.filesizeMaximum size of files (in kilobytes) that CLion is able to open. Working with large files can affect editor performance and increase memory consumption. The default value is
20000.idea.max.intellisense.filesizeMaximum size of files (in kilobytes) for which CLion provides coding assistance. Coding assistance for large files can affect editor performance and increase memory consumption. The default value is
2500.idea.cycle.bufferMaximum size of the console cyclic buffer (in kilobytes). If the console output size exceeds this value, the oldest lines are deleted. To disable the cyclic buffer, set
idea.cycle.buffer.size=disabled.idea.max.vcs.loaded.size.kbMaximum size (in kilobytes) that CLion loads for showing past file contents when comparing changes. The default value is
20480.
Specify each property on a separate line. Example platform properties file:
CLion provides a number of other properties that define interaction with the environment (window managers, launchers, the file system, and so on). Most of them act like hidden settings (in the sense that they are not evidently exposed), which you may need to enable or disable in certain cases. Change these properties only if advised by JetBrains Support.
Adjusting CPU Cores Number
You can adjust the number of CPU cores to be used by the IDE when running the active tasks (e.g indexing header files, updating symbols, and so on) in order to keep the performance properly balanced between CLion and other applications running on your machine.
To set up the number of CPU cores:
Press Ctrl+Shift+A or choose from the main menu. In the popup that opens, start typing
Registry, select the corresponding item and press Enter.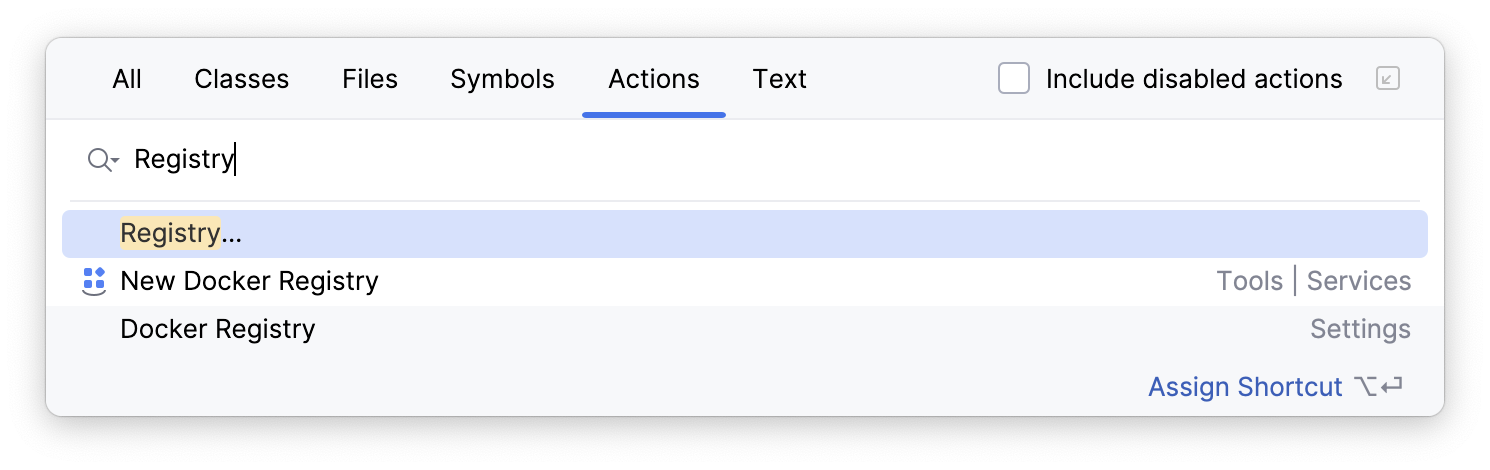
In this dialog, start typing
cidr.indexer.thread.count. The IDE highlights the corresponding key.
Click the Value field of the highlighted string and enter the desired number of CPU cores assuming the following:
Negative value N means that the actual number of CPU cores will be reduced by N to determine how many cores will be used. For example, in case of 8 CPU cores, set -1 to use 7 cores.
Set 0 to use all available cores.
Positive value determines the cores number to be used directly.