Connect to MySQL with named pipes
Named pipes provide a way for communication among processes that run on the same machine. By using named pipes, you can send your data without having the performance penalty that involves the network stack.
Just like you have a server that listens to an IP address and port for incoming requests, a server can also set up a named pipe that can listen for requests. In both cases, the client process must know the address or a pipe name to which it should send the request.
The default pipe name for the MySQL server is \\.\pipe\MySQL.
Step 1. Enable named pipes for the MySQL server
Verify that named pipes are enabled
To ensure that named pipes are enabled, run the following code:
SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'named_pipe'.If the
named_pipevariable has theONvalue, skip Step 1.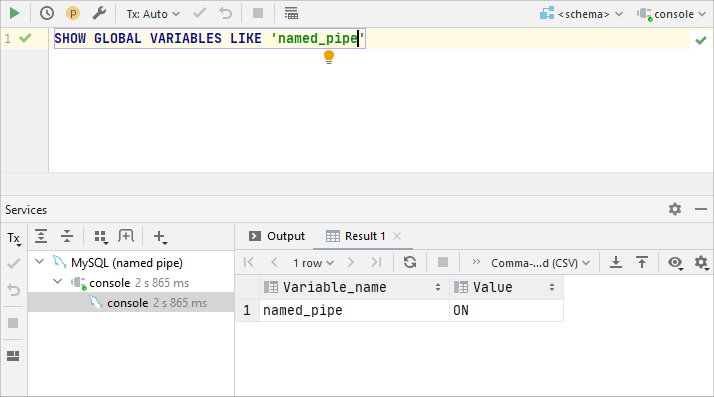
Enable named pipes during server installation
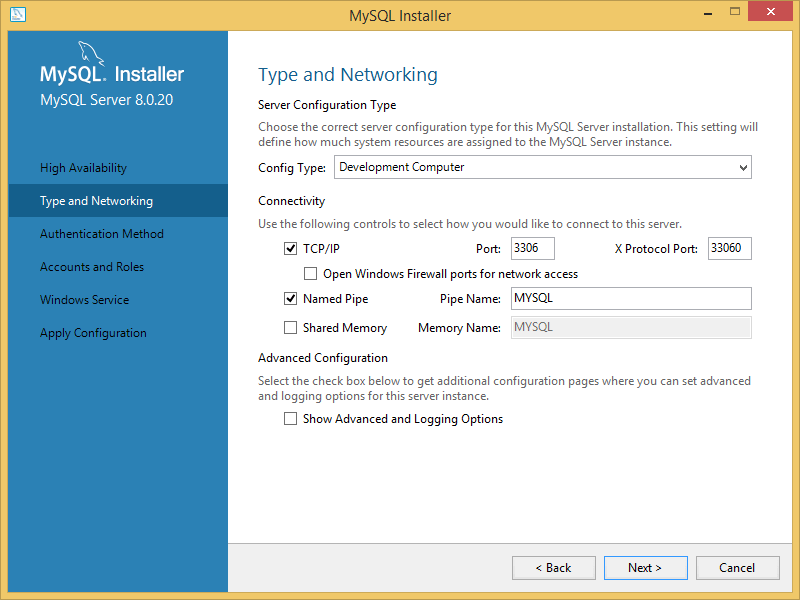
Run the installation wizard of the MySQL server.
On the Type and Networking dialog, select the Named Pipe checkbox. You can change the pipe name or leave the default value.
Finish all the steps of the installation wizard and start the MySQL server.
Enable named pipes in my.ini
Open the my.ini configuration file in a text editor.
Add the
enable-named-pipeparameter to themysqldsection. Consider the following example of themysqldsection:[mysqld] # The next three options are mutually exclusive to SERVER_PORT below. # skip-networking enable-named-pipe # shared-memory # shared-memory-base-name=MYSQL # The Pipe the MySQL Server will use socket=MYSQLSave changes and restart the MySQL server.
How to find my.ini and my.cnf?
In the command line, run
mysql --help. Scroll down to the end of the Options section.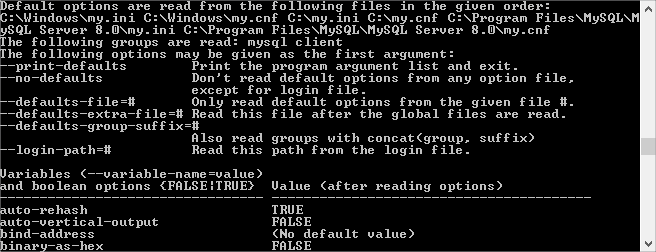
Step 2. Configure a connection in DataGrip
Navigate to or press Ctrl+Alt+Shift+S.
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon (
 ) and select MySQL.
) and select MySQL.At the bottom of the data source settings area, click the Download missing driver files link. Alternatively, you can specify user drivers for the data source. For more information about user drivers, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
On the Advanced tab, find the
serverTimezoneparameter in the list of options. Double-click the Value cell and type your server timezone (for example,UTC).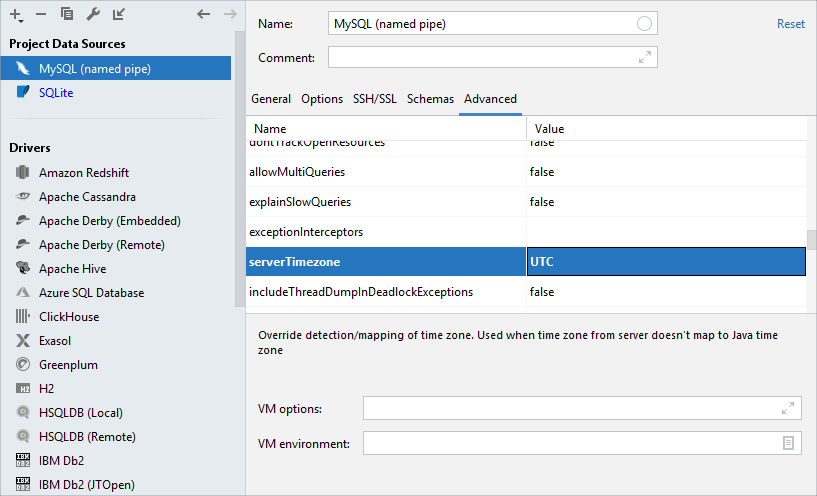
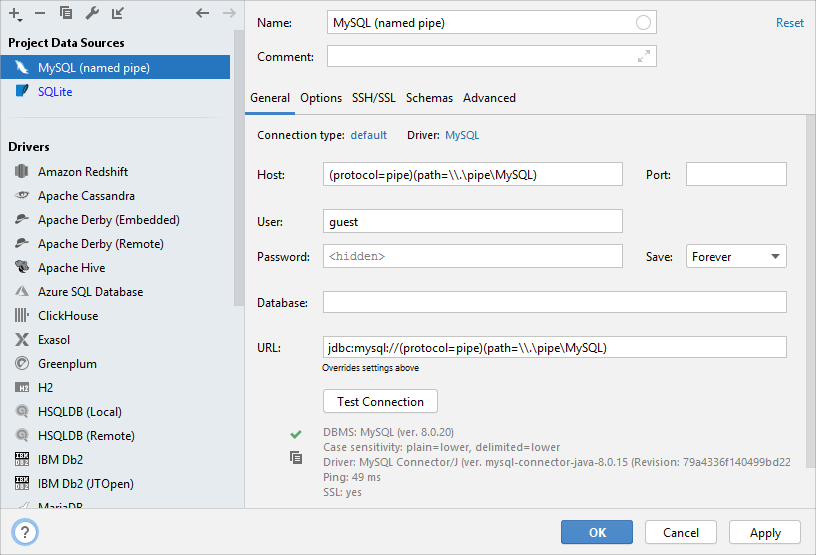
Click the General tab.
In the Host field, type the following text:
(protocol=pipe)(path=\\.\pipe\MySQL), whereMySQLis the pipe name.To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click Test Connection.