Resolve Git conflicts
When you work in a team, you may come across a situation when somebody pushes changes to a file you are currently working on. If these changes do not overlap (that is, changes were made to different lines of code), the conflicting files are merged automatically. However, if the same lines were affected, Git cannot randomly pick one side over the other, and asks you to resolve the conflict.
In Git, conflicts may arise when you attempt to perform one of the following operations: pull, merge, rebase, cherry-pick, unstash changes or apply a patch. If there are conflicts, these operations will fail, and you will be prompted to accept the upstream version, prefer your version, or merge the changes:
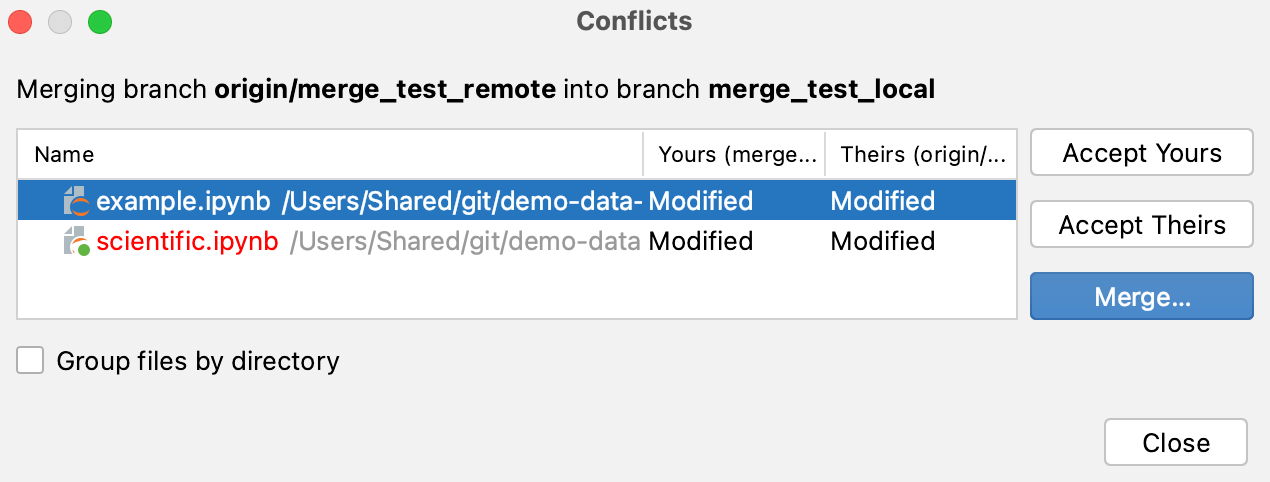
The Conflicts dialog is triggered automatically when a conflict is detected on the Git level.
If you click Close in this dialog or call a Git operation that leads to a merge conflict from the command line, a Merge Conflicts node will appear in the Changes view of the Commit tool window with a link to resolve them:
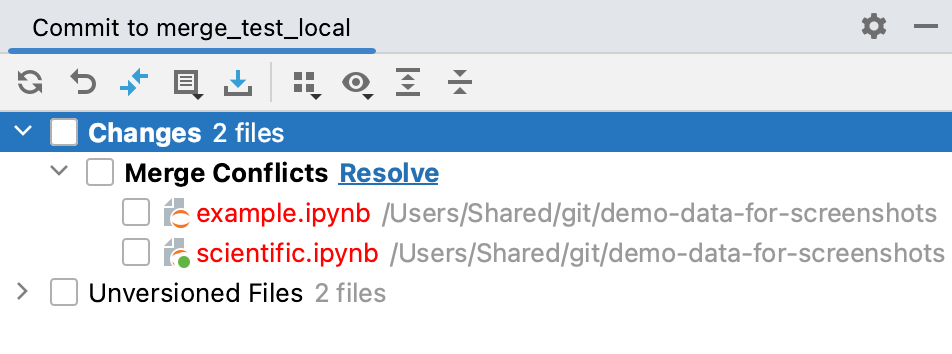
DataSpell provides a tool for resolving conflicts locally. This tool consists of three panes:
The left pane shows the read-only local copy
The right pane shows the read-only version checked in to the repository.
The central pane is a fully-functional editor where the results of resolving conflicts are displayed. Initially, the contents of this pane are the same as the base revision of the file, that is, the revision from which both conflicting versions are derived.
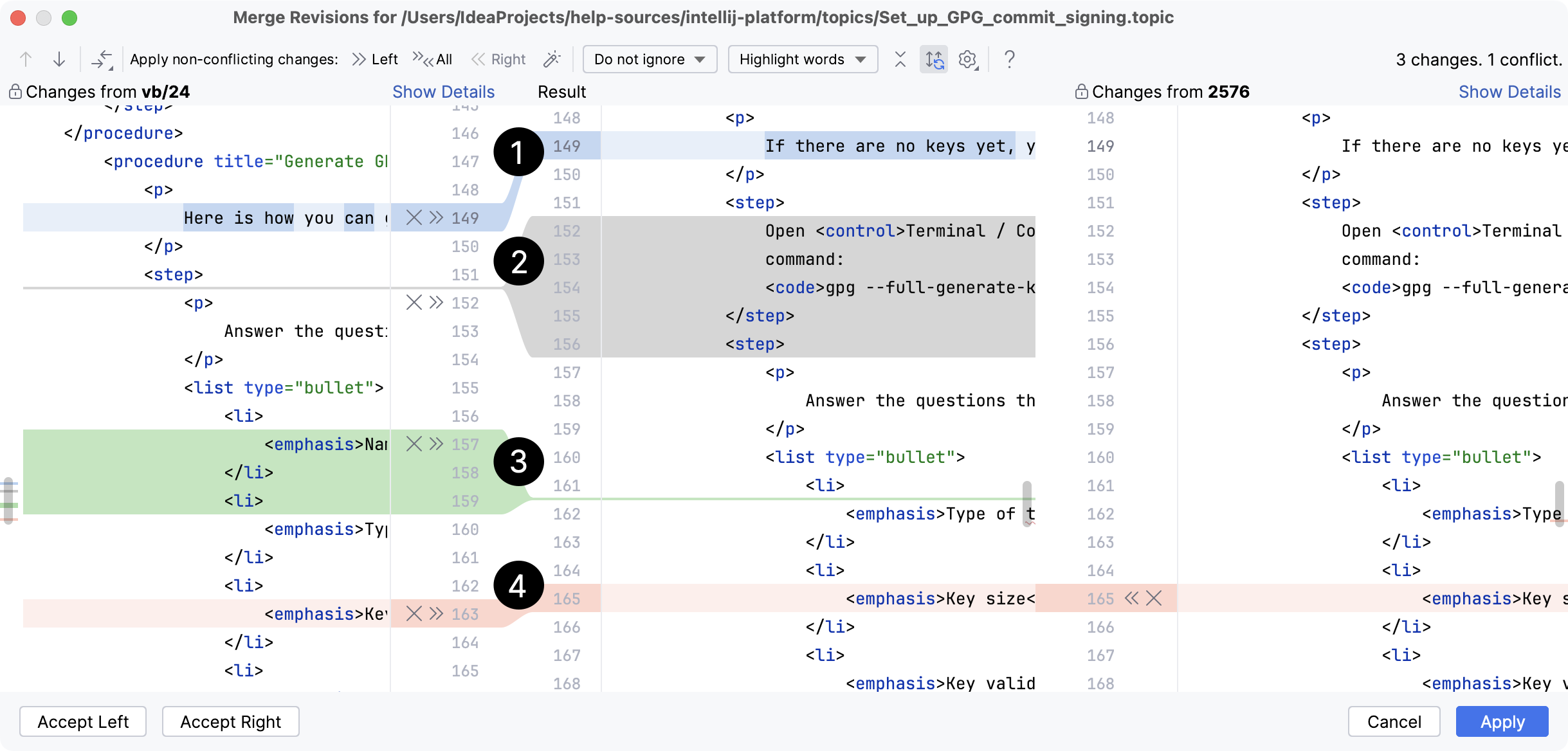
Modified line
Deleted lines
Newly added lines
Conflicting lines
Resolve conflicts
Click Merge in the Conflicts dialog, the Resolve link in the Local Changes view, or select the conflicting file in the editor and choose VCS | Git | Resolve Conflicts from the main menu.
To automatically merge all non-conflicting changes, click
(Apply All Non-Conflicting Changes) on the toolbar. You can also use the
(Apply Non-Conflicting Changes from the Left Side) and
(Apply Non-Conflicting Changes from the Right Side) to merge non-conflicting changes from the left/right parts of the dialog, respectively.
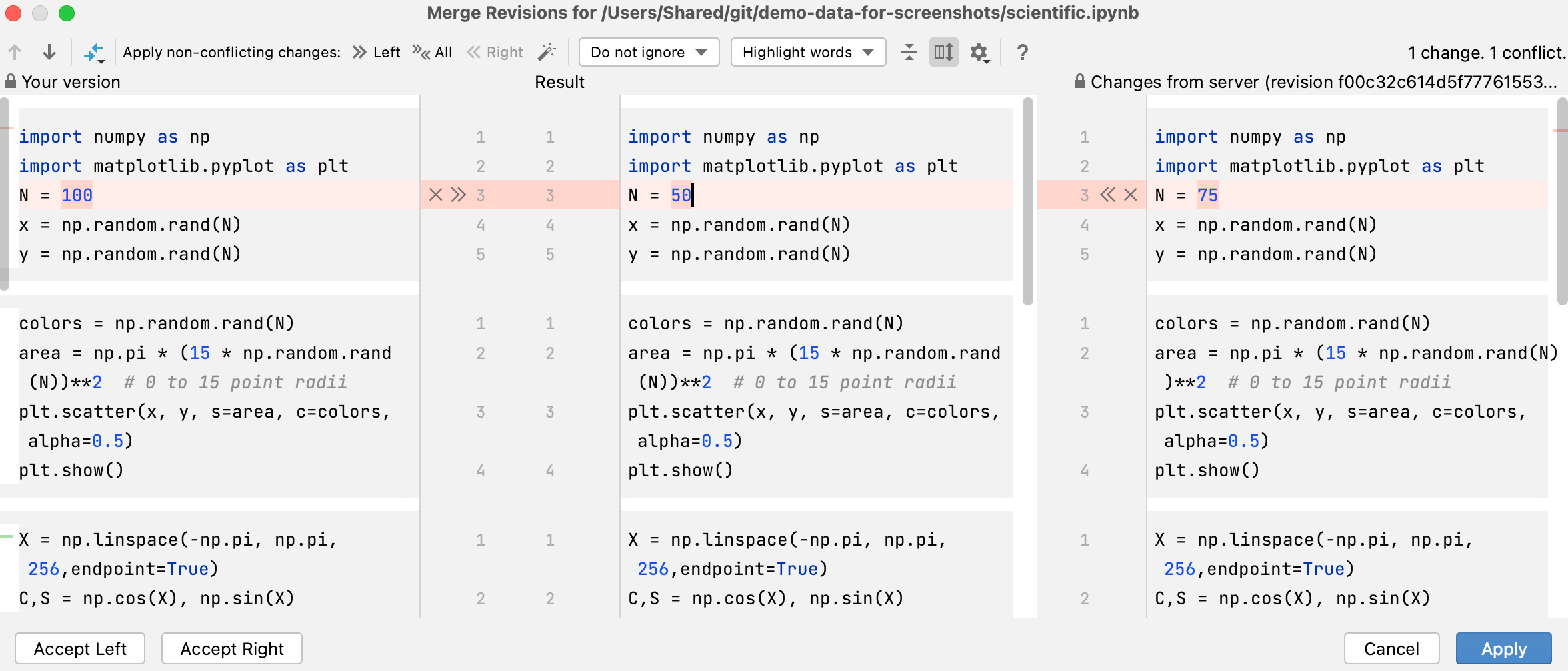
To resolve a conflict, you need to select which action to apply (accept
or ignore
) to the left (local) and the right (repository) versions and check the resulting code in the central pane:
You can also right-click a highlighted conflict in the central pane and use the commands from the context menu. The Resolve using Left and Resolve using Right commands provide a shortcut to accepting changes from one side and ignoring them from the other side, respectively:
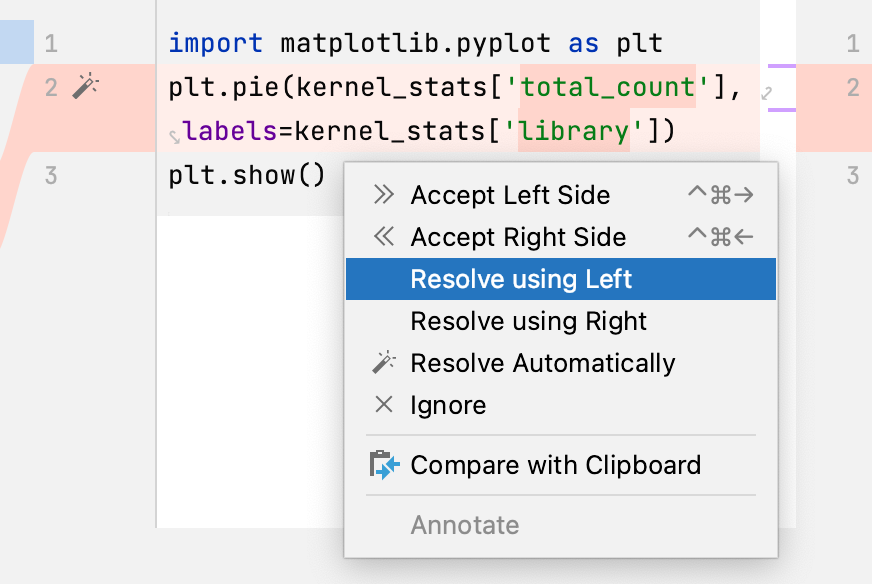
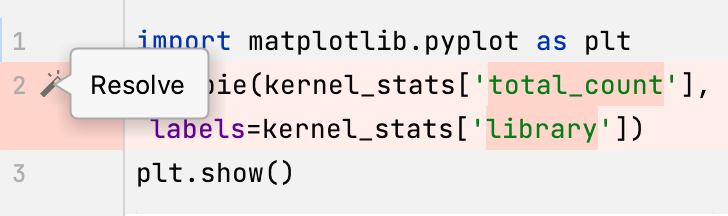
For simple conflicts (for example, if the beginning and the end of the same line have been modified in different file revisions), the Resolve simple conflicts
button that allows merging the changes in one click becomes available.
Such conflicts are not resolved with the Apply All Non-Conflicting Changes action since you must make sure that they are resolved properly.
Review merge results in the central pane and click Apply.
Productivity tips
- Apply non-conflicting changes automatically
You can configure DataSpell to always apply non-conflicting changes automatically instead of telling it to do so from the Merge dialog. To do this, select the Automatically apply non-conflicting changes option on the Tools | Diff Merge settings page Ctrl+Alt+S.
Handle conflicts related to LF and CRLF line endings
Quite often, people working in a team and contributing to the same repository use different operating systems. This may result in problems with line ending, because Unix, Linux and macOS use LF, and Windows uses CRLF to mark the end of a line.
DataSpell displays the discrepancies in line endings in the Diff Viewer, so you can fix them manually. If you want Git to solve such conflicts automatically, you need to set the core.autocrlf attribute to true on Windows and to input on Linux and macOS (for more details, refer to Dealing with line endings). You can change the configuration manually by running git config --global core.autocrlf true on Windows or git config --global core.autocrlf input on Linux and macOS.
However, DataSpell can automatically analyze your configuration, warn you if you are about to commit CRLF into a remote repository, and suggest setting the core.autocrlf setting to true or input depending on your operating system.
To enable smart handling of LF and CRLF line separators, open the Settings dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, and select the Version Control | Git node on the left. Enable the Warn if CRLF line separators are about to be committed option.
After you have enabled this option, DataSpell will display the Line Separators Warning Dialog each time you are about to commit a file with CRLF separators, unless you have set any related Git attributes in the affected file (in this case, DataSpell supposes that you clearly understand what you are doing and excludes this file from analysis).
In the Line Separators Warning Dialog, click one of the following:
Commit As Is to ignore the warning and commit a file with
CRLFseparators.Fix and Commit to have the
core.autocrlfattribute set totrueorinputdepending on your operating system. As a result,CRLFline separators will be replaced withLFbefore the commit.
If, at a later time, you need to review how exactly conflicts were resolved during a merge, you can locate the required merge commit in the Log tab of the Git tool window Alt+9, select a file with conflicts in the Commit Details pane in the right, and click or press Ctrl+D. For more information, refer to Review how changes were merged.