Continuous Testing
Continuous testing is a powerful feature that helps you follow test-driven development practices. It detects changes that affect unit tests, rebuilds all affected projects, and re-runs all new and affected tests. Everything is done automatically in the background.
Enable Continuous Testing
There can be only one continuous testing session in the solution at a time. You can create a continuous testing session from any existing unit test session. The previous continuous testing session will be replaced with the new one.
To enable continuous testing, open the Unit Test Sessions window, select tests, and click the continuous testing icon ![]() .
.
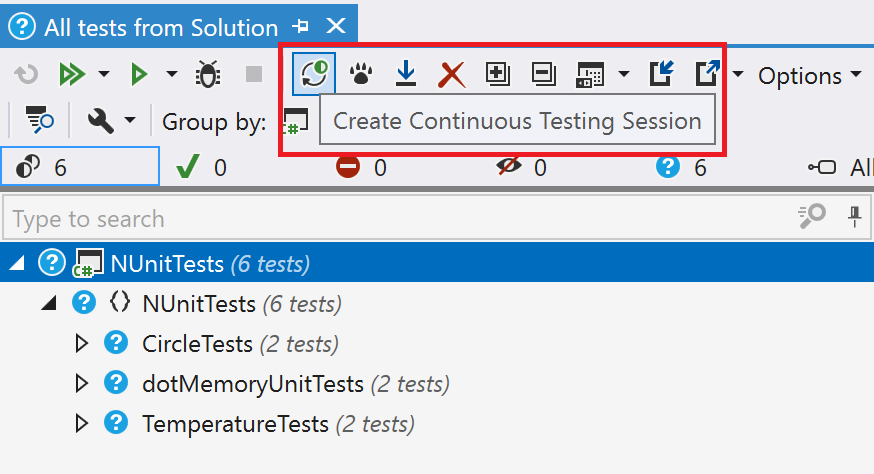
This will create a new Continuous Testing session.
Affected tests
Continuous testing uses the concept of 'affected tests' to define tests with a currently unknown execution result. All tests that have never been executed, were canceled, or didn't finish fall into this category.
Tests that have finished with a definite result (passed or failed) are relevant (not affected), but only until you make any change in your code. To make sure that there are no more affected tests after the change, you need to re-run these affected tests or all tests in the solution.
When continuous testing is enabled, dotCover calculates coverage of all unit tests and monitors changes in the covered code to detect whether the change affects any tests. When a test is affected, dotCover adds the question mark to its icon ![]() and changes the editor status indicator as well.
and changes the editor status indicator as well.
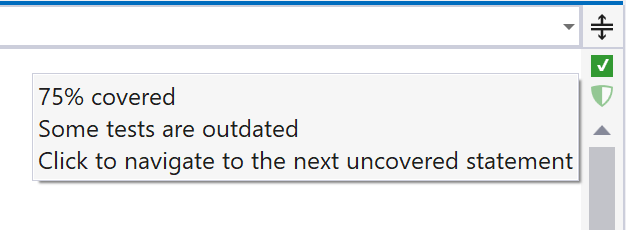
You can visualize code coverage to see which statements in your code are covered by unit tests and navigate from code to covering tests.
At any time, you can clear the information about the test execution result by clicking Drop coverage results ![]() on the toolbar.
on the toolbar.
Continuous testing modes
To select the continuous testing mode means answering two questions:
1. What triggers a test run?
You can select the preferred trigger in the ReSharper options using the main menu .
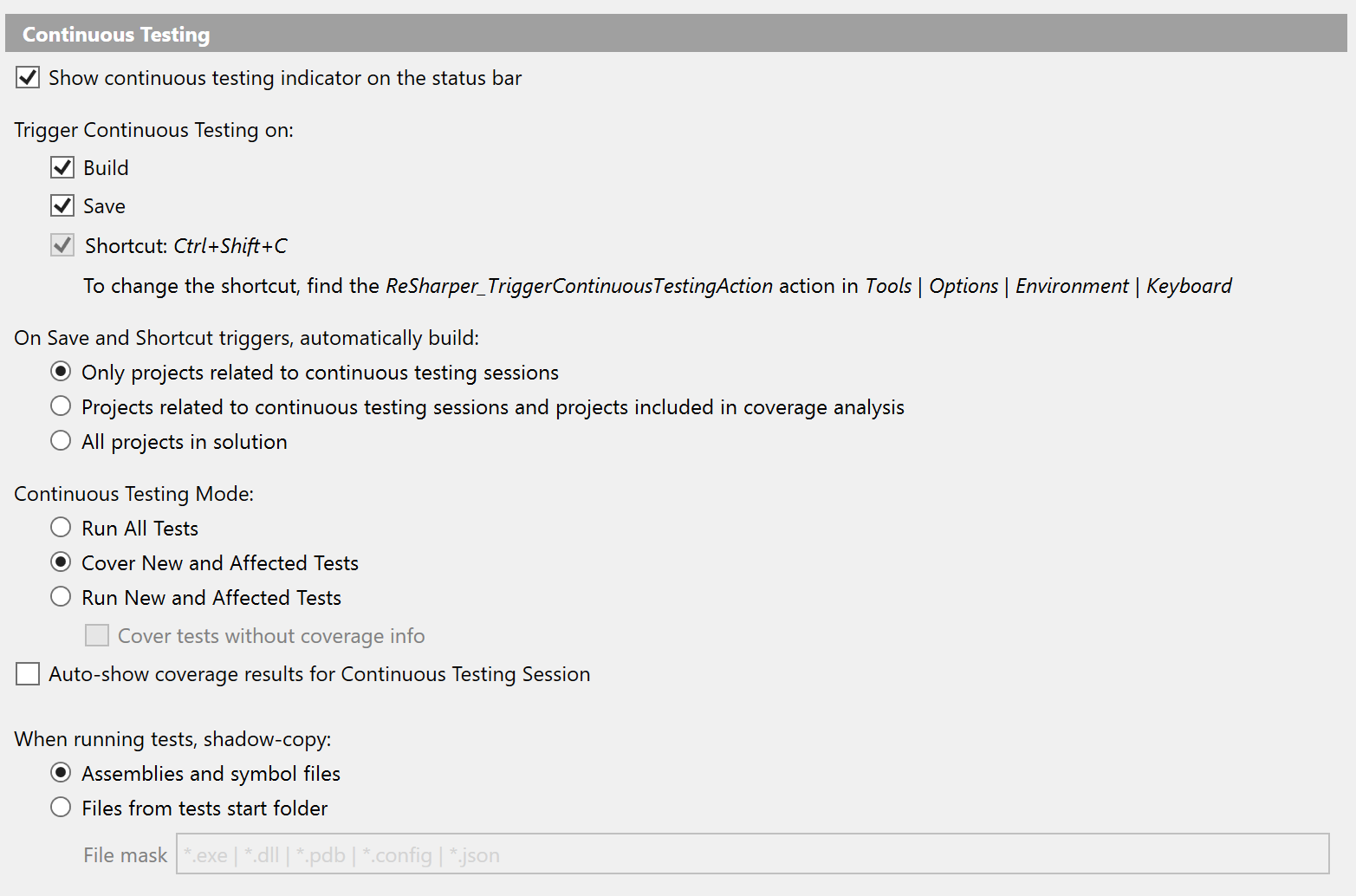
There are three options available:
Build: tests will be started each time you build the solution.
Save: tests will be started each time you save the solution. In this case, dotCover has to build the related projects on its own. To help you find the balance between the build time and the relevance of the coverage data, dotCover offers you three build options:
Only projects related to continuous testing sessions: dotCover will build only unit test projects and projects referenced by these unit test projects.
Projects related to continuous testing sessions and projects included in coverage analysis: dotCover will build projects that fall into the Only projects related to continuous testing sessions category and also projects with code that is not excluded from the coverage analysis.
All projects in solution: dotCover will always build the entire solution.
Shortcut: tests will be started after you apply a shortcut (by default, unassigned).
2. What tests will be run and how?
You can select the preferred mode in the ReSharper options using the main menu . The modes are available under Continuous Testing Mode:
Run All Tests: dotCover runs all tests without coverage analysis.
Cover New and Affected Tests: dotCover runs new and affected tests with enabled coverage analysis. This is the most resource-consuming but the most reliable mode. dotCover always keeps coverage information up to date.
Run New and Affected Tests: dotCover runs only new and affected tests without coverage analysis. This is the most resource-saving mode.
If you select Cover tests without coverage info, dotCover will analyze coverage for tests that have no coverage information. If the coverage information exists for a specific test (even if it is outdated), dotCover will run this test without coverage analysis. We recommend using this mode as a compromise between the resource consumption and the relevance of the coverage data.
Relevancy of coverage data
The Run All Tests and Run New and Affected Tests modes were created specifically to reduce the performance impact of continuous testing. By default, when one of these modes is selected, dotCover collects no new coverage information. Therefore, it makes sense to turn them on only in case you already have relevant coverage info. If you change the code covered by tests, the Unit Test Coverage window will explicitly tell you that coverage info for some tests is outdated:
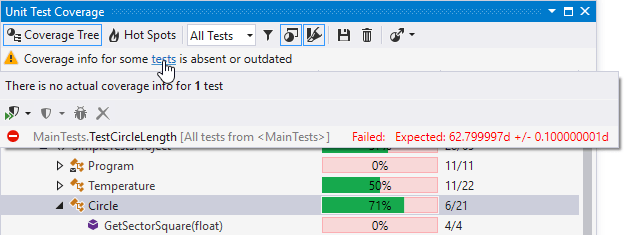
Coverage highlighting will also use pale colors to emphasize that it is based on possibly outdated coverage information.
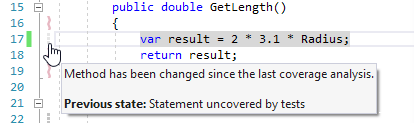
Nevertheless, if you're sure that the coverage info is still relevant, you may use these modes and postpone coverage until the info becomes really outdated.
(Recommended) The best compromise between the performance impact and the relevancy of coverage data is the Run New and Affected Tests mode with the Cover tests without coverage info option. This mode will run tests with outdated coverage info and analyze coverage for tests that have no coverage information.
Scope of continuous testing
Any session in the Unit Test Sessions window can be switched to the continuous testing mode. Therefore, you can have as many continuous testing scopes as many unit test sessions you have.
Continuous testing in action
After you enable Continuous Testing, you should run unit tests with coverage analysis to get the initial coverage data (e.g., use the Cover All Tests action for this). After making sure that all your tests are green, you can close the Unit Test Sessions window and go on working on your project. You will be able to see the current test status on the status bar of the main Visual Studio window.
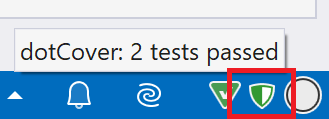
The status icon will notify you if any tests in the continuous testing session scope fail or become outdated after your changes.