Getting started with Java
This tutorial helps you get started with Java development in JetBrains Fleet. It covers installation, project setup, and working with Java code.
Prerequisites
Download and install JetBrains Toolbox
Download and install JetBrains Toolbox.
For macOS, you can also download the installer that matches your processor type: Apple Silicon or Intel. Ensure you select the correct option based on your system's processor.
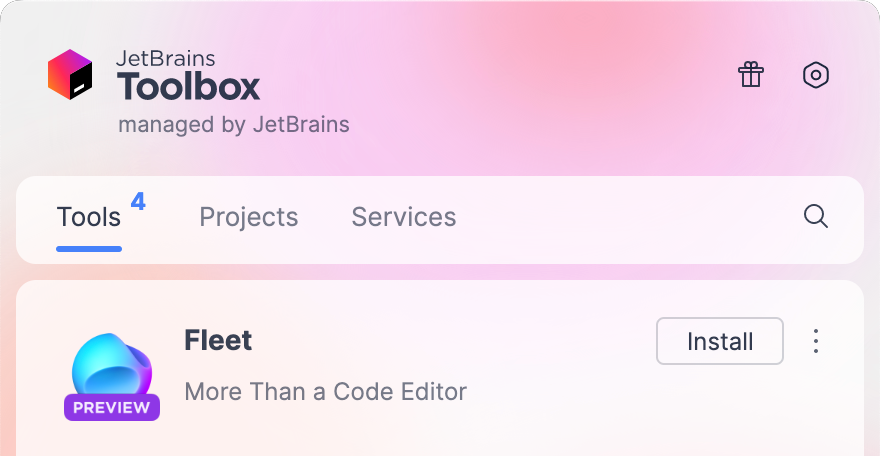
Download and install JetBrains Fleet
In JetBrains Toolbox, click Install next to the JetBrains Fleet icon.
Set up a workspace
A workspace is the directory that contains your project. It includes both project files and settings. You can either open an existing project or start a new one by opening an empty directory.
In this tutorial, you will start a new project and initialize it using a build tool such as Maven or Gradle.
Open a workspace
Press ⌘ O or select File | Open from the main menu.
In the file browser, navigate to an empty folder where you want to store your code, then click Open.
When you open a directory, it becomes the root of a workspace. You can view its contents in the Files view.
Now let's initialize the project. This will generate boilerplate code and some examples that you can use to try out JetBrains Fleet in action. The steps differ depending on the build system. Use the tabs below to view the instructions for your chosen build system.
Initialize the project
Make sure Gradle is installed on your computer.
Press ⌃ ⇧ ` to open a terminal and run the
gradle initcommand.When prompted, select the following options:
Project type: Application
Implementation language: Java
Enter target Java version: press ⏎ to accept the default value
Split functionality across subprojects: no
Build script DSL – Kotlin
Generate build using new APIs and behavior: no
Test framework – JUnit 4
Project name: press ⏎ to accept the default value
Select application structure: press ⏎ to accept the default value
Source package: press ⏎ to accept the default value
Initialize the project
Ensure Maven is installed on your computer.
Press ⌃ ⇧ ` to open a terminal and run the following command:
mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=com.mycompany.app -DartifactId=my-app -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart -DarchetypeVersion=1.4 -DinteractiveMode=false
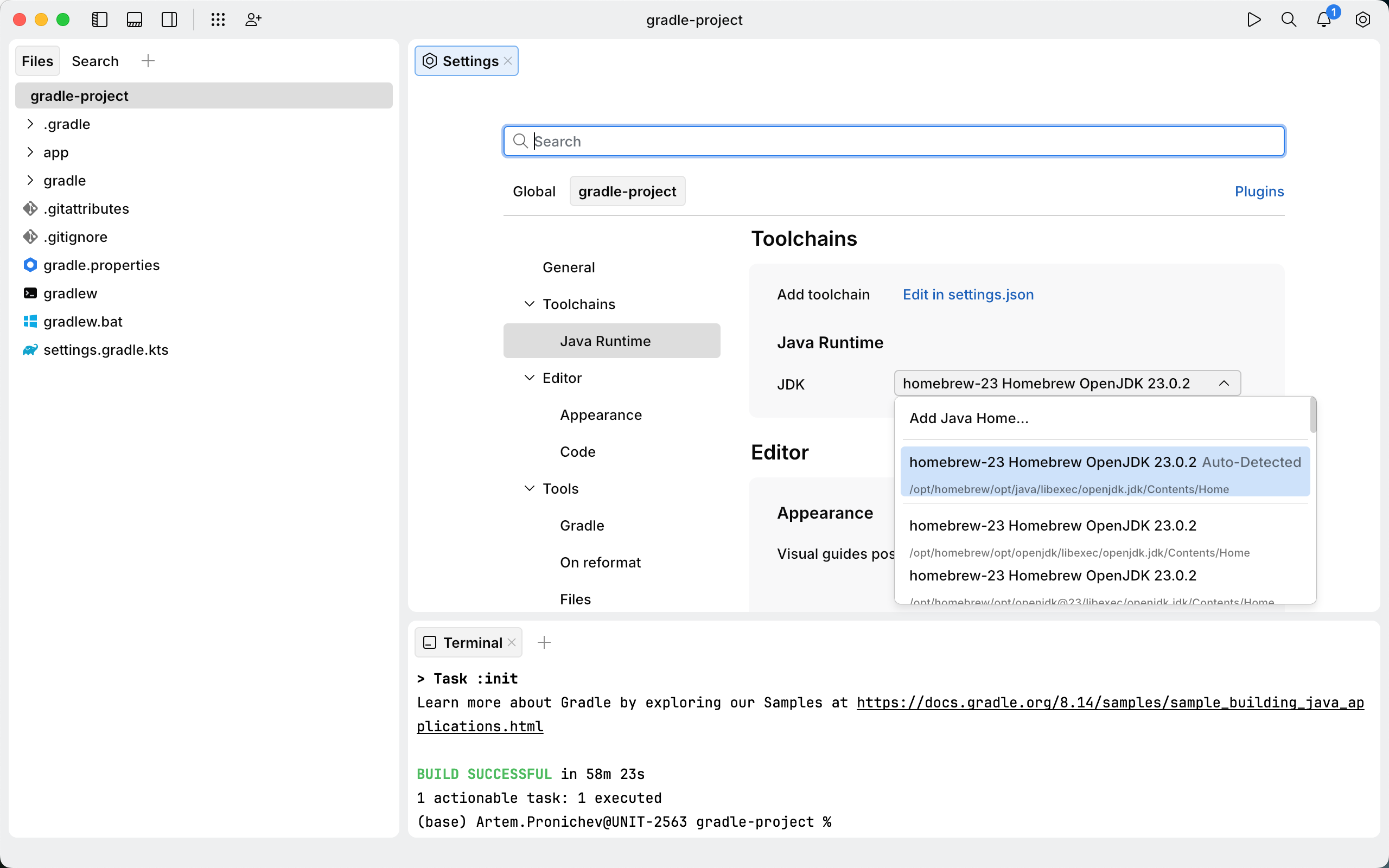
By default, JetBrains Fleet uses the JDK from your JAVA_HOME environment variable. Before proceeding, make sure it is configured in your environment. Otherwise, you can configure a custom JDK for your project.
Configure project JDK
Code assistance
You can use JetBrains Fleet as a smart text editor, rather than a full-fledged code editor. However, if you need code intelligence features, you can enable them by turning Smart Mode on.
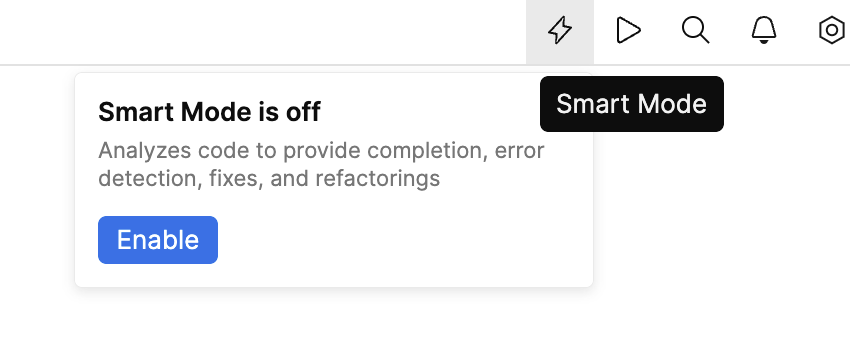
Enable Smart Mode
In the top-right corner of the window, click Smart Mode, then Enable.
After you click the Enable button, you may have to wait for some time, while the backend is being prepared.
JetBrains Fleet provides a variety of coding assistance features. Below are a few examples to help you get a sense of how they work in practice. This is not a complete list, but a good starting point for exploring what JetBrains Fleet can do.
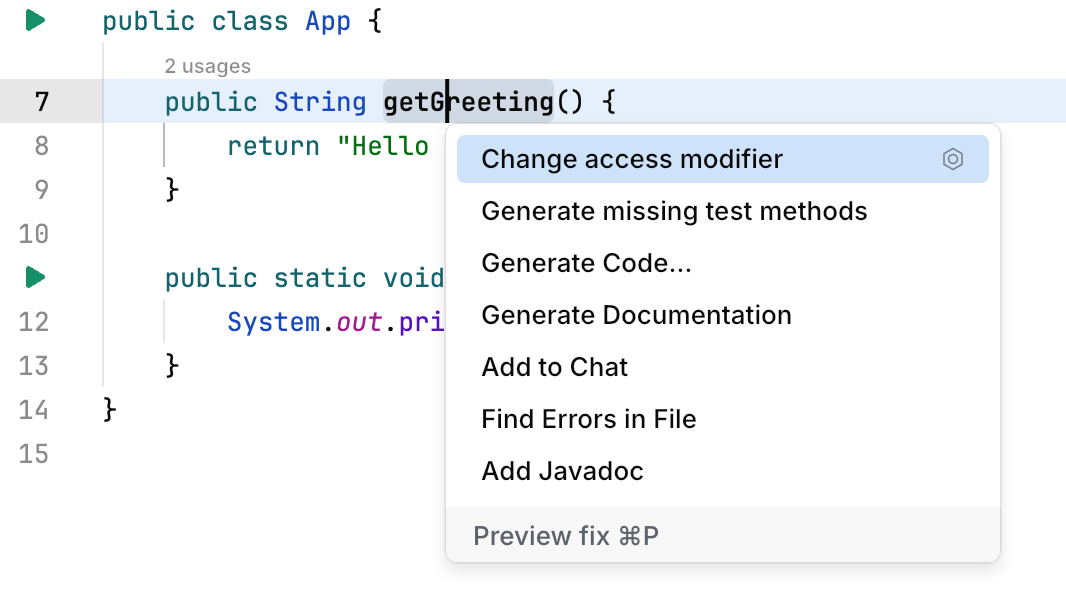
Use quick-fixes and intention actions
Press ⌥ ⏎ to access actions that Fleet suggests in the current context.
Refactor code
Place the caret on a literal or select an expression, then press ⌘ ⌥ V.
A variable will be extracted from the selected expression.

Navigate the codebase
Navigate to a symbol’s declaration by pressing ⌘ B.
Use code interlines to navigate to usages and hierarchy members.

Navigate between errors using ⌘ E and ⌘ ⇧ E.
Use live templates
To generate a
forloop, typeforiand press ⇥. Press ⇥ as you fill in the necessary variables.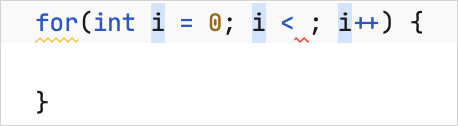
Run and Debug
With Smart Mode enabled, you can run your project.
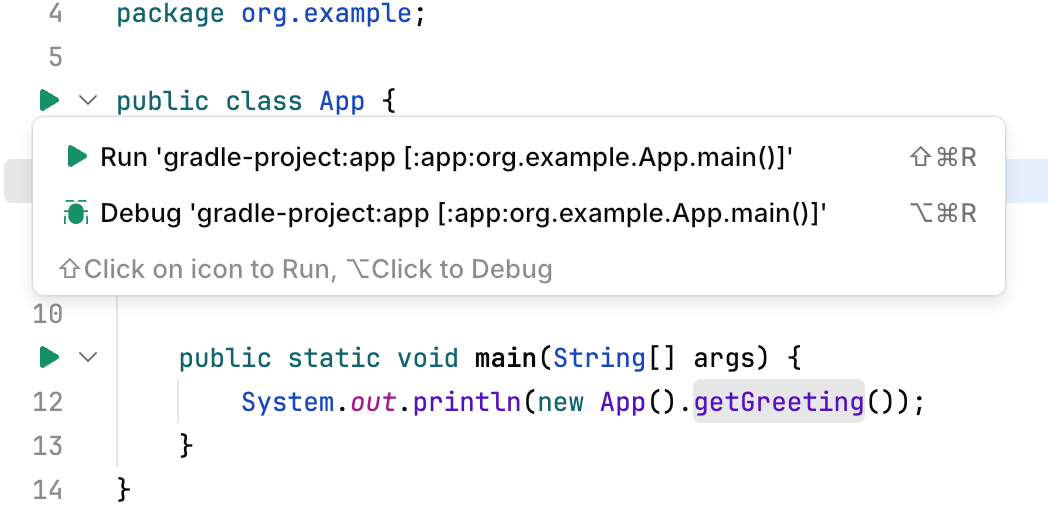
Run from the editor
Navigate to the entry point of your application and click the run icon in the gutter. Select Run.
Another way to run a program is to use a run configuration. It allows you to customize the startup: add arguments, use custom commands, environment variables and so on.
Create a run configuration
Press ⌘ R. Run & Debug dialog opens.
Click Create Run Configurations.
In run.json, append a gradle run configuration to the array, so that the resulting JSON looks like the following:
{ "configurations": [ { "name": "run sh", "type": "command", "program": "/bin/sh" }, { "name": "gradle run", "type": "gradle", "tasks": [ "run" ] } ] }
Launch a run configuration
Press ⌘ R. The Run dialog opens. Select the newly created
gradle runconfiguration.The application runs, and you can review its output in the console that opens.

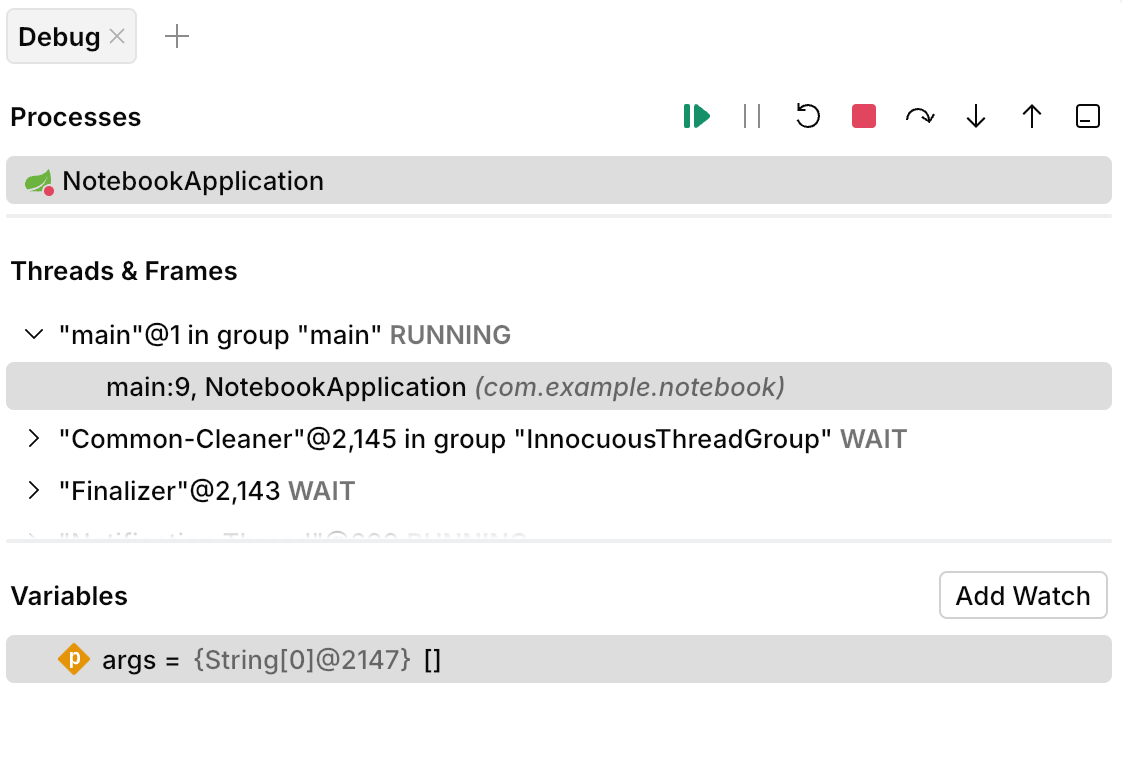
Debug the application
Set a breakpoint by clicking at an executable line in the gutter. This will suspend the application just when this line is about to execute.
Run the application by selecting Debug from the gutter menu or in the Run dialog.
All application threads get suspended when any of them reaches the line with the breakpoint.
Inspect the program state in the Run and debug panel. As we are using a hello-world type of app here, we don't have a lot of state to inspect.
The buttons above the threads list let you control the program execution. You can advance it line-by-line, step in and out of methods, resume and stop the program.