Run/debug configurations
GoLand uses run/debug configurations to run, debug, and test your code. Each configuration is a named set of run/debug startup properties.
If the Navigation bar is visible (), you can access all available run/debug configurations from the selector on the toolbar.
Run/debug configurations can be created as:
Temporary– created every time you run or debug functions or tests.
The maximum number of temporary configurations is 5. The older ones are automatically deleted when new ones are added.Permanent– created explicitly from a template or by saving a temporary configuration. Permanent configurations remain as part of your project until you remove them.
So whenever you run/debug or test your code, GoLand either uses an existing permanent run/debug configuration or creates a new temporary one.
Permanent configurations have opaque icons while the icons of temporary configurations are semi-transparent.
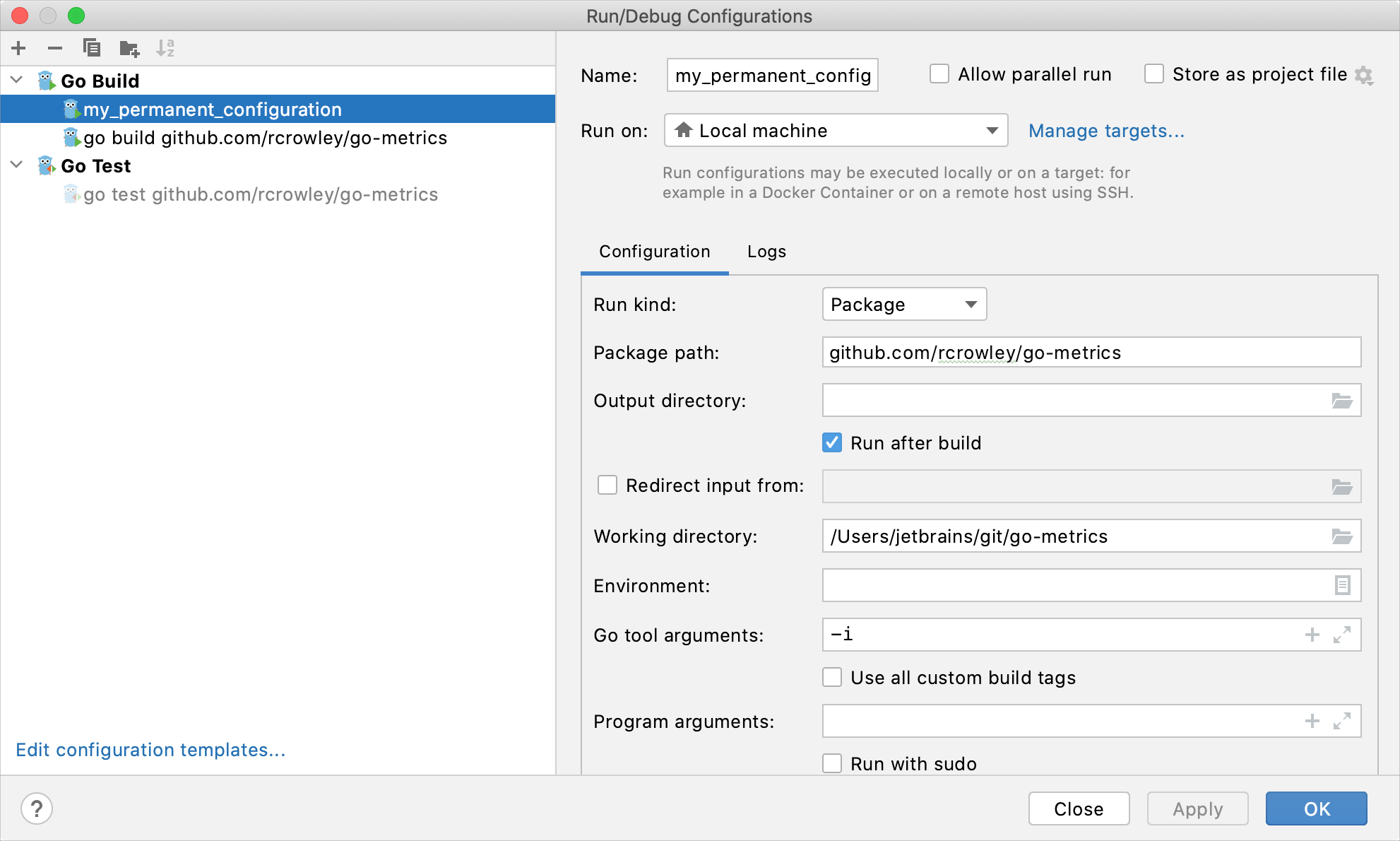
Create permanent run/debug configurations
GoLand provides the following ways to create a permanent run/debug configuration:
Create from a template or copy an existing configuration.
Save a temporary configuration as permanent
Select a temporary configuration in the run/debug configuration switcher and then click Save Configuration.

Alternatively, select a temporary configuration in the Run/debug configurations dialog and click
on the toolbar.
GoLand provides run/debug configuration templates for different languages, tools, and frameworks. The list of available templates varies depending on the installed/bundled plugins.
Create a run/debug configuration from a template
Open the Run/Debug Configuration dialog in one of the following ways:
Select from the main menu.
With the Navigation bar visible (), choose from the run/debug configuration selector.
Press Alt+Shift+F10, then press 0 or select the configuration from the popup and press F4.
In the Run/Debug Configuration dialog, click
on the toolbar or press Alt+Insert. The list shows the run/debug configuration templates. Select Go build.
Specify the run/debug configuration name in the Name field. This name will be shown in the list of the available run/debug configurations.
On the Configuration tab, you can set the following options:
Run kind: a building scope for your application. File and Package scopes work similarly in tests and compilation/running configurations (in terms of the scope they cover).
Directory: build an application in the specified directory as a package, without processing any subdirectories.
For test configurations, GoLand runs all the tests in the specified directory and all its subdirectories.
File: build an application from files specified in the Files field. To pass multiple file paths, use the vertical bar (
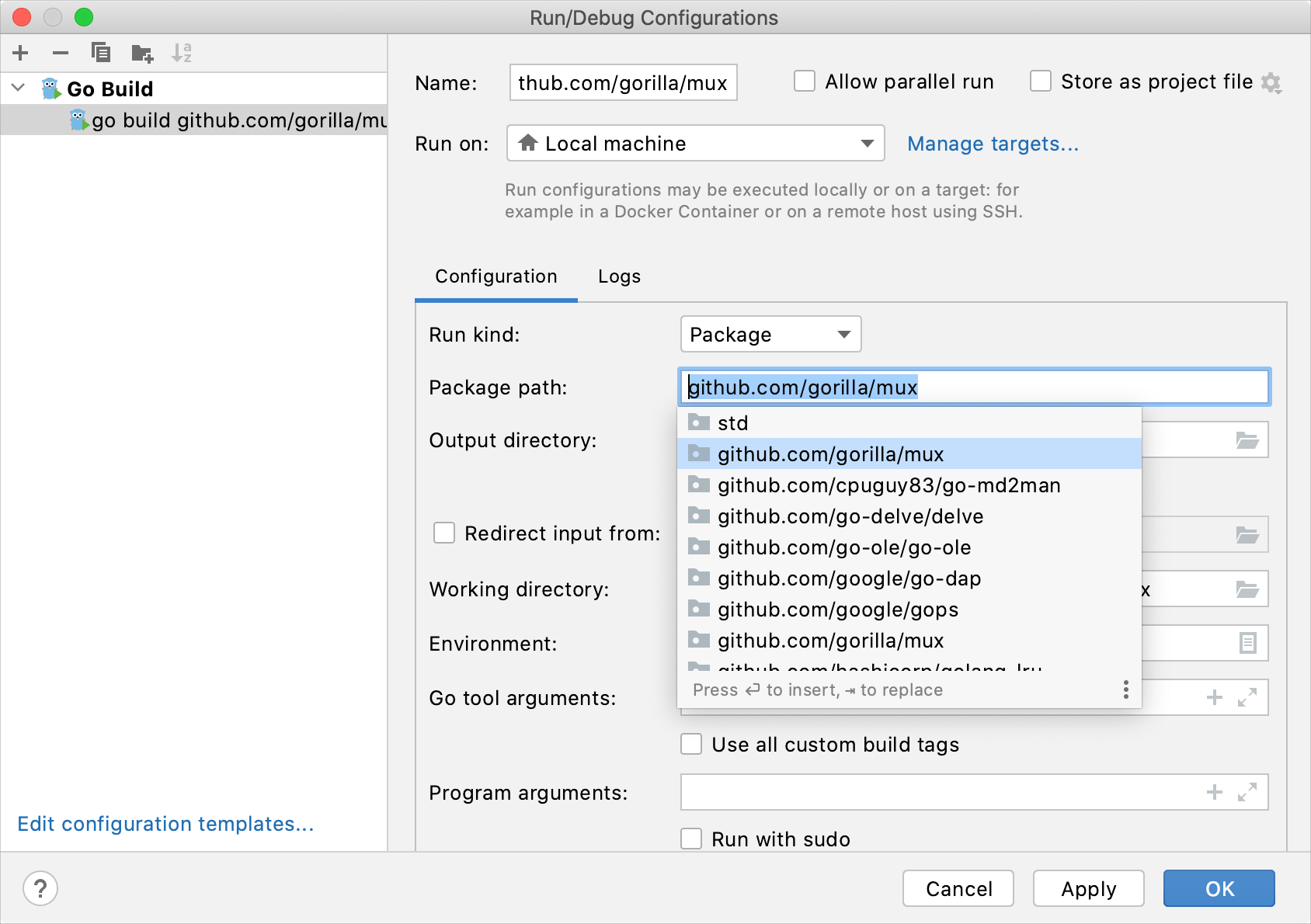
|) as a delimiter. This configuration is automatically selected when you run your program from scratch files.Package: build a single package with all its dependencies. Specify a full import path to the package that you want to build in the Package path field (for example,
github.com/gorilla/mux). This configuration is automatically selected when you run themainfunction or a separate test by using the Run icon () in the gutter.
Package path: a full import path of the package that you want to compile (for example,
github.com/gorilla/mux). This field is available only when you select the Package run kind.You can press Ctrl+Space to see a list of available packages.
Output directory: a directory for the executable file.
Run after build: execute the application after the build.
Working directory: a directory that is used for the built application. If you have any code that creates relative files or directories, they will be relative to this directory.
Environment: environment variables for your application.
To edit environment variables, click the Browse button at the end of the field. In the Environment Variables dialog, click the Add button and add the environment variables that you need.

Go tool arguments: arguments for the go tool (for example,
-o). Also, you can use macros in this field.Use all custom build tags: all tags that are applied during the build. Tags are listed in settings Ctrl+Alt+S under .
Program arguments: arguments for the built application. Also, you can use macros in this field.
Run with sudo: grant sudo privileges for the application.
Module: name of the current module.
Before launch: add tasks that you want to launch before the launch of the selected run/debug configuration. To add a task click the Add button Alt+Insert and select the tool that you want to add.
Store as project file: Enable this option to save your configuration as a project file and share it with team members through VCS.
In the Before launch section, define whether you want to perform any specific actions before launching the application, for example, launch an external tool or another build configuration before run. To skip the build stage, remove Build from the Before launch list.
Apply the changes and close the dialog.
Templates for tests and benchmarks
Templates for Go tests work the same way as templates for Go applications (Go Build). But instead of selecting Go Build, you should select Go Test.
Run/debug configuration templates for tests
Navigate to .
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, click Add New Configuration Alt+Insert and select Go Test.
From the Test kind list, select the scope from which you want to run tests:
Directory: to run all the tests in the specified directory. In the Directory field, specify a path to a directory that includes an application file and a test file (for example, applicationFolder/ with main.go and main_test.go).
Package: to run all the tests that belong to a package. In the Package path field, select a path to the package with tests that you want to run (for example,
github.com/rcrowley/go-metrics).To enable package tests, open setting by pressing Ctrl+Alt+S, navigate to , and select the Enable Go modules integration checkbox.
File: to run all tests from a testing file. In the Files field, type a path to a testing file.
Ensure that the Files field does not include other paths.
(Optional) Also, you can specify the following settings:
Working directory: a directory that is used for the built application. If you have any code that creates relative files or directories, they will be relative to this directory.
Output directory: directory that stores your test results if any.
Run after build: execute a test after the build.
Redirect input from: a path to the file that will to take program input instead of the console.
Working directory: directory that is used for the built application. If you have any code that creates relative files or directories, they will be relative to this directory.
Environment: environment variables that you need to run the test.
To edit environment variables, click the Browse button at the end of the field. In the Environment Variables dialog, click the Add button and add the environment variables that you need.

Go tool arguments: arguments for the go tool (for example,
-tags).Use all custom build tags: all tags that are applied during the build. Tags are listed in settings Ctrl+Alt+S under .
Program arguments: arguments for the test.
Run with sudo: grant sudo privileges to the test.
Before launch: Activate tool window: add tasks that you want to launch before the launch of the selected run/debug configuration. To add a task, click the Add button Alt+Insert and select the tool that you want to add.
Click Apply.

Share run/debug configurations
If you are working in a team, you might want to share your run/debug configurations so that your teammates could run the application using the same configuration or enable them to remotely attach to the process you are running.
For these purposes, GoLand provides a mechanism to store your run/debug configurations as project files and share them through VCS. The same mechanism can also be used when you want to send your configuration as a file to someone else. This saves a lot of time as run/debug configurations sometimes get sophisticated, and keeping them in sync manually would be tedious and error-prone.
From the main menu, select . Alternatively, press Alt+Shift+F10, then 0.
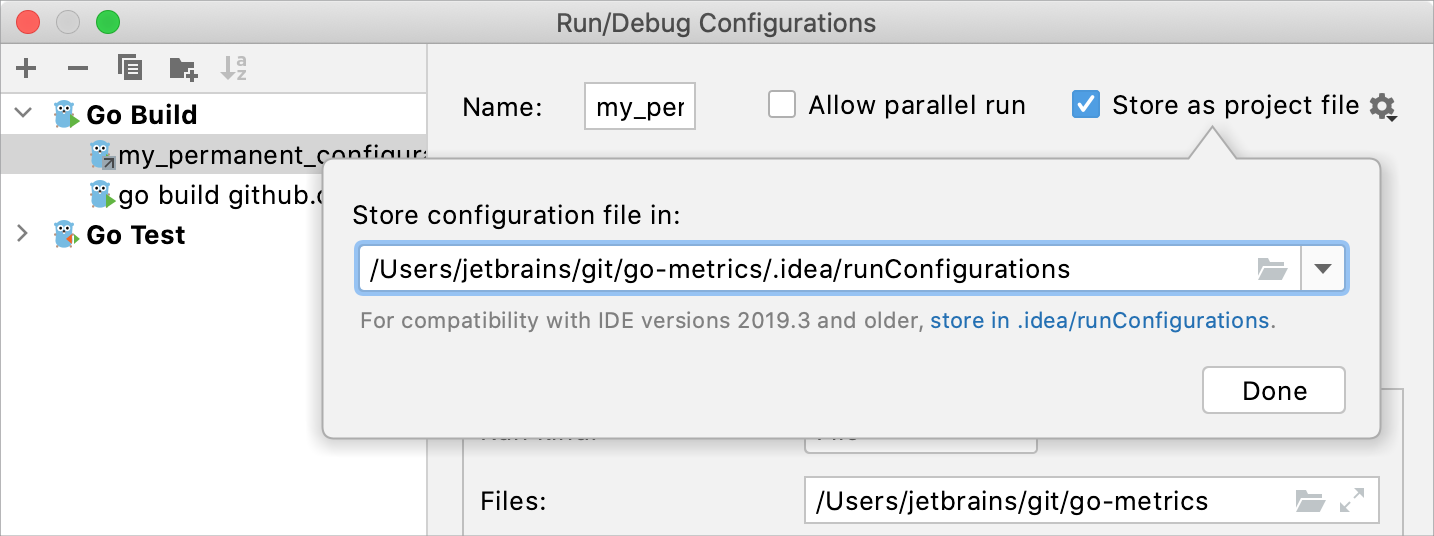
Select the run/debug configuration you want to share, enable the Store as project file option, and specify the location where the configuration file will be stored.
If compatibility with GoLand 2019.3 and earlier is required, store the file in the default location.
(Optional) If the .idea directory is added to VCS ignored files, the .idea/runConfigurations subfolder will be ignored, too. If you use Git for your project, you can share .idea/runConfigurations only and leave .idea ignored by modifying .gitignore as follows:
/.idea/* !/.idea/runConfigurations
Run/debug configuration templates
Each type of run/debug configuration is a template that you can edit, so the next time you create a new configuration of that type, its parameters already have the desired values.
Configure the default values for a template
From the main menu, select . Alternatively, press Alt+Shift+F10, then 0.
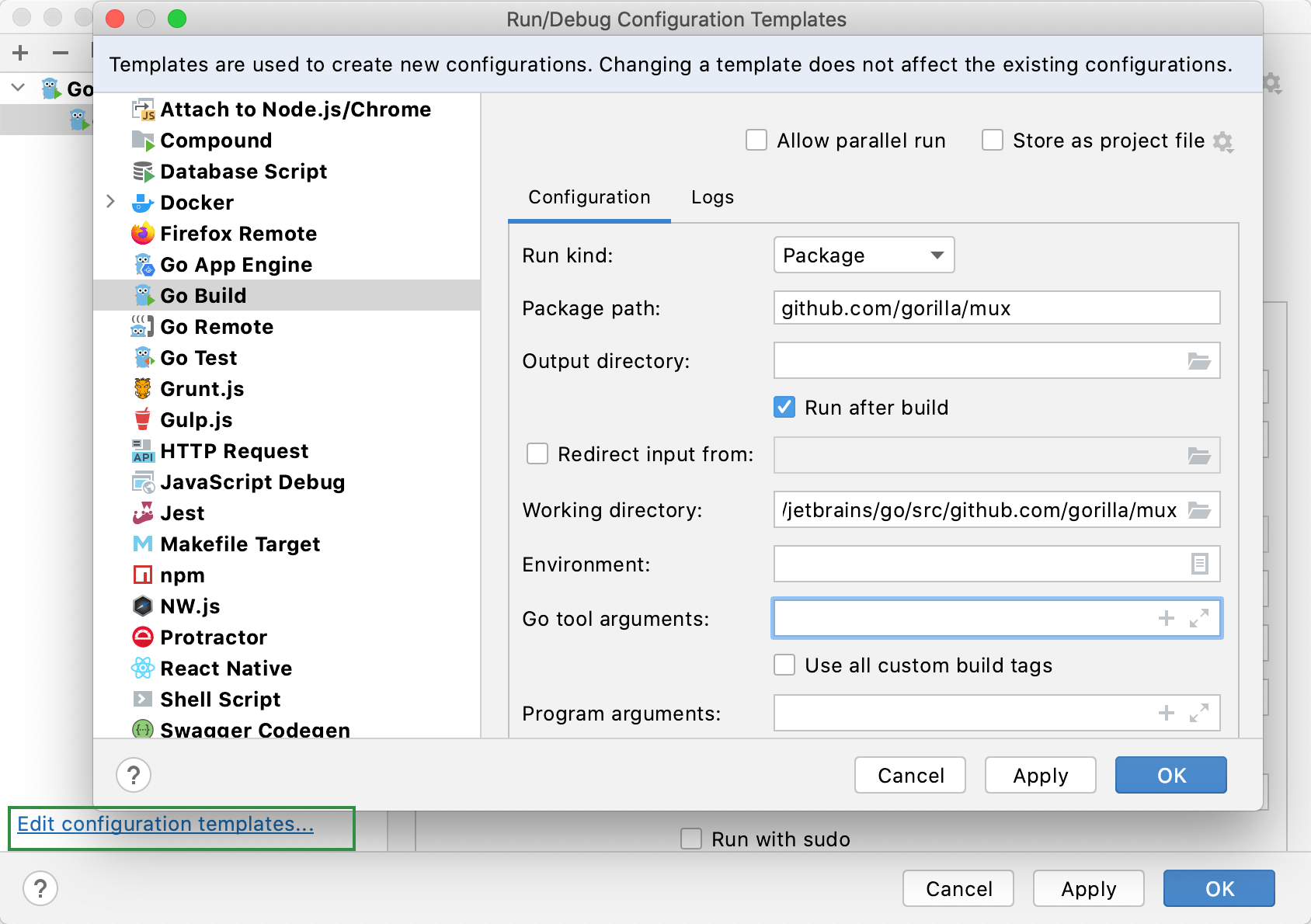
In the left-hand pane of the run/debug configuration dialog, click Edit configuration templates.
In the Run/Debug Configuration Templates dialog that opens, select a configuration type.
Specify the desired default parameters and click OK to save the template.
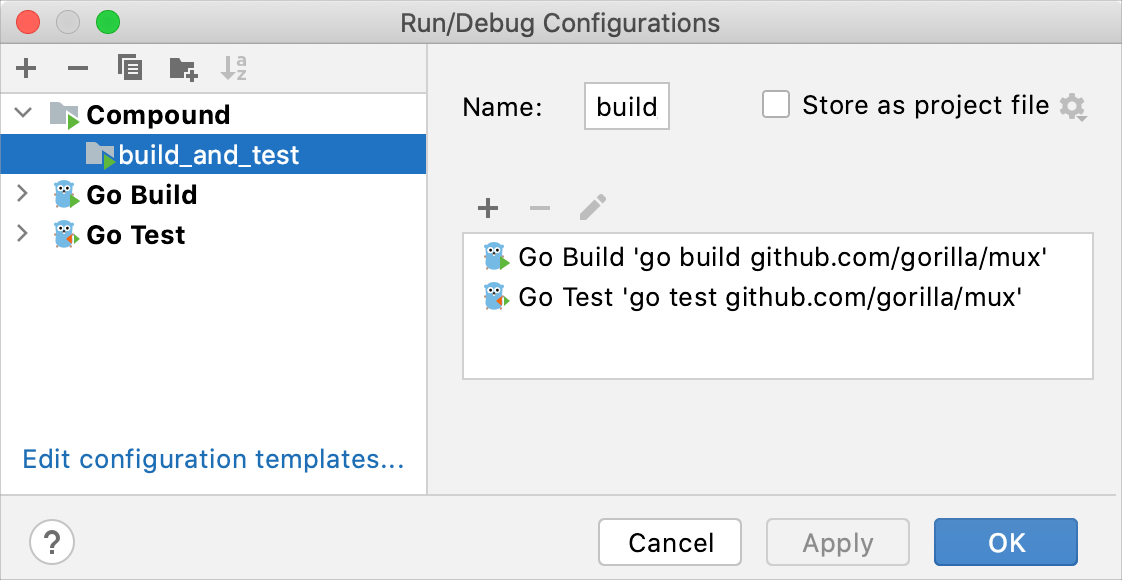
Compound run/debug configurations
Suppose you would like to launch multiple run/debug configurations simultaneously. For example, you may want to run several configurations of different types or a sequence of several test configurations. You can configure this behavior with a compound run/debug configuration.
When you run or debug your code using a compound configuration, you actually launch a sequence of configurations in the order they are listed.
Create a compound run/debug configuration
From the main menu, select . Alternatively, press Alt+Shift+F10, then 0.
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, click
or press Alt+Insert, then select Compound.
Specify the run/debug configuration name in the Name field. This name will be shown in the list of the available run/debug configurations.
Select Store as project file to make this run/debug configuration available to other team members.
To include a new run/debug configuration into the compound configuration, click Add
and select the desired one from the list.
Apply the changes.
Run/debug configuration folders
When there are many run/debug configurations of the same type, you can group them in folders so they become easier to distinguish visually.
Once grouped, the run/debug configurations appear in the list under the corresponding folders.
Create a folder for run/debug configurations
From the main menu, select . Alternatively, press Alt+Shift+F10, then 0.
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, select a configuration type and click
on the toolbar. A new empty folder for the selected type is created.
Specify the folder name in the text field to the right or accept the default name.
Select the desired run/debug configurations and move them under the target folder.
Apply the changes. If a folder is empty, it will not be saved.
When you no longer need a folder, you can delete it Delete. The run/debug configurations grouped under this folder will be moved under the root of the corresponding run/debug configuration type.