How to run PostgreSQL queries from GoLand
Starting a project
Create a Go project
Select .
Alternatively, navigate to New | Project on the Welcome to GoLand dialog.
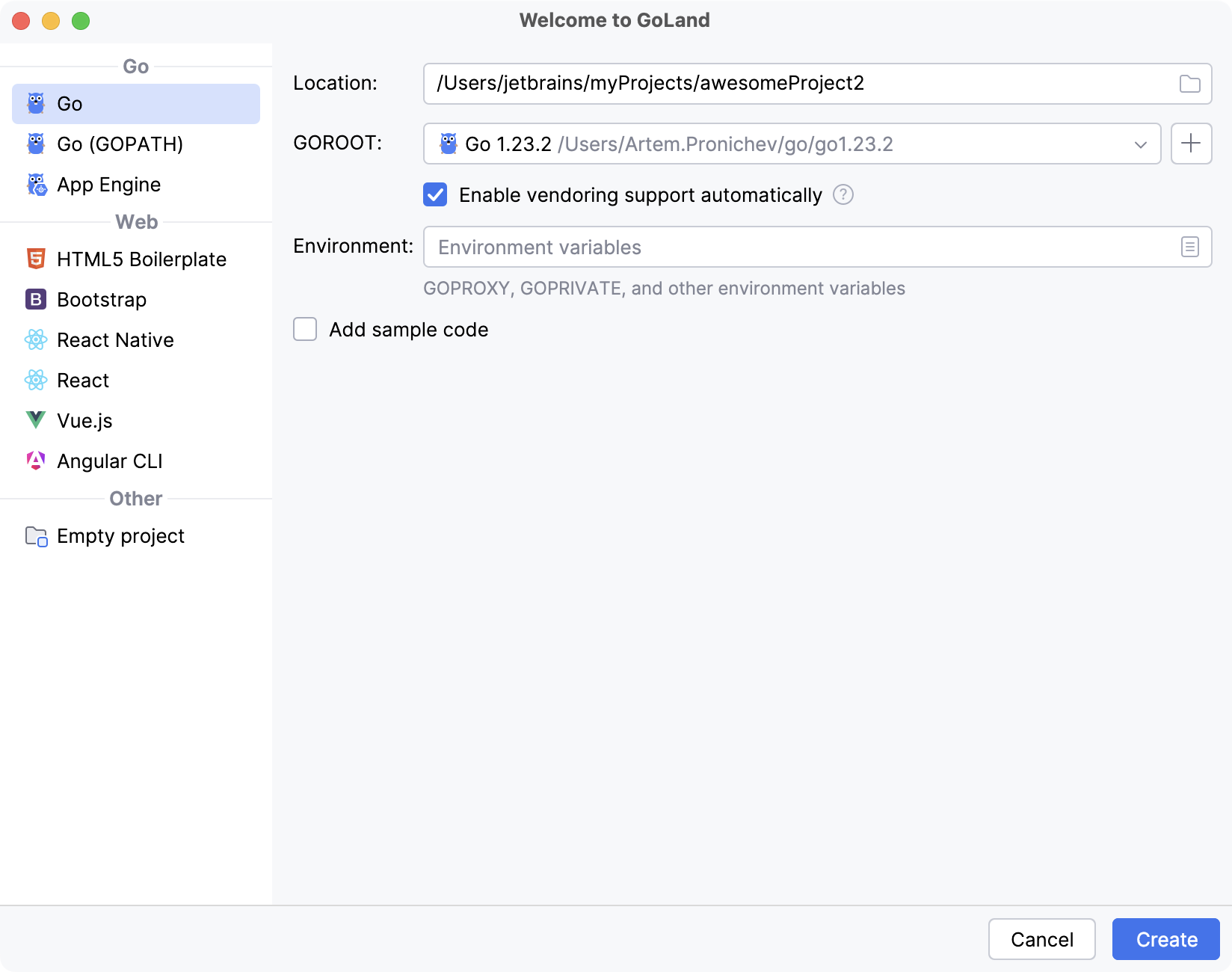
In the New Project dialog, select Go from the list of available project types.
In the GOROOT field, specify the location of your Go installation. GoLand usually detects this location automatically.
To change or install a new Go SDK version, click Add SDK (
) and choose one of the following options:
Local: to use an existing SDK from your local system.
Download: to download a Go SDK version from the official repository.
Click Create to create the project.
Create a Go file
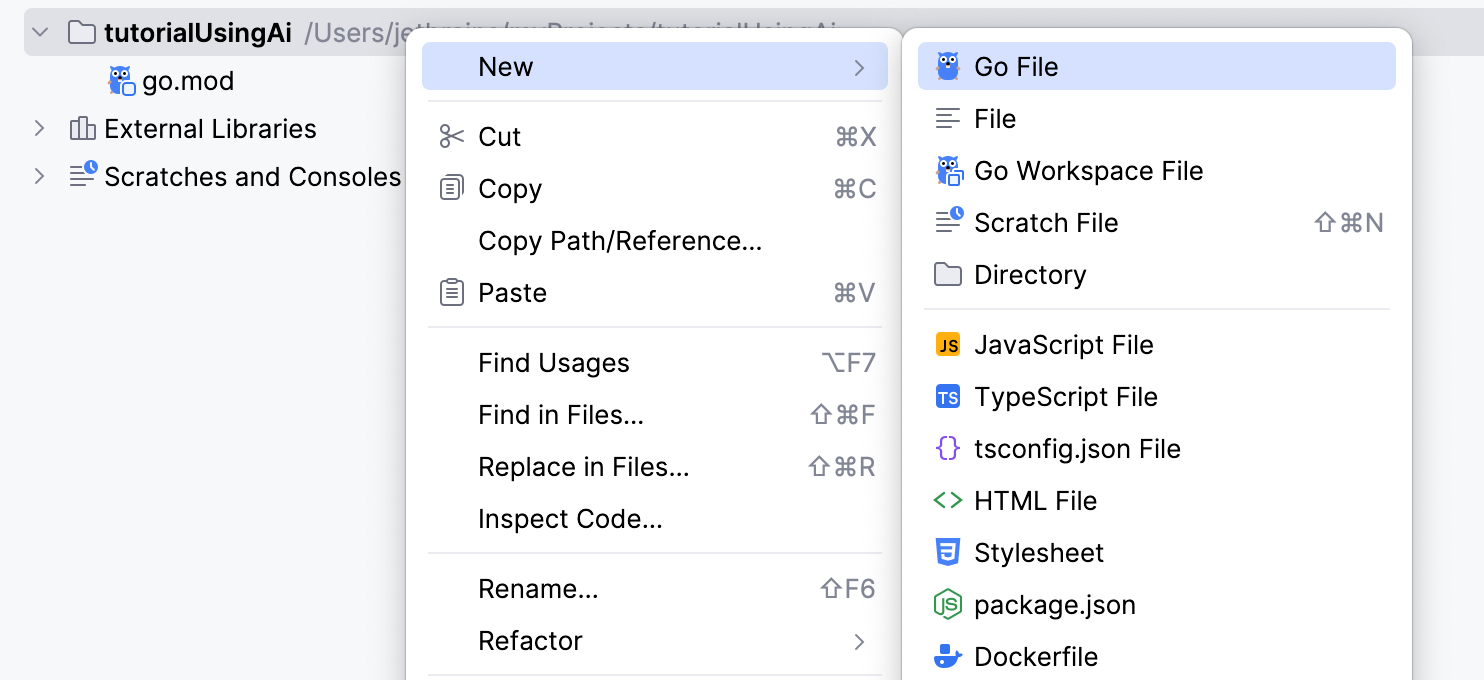
To create a Go file, use one of the following options:
In the Project tool window, right-click the parent folder of your project and select .
Click the parent folder of your project, press Alt+Insert, and select Go File.
Click the parent folder of your project, then go to .
In the New Go File dialog, enter a file name and choose the file type:
Empty file — creates an empty Go file.
Simple application — creates a Go file with a predefined
mainfunction.
Clone files from repositories
For this example, we will use the following two repositories: the Sakila dump files (https://github.com/DataGrip/dumps) and a Docker Compose file (https://github.com/DataGrip/datagrip-documentation). The Sakila repository includes SQL scripts to create and populate the Sakila sample database. The Docker repository contains YAML files that define services, networks, and volumes.
Clone repositories
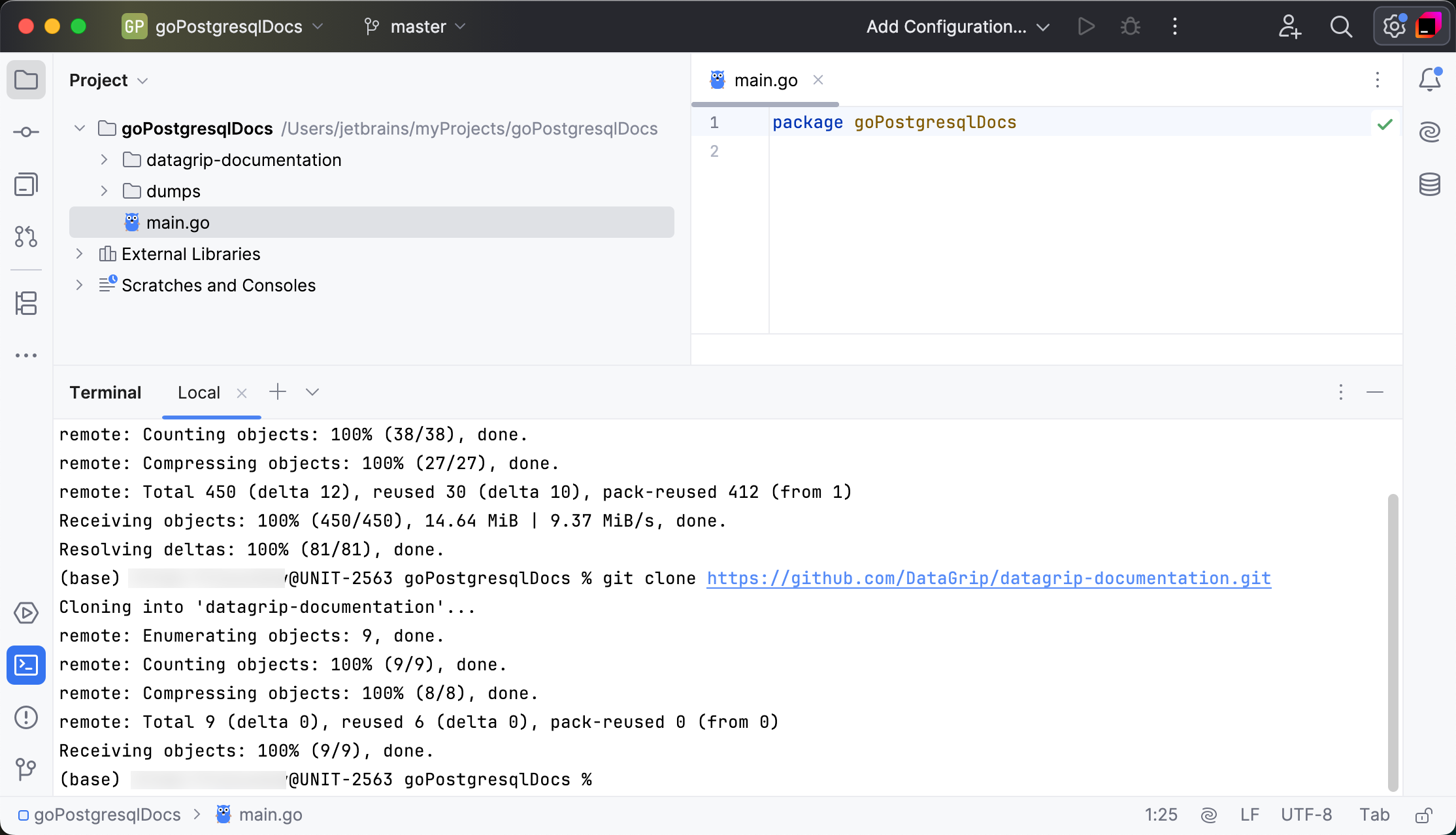
Select or press Alt+F12.
In the terminal, run the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/DataGrip/dumps.gitgit clone https://github.com/DataGrip/datagrip-documentation.gitTwo new folders for the cloned repositories will appear in the Project tool window.
Run a Docker container
In this tutorial, we will run a PostgreSQL container using Docker, based on the datagrip-documentation repository. Inside the repository's Docker directory, you will find the .env and docker-compose.yml files. The .env file contains credentials for the PostgreSQL service. The docker-compose.yml file defines how the service is created and configured.
The service name appears on the first line of the service definition, above the JDBC URL. In our example, the service name is postgresql_12, and the JDBC URL is: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:54333/guest?user=guest&password=guest
To run the container from the command line, use the following command:
Make sure to navigate to the directory that contains the docker-compose.yml file before running the command.
Alternatively, you can enable and use the Docker plugin in GoLand.
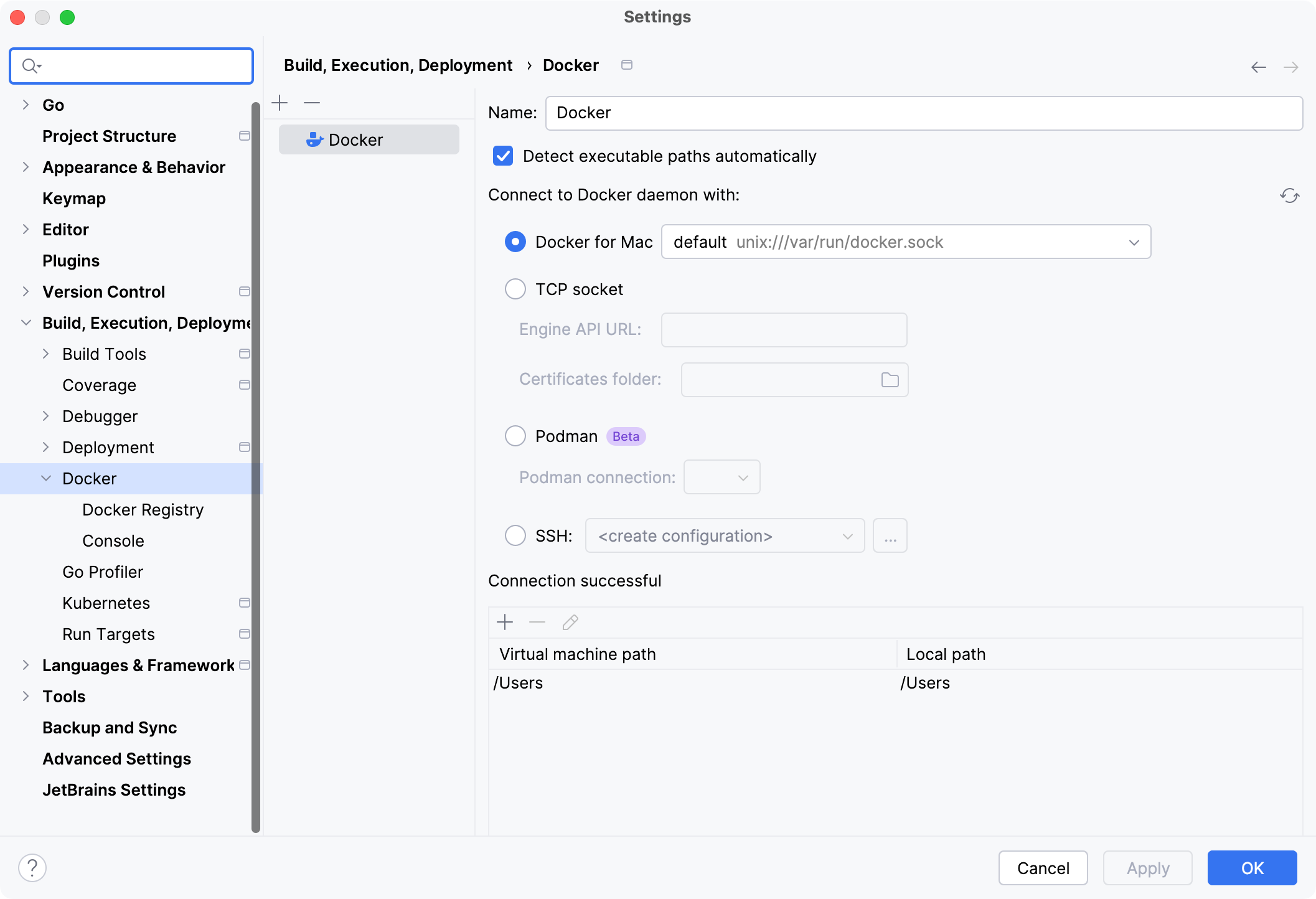
Connect to the Docker daemon
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Click
to add a Docker configuration and specify how to connect to the Docker daemon.
The connection settings depend on your Docker version and operating system.
The Connection successful message should appear at the bottom of the dialog.
For more information about mapping local paths to the virtual machine running the Docker daemon when using Docker on Windows or macOS, refer to Virtual machine path mappings for Windows and macOS hosts. You will not be able to use volumes and bind mounts for directories outside of the mapped local path.
This table is not available on a Linux host, where Docker runs natively and you can mount any directory to the container.
Open the Services tool window ( or Alt+8), select the configured Docker connection node
and click
, or select Connect from the context menu.
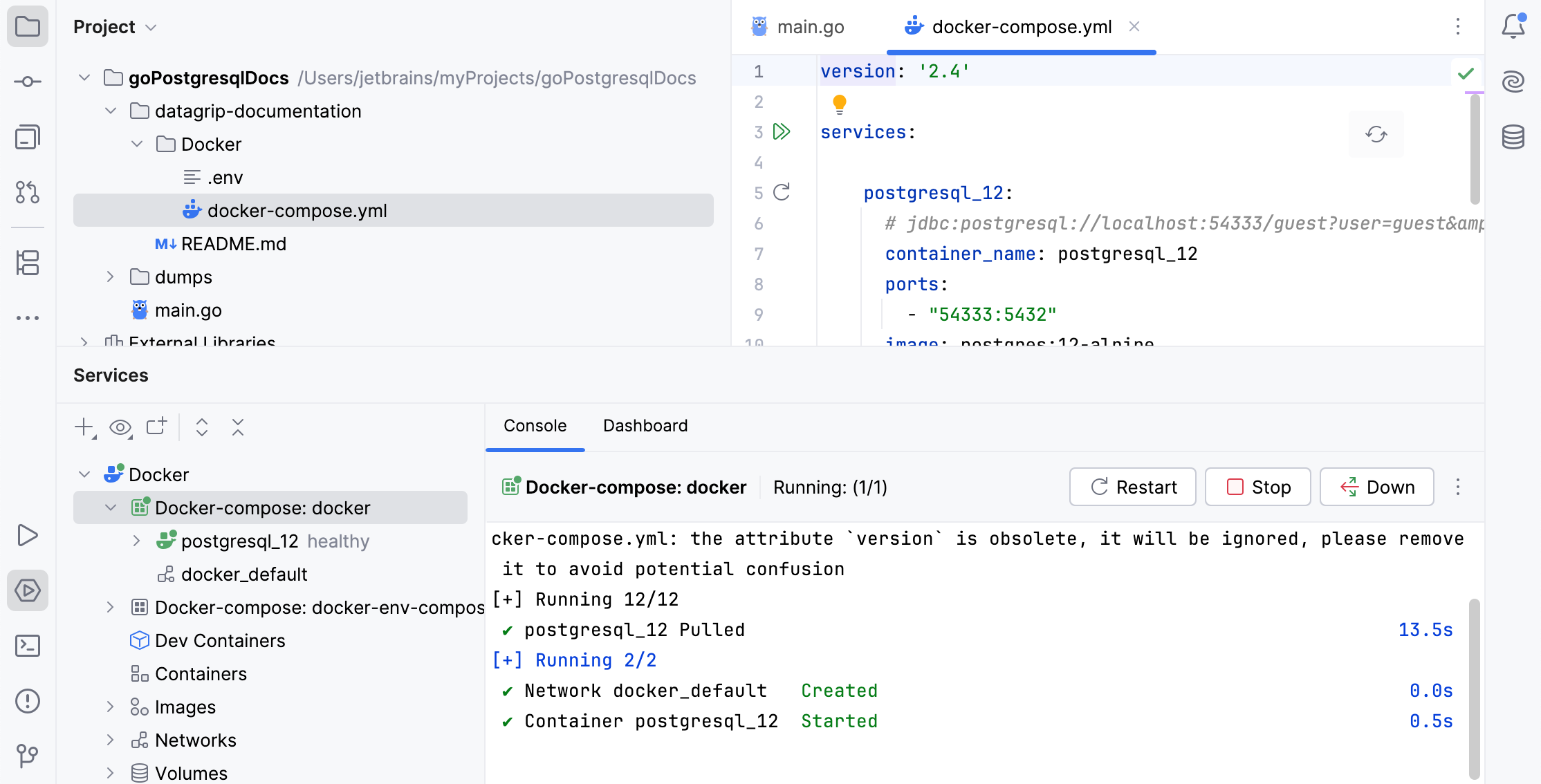
To edit the Docker connection settings, select the Docker node and click
on the toolbar, or select Edit Configuration from the context menu.
You can also click
and select Docker Connection to add a Docker connection directly from the Services tool window. If you have Docker contexts configured, you can select Docker Connections from Docker Contexts to add the corresponding connections.
Create the Docker Compose deployment configuration
In the Project tool window (), locate the docker-compose.yml file from the cloned repository.
Click the Run icon in the gutter.
The
postgresql_12container will start and appear in the Services tool window.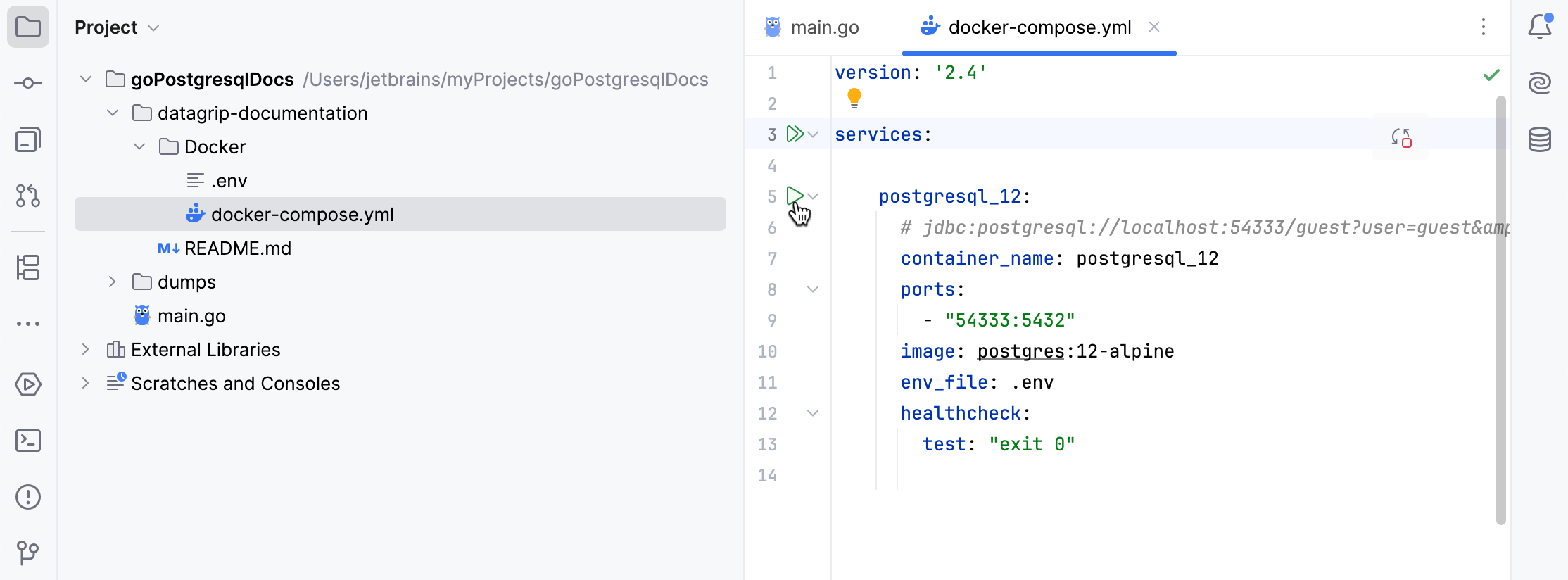
Connect to a data source
Depending on the database vendor (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle), you need to create a corresponding data source connection. In this tutorial, we will create a PostgreSQL connection. If you want to connect to a different database management system (DBMS), refer to Create a data source.
Open data source properties by doing one of the following:
On the Database tool window toolbar, click
Data Sources.
Press Shift+Enter.
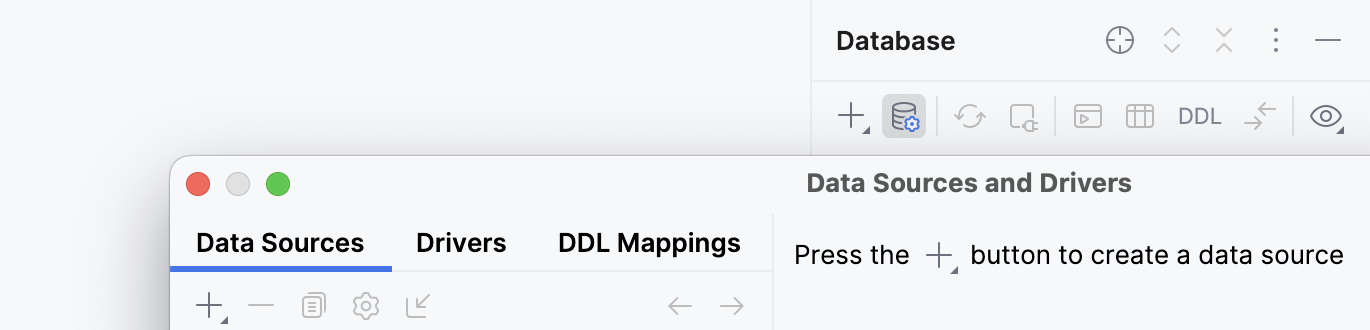
In the Data Sources and Drivers dialog, click the Add icon (
) and select PostgreSQL.
Check if there is a Download missing driver files link at the bottom of the connection settings area. Click this link to download drivers that are required to interact with a database. For a direct download link, refer to the JetBrains JDBC drivers page.
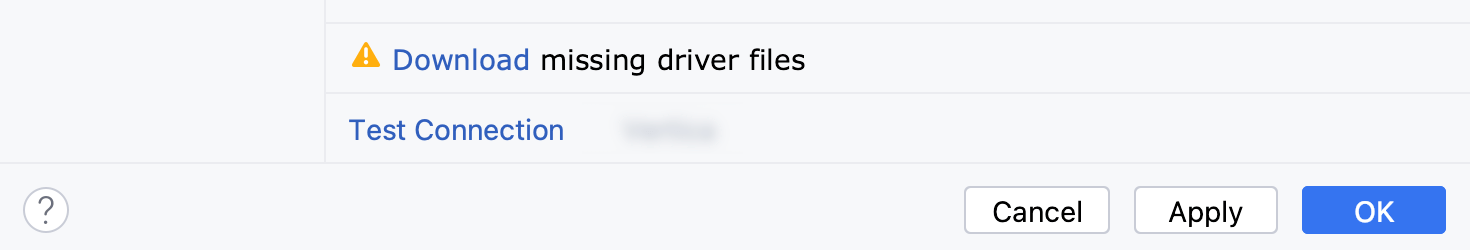
Location for the downloaded JDBC drivers is the GoLand configuration directory.
You can also use your drivers for the database instead of the provided ones. For more information about connecting to a database with your driver, refer to Add a user driver to an existing connection.
If there is no Download missing driver files link, then you already have the required drivers.
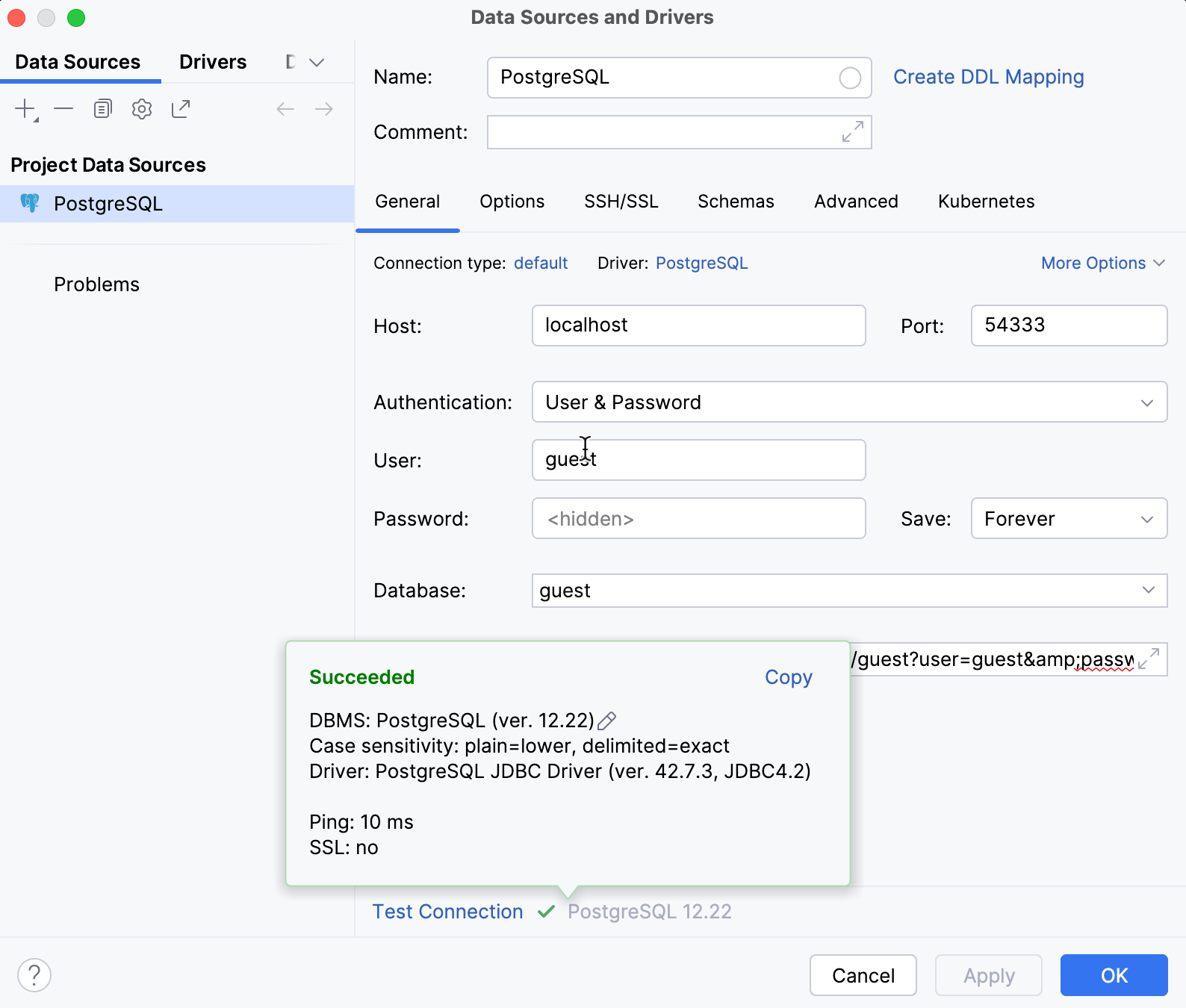
In the URL field, paste the following JDBC URL:
jdbc:postgresql://localhost:54333/guest?user=guest&password=guestYou can find JDBC URLs for other DBMSs in the docker-compose.yml file. Open the file in a text editor to review available connection details.
(Optional) In the Name field, enter a custom name for the connection (for example, PostgreSQL).
Ensure that the database connection can be established using the provided details. To do this, click the Test Connection link at the bottom of the connection details section.
If you encounter any connection issues, refer to the Cannot connect to a database page.
(Optional) By default, only the default database and schema are introspected and available to work with. If you also want to work with other databases and schemas, in the Schemas tab, select them for the introspection.
Click OK to create the data source.
Run the dump files
Create the database structure
In the Project () tool window, navigate to dump/postgres-sakila-db/postgres-sakila-schema.sql.
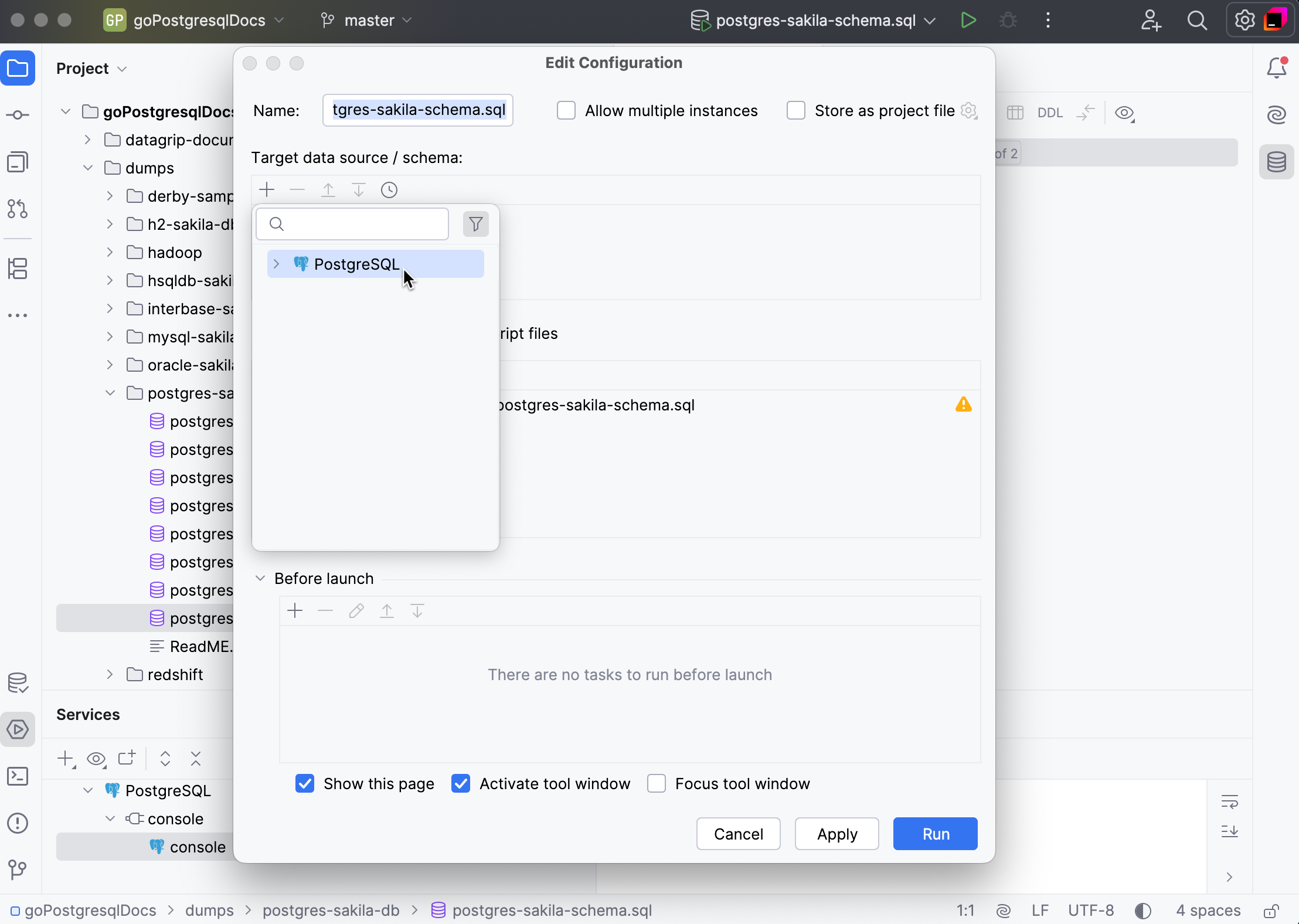
Right-click postgres-sakila-schema.sql and select Run postgres-sakila-schema.sql. Alternatively, open the file and press Ctrl+Shift+F10.
In the Edit Configuration dialog, click the Add button in the Target data source/schema pane and select PostgreSQL.
Click Run to execute the script.
Load sample data into the database
In the Project () tool window, navigate to the dump/postgres-sakila-db directory.
Expand the postgres-sakila-db directory.
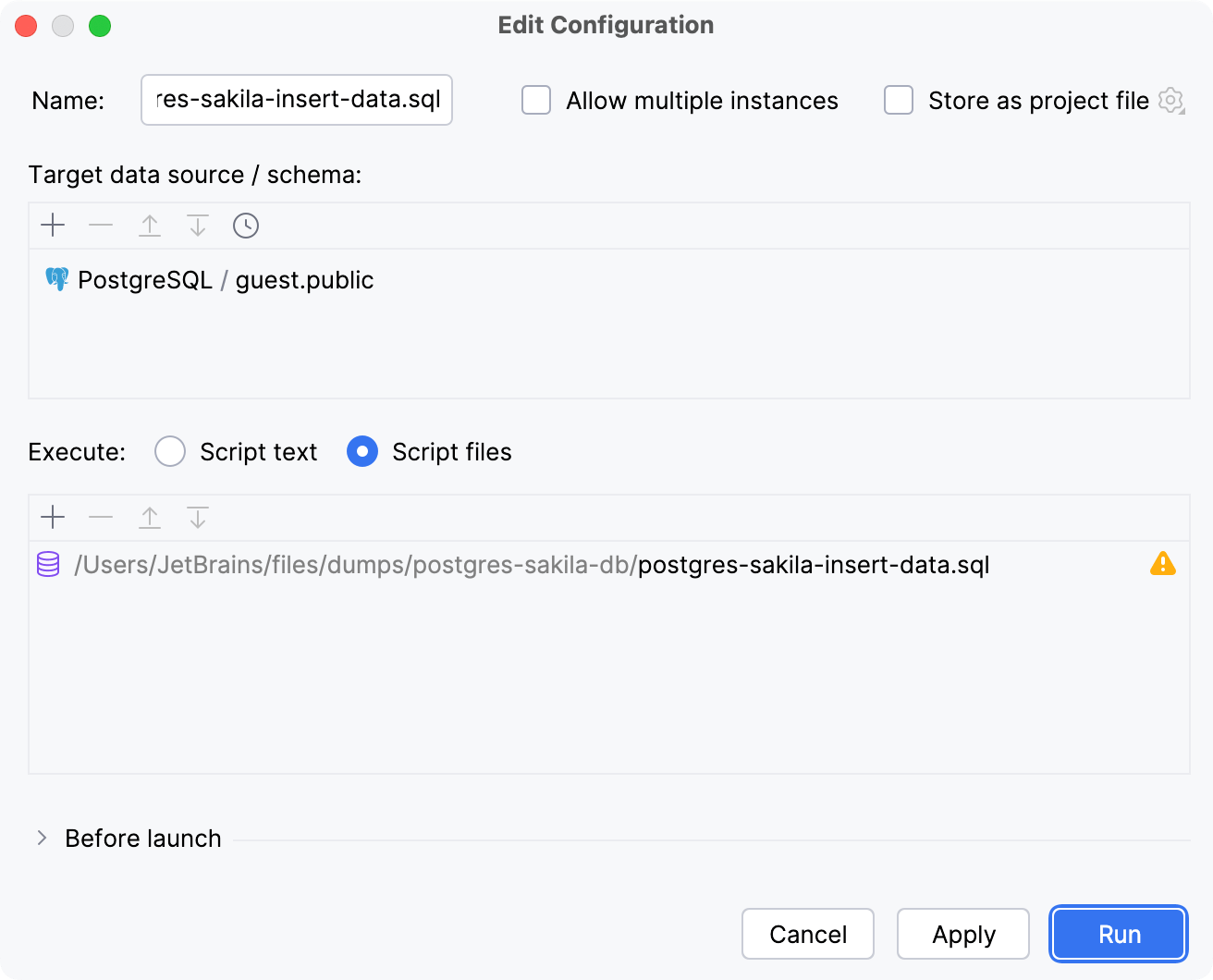
Right-click postgres-sakila-insert-data.sql and select Run postgres-sakila-insert-data.sql. Alternatively, open the file and press Ctrl+Shift+F10.
In the Edit Configuration dialog, click the Add button and select PostgreSQL.
Click Run to execute the script.
Fetch dependencies from the Go code
To issue a query to PostgreSQL, we are going to use the sqlx library, which provides a set of extensions for the Go standard database/sql package. For more information about the library, refer to For more details, visit sqlx on GitHub.
Open the created main.go file and paste the following code from GitHub into it.
Place the caret on the "github.com/jmoiron/sqlx" import statement, press Alt+Enter, and select Fix missing dependencies (go mod tidy).
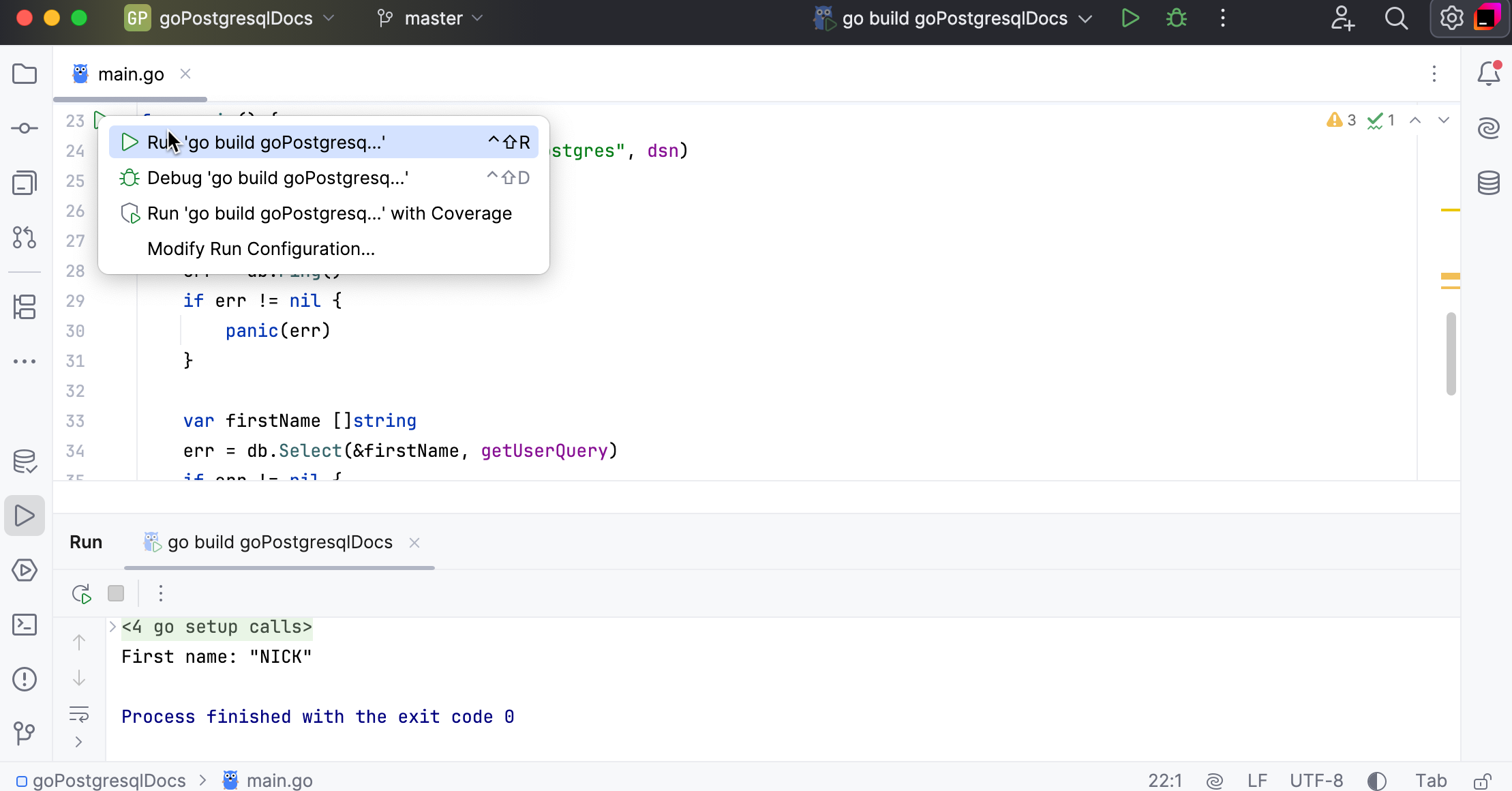
Run your code
To run the configuration, click the Run icon (
) in the gutter near the
mainfunction and select Run 'go build main.go'.