Code completion
Basic code completion helps you complete the names of classes, methods, fields, and keywords within the visibility scope.
IntelliJ IDEA analyzes the context and suggests the choices that are reachable from the current caret position. Suggestions also include Live templates. Completion is available for a non-English keyboard layout.
Invoke basic completion
By default, IntelliJ IDEA displays the code completion popup automatically as you type.
Alternatively, you can press Ctrl+Space or select from the main menu.
Invoking code completion for the second time shows inaccessible classes and members (these can be made public by applying an intention action).
When invoked for the third time in a row, completion looks for suggestions for classes and interface names in the entire project, regardless of dependencies. If the necessary class is not yet imported, it will be imported automatically.
Code completion is available for custom file types. However, IntelliJ IDEA does not recognize the structure of such files and suggests options regardless of whether they are appropriate in the current context.
Accept a suggestion from the list
Press Enter or double-click the relevant list item to insert it to the left of the caret.
Press Tab to replace the characters to the right from the caret.
Use Ctrl+Shift+Enter to make the current code construct syntactically correct (balance parentheses, add missing braces and semicolons, and so on).
Use specific keys and custom characters to accept the selected completion suggestion. To enable these features, go to the Editor | General | Code Completion settings page Ctrl+Alt+S and do the following:
To use specific keys, select the Insert selected suggestion by pressing space, dot, or other context-dependent keys checkbox. These keys depend on the language, your context, and so on. For Java, such keys include
Space, Tab,[and],(and), and some more.To also use custom characters, enter the characters into the Additional characters to accept the completion field.
Exclude and prioritize classes for completion
Exclude a class or package from completion
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Under Exclude from import and completion, add the names of classes or packages that you want to exclude from completion. The classes you specify here will not appear in the suggestion list.
You can also exclude items from the completion list: press Alt+Enter when the list with completion suggestions is open and select the item you want to exclude.
Prioritize classes for completion
This feature allows you to import frequently used static methods automatically. When you type a method from a prioritized class, the IDE shows completion suggestions. Selecting a suggestion from the list inserts the corresponding import statement without requiring manual edits.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
In the Include auto-import of static members in completion section, click
or press Alt+Insert.
In the dialog that opens, specify the class you want to add to the list. You can search for the classes by name of select them from the project structure.
To the right from the class name, you can also select whether you want to prioritize it in the current project only or in all projects (globally).
Machine learning-assisted completion ranking
IntelliJ IDEA allows you to prioritize completion suggestions based on choices that other users made in similar situations.
The ML completion mechanism does not add any new elements but orders the elements retrieved from code. Data is not exposed anywhere; it is collected locally.
Enable ML completion ranking
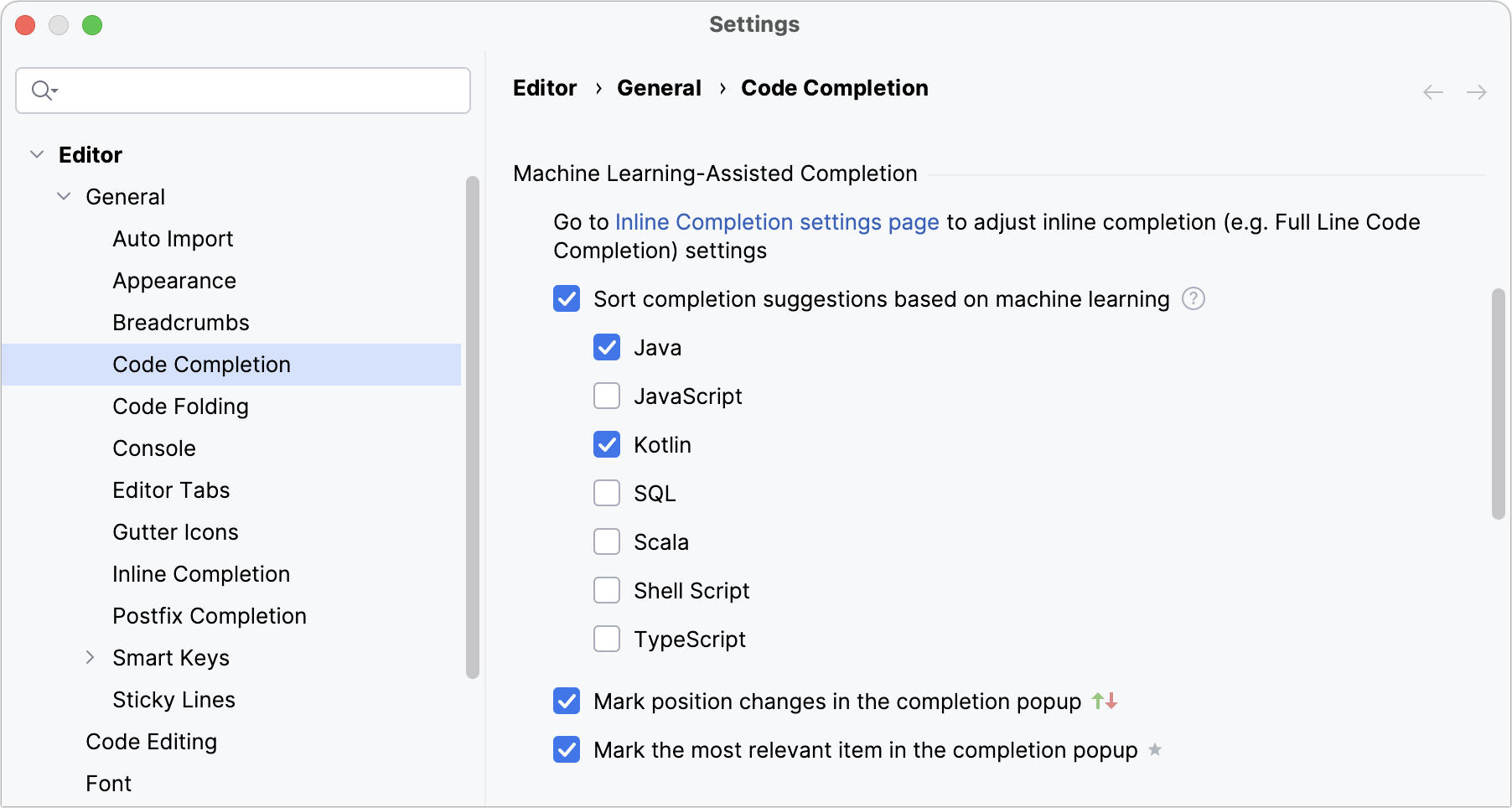
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and select Editor | General | Code Completion.
Under Machine Learning-Assisted Completion, enable the Sort completion suggestions based on machine learning option and select the languages for which you want to use the ML completion.
Enable relevance markers
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and select Editor | General | Code Completion.
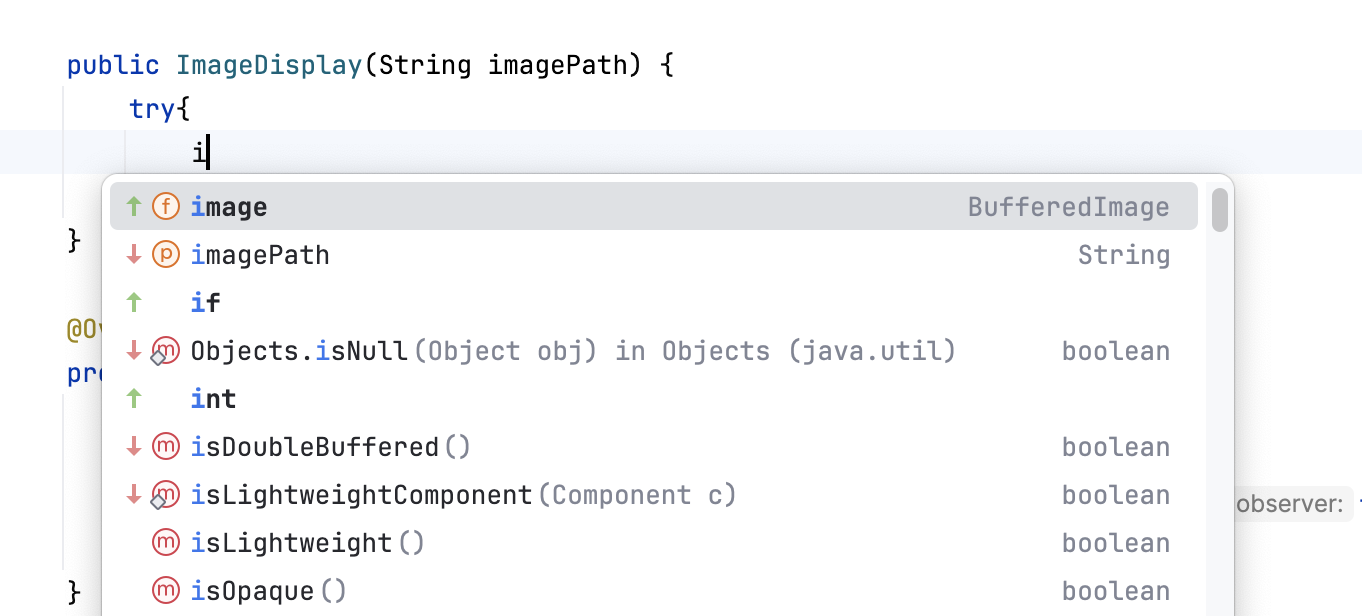
Enable the following options:
Mark position changes in the completion popup: use the
and
icons to indicate whether the relevance of a suggestion is increasing or decreasing and therefore the suggestion has moved up or down the suggestion list.
Mark the most relevant item in the completion popup: use the
icon to indicate the most suitable suggestion on the list.
The suggestion list will look as follows with the icons marking reordered and the most relevant items.
Configure code completion settings
To configure code completion options, go to the Editor | General | Code Completion settings page Ctrl+Alt+S.
You can choose the following settings:
Item | Description | |
|---|---|---|
Match case | Select if you want the letter case to be taken into account for completion suggestions. Choose whether you want to match the case for the first letter or for all letters. | |
Automatically insert single suggestions for | Automatically complete code if there is only one suggestion for basic and smart type-matching completion. | |
Sort suggestions alphabetically | Select if you want to sort items in the suggestion list in the alphabetical order instead of sorting them by relevance. You can change this behavior at any time by clicking | |
Show suggestions as you type | Select if you want the suggestion list to be invoked automatically, without having to call completion explicitly. This option is enabled by default. | |
Insert selected suggestion by pressing space, dot, or other context-dependent keys | Select if you want to insert the selected suggestion by typing certain keys that depend on the language, your context, and so on. For Java, such keys include Space, Tab, [ and ], ( and ), and some more. | |
Show the documentation popup in | Automatically show a popup for each item in the suggestion list with the documentation for the class, method, or field currently highlighted in the lookup list. When this option is disabled, press Ctrl+Q to display documentation for elements. In the field to the right, specify the delay (in milliseconds), after which the popup should appear. | |
Insert parentheses automatically when applicable | If this option is enabled, IntelliJ IDEA automatically inserts a pair of opening and closing parentheseswhen you complete a function/method. 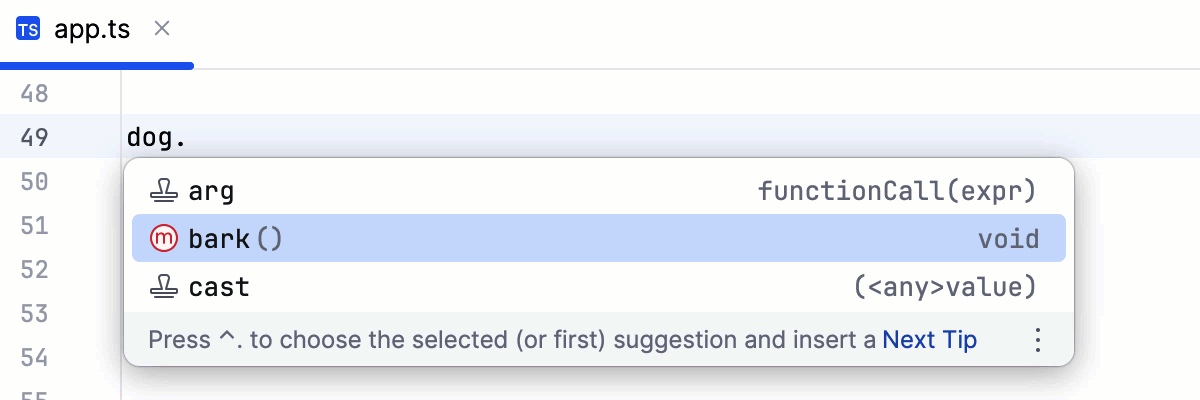 Clear the checkbox to suppress inserting parentheses automatically. If you use an opening parentheses  To use an opening parentheses For more information, refer to Use specific keys to insert suggestions. | |
Command Completion | ||
Enable command completion | Show command completion suggestions when you type a dot in the editor. Command completion serves as an entry point to various commands that represent common code actions. | |
Machine Learning-Assisted Completion | ||
Sort completion suggestions based on machine learning | Select this option if you want to use machine learning models to rank the most suitable items higher in the suggestion list. Select the languages for which you want to enable suggestions based on machine learning. | |
Mark position changes in the completion popup | Use the | |
Mark the most relevant item in the completion popup | Use the | |
JavaScript | ||
Only type-based completion | By default, IntelliJ IDEA suggests completion for symbols regardless of their types. With this approach, in complicated cases the list shows multiple completion variants. To make completion more precise, select this option. The completion list will strongly depend on the IntelliJ IDEA inference. As a result, the list may remain empty in case of poor inference. | |
Suggest items with optional chaining for nullable types | By default, IntelliJ IDEA suggests completion for symbols with the optional chaining operator (?). Clear this checkbox to suppress this behavior. | |
Expand method bodies in completion for overrides | By default, when you want to override a method from the parent class or interface and select this method from the list of completion suggestions, IntelliJ IDEA automatically adds parameters, generates a Clear this checkbox to suppress automatic generation of method bodies for overrides during completion. | |
Completion of names |
| |
Parameter Info | ||
Show parameter name hints on completion | Select if you want hints for parameter values to be displayed. | |
Show the parameter info popup (in ms) | Select this checkbox to have IntelliJ IDEA automatically show a popup with all available method signatures when an opening bracket is typed in the editor, or a method is selected from the suggestion list. In the text field to the right, specify the delay (in milliseconds) after when the popup window should appear. If this checkbox is not selected, use Ctrl+P to show parameter info. | |
Show full method signatures | If this checkbox is selected, the parameter info displays full signatures, including method name and returned type. | |
SQL | ||
Suggest objects from | Select where the objects are suggested from:
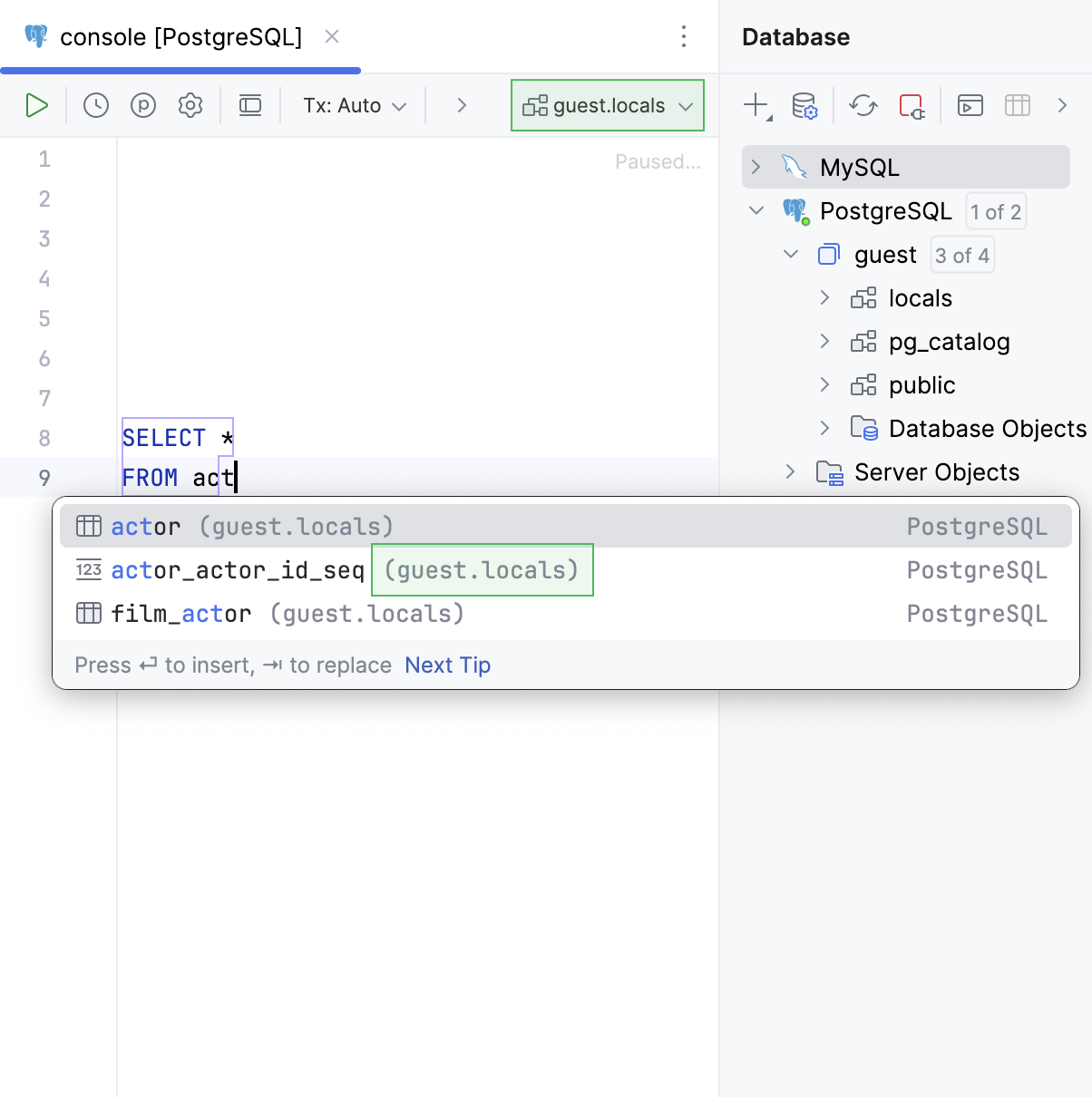 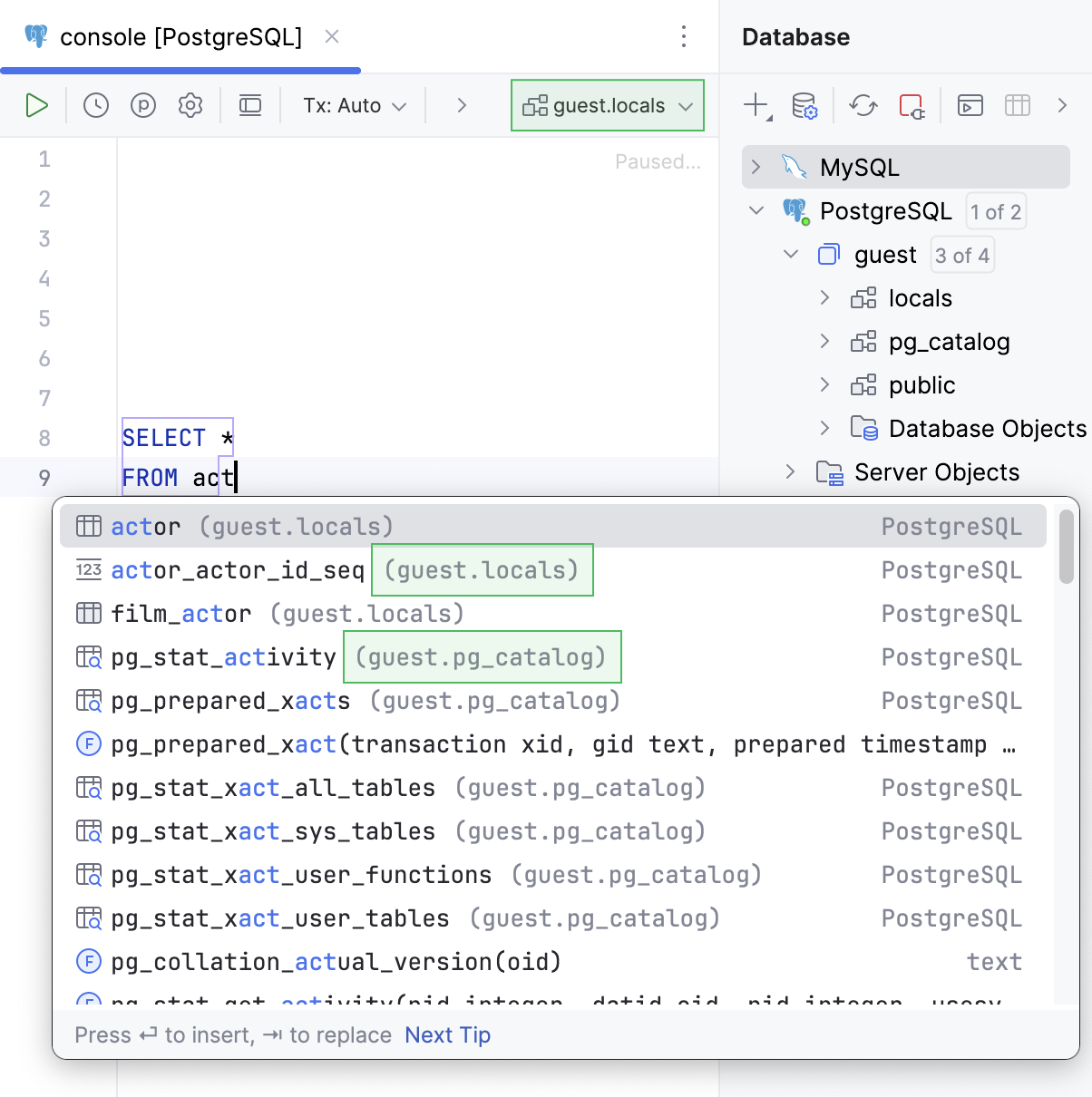 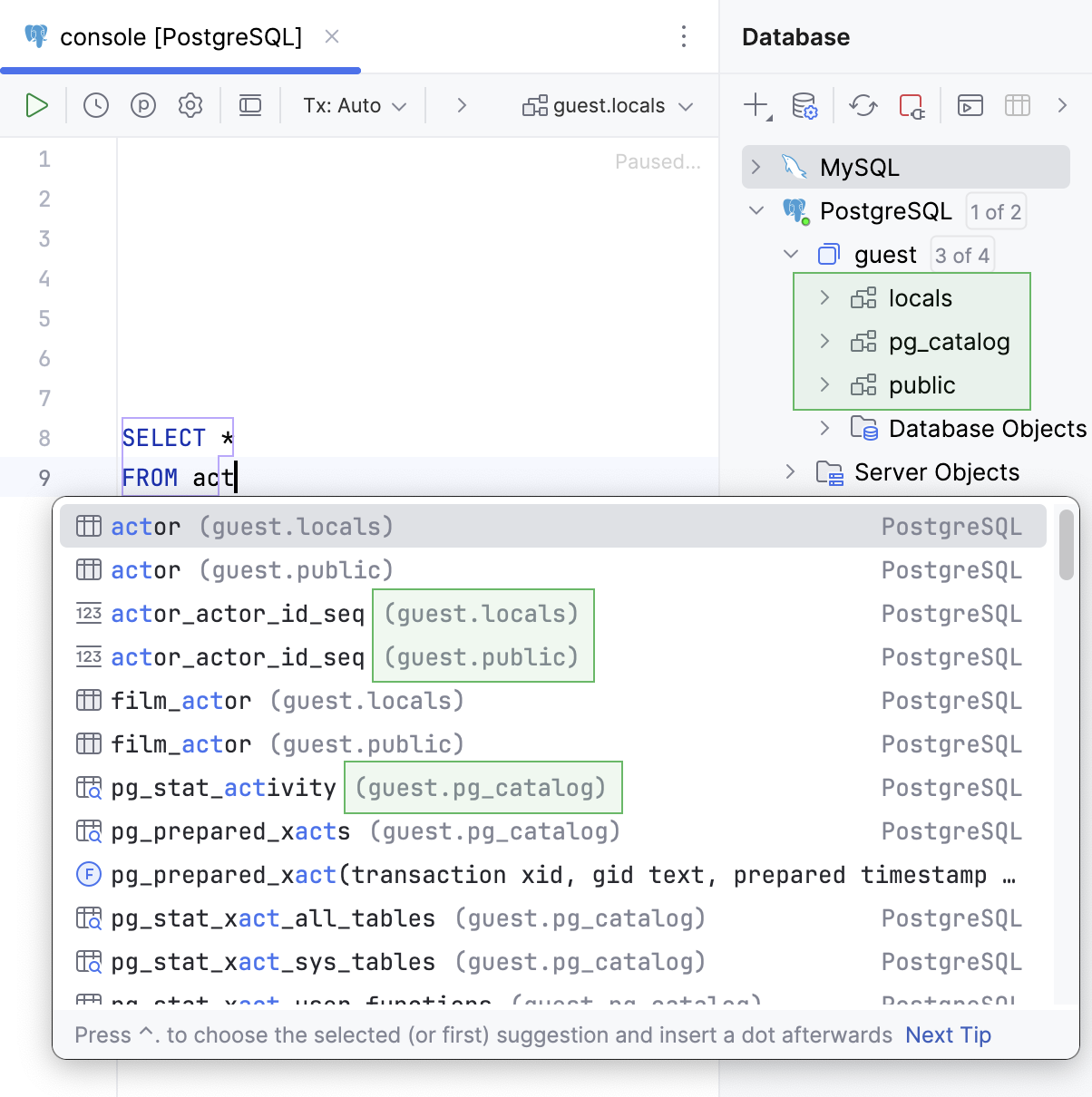 | |
Qualify objects with | Select when to qualify the objects with databases, schemas, tables and views, and aliases of tables and views.
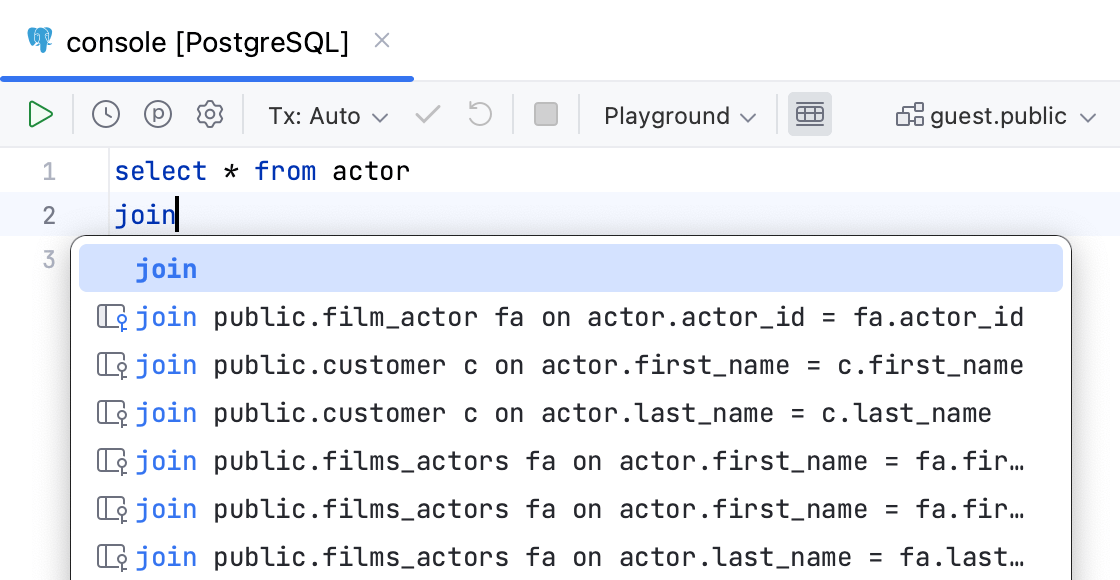 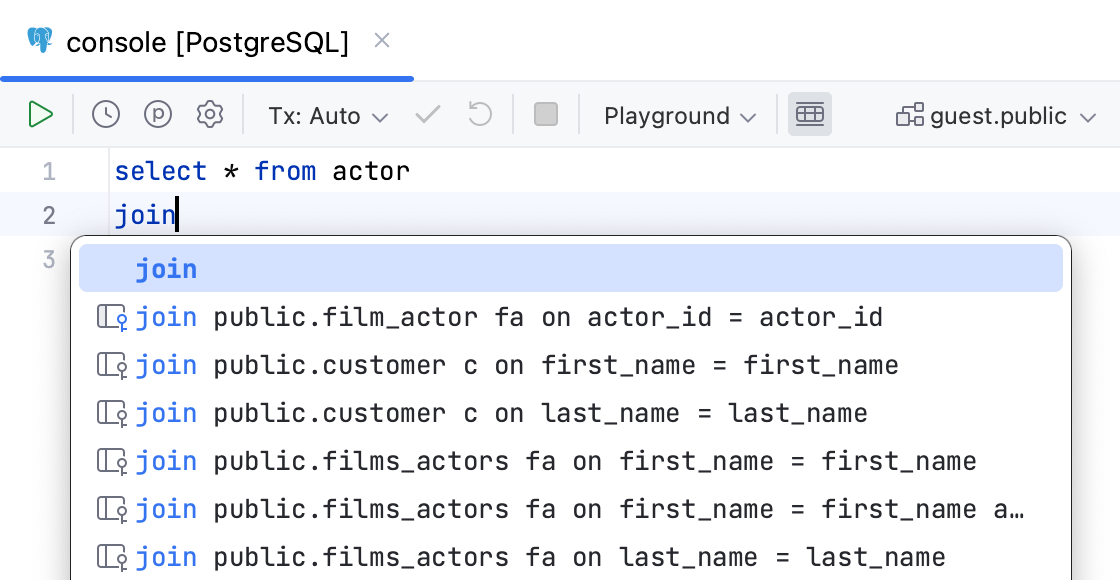 | |
Qualify objects in | Select when to qualify the objects in the given cases.
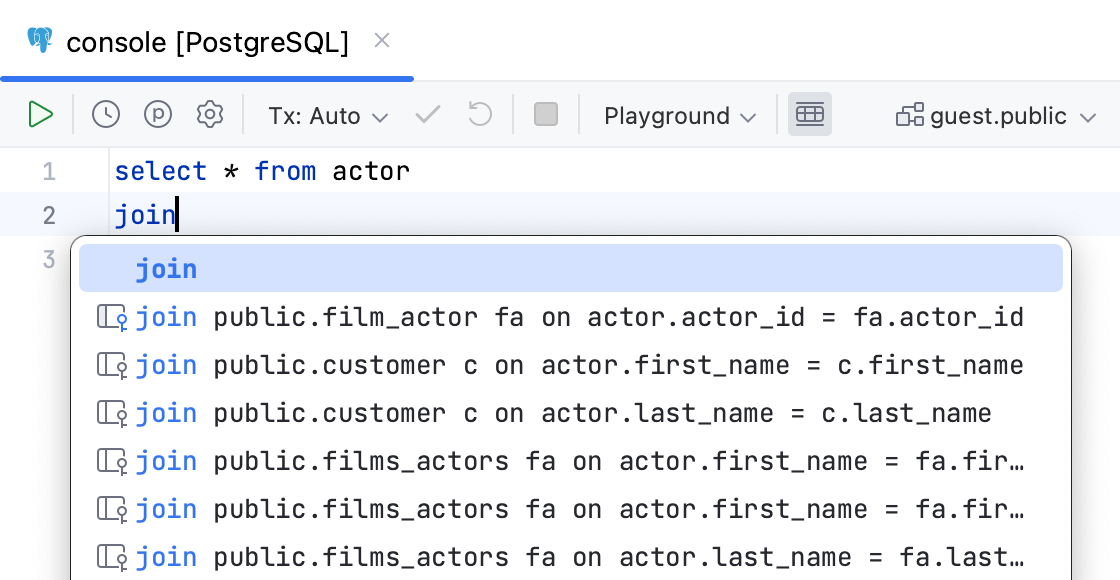 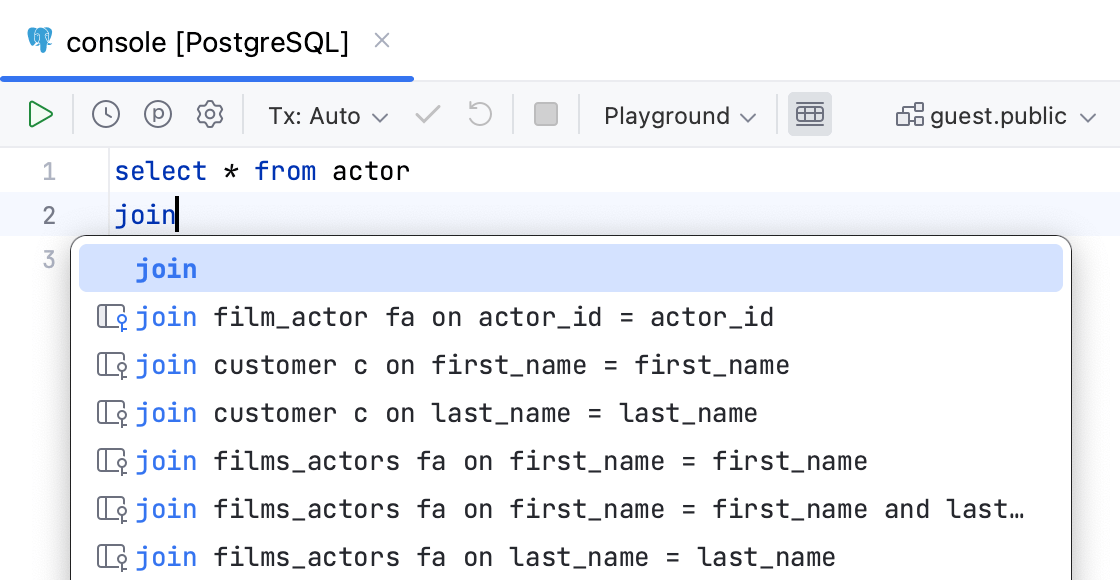 | |
Use aliases in completion for JOIN | Creates aliases for tables in the  | |
Invert order of operands in auto-generated ON clause | Switches operands in the 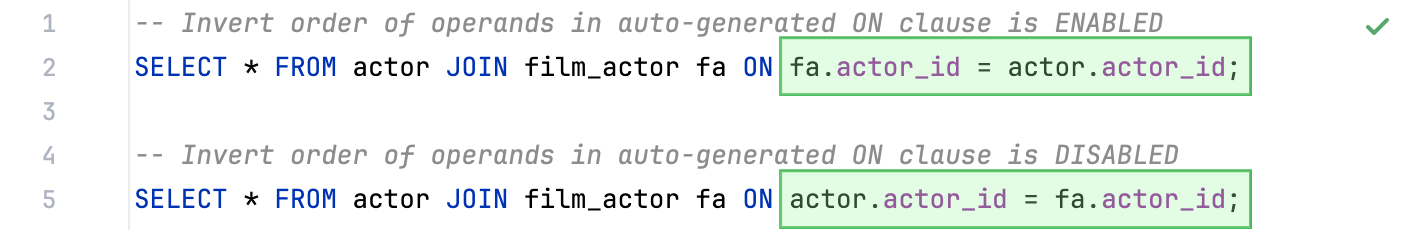 | |
Suggest non-strict foreign keys based on the name matching | Generates you a list of possible code completion suggestions for Read more about debugging rules for this option in Debug rules for virtual foreign keys.   | |
Automatically add aliases when completing table names | Creates an alias for a table name.  | |
Suggest alias names in completion after table names | Suggests an alias for a table name when you use code completion (Ctrl+Space). 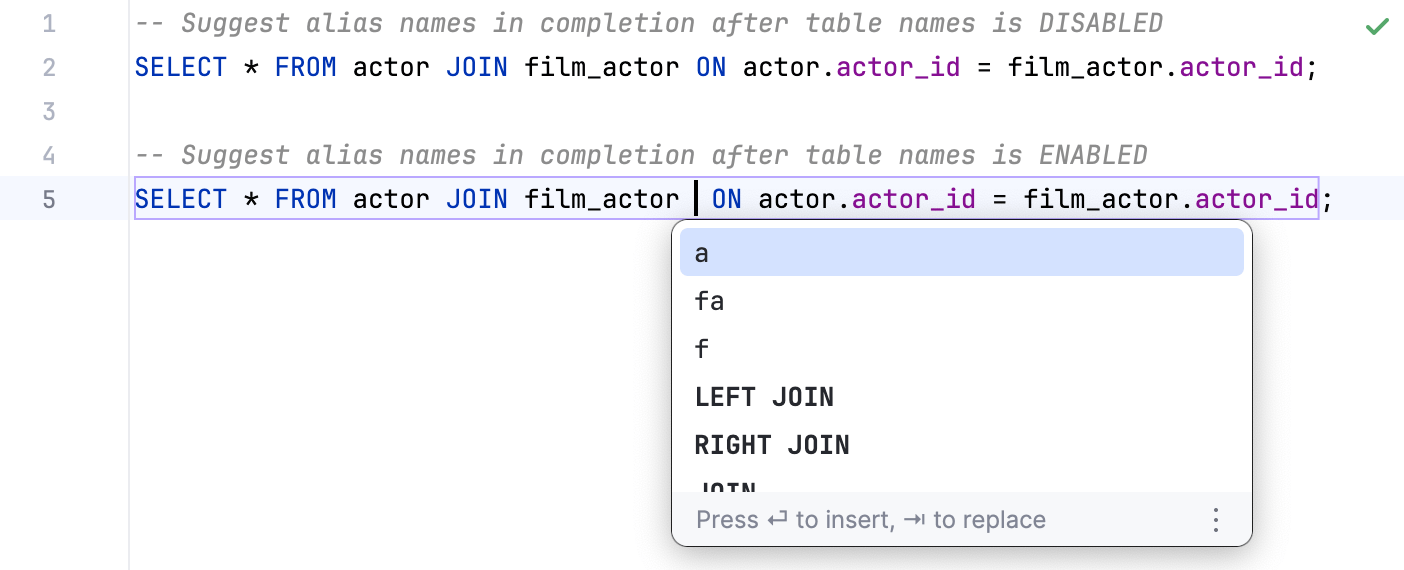 | |
Custom aliases (table) | You can add a table name and the alias that you want to use for this table. To add the table-alias pair, click the Add alias button ( | |
Completion tips and tricks
Autocomplete HTTP constants by typing the code number
After you specify an imported package name, such as
http, you can type404to autocomplete the value tohttp.StatusNotFound.
Narrow down the suggestion list
Narrow down the suggestion list by typing any part of a word (even characters from somewhere in the middle) or invoking code completion after a dot separator .
IntelliJ IDEA displays suggestions containing the characters you've entered, regardless of their position. This makes the use of wildcards unnecessary.
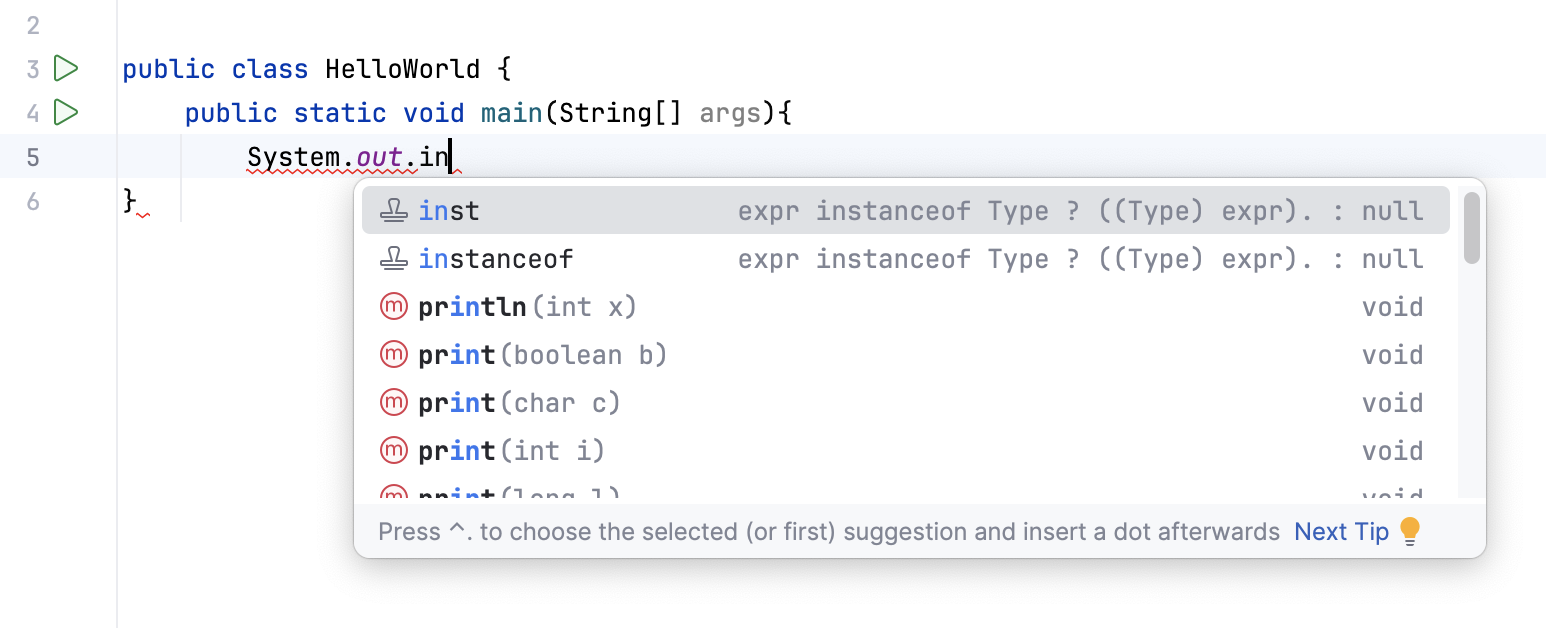
In case of CamelCase or snake_case names, type the initial letters only. IntelliJ IDEA automatically recognizes and matches the initial letters.
Negate an expression
You can negate an expression in Java by pressing ! after you have selected it from the suggestion list. As a result, the expression will be negated:
Negating an expression works this way if you have the Insert selected suggestion by pressing space, dot, or other context-dependent keys option enabled in the Code Completion settings page, or invoke code completion explicitly, or change a selection in the suggestion list explicitly.
Completion shortcuts
You can use the following live templates shortcuts for one of the most frequently used statements:
sout: printsSystem.out.printIn()soutm: adds the current class and method namessoutp: adds method parameter names and valuessoutv: adds the last variable valuesoutc: inserts theSystem.out::printInmethod reference where a consumer function is expected
View reference
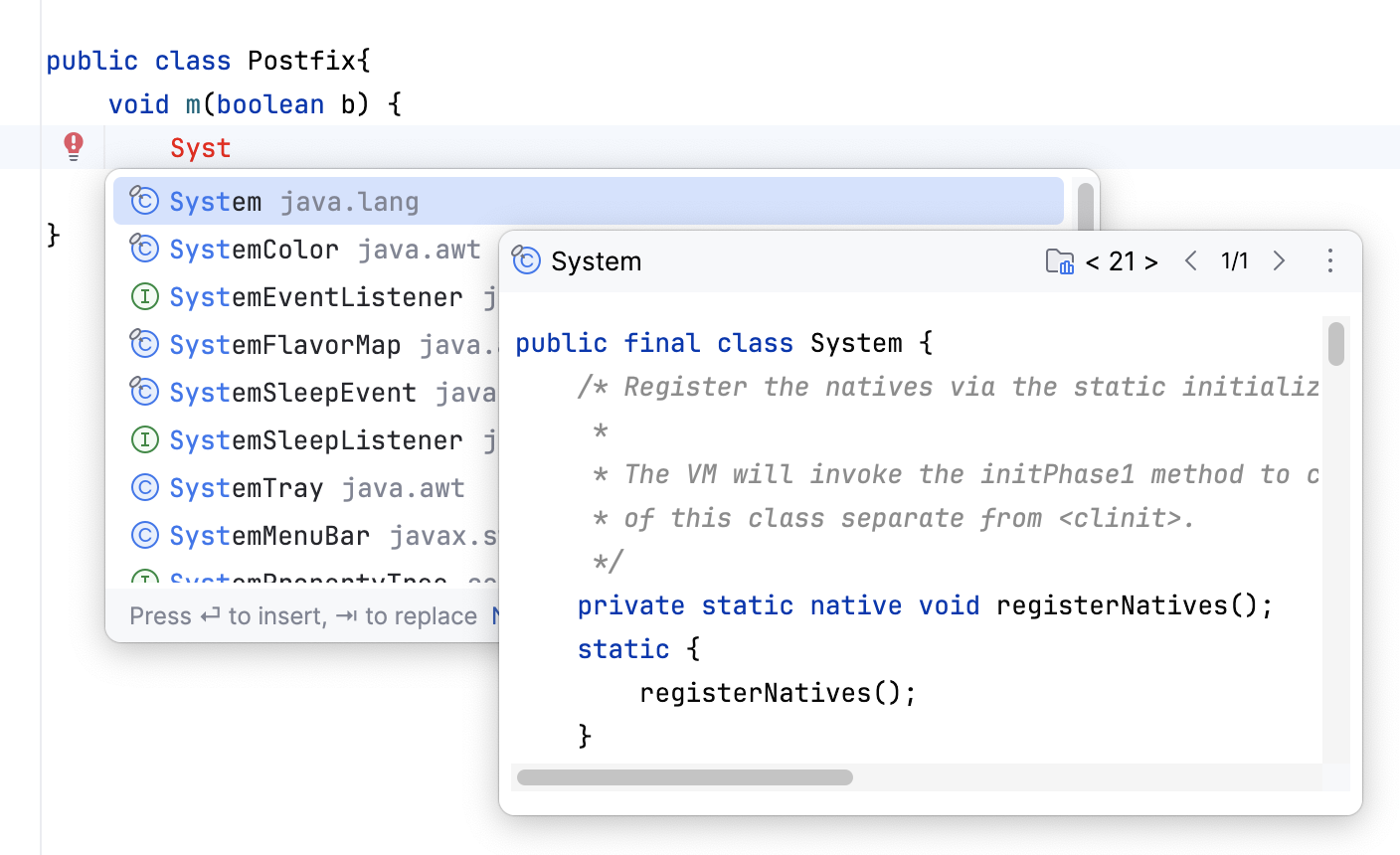
You can use the Quick Definition view by pressing Ctrl+Shift+I when you select an entry in the suggestion list:
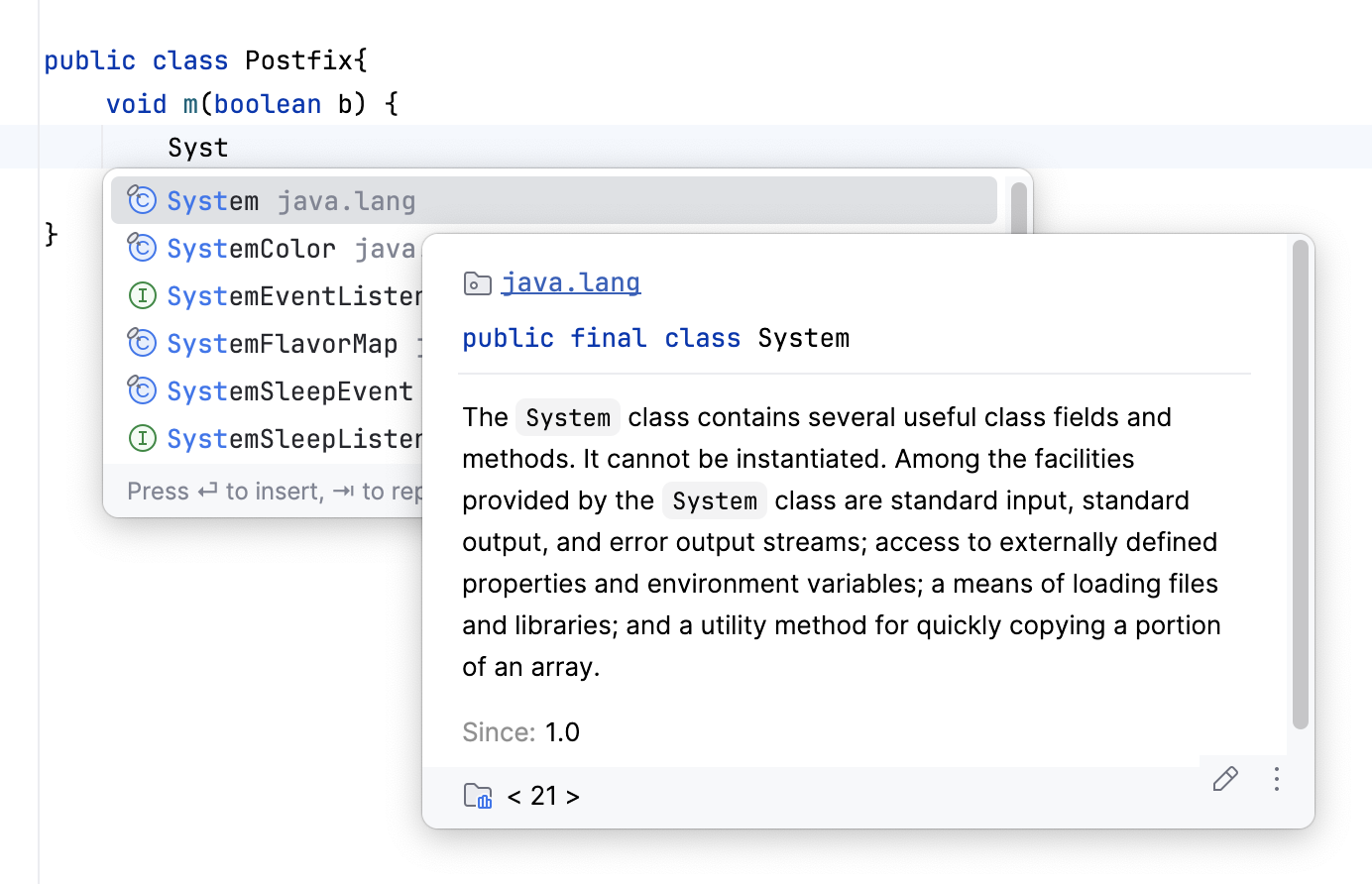
You can use the Quick Documentation view by pressing Ctrl+Q or automatically when you select an entry in the suggestion list:
View code hierarchy
You can view code hierarchy when you've selected an entry from the suggestion list:
Ctrl+H: view type hierarchy
Ctrl+Alt+H: view call hierarchy.
Ctrl+Shift+H: view method hierarchy.
Watch this video to learn more about how completion works in IntelliJ IDEA:
Troubleshooting
If code completion does not work, this may be due to one of the following reasons:
The Power Save Mode is on (). Turning it on minimizes power consumption of your laptop by eliminating the background operations, including error highlighting, on-the-fly inspections, and code completion.
JDK is not configured for your project.
Your file does not reside in a content root and is not bound to a build path, so it does not get the required class definitions and resources needed for code completion.
A file containing classes and methods that you want to appear in the completion suggestion list is marked as a plain text file.
External libraries that contain methods that you want to appear in the completion suggestion list are not added as dependencies or global libraries.
Code completion popup might not appear automatically if it takes too long to gather the completion options. For example, if the computer is busy with another task. In this case, you may still activate the completion popup manually via Ctrl+Space.