Node.js
Node.js is a lightweight runtime environment for executing JavaScript outside the browser, for example, on the server or in the command line. IntelliJ IDEA integrates with Node.js providing assistance in configuring, editing, running, debugging, testing, profiling, and maintaining your applications.
If you need Node.js only as a local runtime for your application or for managing npm packages, running JavaScript linters, build tools, test frameworks, and so on, just install Node.js. If you follow the standard installation procedure, in most cases IntelliJ IDEA detects Node.js itself.
And even if you have no Node.js on your computer, you can install it when creating a new Node.js application in the Create New Project dialog, refer to Creating a new Node.js application below.
If you want to switch among several Node.js installations, they must be configured as local Node.js runtimes. In most cases, IntelliJ IDEA detects Node.js installations, configures them as runtimes automatically, and adds them to the list where you can select the relevant one.
To run a Node.js application remotely, configure it as a remote runtime. For more information, refer to Node.js with Docker, Node.js via SSH, and Node.js with Vagrant.
Before you start
Download and install Node.js.
Make sure the JavaScript and TypeScript and Node.js required plugins are enabled on the Settings | Plugins page, tab Installed. For more information, refer to Managing plugins.
Switching between Node.js installations
With IntelliJ IDEA, you can have several installations of Node.js and switch between them while working on the same project.
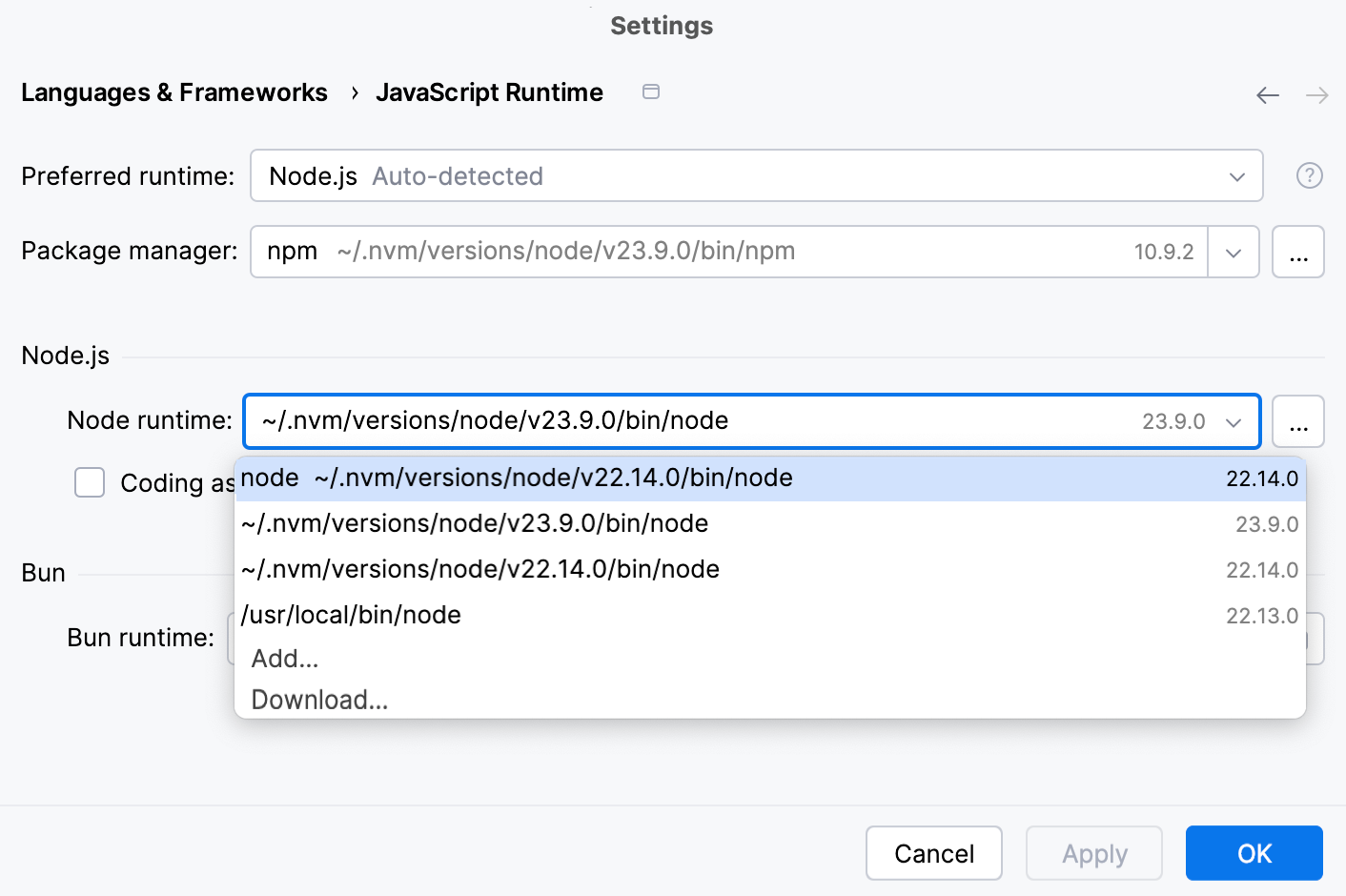
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Make sure that Node.js is selected in the Preferred runtime field.
Select the required Node.js installation from the Node.js runtime list.
If you followed the standard installation procedure, in most cases the required Node.js installation is on the list. If the installation is missing, click
and configure it as a local runtime manually.
Using a system Node.js version
With IntelliJ IDEA, you can set the default system node alias as your project’s Node.js version. After that, this version will be automatically used by all the tools that require Node.js and in all new run/debug configurations. In particular, this means that you will not have to update the settings for each tool if you install a new Node.js version and make it the default node alias in your system.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Make sure that Node.js is selected in the Preferred runtime field.
From the Node.js runtime list, select node.
Specify this new Node.js runtime where applicable, for example, in your run/debug configurations or settings of specific tools.
Configuring a local Node.js runtime
You may need to configure Node.js installation as an runtime manually, for example, if Node.js is installed in a non-default location so IntelliJ IDEA does not detect it automatically.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Make sure that Node.js is selected in the Preferred runtime field.
Click
next to the Node runtime list.
In the Node.js Runtimes dialog with a list of all the currently configured runtimes, click
on the toolbar and select Add Local from the context menu and choose the installation of Node.js, then click OK. You return to the Node.js Runtimes dialog where the Node runtime read-only field shows the path to the new runtime.
In the Package manager field, choose the package manager (npm, Yarn, pnpm, bun) for the current project.
For more information, refer to Configuring a package manager for a project.
When you click OK, you return to the JavaScript Runtime page where the Node runtime field shows the new runtime.
Using Node.js on Windows Subsystem for Linux
IntelliJ IDEA lets you run and debug Node.js applications using Node.js on Windows Subsystem for Linux. You can choose Node.js on WSL as the default runtime for the current project or you can configure and use this Node.js version in a Node.js Run/Debug configuration.
Configure Node.js on WSL as the default project Node.js runtime
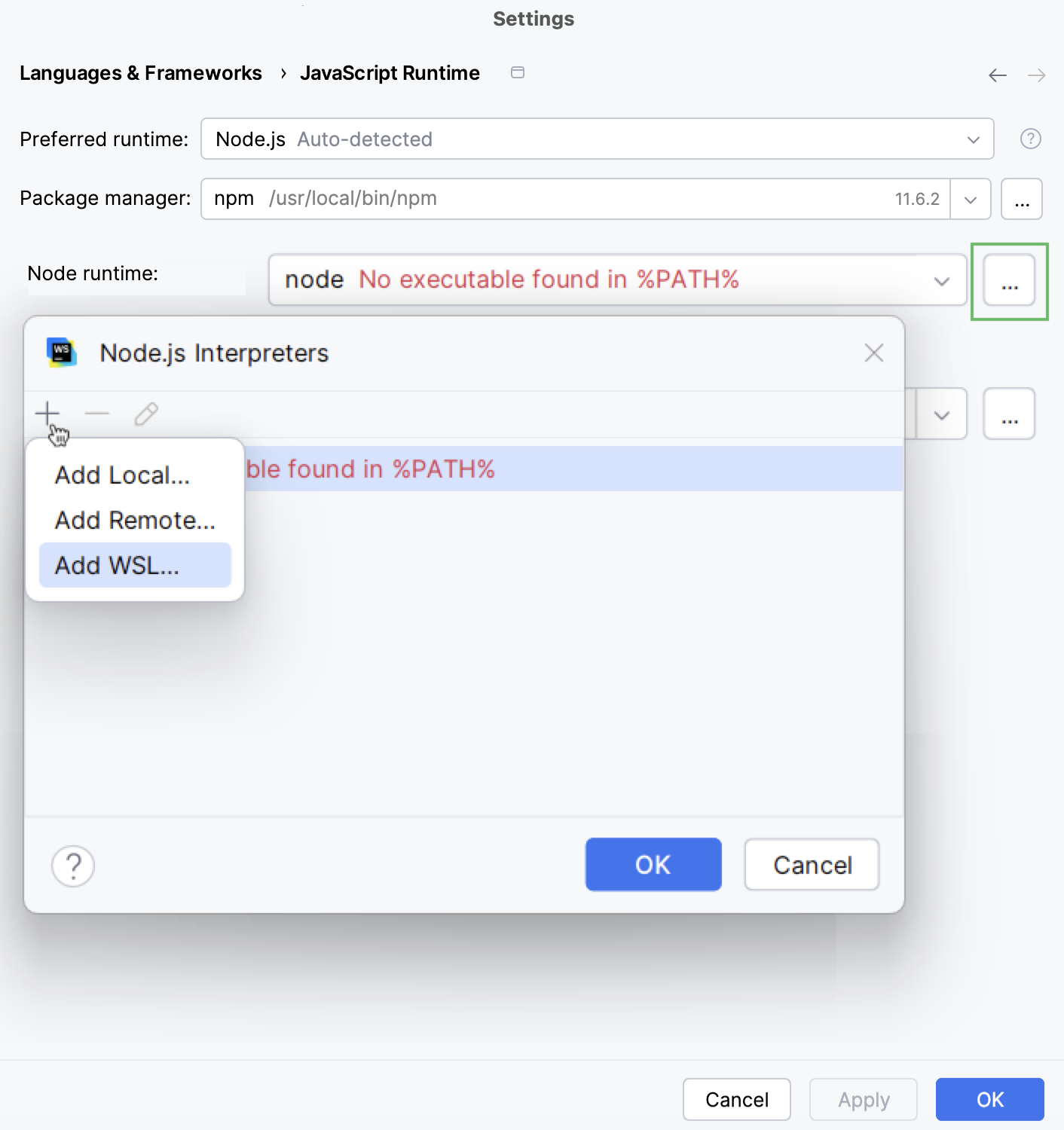
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to .
Click
next to the Node.js runtime field, in the Node.js Runtimes dialog that opens, click
, and then select Add WSL from the list.
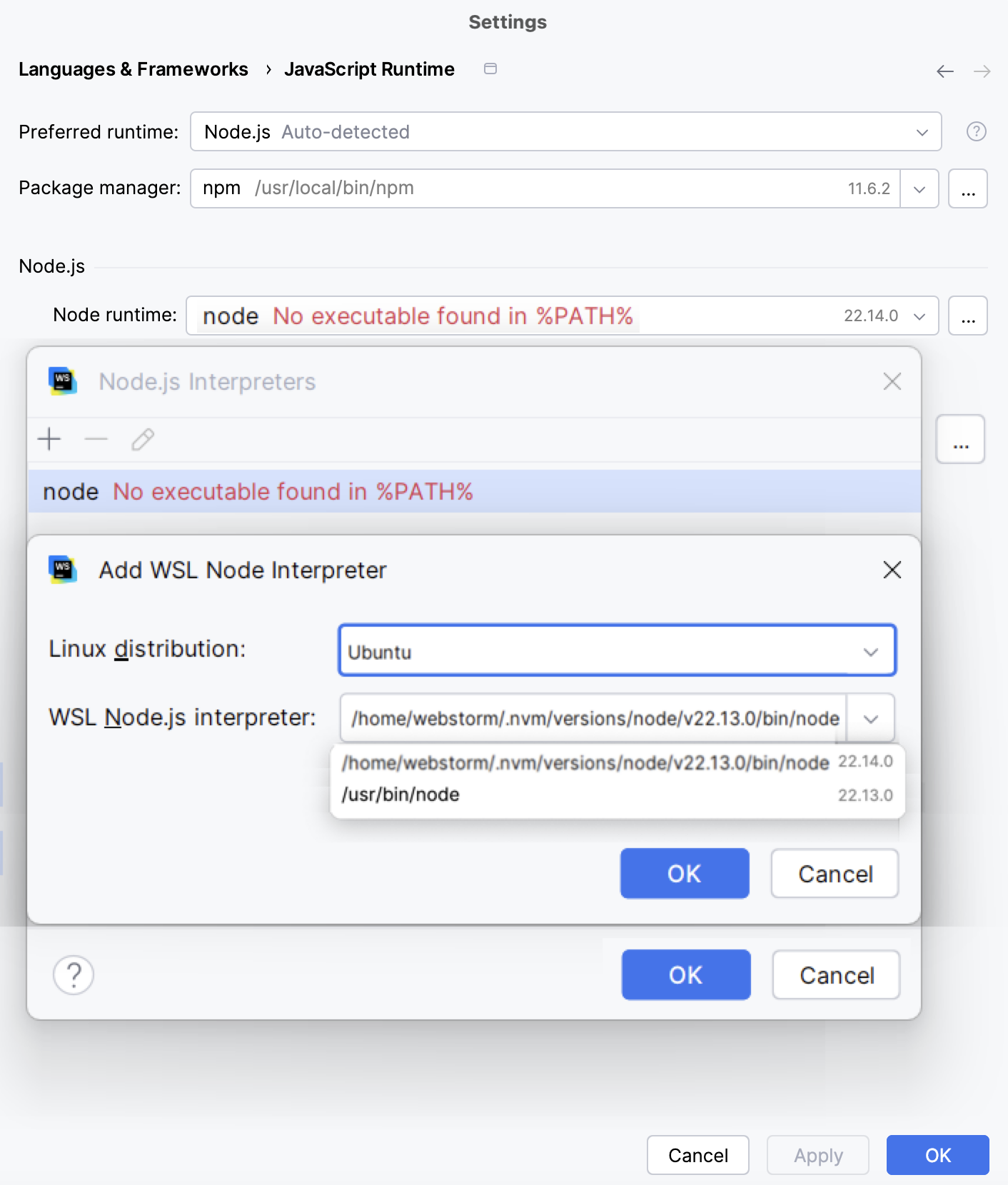
In the Add WSL Node Runtime dialog that opens, select the Linux distribution you’re using and specify the path to Node.js.
Creating a Node.js application
If you have no application yet, you can generate an IntelliJ IDEA project with Node.js-specific structure from a template or create an empty IntelliJ IDEA project and configure Node.js in it as described in Starting with an existing Node.js application below.
You can also create a module from an existing Node.js application.
Create a new Node.js application
Select from the main menu or click the New Project button on the Welcome screen.
In the New Project dialog, select Express in the left-hand pane.
In the right-hand pane, specify the project folder and the Node.js runtime to use. For more information, refer to Configuring a local Node.js runtime.
Specify the express -generator in the express-generator field.
It is recommended that you use npx that downloads and runs the generator. To do that, select npx --package express-generator express from the express -generator list.
Alternatively, open the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) and type
npm install --g express-generatorand then select the downloaded generator from the express-generator list.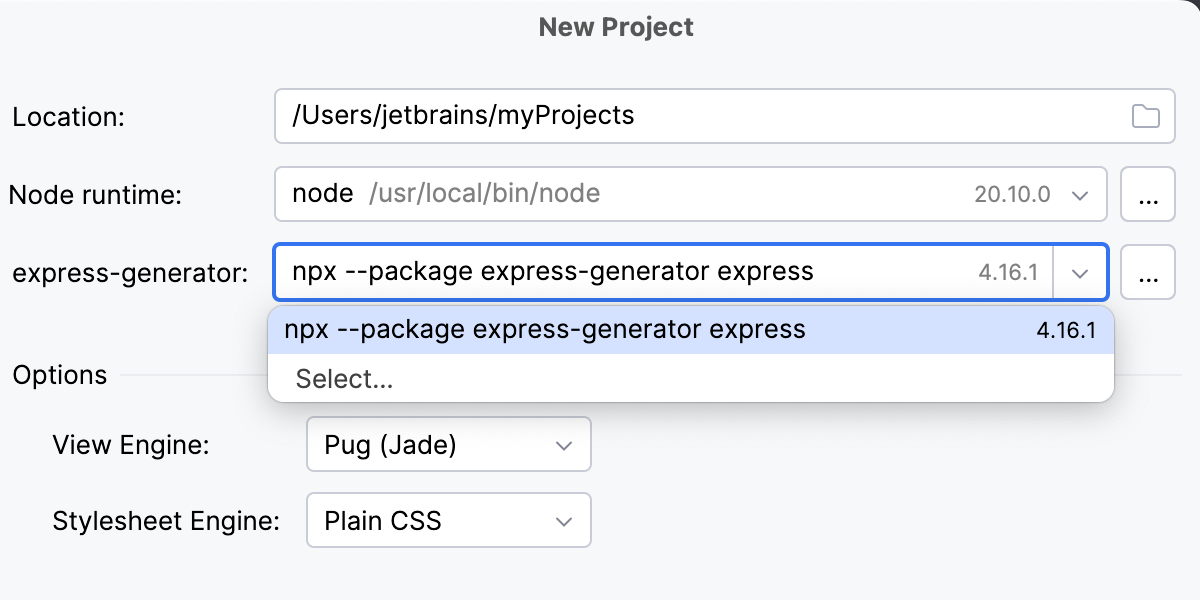
Select the template language and the Style Sheet language to use.
When you click Create, IntelliJ IDEA downloads the necessary dependencies and enables code completion for them as well as for the Node.js core APIs. For more information, refer to Configuring node_modules library and Configuring Node.js Core library.
IntelliJ IDEA creates a run/debug configuration of the type Node.js with default settings and generates a basic Express-specific directory structure.
Create an empty IntelliJ IDEA project
Select from the main menu or click the New Project button on the Welcome screen.
In the New Project dialog, select New Project in the left-hand pane.
In the right-hand pane, select JavaScript in the Language area and specify the project folder and name.
To have a sample application generated, select the Add sample code checkbox.
Create a module from an existing Node.js app
Download your application sources and store them on your computer.
Go to .
In the dialog that opens, select the location of your application sources.
Learn more from Modules.
Starting with an existing Node.js application
If you are going to continue developing an existing Node.js application, open it in IntelliJ IDEA, configure Node.js in it, and download the required dependencies.
Open the application sources that are already on your machine
Click Open or Import on the Welcome screen or select from the main menu. In the dialog that opens, select the folder where your sources are stored.
Check out the application sources from your version control
Click Clone Repository on the Welcome screen.
Alternatively, select or or from the main menu.
Instead of Git in the main menu, you may see any other Version Control System that is associated with your project. For example, Mercurial or Perforce.
In the dialog that opens, select your version control system from the list and specify the repository to check out the application sources from. For more information, refer to Check out a project (clone).
Configure Node.js in a project
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to .
In the Node runtime field, specify the default Node.js runtime for the current project. IntelliJ IDEA automatically uses it every time you select the
Projectalias from Node runtime lists, for example, when creating run/debug configurations.Select a configured runtime from the list or click
and configure a new one in the dialog that opens as described in Configuring a local Node.js runtime. If you select node, the system Node.js version is used.
Select the Coding assistance for Node.js checkbox to configure the Node.js Core module sources as a JavaScript library and associate it with your project. As a result, IntelliJ IDEA provides code completion, reference resolution, validation, and debugging capabilities for
fs,path,http, and other parts of Node.js that are compiled into the Node.js binary.When the configuration is completed, IntelliJ IDEA displays information about the currently configured version.
If you need code completion for Node.js APIs only in some parts of your project, you can configure that using the Manage scopes link. In the Usage dialog that opens, click the relevant directories and for each of them select the configured Node.js Core library from the list. Learn more from Configuring the scope of a library.
Download the project dependencies
In the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) , type:
npm installAlternatively, select Run 'npm install' from the context menu of the package.json file in your project root.
Project security
When you open a project that was created outside IntelliJ IDEA and was imported into it, IntelliJ IDEA displays a dialog where you can decide how to handle this project with unfamiliar source code.
Select one of the following options:
Preview in Safe Mode: in this case, IntelliJ IDEA opens the project in a preview mode. It means that you can browse the project's sources but you cannot run tasks and script or run/debug your project.
IntelliJ IDEA displays a notification on top of the editor area, and you can click the Trust project link and load your project at any time.
Trust Project: in this case, IntelliJ IDEA opens and loads a project. That means the project is initialized, project's plugins are resolved, dependencies are added, and all IntelliJ IDEA features are available.
Don't Open: in this case, IntelliJ IDEA doesn't open the project.
Learn more from Project security.