Working with libraries
A library is a collection of compiled code that a module can depend on. In IntelliJ IDEA, libraries can be defined at three levels: global (available for many projects), project (available for all modules within a project), and module (available for one module).
A Java library can include class files, archives and directories with class files as well as directories with Java native libraries (.dll, .so or .jnilib).
Define a library
After you define a library and add it to module dependencies, the IDE will be supplying its contents to you as you write your code. IntelliJ IDEA will also use the code from the libraries to build and deploy your application.
From the main menu, select (Ctrl+Shift+Alt+S).
Under the Platform Settings, select Global Libraries.
Click the
 button and select how do you want to add a new library: you can add a Java and Kotlin libraries from files on your machine, or download a library from Maven.
button and select how do you want to add a new library: you can add a Java and Kotlin libraries from files on your machine, or download a library from Maven.
From the main menu, select (Ctrl+Shift+Alt+S).
Under the Project Settings, select Libraries.
Click the
 button and select how do you want to add a new library: you can add a Java and Kotlin libraries from files on your machine, or download a library from Maven.
button and select how do you want to add a new library: you can add a Java and Kotlin libraries from files on your machine, or download a library from Maven.
From the main menu, select (Ctrl+Shift+Alt+S).
Under the Project Settings, select Modules section.
Open the Dependencies tab.
Click the
 button and select Library.
button and select Library.-
Click New Library at the bottom of the dialog and select how do you want to add a new library: you can add a Java and Kotlin libraries from files on your machine, or download a library from Maven.
Download a library from Maven
Press Ctrl+Shift+Alt+S to open the Project Structure dialog, and click Libraries.
Click
 , and select From Maven.
, and select From Maven. -
In the next dialog, specify the library artifact (for example,
org.jetbrains:annotations:16.0.2). If you don't know its exact name, enter the key words and click .
.You can also specify another library location, and select whether you want to download transitive dependencies, source files, JavaDoc files, or annotations.
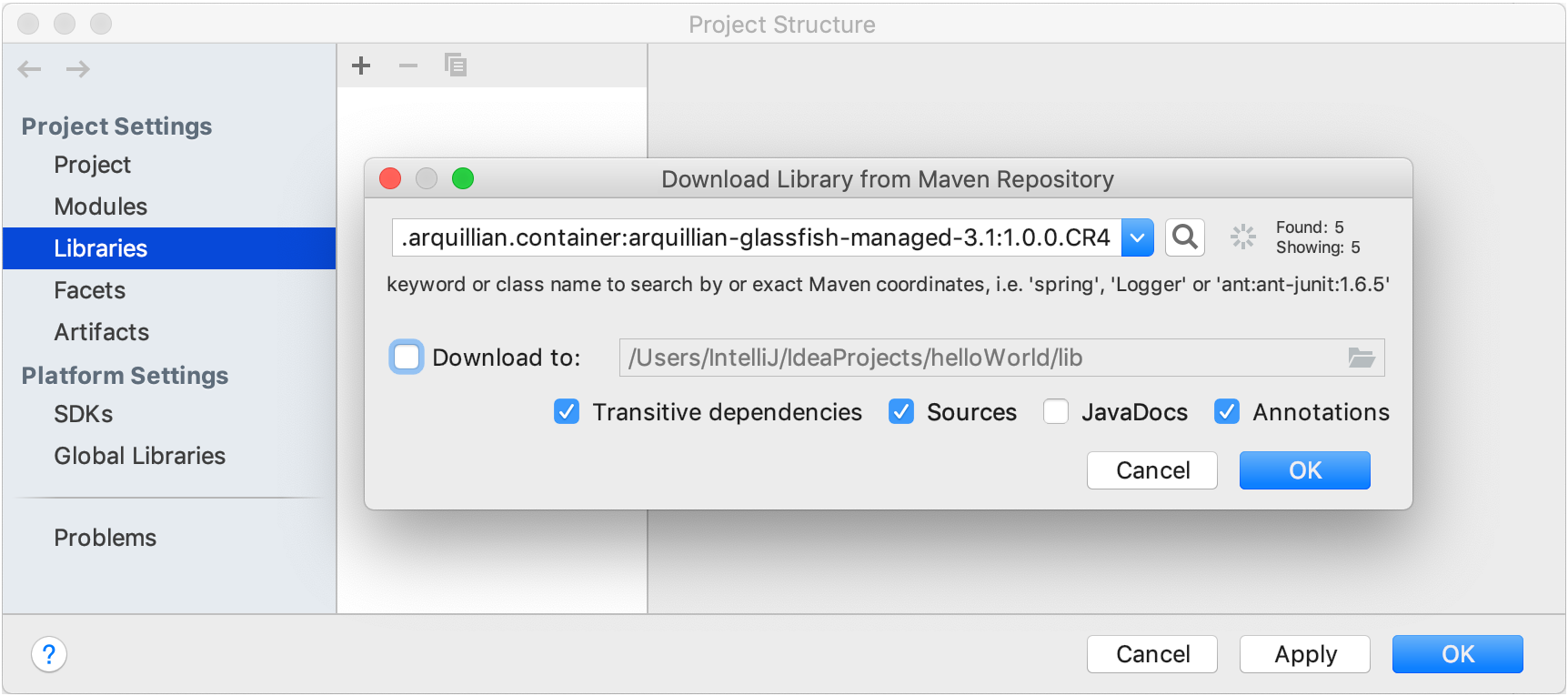
IntelliJ IDEA will download the library from Maven or Nexus public repositories. You can also configure the custom remote repository.
Configure a custom remote repository
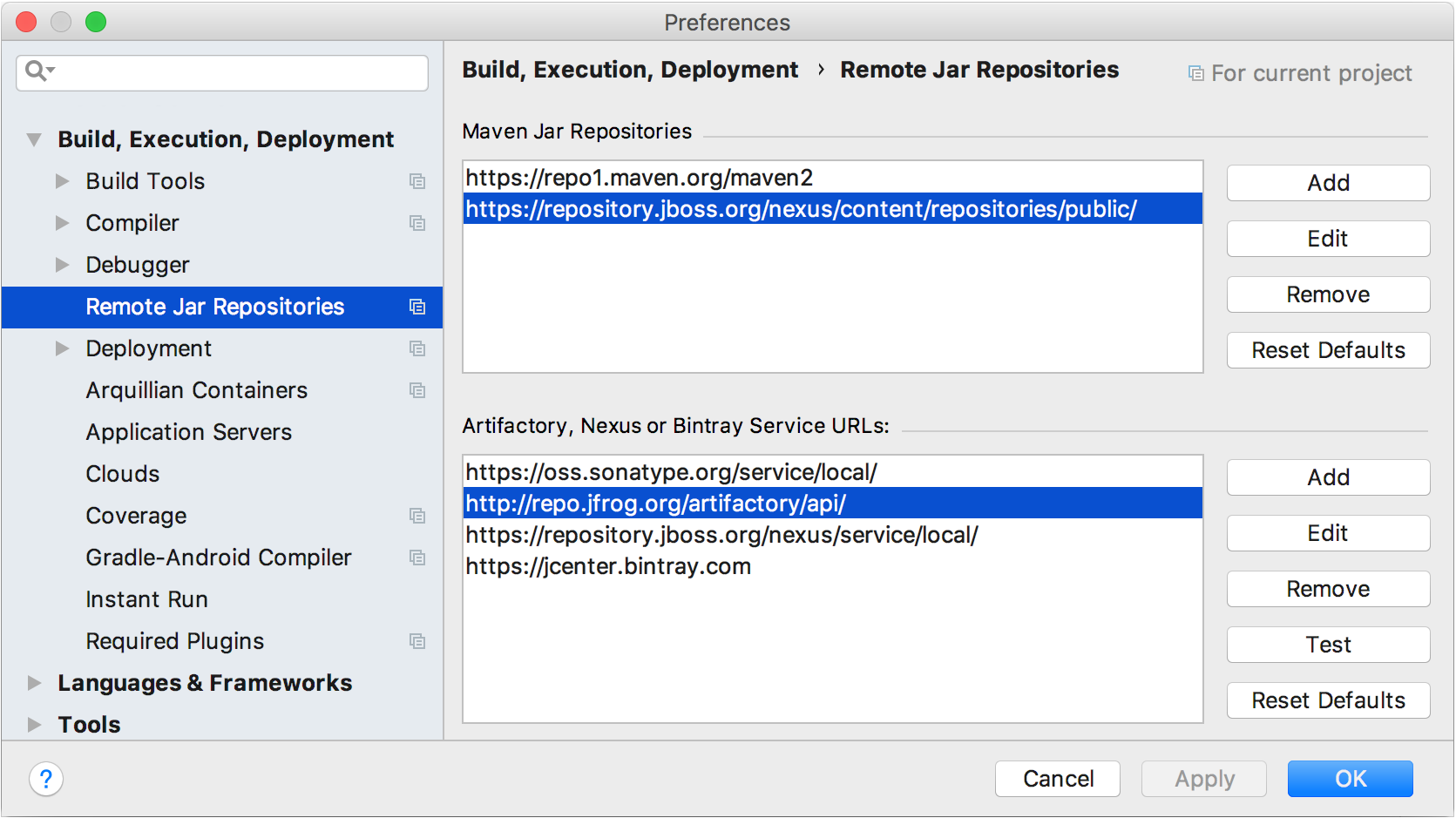
You can view the full list of remote repositories and add a custom repository in the settings. Note that IntelliJ IDEA can load libraries from Maven even if you don't use Maven as a build tool for your project.
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), go to .
Click Add in the corresponding dialog section, and specify the repository URL.
Add a library to module dependencies
Global and project libraries are not available until you add them to module dependencies:
Open the Project Structure dialog (Ctrl+Shift+Alt+S) and select Modules.
Open the Dependencies tab and click
 .
. Select a library you want to add and click Add Selected at the bottom of the dialog.
Include specific transitive dependencies
If you want to include only specific transitive dependencies, you can use the library properties editor.
Press Ctrl+Shift+Alt+S to open the Project Structure dialog, and go to .
Select the necessary Maven library and click
 .
.In the next dialog, click Edit, and then click Configure next to the Include transitive dependencies option.
Select the dependencies you want to include in the library and click OK.
Exclude library items
IntelliJ IDEA allows you to temporarily exclude library items in order to increase IDE performance. You can exclude folders, archives (e.g. JARs) and folders within archives.
Classes from excluded packages won't be shown in code completion suggestion lists, references to such classes will be shown in the editor as unresolved, etc. However, when you compile or run your code, a library will still be used as a whole, irrespective of whether there are excluded items in that library or not.
Exclude items from a project or a global library
Press Ctrl+Shift+Alt+S to open the Project Structure dialog, and click Libraries.
Click
 , and select the library items that you want to exclude.
, and select the library items that you want to exclude.
Exclude items from a module library
Press Ctrl+Shift+Alt+S to open the Project Structure dialog, and go to .
Click
 , and select the library items that you want to exclude.
, and select the library items that you want to exclude.
Excluded items will be marked with the ![]() icon. To return library items to their original state, remove the excluded items.
icon. To return library items to their original state, remove the excluded items.
Change library level
In IntelliJ IDEA, you can move a project or a module library to a higher level. This is helpful if you want to extend its scope of usage. For example, if you want to use a module library across the project or the entire IDE. To move a library to a higher level, right-click this library in the Project Structure dialog, and select Move to Project Libraries or Move to Global Libraries.
You can also create a copy of a library on a lower level. For example, if you want to add more classes to a project library, but you want to use them in one module only.
Right-click the necessary global library and select Copy to Project Libraries. Then specify if you also want a copy of the library files and where that copy should be created. For a global or project library included in the dependencies of a module, to start creating a copy at the module level, right-click the required library and select Copy to Module Libraries.