Microsoft SQL Server LocalDB
Enable the Database Tools and SQL plugin
This functionality relies on the Database Tools and SQL plugin, which is bundled and enabled in IntelliJ IDEA by default. If the relevant features are not available, make sure that you did not disable the plugin.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Open the Installed tab, find the Database Tools and SQL plugin, and select the checkbox next to the plugin name.
Official documentation
For full information about Microsoft SQL Server LocalDB, refer to the official documentation.
Before you begin
This topic presents a general procedure on how you can create a data source for the connection to your Microsoft SQL Server LocalDB database in IntelliJ IDEA, and run a test connection. It is assumed that you already have the necessary connection details and the database is up and running.
To learn about your DBMS software, refer to its official documentation.
Connect to a Microsoft SQL Server LocalDB database
To connect to a database, create a data source that will store your connection details.
Select the data source you want to create. You can do this using one of the following ways:
In the main menu, go to and select Microsoft SQL Server LocalDB.
In the Database tool window, click
New on the toolbar. Navigate to Data Source and select Microsoft SQL Server LocalDB.
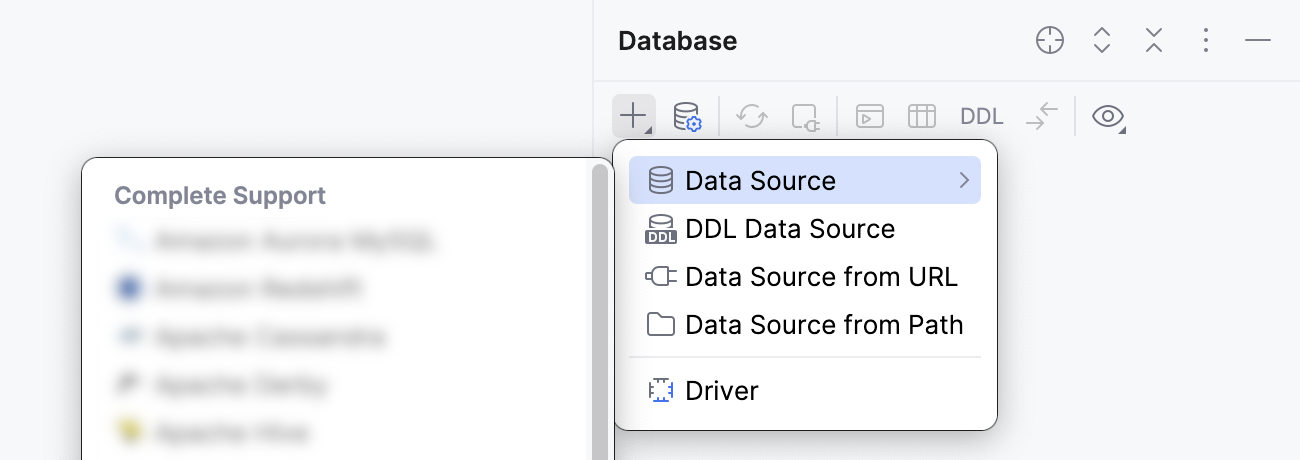
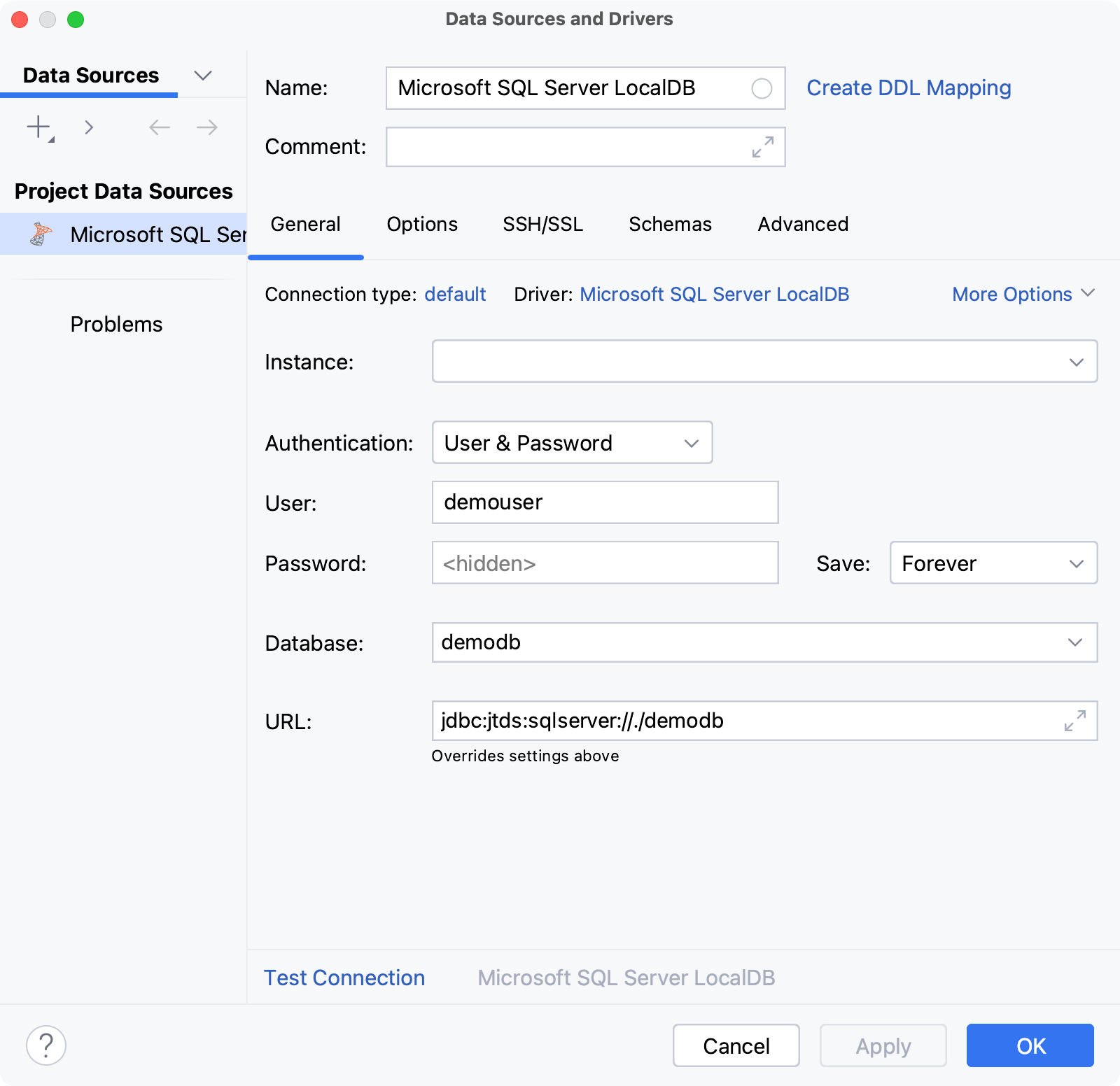
In the General tab of Data Sources and Drivers dialog right pane, specify the driver and connection type.
In the Driver list, leave the default driver option, unless another driver is required for your connection.
From the Connection type list, select the connection type depending on the connection details that you have:
default: connect by using Instance, Database, and URL.
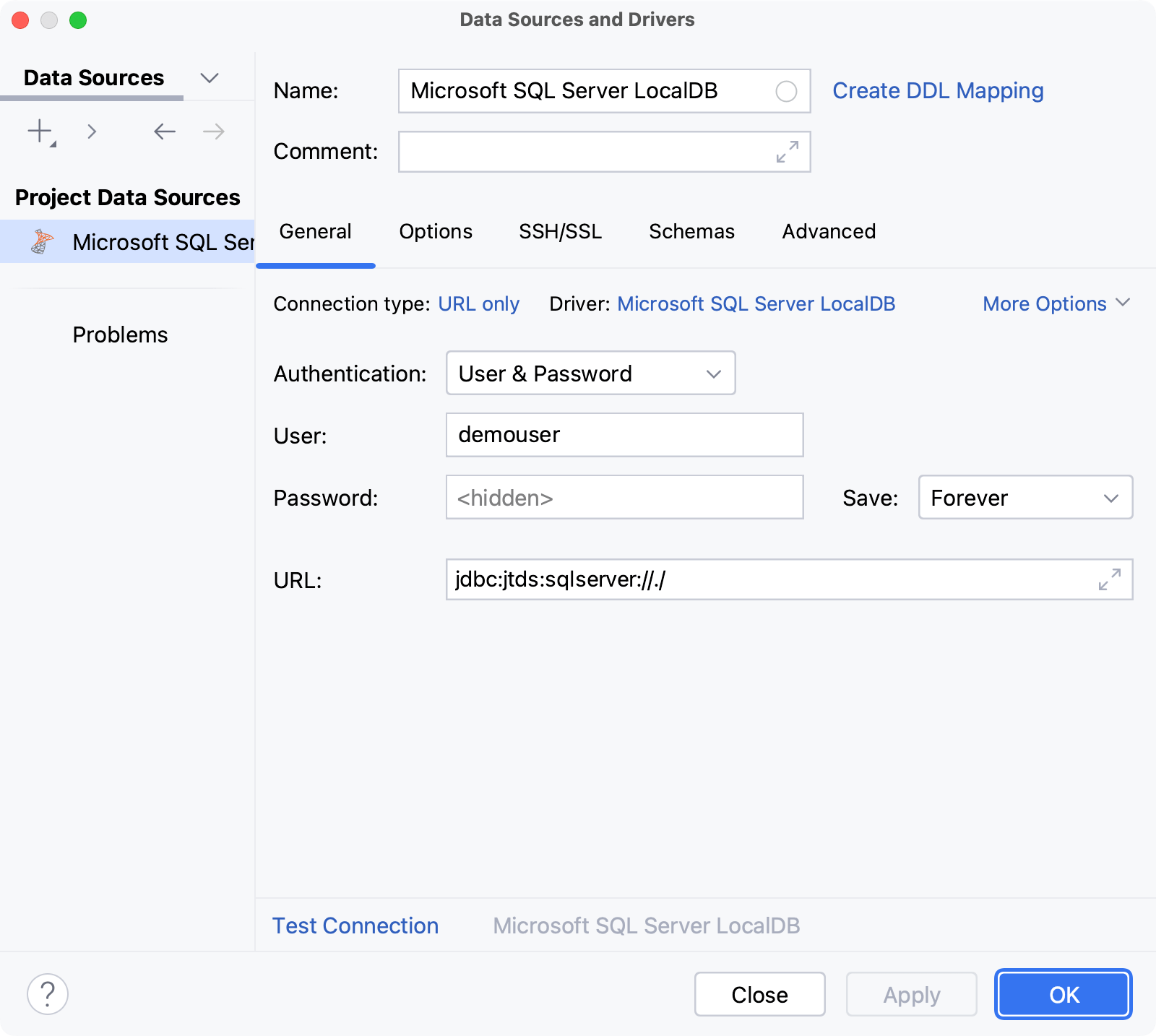
URL only: connect by using only the URL.
For the URL only connection type, the JDBC URL that you enter is used as is, including the database credentials.
For the other connection types, the JDBC URL is broken down into connection details. You can either specify them separately and use the automatically generated URL, or you can enter the URL directly in the corresponding field.
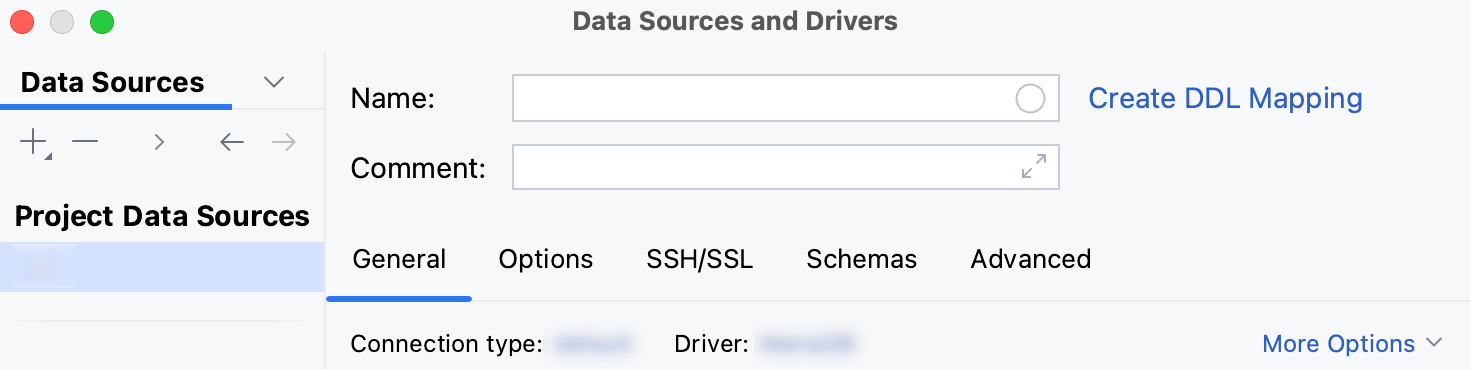
Check if there is a Download missing driver files link at the bottom of the connection settings area. Click this link to download drivers that are required to interact with a database. For a direct download link, refer to the JetBrains JDBC drivers page.
Location for the downloaded JDBC drivers is the IntelliJ IDEA configuration directory.
You can also use your drivers for the database instead of the provided ones. For more information about connecting to a database with your driver, refer to Add a user driver to an existing connection.
If there is no Download missing driver files link, then you already have the required drivers.
Specify the database connection details. Alternatively, paste the JDBC URL in the URL field.
From the Instance list, select the instance to connect to.
From the Authentication dropdown, select the authentication method that you want to use to authenticate the connection. The following options are available:
User & Password: by using your login and password.
Windows credentials: use the current Windows user's credentials for authentication.
Kerberos: use Kerberos for authentication. Requires a Kerberos server and authentication with
kinit.No auth: authentication is not required.
Domain credentials: use Windows domain authentication for the connection (Domain, User, and Password). For more information about Windows domain authentication, refer to the Microsoft SQL Server data source tutorial.
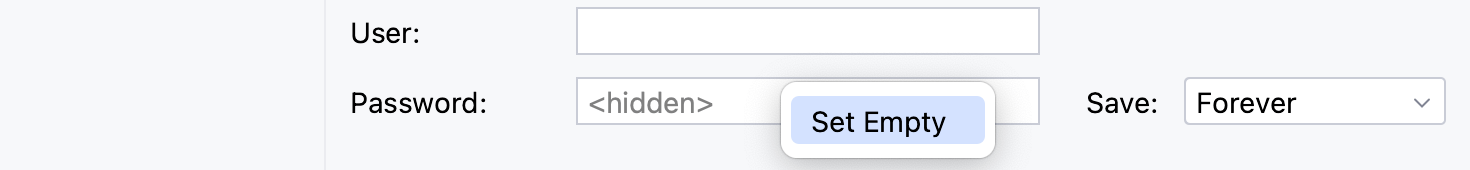
In the User and Password fields, type your user credentials.
To use no password, leave the Password field empty.
To delete a once entered password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.
In the Database field, type the database name to which you want to connect.
In the URL field, IntelliJ IDEA generates the JDBC URL automatically using the values of other connection settings.
If you need to use a JDBC URL with certain additional settings, paste it in the URL field. The general URL to use is as follows:
Format:
jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://./<database_name>Example:
jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://./myDatabase
From the Authentication dropdown, select the authentication method that you want to use to authenticate the connection. The following options are available:
User & Password: by using your login and password.
Windows credentials: use the current Windows user's credentials for authentication.
Kerberos: use Kerberos for authentication. Requires a Kerberos server and authentication with
kinit.No auth: authentication is not required.
Domain credentials: use Windows domain authentication for the connection (Domain, User, and Password). For more information about Windows domain authentication, refer to the Microsoft SQL Server data source tutorial.
In the User and Password fields, type your user credentials.
To use no password, leave the Password field empty.
To delete a once entered password, right-click the Password field and select Set Empty.

In the URL field, IntelliJ IDEA generates the JDBC URL automatically using the values of other connection settings.
If you need to use a JDBC URL with certain additional settings, paste it in the URL field. The general URL to use is as follows:
Format:
jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://./<database_name>Example:
jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://./myDatabase
For the reference information about connection settings and properties on the General and other tabs of Data Sources and Drivers dialog ( Shift+Enter) , see Connection settings and DBMS-specific properties.
Ensure that the database connection can be established using the provided details. To do this, click the Test Connection link at the bottom of the connection details section.
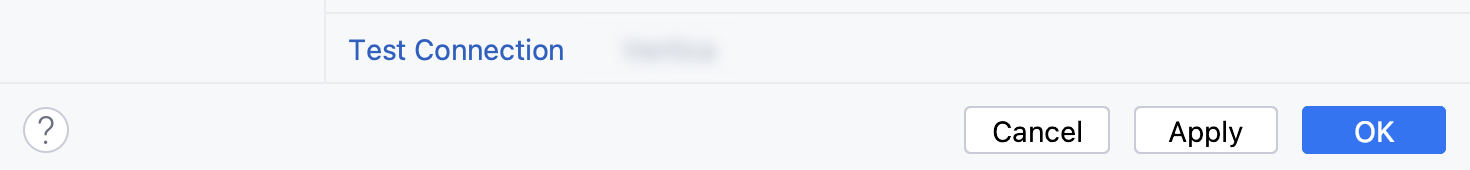
If you encounter any connection issues, refer to the Cannot connect to a database page.
(Optional) By default, only the default database and schema are introspected and available to work with. If you also want to work with other databases and schemas, in the Schemas tab, select them for the introspection.
Click OK to create the data source.
Find your new data source in the Database tool window.
For more information about the Database tool window, see the corresponding reference topic.
For more information about working with database objects in IntelliJ IDEA, refer to Database objects.
To write and run queries, open the default query console by clicking the data source and pressing F4.
To view and edit data of a database object, open Data editor and viewer by double-clicking the object.
Connection settings and DBMS-specific properties
Connection settings
For the reference information about connection settings (for example, Host, Port, and so on) on the General and other tabs of Data Sources and Drivers dialog ( Shift+Enter) , see Data Sources.
DBMS-specific properties
General tab
Item | Description | Connection type |
|---|---|---|
Instance | The list of instances available to connect to. For more information about instances, refer to MS SQL Server official documentation. | default |