Maven projects
IntelliJ IDEA lets you manage Maven projects. You can link, ignore projects, synchronize changes in Maven and IntelliJ IDEA projects, and configure the build and run actions.
Navigate to POM
In the Maven tool window, right-click a linked project.
From the context menu, select Jump to Source F4.
IntelliJ IDEA navigates to the appropriate Maven configuration file, and the related POM opens in the editor.
Ignore a Maven project
You can deactivate a Maven project using the Ignore Projects option. In this case, IntelliJ IDEA keeps the ignored Maven projects and subprojects in the Maven tool window, but stops their import (modules, content roots, goals, and so on) to the project. However, IntelliJ IDEA synchronizes the ignored projects with the current one. It might be helpful when you work with a project that has multiple subprojects and need to skip irrelevant ones.
In the Maven tool window, right-click the project that you want to ignore.
From the context menu, select Ignore Project.
In the window that opens, click Yes if you want to remove the project from the Projects tool window.
If you want to activate your Maven projects or subprojects, select Unignore Projects from the context menu.
Ignore POM of a linked project from the Maven settings
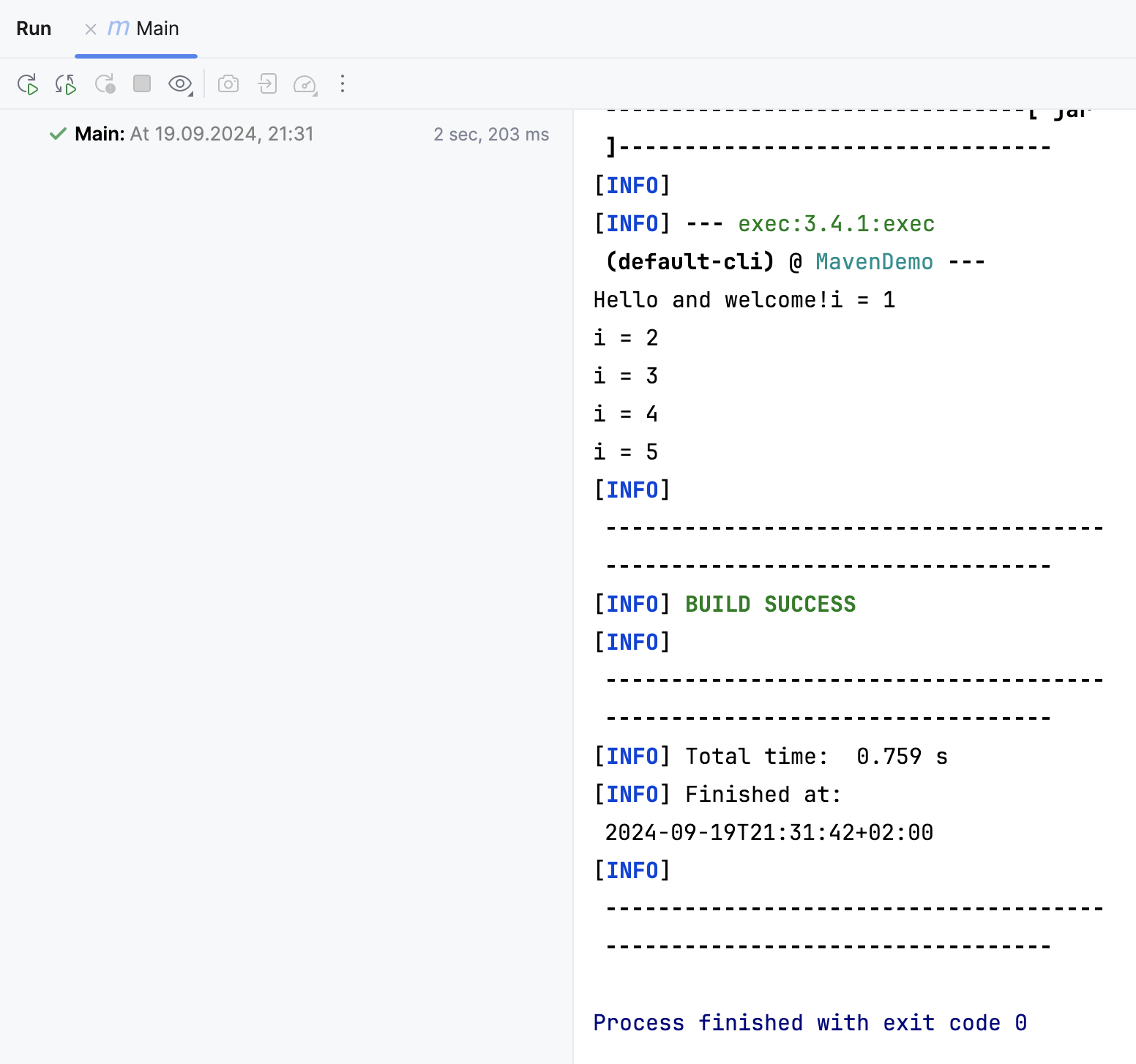
You can ignore a POM file using the Ignored Files settings.
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to .
On the Ignored Files page, select a POM you want to ignore and click OK to save the changes.
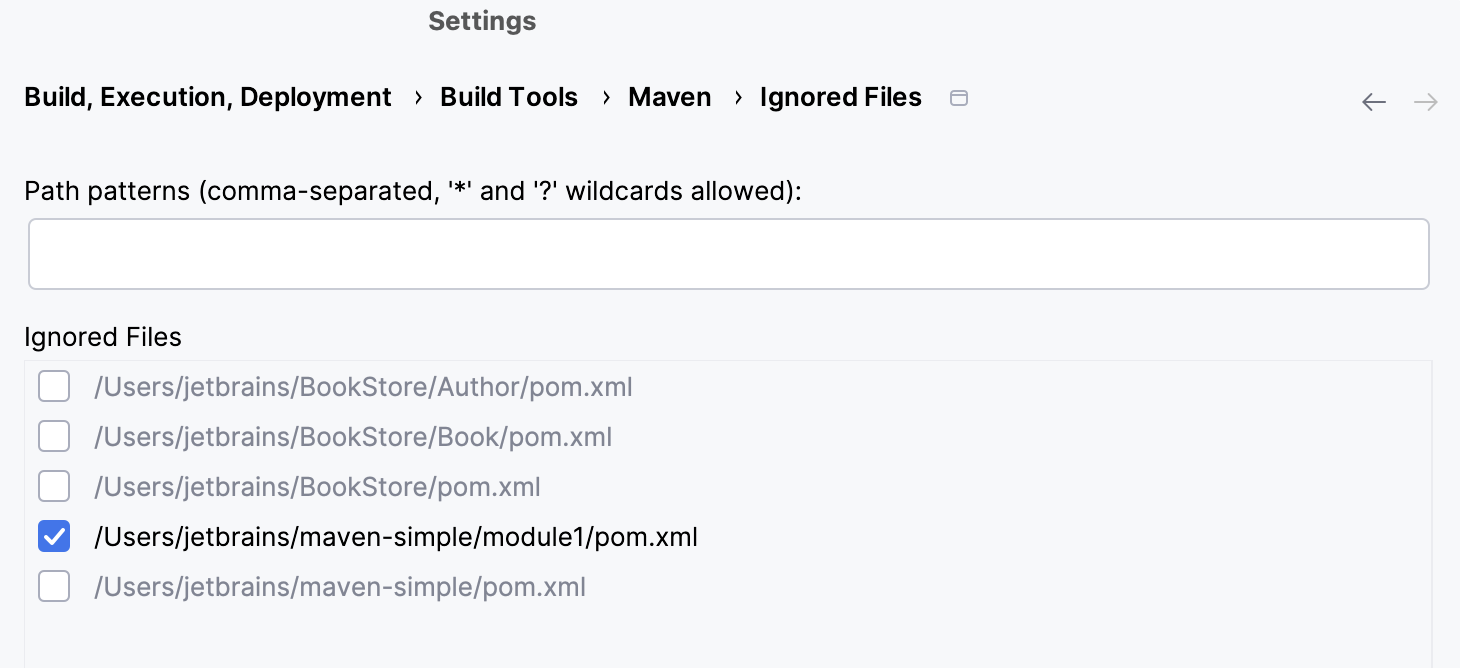
IntelliJ IDEA displays an ignored file in the Maven tool window and in the Project tool window.
If you keep the ignored file in the Project tool window, the POM will be displayed as ignored, however, you can still work with the file and modify it in the editor.
Sync a Maven project
Every time you manually change the pom.xml file in the editor, you need to synchronize the changes. IntelliJ IDEA displays a notification icon in the right part of the editor suggesting to Sync Maven Changes made to the project (Ctrl+Shift+O).
If you want to control the importing process of your project, you can manually trigger the action.
In the Maven tool window, right-click a linked project.
From the context menu, select Sync Project
.
On invoking this action, IntelliJ IDEA parses the project structure in the Maven tool window.
IntelliJ IDEA reloads only the changed part of your project.
If you configure a dependency through the Project Structure dialog (Ctrl+Alt+Shift+S), the dependency will only appear in the IntelliJ IDEA Project tool window, not in the Maven tool window. Note that the next time you synchronize your project, IntelliJ IDEA will remove the added dependency since IntelliJ IDEA considers the Maven configuration as a single source of truth.
Sync or Reload all Maven projects
When you initially open your project, IntelliJ IDEA performs the full sync (reload). When you make changes to the project, instead of calling reload for the entire project, you can limit the scope and only sync what is necessary.
In the Maven tool window, click
on the toolbar.
Depending on the synchronization you want to perform, choose one of the following options from the drop-down:
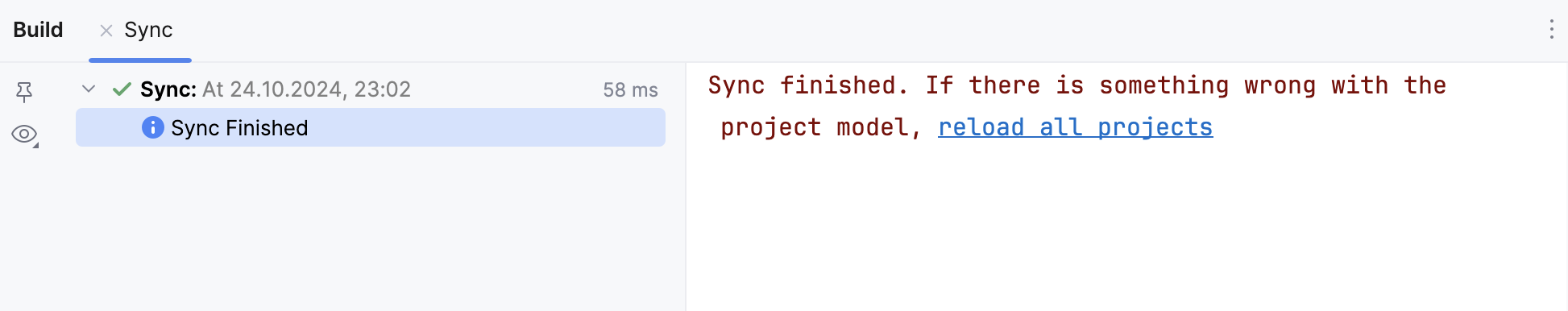
Sync All Maven Projects: syncs all the projects incrementally.
The sync results are displayed in Build tool window.
Reload All Maven Projects: performs the full synchronization of all your Maven projects.
The results of the reload are displayed in Build tool window.
Configure the auto-sync
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to .
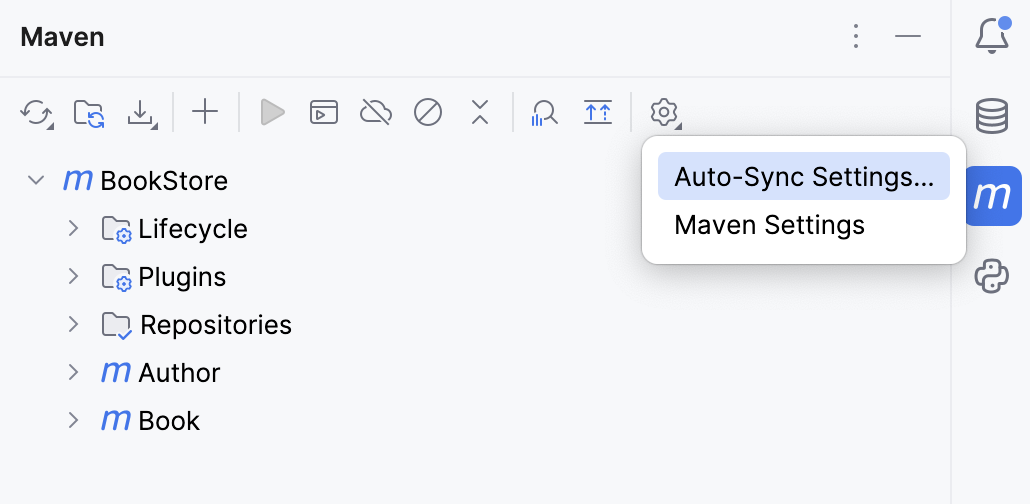
Alternatively, In the Maven tool window, click
and select the Auto-Sync Settings option.
In the Build tools settings, specify the following options:
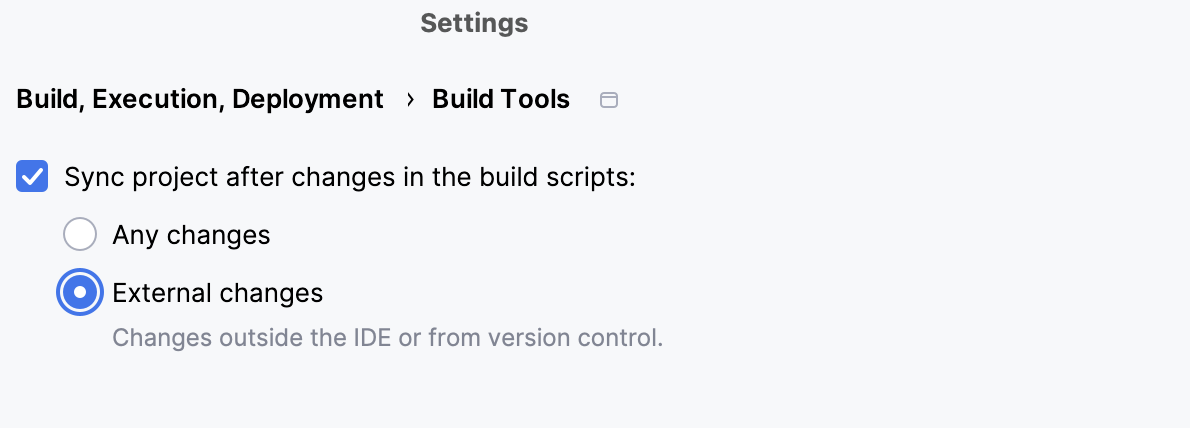
Sync project after changes in the build scripts: this option is selected by default. If you want to disable the auto-sync and manually control the synchronization process, unselect this checkbox.
Any changes: select this option if you want to automatically sync the project after any changes you make to pom.xml or external changes.
Every time you manually change the Maven build script in the editor, you need to synchronize the changes. IntelliJ IDEA displays a notification icon in the right part of the editor suggesting to Sync Maven Changes made to the project (Ctrl+Shift+O). With the Any changes option, IntelliJ IDEA synchronizes all the changes automatically.
External changes: when you select this option, IntelliJ IDEA automatically synchronizes the project only after the VCS changes and changes made to the build files outside the IDE.
Add a Maven config file to a Maven project
If you want to add files such as maven.config or jvm.config, you can do so by creating an empty file in the project.
In the Project tool window, right-click a directory where you want to create a file.
In the context menu, select New | File.
In the dialog that opens, enter a name of the file (maven.config or jvm.config) and click OK.
When you import your project, IntelliJ IDEA reads a content located in the maven.config file, but keep in mind that the content of the jvm.config is ignored.
For more information about the Maven config files, refer to https://maven.apache.org/configure.html.
Link and unlink a Maven project
You can have multiple Maven projects inside one IntelliJ IDEA project. It might be helpful if you keep parts of code in different projects or have some legacy projects on which you need to work. You can link such projects in IntelliJ IDEA and manage them simultaneously. You can also quickly remove such projects from the Maven structure.
Link a Maven project
Open the Maven tool window.
In the Maven tool window, click
to attach a Maven project.
In the dialog that opens, select the desired pom.xml file, and click OK.
The project is linked. The Maven tool window shows the toolbar and a tree view of Maven entities.
Unlink a Maven project
When you unlink a Maven project, IntelliJ IDEA removes all relevant projects and content roots, removes the Maven project from both the Maven tool window and the Project tool window, and stops its synchronization. It might be helpful if you need to fully remove the previously linked Maven project from the current IntelliJ IDEA project.
In the Maven tool window, right-click a linked project.
From the context menu, select Unlink Maven Projects (Delete). Alternatively, you can select the linked project and click
on the tool window's toolbar.
Click OK.
Delegate build and run actions to Maven
By default, IntelliJ IDEA uses the native IntelliJ IDEA builder to build a Maven project. It might be helpful if you have a pure Java or a Kotlin project since IntelliJ IDEA supports the incremental build which significantly speeds up the building process. However, if you have a configuration that changes the compilation on the fly, or your build generates an artifact with a custom layout, then Maven is preferable for the building process.
Build a project with Maven
Click
in the Maven tool window. Alternatively, from the main menu, select .
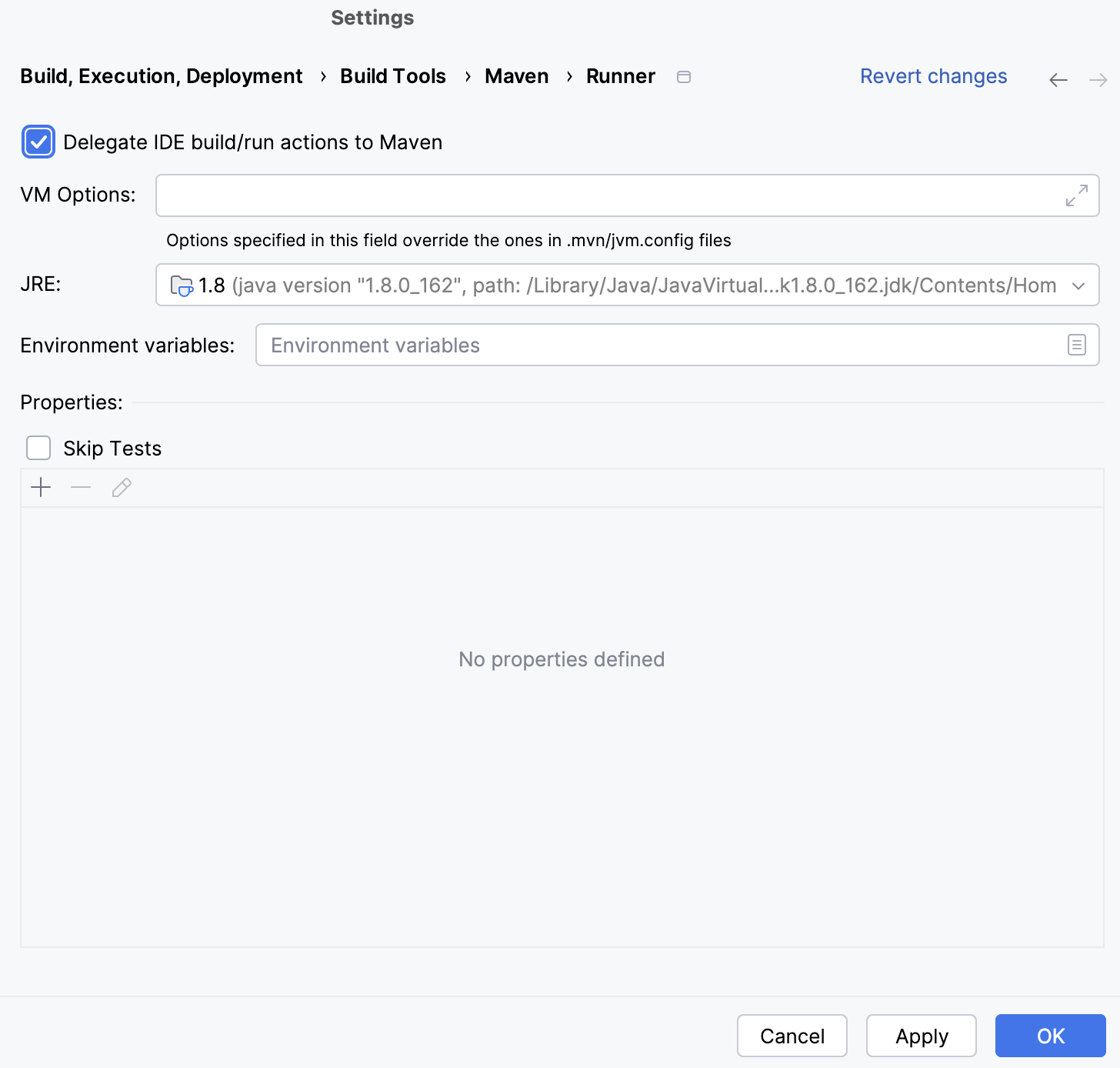
Click Maven and from the list, select Runner.
On the Runner page, select Delegate IDE build/run actions to Maven.
Click OK.
In the main menu, go to Ctrl+F9. IntelliJ IDEA invokes the appropriate Maven goals.
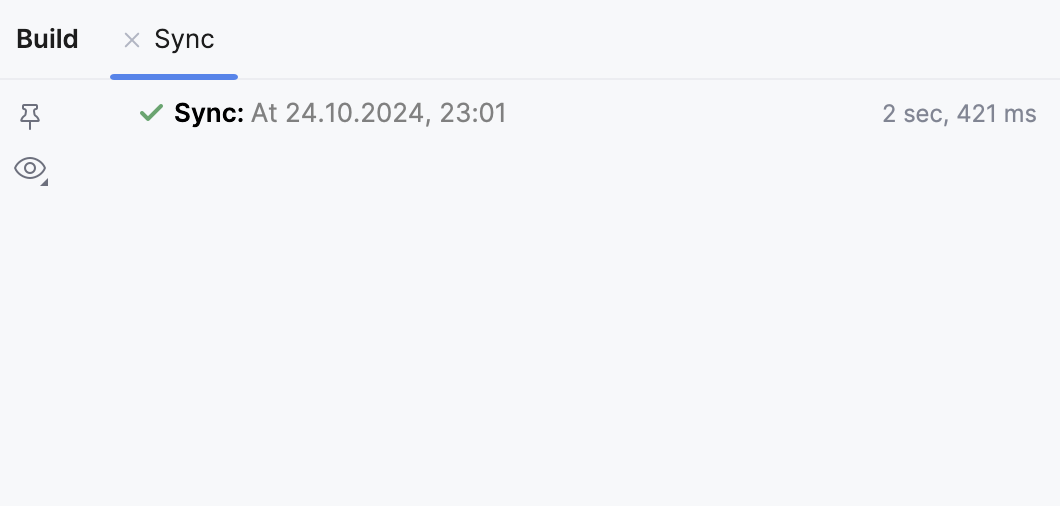
Click
on the status bar to view the results of the sync in the Build tool window.
Run and debug with Maven
When the Delegate IDE build/run actions to Мaven is selected, IntelliJ IDEA runs and debugs your code using Maven. HotSwap is also gets triggered, and the classes are reloaded during a debugging process.
You can use regular run and debug actions as you use in any other projects.
Depending on what action you want to use, from the main menu, select or .
Check the results in the Run tool window or in the Debug tool window if you are debugging your code. For example, when you run the main method Ctrl+Shift+F10 in your Java project, IntelliJ IDEA uses Maven to run the class.