Debug a Java application using a Dockerfile
You can use IntelliJ IDEA to debug a Java application running in a Docker container. This tutorial describes how to create a Dockerfile for running a simple Java console application inside a Docker container with OpenJDK 8 and then debug it by setting breakpoints in the source code and using a remote debug configuration.
For this tutorial, you will need a running Docker daemon and connect IntelliJ IDEA to it as described in Enable Docker support.
Create a sample Java console application
The sample application for this tutorial emulates a console utility to change the password. It asks to enter the login name and the current password. After verifying the credentials, it asks to type the new password twice. If the passwords don't match, it asks for the new password again, until they match, and then changes the password. The methods for verifying and changing the password are not implemented for the purposes of this tutorial.
Create a new empty Java project that uses JDK 8.
Add the
JavaPassFromConsoleclass in the src directory with the following code:import java.io.Console; import java.util.Arrays; public class JavaPassFromConsole { public static void main (String[] args) { Console c = System.console(); String login = c.readLine("Enter your login: "); char[] oldPassword = c.readPassword("Enter your old password: "); if (verify(login, oldPassword)) { boolean match =false; while(!match) { char[] newPassword1 = c.readPassword("Enter your new password: "); char[] newPassword2 = c.readPassword("Enter new password again: "); match = Arrays.equals(newPassword1, newPassword2); if (match) { change(login, newPassword1); c.format("Password for %s changed.%n", login); } else { c.format("Passwords don't match. Try again.%n"); } Arrays.fill(newPassword1, ' '); Arrays.fill(newPassword2, ' '); } } Arrays.fill(oldPassword, ' '); } // Dummy verify method static boolean verify(String login, char[] password) { return true; } // Dummy change method static void change(String login, char[] password) { } }If you try to run this application in IntelliJ IDEA, it will throw a
NullPointerException. This happens because the IDE runs Java applications with thejavawcommand: without an associated console. As a result,System.console()returnsnull. You can try to compile the JavaPassFromConsole.java file and run it using thejavacommand from the command line to see that the code is actually correct.From the main menu, select Ctrl+Alt+Shift+S.
In the Project Structure dialog, select Artifacts, click
and select JAR | From modules with dependencies.
In the Create JAR from Modules dialog, specify
JavaPassFromConsoleas the Main Class and click OK.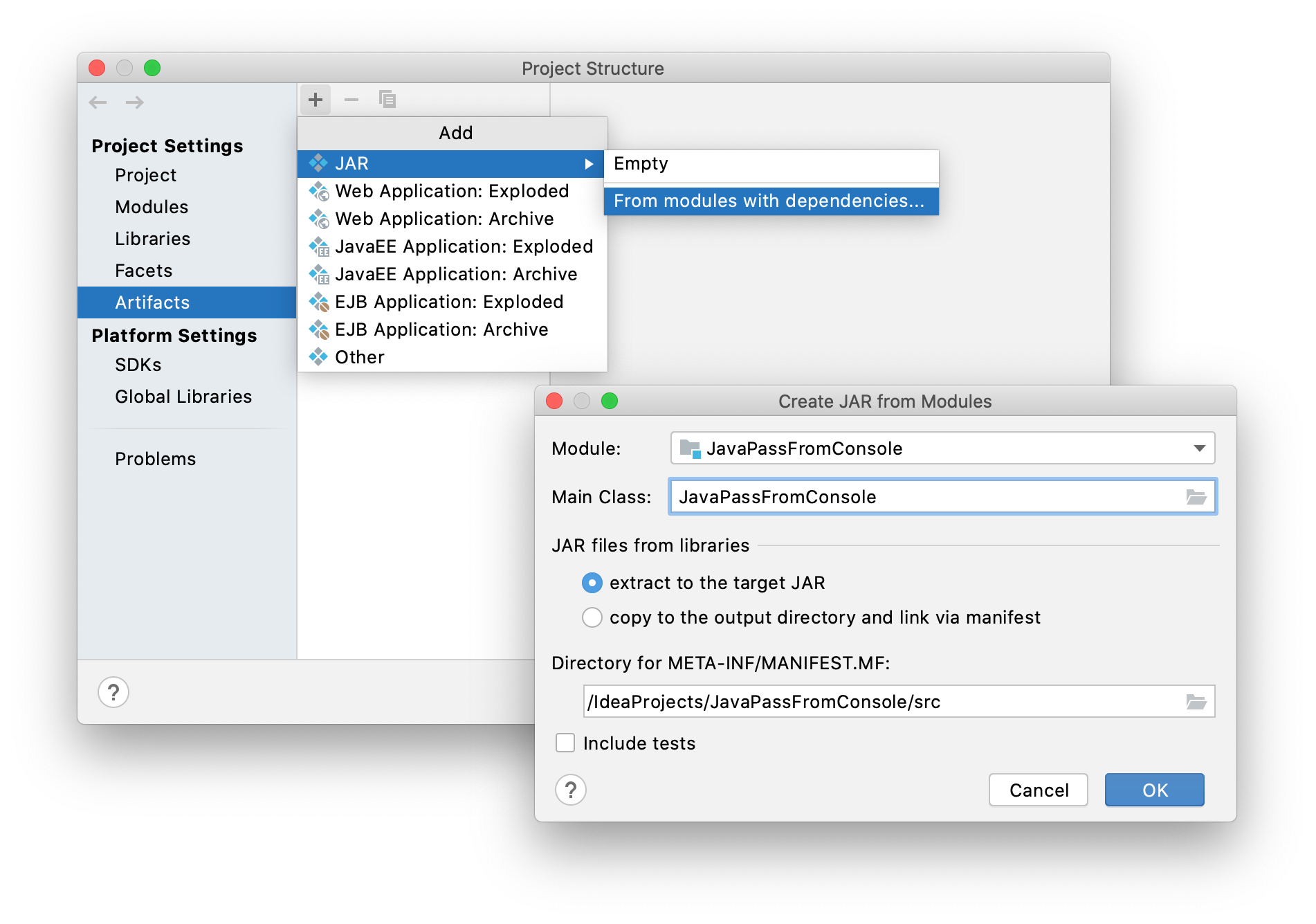
From the main menu, select . Then select Build for the
JavaPassFromConsole:jarartifact. IntelliJ IDEA builds the artifact to out/artifacts/JavaPassFromConsole_jar/JavaPassFromConsole.jar.
Create a Dockerfile and a Docker run configuration
In the Project tool window, right-click the src directory and select New | File.
Type Dockerfile as the name of the file and add the following to it:
FROM openjdk:8 COPY . /tmp WORKDIR /tmp CMD ["java", "-jar", "JavaPassFromConsole.jar"]These instructions tell Docker to run a container from the
openjdk:8image, which contains the Java 8 JDK. Then it copies the current directory (we will set it to be the artifact output directory) to /tmp inside the container. Then it changes the working directory to /tmp and runs the following command:java -jar JavaPassFromConsole.jarClick
in the gutter and select New Run Configuration.
In the Edit Run Configuration dialog, change the context folder to out/artifacts/JavaPassFromConsole_jar (where the JAR artifact is built to), give a name for the container (for example, MyPassAppContainer), and specify the command to run your application:
java -jar JavaPassFromConsole.jar.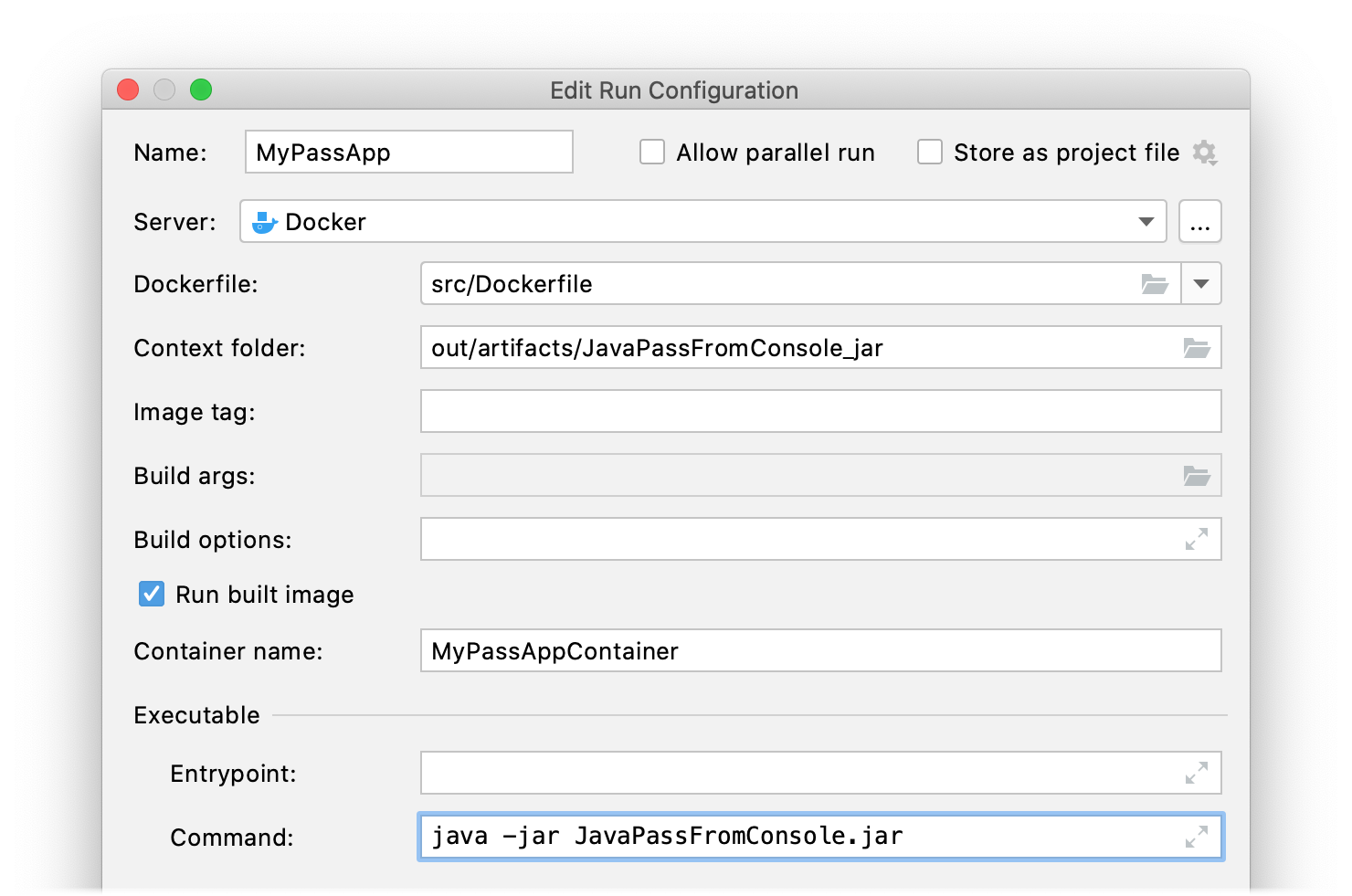
Click Run to check that the application works correctly inside a Docker container. When the container starts, select it in the Services tool window and open the Attached Console tab. You should see the prompt with the words
Enter your login:.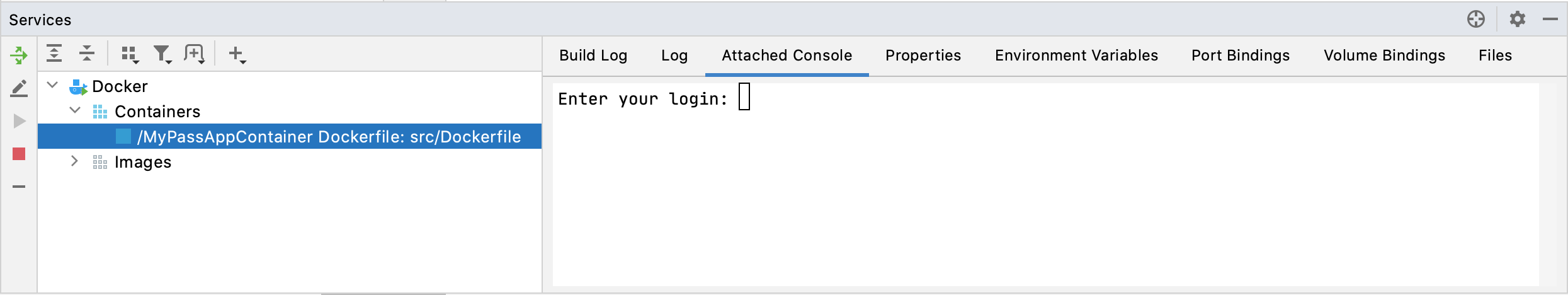
Create a remote debug configuration
To attach the debugger to the running application, you need a remote debug configuration. Before starting, it should first launch the Docker run configuration and start the application in debug mode.
From the main menu, select .
Click
and select Remote.
In the Before launch section, click
and select Launch Docker before debug.
Select the Docker configuration that runs your app and specify the command to use when running your app in the Custom Command field. The remote debug configuration will use this custom command instead of the one defined in the Dockerfile. This command should contain the
-agentliboption to let the debugger attach to the process:java -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=y,address=5005 -jar JavaPassFromConsole.jar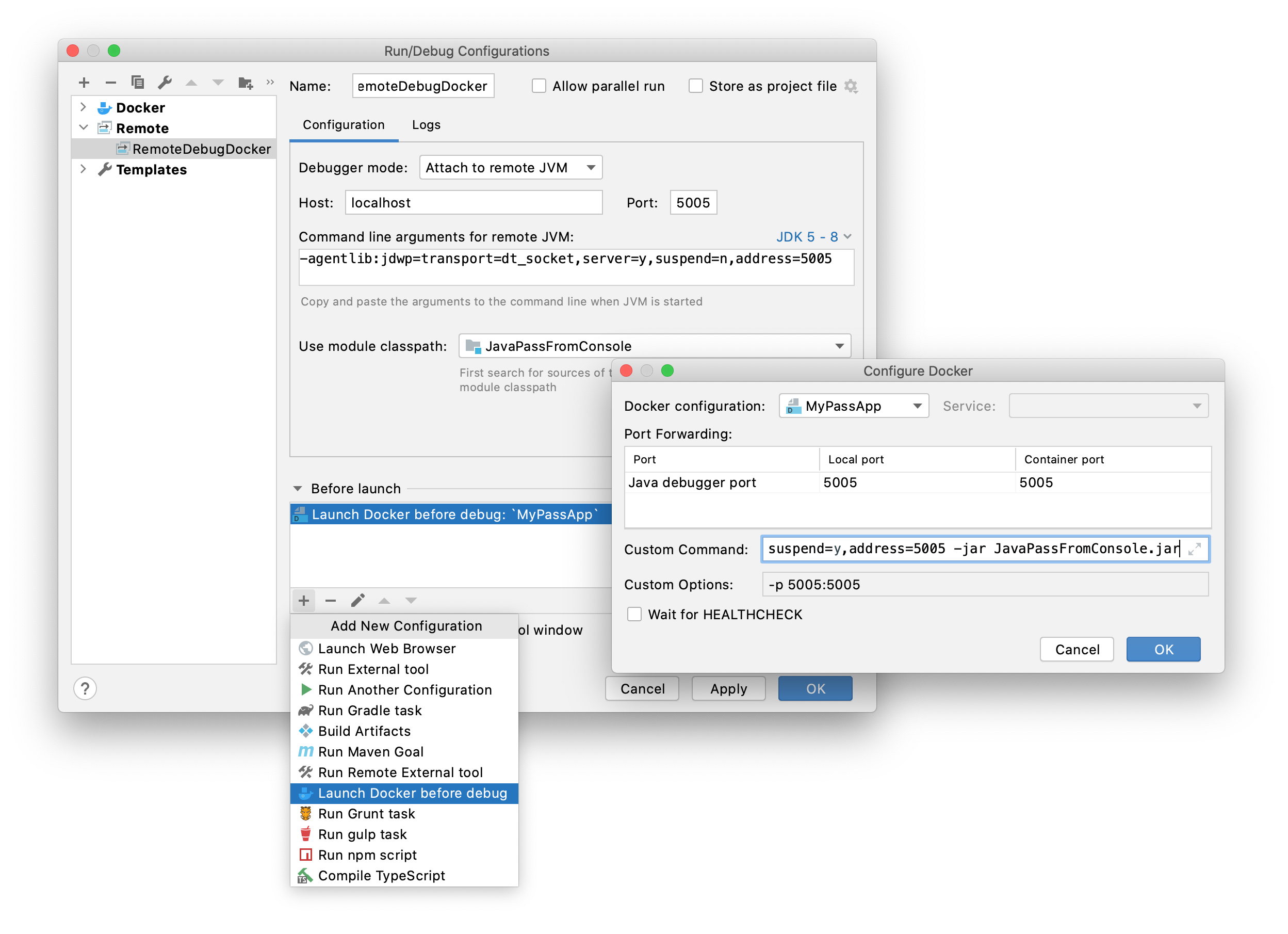
Make sure that the ports in the Configure Docker dialog and in the remote debug configuration match. Click OK.
Click OK in the Run/Debug Configurations dialog.
Set breakpoints and debug your application
By this moment you should have the following:
The source code of your application (the JavaPassFromConsole class)
The built JAR file in out/artifacts/JavaPassFromConsole_jar/JavaPassFromConsole.jar
The Docker run configuration that runs the application in a container based on the Dockerfile
The remote debug configuration that first launches the Docker run configuration and then attaches to the application in the started container
Before starting the debug configuration, you need to set breakpoints in the source code.
Open the JavaPassFromConsole.java file and set breakpoints at key points in the code:
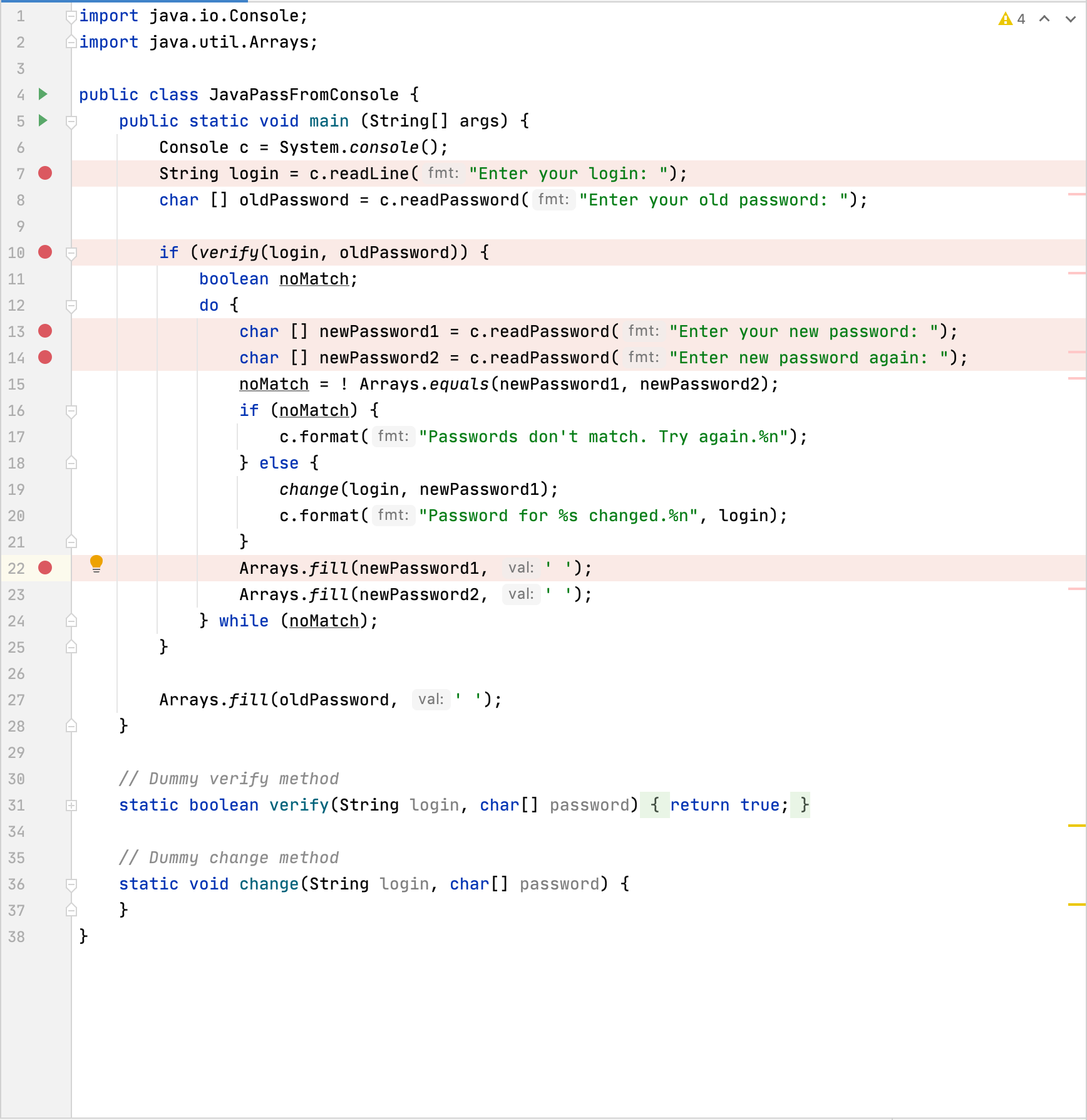
Select the remote debug configuration in the main toolbar and click
.

Alternatively, you can press Alt+Shift+F9 and select the remote debug configuration.
It should now rebuild the image from the Dockerfile and start the container with the application. The debugger should attach to the running application and show you the Debug tool window. When the application hits the first breakpoint (at the Enter your login: prompt), the debugger will suspend the application and you can analyze the current state. To step over to the next statement in you code, click or resume the execution of the application until it hits the next breakpoint with
.
To interact with the application directly, you can switch to the Services tool window, select the container under the Docker node and open the attached console tab.