Shared indexes
One of the possible ways of reducing the indexing time is by using shared indexes. Unlike the regular indexes that are built locally, shared indexes are generated once and are later reused on another computer whenever they are needed.
IntelliJ IDEA can connect to the dedicated resource to download shared indexes for your JDK and build shared indexes for your project's code. Whenever IntelliJ IDEA needs to re-index your application, it will use the available shared project and JDK indexes and will build local indexes for the rest of the project. Normally, this is faster than building local indexes for the entire application from scratch.
Install the Shared Indexes plugin
To be able to use shared indexes, install the Shared Indexes plugin.
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, select Plugins.
Switch to the Marketplace tab, type
Shared Indexes, and click Install.Apply the changes and close the dialog. Restart the IDE if prompted.
Shared JDK indexes
JDK indexes are built by JetBrains and stored on the dedicated CDN resource. When you open a project, IntelliJ IDEA shows a notification prompting you to enable the automatic download.
If you miss the notification, go to . Select the Download automatically option to allow IntelliJ IDEA to download the JDK indexes silently whenever they are needed or select Ask before download if you prefer to confirm every download manually.
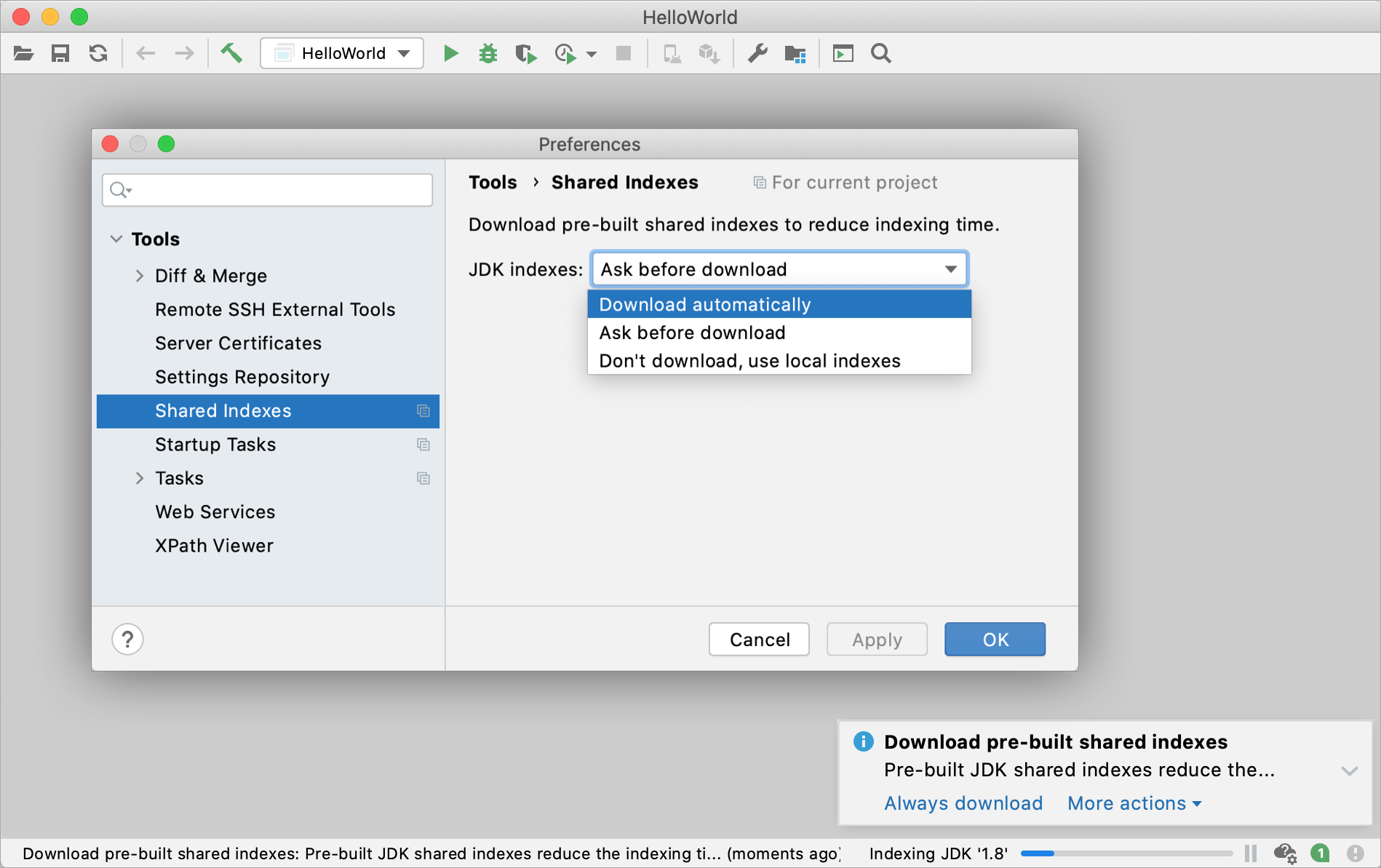
JDK indexes will be downloaded to index/shared_indexes in the IDE system directory. After that, IntelliJ IDEA will be using the suitable indexes whenever they are needed.
Shared project indexes
Shared project indexes are built for all project sources, libraries, and SDKs. You can generate them on one computer and then apply on another computer. This is the main advantage of shared indexes over ordinary indexes.
Using shared indexes is reasonable for large projects, where indexing might take a lot of time, creating inconveniences for the teams involved. For smaller projects, we recommend other ways of reducing the indexing time.
Before you begin
Before you start using shared project indexes, note the following limitations:
Currently, shared project indexes are OS-specific, so it is crucial that you have the same operating system on the source and the target computer.
Use the same IDE version on the source and the target computer as it ensures index compatibility.
Share project indexes from the command line
In order to share project indexes, install a command line tool and prepare the IDE. By doing so, you're making sure that no caches or other internal files interfere with the information that you are going to export from your project.
When the indexes and related metadata are exported, upload them to your file storage. Other members of your team can then configure their IDEs to automatically connect to that storage and download the indexes whenever they are needed.
Prepare a file storage
Sharing indexes from the command line requires that you have a file storage that will keep the exported project indexes.
Make sure that you have a file storage ready, and all members of your team have access to this storage.
Install the upload-local tool
To be able to export and share project indexes, install the upload-local tool:
Download the upload-local/<version>/upload-local-<version>.zip artifact from Bintray. We recommend that you get the latest version of the tool.
Extract the contents of the .zip file.
Among the .zip file's content, there's a bin directory. There, you will find an OS-specific startup script that you will need later for generating metadata.
Prepare the IDE for sharing project indexes
Create the following directories or remove the contents from the existing ones:
- <temp>/ide-system
- <temp>/ide-config
- <temp>/ide-log
Note that in different operating systems, the temp directory has a different location.
Copy the <IDE home>/bin/idea.properties file to the <temp> directory. For more information on idea.properties, refer to Common properties.
Rename idea.properties to ide.properties in <temp>.
Change the following properties in the <temp>/ide.properties file:
- idea.system.path=<temp>/ide-system
- idea.config.path=<temp>/ide-config
- idea.log.path=<temp>/ide-log
If you don't have these properties in the file, add them at the end.
Set a temporary environment variable to specify the custom IDE properties file. To do so, run the following command:
set IDEA_PROPERTIES=<temp>\ide.propertiesexport IDEA_PROPERTIES=<temp>/ide.properties
Export project indexes
Make sure that the <temp>/generate-output directory is empty. If there's no such directory, do not create it as this will be done automatically during the export.
Run the IDE with the following command line to export the project indexes to <temp>/generate-output.
<IDE command-line launcher> dump-shared-index project --output=<temp>/generate-output --tmp=<temp>/temp --project-dir=<path> --project-id=<project-name> --commit=<Git HEAD>You can find the script for running IntelliJ IDEA in the installation directory under bin. To use this script as the command-line launcher, add it to your system
PATHas described in Command-line interface.- Syntax
- idea.bat dump-shared-index project --output=<temp>/generate-output --tmp=<temp>/temp --project-dir=<path> --project-id=<project-name> --commit=<Git HEAD>
- Options
--output=<temp>/generate-outputOutput location for the generated shared indexes in the <temp> folder. --tmp=<temp>/tempThe temp directory used for the internal needs of the IDE. --project-dir=<path>The path to the project for which you want to export indexes. --project-id=<id>The name of the project. --commit=<vcs revision>The VCS revision identifier (for example, Git commit hash) representing the state of the project for which the shared index is being generated.
This is needed to lay out the shared indexes of several VCS revisions in the file storage.
This identifier is optional. If it is not specified, it will be set to
-.
By default, IntelliJ IDEA does not provide a command-line launcher. For information about creating a launcher script for IntelliJ IDEA, see Command-line interface.
- Syntax
- idea dump-shared-index project --output=<temp>/generate-output --tmp=<temp>/temp --project-dir=<path> --project-id=<project-name> --commit=<Git HEAD>
- Options
--output=<temp>/generate-outputOutput location for the generated shared indexes in the <temp> folder. --tmp=<temp>/tempThe temp directory used for the internal needs of the IDE. --project-dir=<path>The path to the project for which you want to export indexes. --project-id=<id>The name of the project. --commit=<vcs revision>The VCS revision identifier (for example, Git commit hash) representing the state of the project for which the shared index is being generated.
This is needed to lay out the shared indexes of several VCS revisions in the file storage.
This identifier is optional. If it is not specified, it will be set to
-.
You can find the script for running IntelliJ IDEA in the installation directory under bin. To use this script as the command-line launcher, add it to your system
PATHas described in Command-line interface.- Syntax
- idea.sh dump-shared-index project --output=<temp>/generate-output --tmp=<temp>/temp --project-dir=<project> --project-id=<project-name> --commit=<Git HEAD>
- Options
--output=<temp>/generate-outputOutput location for the generated shared indexes in the <temp> folder. --tmp=<temp>/tempThe temp directory used for the internal needs of the IDE. --project-dir=<path>The path to the project for which you want to export indexes. --project-id=<id>The name of the project. --commit=<vcs revision>The VCS revision identifier (for example, Git commit hash) representing the state of the project for which the shared index is being generated.
This is needed to lay out the shared indexes of several VCS revisions in the file storage.
This identifier is optional. If it is not specified, it will be set to
-.
The export might take some time. When the process is finished, the following files are placed to <temp>/generate-output:
- shared-index-project-<name>-<hash>.ijx.xz
- shared-index-project-<name>-<hash>.metadata.json
- shared-index-project-<name>-<hash>.sha256
Copy the generated files to a new folder
Create a new directory <temp>/indexes and download there all the contents of your remote file storage.
Copy the generated files (.ijx.xz, .metadata.json, .sha256) from <temp>/generate-output to a subdirectory of <temp>/indexes.
This can be any folder, for example <temp>/indexes/project/<project name>/<VCS hash>/<indexes>.
Generate metadata
Generate auxiliary files used by the IDE to look up for and download shared indexes. To do so, run the upload-local tool with the following command line.
<upload-local tool> --indexes-dir=<temp>/indexes --url=<file storage root UR>- Options
<upload-local tool>The path to the upload-local tool startup script located in bin in the tool directory. --indexes-dir=<dir>The directory containing all the files available in the file storage, as well as the newly generated shared indexes residing in a suitable location beneath this directory.
The tool will generate the missing files and replace existing ones if necessary. After the tool has finished running, all the contents of this directory must be uploaded to the file storage. This will set the new state of the storage.
--url=<file storage root URL>The base URL of the file storage root directory. The upload-local tool will substitute the download URL in all the corresponding .json index lists. - Example
- /Users/User/Desktop/upload-local-1.0.3/bin/upload-local --indexes-dir=/var/folders/dr/xxx_x00x0x0_x0xx000xx000000xx/T/indexes --url=https://my-file-storage.com/intellij-indexes
Upload the index files to your file storage
Upload all the files from <temp>/indexes to the file storage as is.
If there are already uploaded index files in the storage, update them.
Download indexes from the file storage
Once the project indexes are uploaded to the file storage, they can be downloaded and applied on another computer.
In the project directory, create a new file intellij.yaml and add the following code:
sharedIndex: project: - url: <feed URL>Replace <feed URL> with the URL of your file storage in the following format: <file storage root URL>/project/<project-id>.
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, select .
From the Project indexes list, select how you want to download shared indexes from the storage.
Select Download automatically to allow IntelliJ IDEA to download the JDK indexes silently whenever they are needed or select Ask before download if you prefer to confirm every download manually.
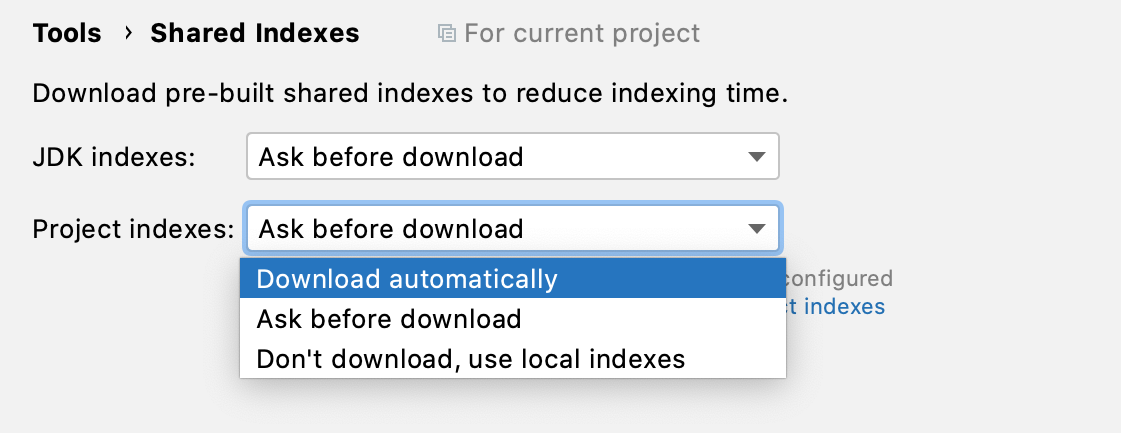
Apply the changes and close the dialog.
Project indexes will be downloaded to index/shared_indexes in the IDE system directory.
Remove the downloaded shared indexes
If you don't need project indexes anymore (for example, if the project is no longer in development), you can remove them all together. In this case, the IDE will remove the regular indexes and all the downloaded shared indexes for the project and the JDK.
From the main menu, select .
In the dialog that opens, select Invalidate and Restart.