Testing
Testing ensures that behavior of your code is correct and expected. Good-written tests allow you to develop with confidence that your code will work and will not break your existing code.
IntelliJ IDEA includes several packages that you can use to run your tests. Also, you can apply a specific testing scope for the selected package.
Packages for testing
For testing purposes, IntelliJ IDEA includes the following packages:
- gotest
Use for running standard unit tests. For more information about
go test, see Package testing.- gocheck
Use to have extended functionality of
go checkand running more complex tests. For more information aboutgo check, see go check.- gobench
Use for running performance tests. For more information about
gobench, see Package testing: Benchmarks.
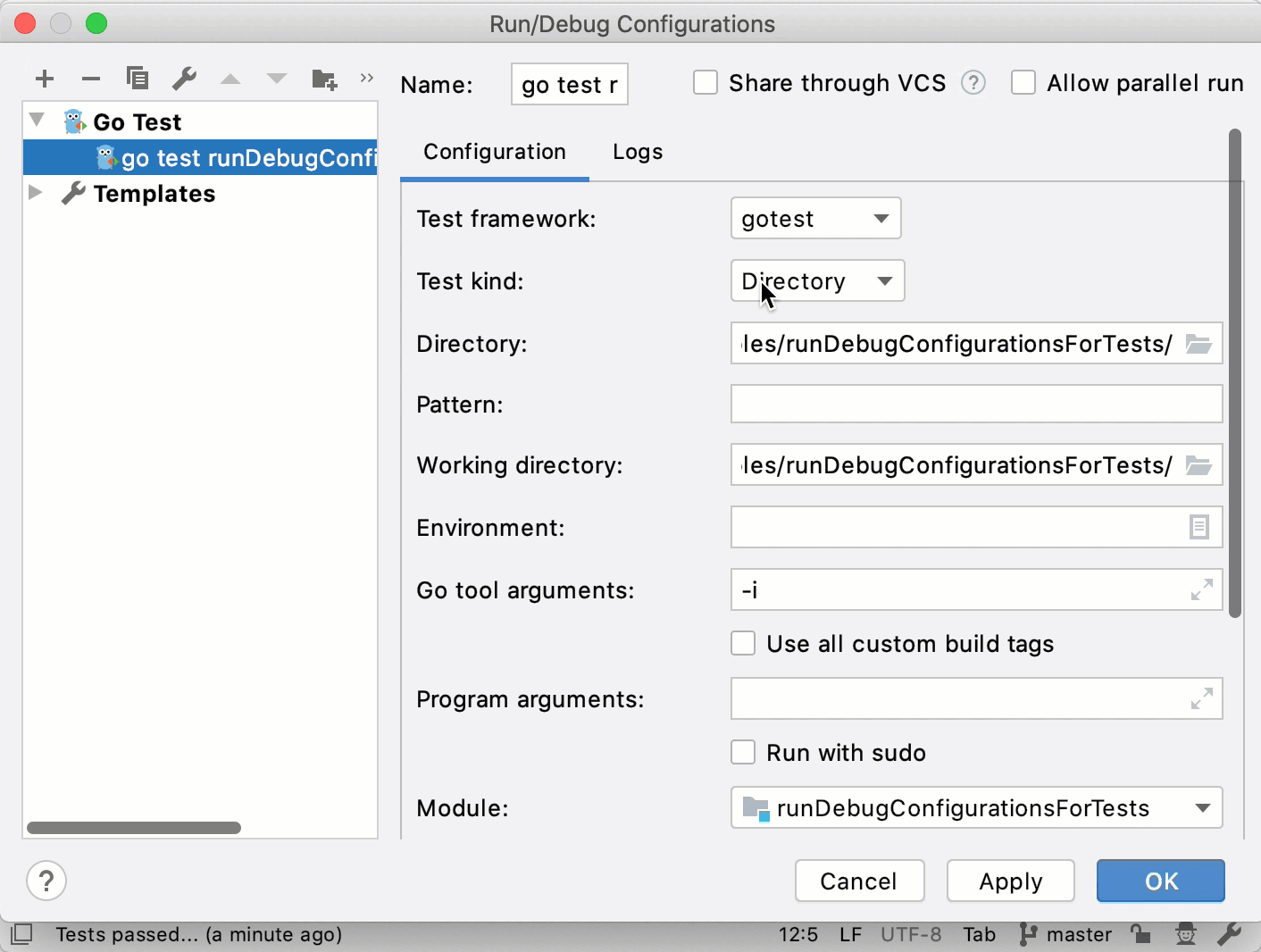
Run tests in a directory
Navigate to .
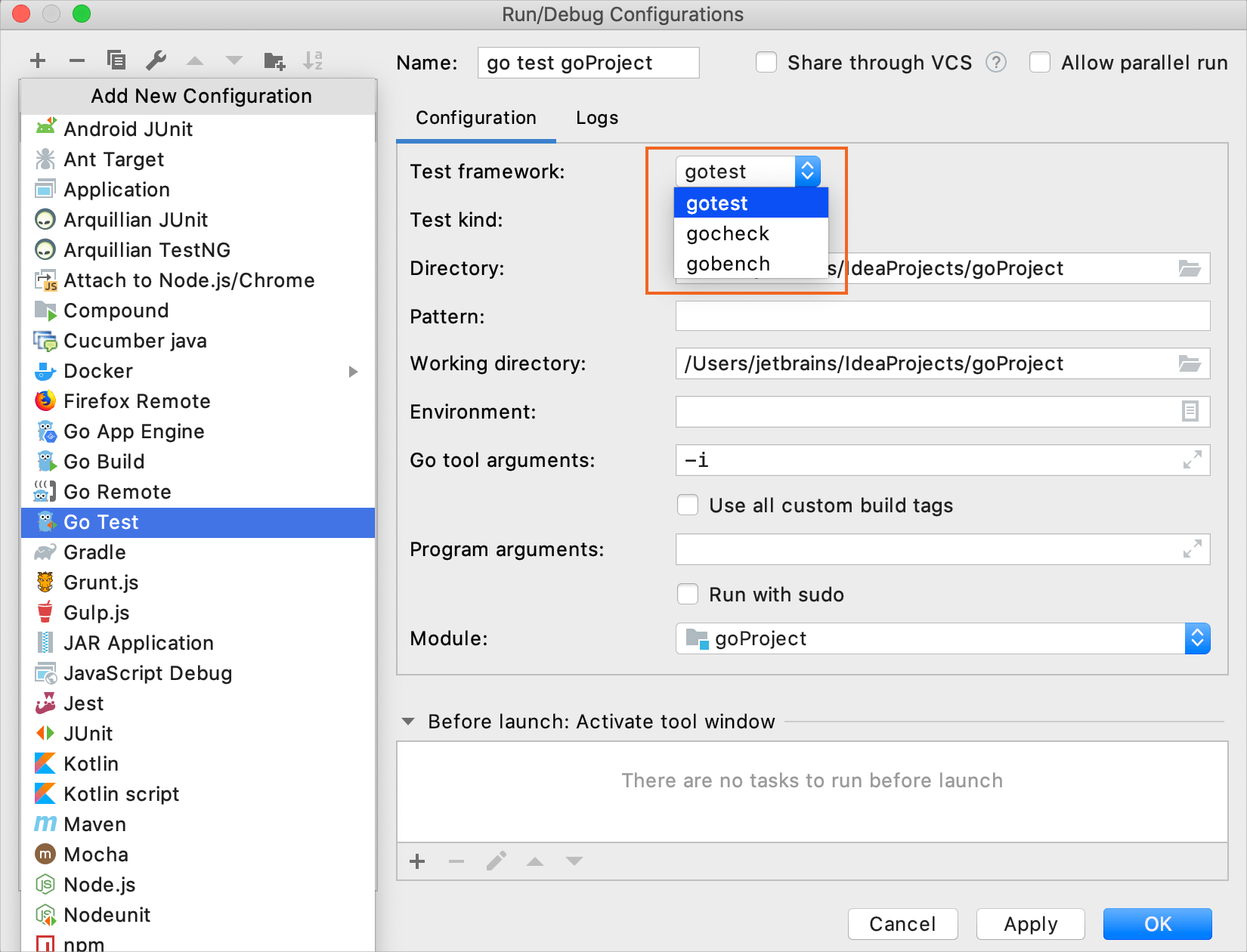
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, click Add New Configuration Alt+Insert and select %run_debug_var%.
In the Directory field, specify a path to a directory that includes an application file and a test file (for example, applicationFolder/main.go and applicationFolder/main_test.go ).
(Optional) Also, you can specify the following settings:
Pattern: arguments that you define for running subtests and sub-benchmarks. For more information about subtests and sub-benchmarks, see Subtests and Sub-benchmarks at golang.org. Consider the following test function:
func MyTestFunc(t *testing.T) { ... t.Run("ID=1", func(t *testing.T) { ... }) t.Run("ID=2", func(t *testing.T) { ... }) t.Run("UID=1", func(t *testing.T) { ... }) ... }For the
MyTestFuncfunction, you can use the followinggo testarguments:Code Description go test -runRun all tests. go test -run TestRun tests that match the Testpattern (for example,MyTestFunc).go test -run MyTestFunc/ID=Run subtests that belong to the top-level MyTestFuncfunction and match theID=pattern.go test -run /UID=1Run subtests matching UID=1from all top-level test functions.For the Pattern field, you list only arguments (for example,
Test,MyTestFunc/ID=,/UID=1).Working directory: a directory that is used for the built application. If you have any code that creates relative files or directories, they will be relative to this directory.
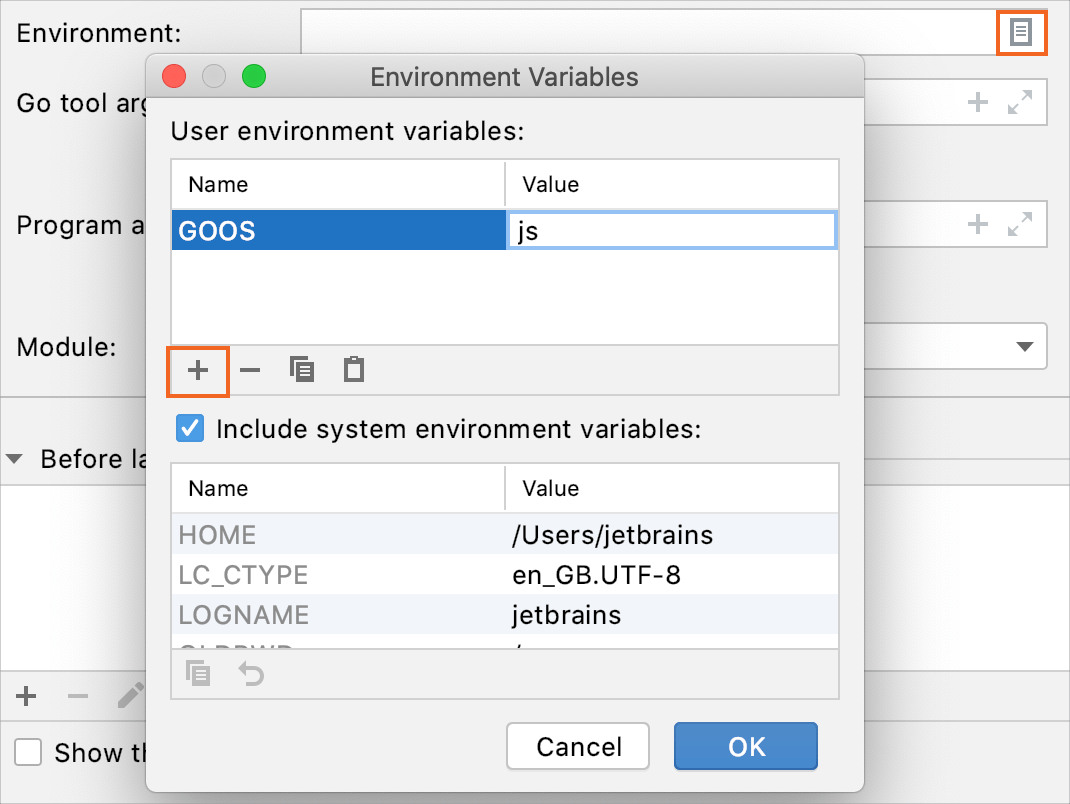
Environment: environment variables that you need to run the test.
To edit environment variables, click the Browse button at the end of the field. In the Environment Variables dialog, click the Add button and add the environment variables that you need.
Go tool arguments: arguments for the go tool (for example,
-tags).Use all custom build tags: all tags that are applied during the build. Tags are listed in settings Ctrl+Alt+S under .
Program arguments: arguments for the built application.
Run with sudo: grant sudo privileges for the application.
Before launch: Activate tool window: add tasks that you want to launch before the launch of the selected run/debug configuration. To add a task click the Add button Alt+Insert and select the tool that you want to add.
Click Apply.
Run tests for a package
To enable package tests, open setting by pressing Ctrl+Alt+S, navigate to , and select the Enable Go Modules integration checkbox.
Navigate to .
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, click Add New Configuration Alt+Insert and select %run_debug_var%.
From the Test kind list, select Package.
In the Files field, type a name of a testing file (for example, main_test.go ). You can use Smart Completion Ctrl+Shift+Space in this field.
(Optional) Also, you can specify the following settings:
Pattern: arguments that you define for running subtests and sub-benchmarks. For more information about subtests and sub-benchmarks, see Subtests and Sub-benchmarks at golang.org. Consider the following test function:
func MyTestFunc(t *testing.T) { ... t.Run("ID=1", func(t *testing.T) { ... }) t.Run("ID=2", func(t *testing.T) { ... }) t.Run("UID=1", func(t *testing.T) { ... }) ... }For the
MyTestFuncfunction, you can use the followinggo testarguments:Code Description go test -run ''Run all tests. go test -run TestRun tests that match the Testpattern (for example,MyTestFunc).go test -run MyTestFunc/ID=Run subtests that belong to the top-level MyTestFuncfunction and match theID=pattern.go test -run /UID=1Run subtests matching UID=1from all top-level test functions.For the Pattern field, you list only arguments (for example,
Test,MyTestFunc/ID=,/UID=1).Output directory: directory that stores your test results if any.
Working directory: directory that is used for the built application. If you have any code that creates relative files or directories, they will be relative to this directory.
Environment: environment variables that you need to run the test.
To edit environment variables, click the Browse button at the end of the field. In the Environment Variables dialog, click the Add button and add the environment variables that you need.

Go tool arguments: arguments for the go tool (for example,
-tags).Use all custom build tags: all tags that are applied during the build. Tags are listed in settings Ctrl+Alt+S under .
Program arguments: arguments for the built application.
Run with sudo: grant sudo privileges for the application.
Before launch: Activate tool window: add tasks that you want to launch before the launch of the selected run/debug configuration. To add a task, click the Add button Alt+Insert and select the tool that you want to add.
Click Apply.
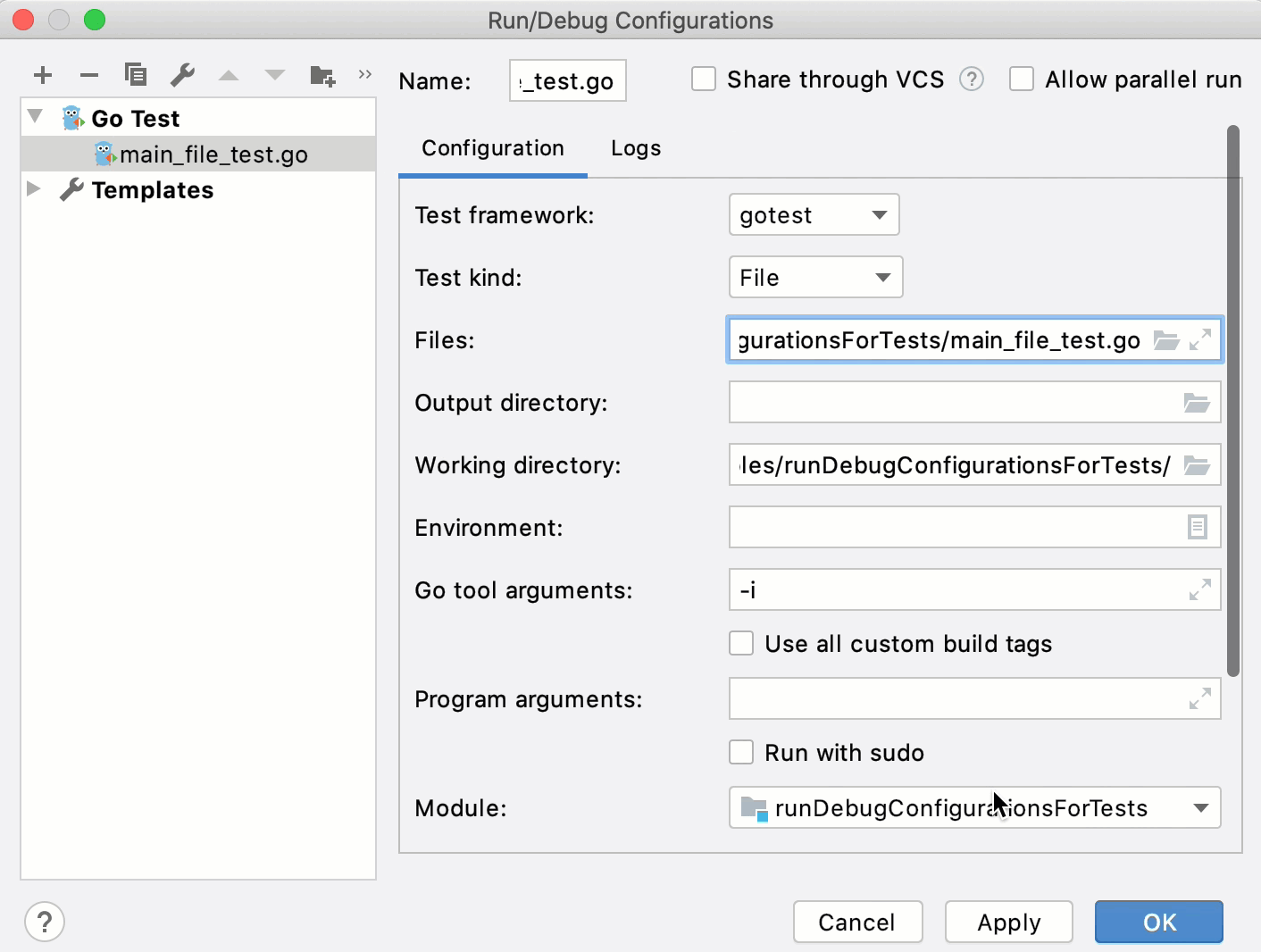
Run tests for a file
Navigate to .
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, click Add New Configuration Alt+Insert and select %run_debug_var%.
From the Test kind list, select File.
In the Files field, type a name of a testing file (for example, /Users/jetbrains/runDebugConfigurationsForTests/main_file_test.go ).
Ensure that the Files field does not include other paths. Otherwise, you will get the
Named files must all be in one directoryerror.(Optional) Also, you can specify the following settings:
Output directory: directory that stores your test results if any.
Working directory: directory that is used for the built application. If you have any code that creates relative files or directories, they will be relative to this directory.
Environment: environment variables that you need to run the test.
To edit environment variables, click the Browse button at the end of the field. In the Environment Variables dialog, click the Add button and add the environment variables that you need.

Go tool arguments: arguments for the go tool (for example,
-tags).Use all custom build tags: all tags that are applied during the build. Tags are listed in settings Ctrl+Alt+S under .
Program arguments: arguments for the built application.
Run with sudo: grant sudo privileges for the application.
Before launch: Activate tool window: add tasks that you want to launch before the launch of the selected run/debug configuration. To add a task, click the Add button Alt+Insert and select the tool that you want to add.
Click Apply.