Spring Boot run configuration
The Spring Boot run configuration defines how to run your Spring Boot application in IntelliJ IDEA. The IDE creates a Spring Boot run configuration when you run the application from the main class file. For more information, see Run a Spring Boot application.
Create the Spring Boot run configuration
From the main menu, select .
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, click
and select Spring Boot.

Name | Specify a name for the run configuration to quickly identify it among others when editing or running. |
Run on | Select the target environment where you want to run the configuration. Besides running it locally, you can select to run your application on a remote machine via SSH or in a Docker container. For more information, see Run targets. |
Store as project file | Save the run configuration settings to a file that you can share with other team members. The default location is .idea/runConfigurations. However, if you do not want to share the .idea directory, you can save the configuration to any other directory within the project. By default, this option is disabled, and IntelliJ IDEA stores run configuration settings in .idea/workspace.xml. |
Required options
The following options are mandatory to run your Spring Boot application:
JRE | Specify the Java runtime environment to use. In most cases, you should use the runtime that comes with the JDK configured for your project. IntelliJ IDEA tries to detect and list the runtime environments that are available on your computer, including the one that is bundled with the IDE. You can also click Select alternative JRE… to manually specify the path to a runtime that the IDE failed to detect. For more information, see SDKs. |
Main class | Specify the fully qualified named of the class that will be passed to the Java runtime for execution. This class must contain the |
Modify options
Click Modify options to select additional options for running the configuration.
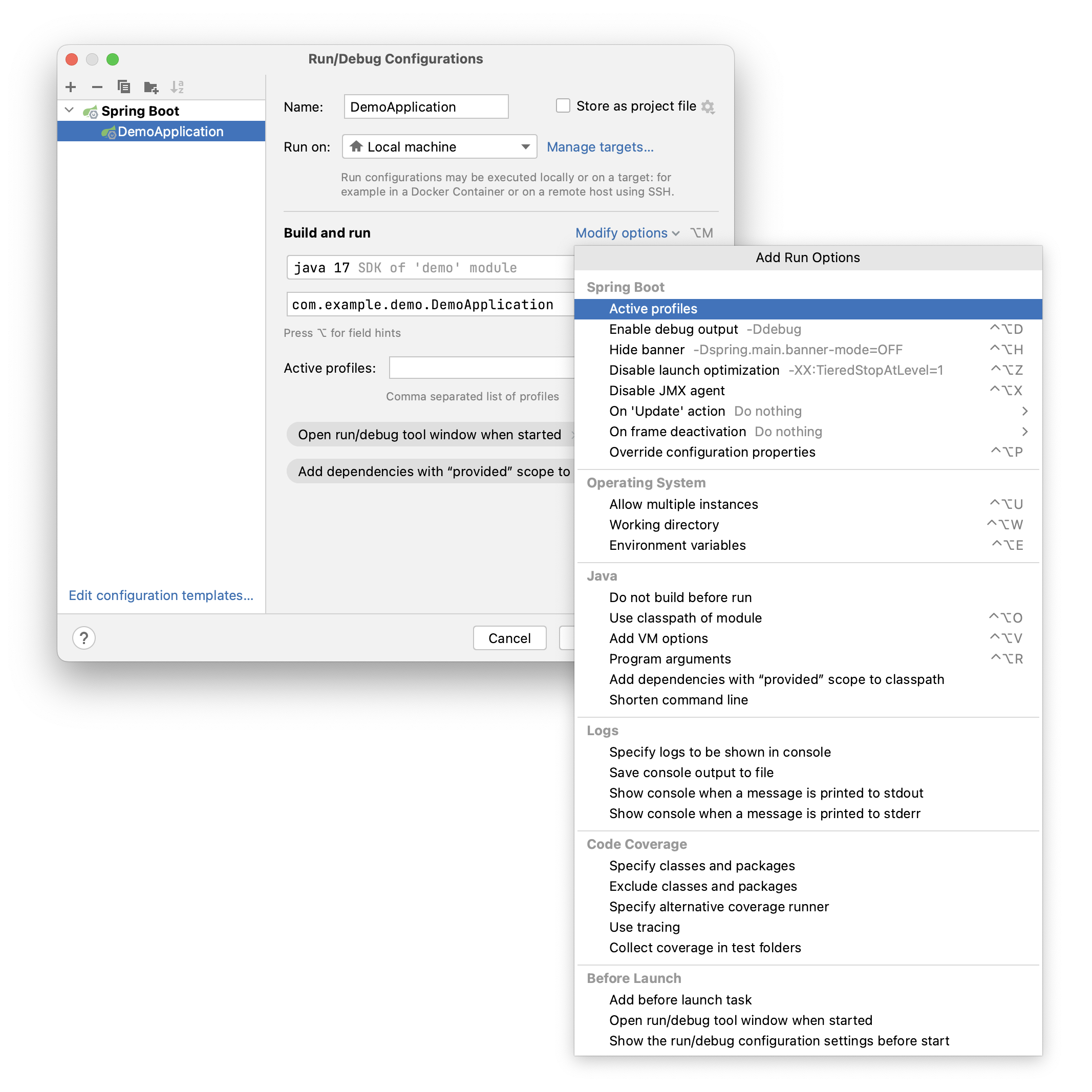
Spring Boot
The following options are specific to running Spring Boot applications:
Active profiles | Specify which Spring profiles should be active. This passes For more information, see Spring Boot: Profiles. |
Enable debug output | Enable logging of the debug output. This passes For more information, see Spring Boot: Logging. |
Hide banner | Disable the start-up banner entirely. This passes For more information, see Spring Boot: Customizing the banner. |
Disable launch optimization | Do not speed up the start-up time of your application. By default, this optimization is enabled by passing the following JVM options on the command line: |
Disable JMX endpoints | Disable the JMX agent that shows the application endpoints data in the Actuator tab of the Run tool window. By default, the JMX agent is enabled by passing the following JVM options on the command line:
This slows down the application startup. If you disable the JMX agent, the above options will not be added to the command line. For more information, see Spring: JMX |
On 'Update' action | Specify what to do when you modify the code and want to update the running application:
|
On frame deactivation: | Specify what to do when you switch from IntelliJ IDEA to another application (for example, a web browser):
|
Override configuration properties | Override any configuration property by passing it as a JVM option. For example, if you override the value of the |
Operating System
The following options are related to the operating system:
Allow multiple instances | Allow multiple instances of this run configuration to execute at the same time. By default, this option is disabled, which means that when you run the configuration, other active sessions of the configuration will terminate. |
Working directory | Specify the directory that will be used for all relative input and output paths. By default, IntelliJ IDEA uses the project root as the working directory. |
Environment variables | Specify the names and values of environment variables that are necessary when running this configuration. |
Java
The following options are specific to the Java compiler and runtime for your Spring application:
Do not build before run | Do not compile the code before running it. This may be useful if you are only changing the resources, not the source code of your application. |
Use classpath of module | Select the IntelliJ IDEA project module whose classpath to use when running the application. For more information, see Module dependencies. |
Add VM options | Specify additional JVM options for the Separate options with spaces, enclose the values in double quotes if the value has spaces, escape quotes with backslashes, and pass environment variables if necessary. |
Program arguments | Pass command-line arguments to your application. |
Add dependencies with “provided” scope to classpath | Add the dependencies with the This option is enabled by default in Spring Boot run configurations. |
Shorten command line | Select a method that will be used to shorten the command line if it exceeds the limitation of your OS.
|
Logs
The following options are related to logging the execution of your Spring Boot application. For more information, see View logs.
Specify logs to be shown in console | Specify which log files to display while running the application. Click
For logs in the table, you can configure the following options:
|
Save console output to file | Specify a file to save the console output of your application. |
Show console when a message is printed to stdout | Activate the console when the application writes to the standard output stream. |
Show console when a message is printed to stderr | Activate the console when the application writes to the standard error stream. |
Code Coverage
The following options are related to collecting code coverage statistics for your Spring Boot application. For more information, see Code coverage.
Specify classes and packages | Specify classes and packages to include in coverage data. |
Exclude classes and packages | Specify classes and packages to exclude from coverage data. |
Specify alternative coverage runner | Select a code coverage runner. You can choose between the default IntelliJ IDEA coverage engine and JaCoCo. |
Use tracing | Use the tracing mode to collect accurate branch coverage with the ability to track tests, view coverage statistics, and get additional information on each covered line. By default, IntelliJ IDEA uses the sampling mode, which is faster but less accurate. |
Collect coverage in test folders | Collect code coverage statistics for tests. |
Before Launch
The following options configure what else to do when launching this run configuration.
Add before launch task | Specify other tasks to execute before launching this run configuration. For example, by default IntelliJ IDEA compiles the code before running the application. You can select to launch another run configuration, open some URL in a web browser, run an external tool, and so on. IntelliJ IDEA will execute the tasks in the order that you specify them. |
Open run/debug tool window when started | Open the corresponding tool window when you start this run configuration:
|
Show the run/debug configuration settings before start | Show the run configuration setting before starting it. |