Analyze duplicates
IntelliJ IDEA helps you find repetitive blocks of code in a certain set of files by means of the Duplicated code fragment inspection. If you create a duplicate by writing or pasting code, IntelliJ IDEA highlights it right away and suggests quick-fixes.
The inspection works out of the box and has a number of settings that you can change to adjust its behavior.
To see all duplicates in the selected set of files at once, run the inspection by name.
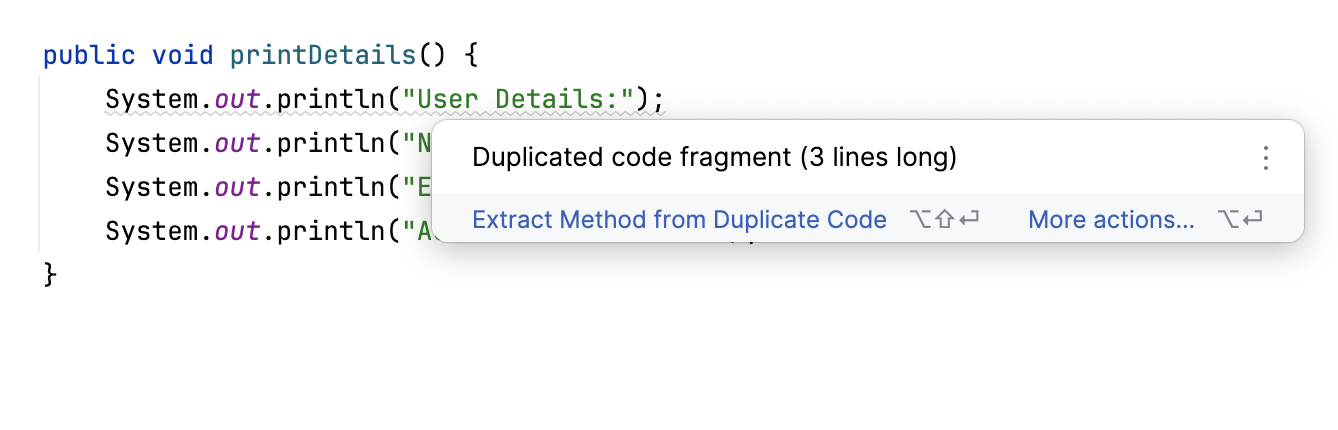
Configure the inspection
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Make sure that the necessary inspection profile is selected in the Profile list.
In the search field of the Inspections dialog, type
duplicated code fragmentto locate the inspection in the list.Once you click the inspection, its settings appear on the right.
Severity: select a severity level from the list or create a new one.
Scope: select the scope of files that the inspection will run on (the code to be analyzed).
Show duplicates from: select the set of files from which duplicates are going to be shown.
To minimize false positives, restrict the analysis to detect duplicates only within the same module or file.
Skip duplicates simpler than: configure the size of the code fragment that is compared against the rest of the code in the selected set of files in units.
The default value is a compromise between accuracy and the number of found duplicates. Increase the value to get more accurate results. Decrease the value to find more duplicates.
The exact value of units can be calculated as follows:
units = 2 * number of statements + number of expressions.Select the languages for which this inspection is going to work.
Apply the changes and close the dialog.
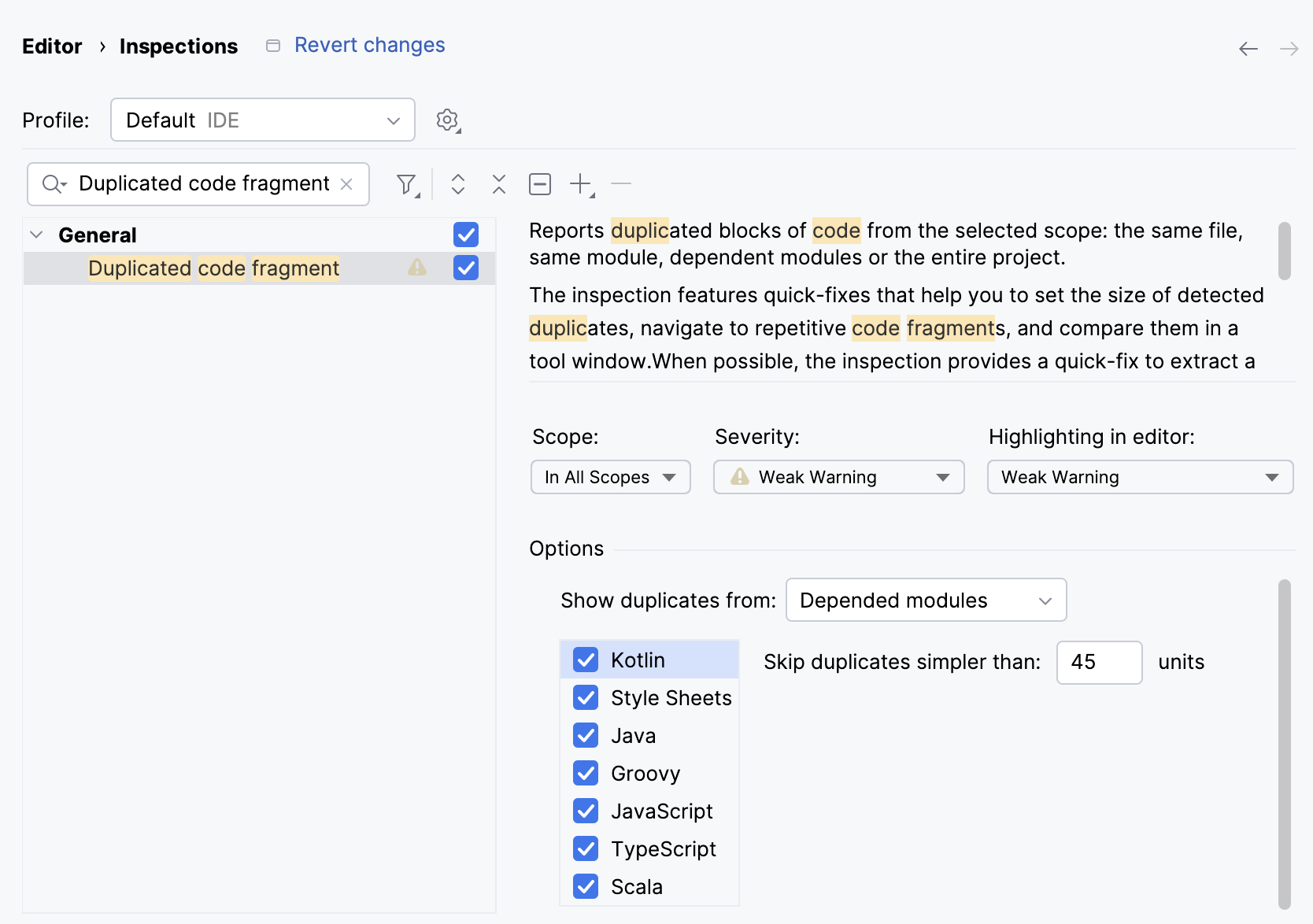
Ignore names and values while searching for duplicates
For each file type, you can define whether identical entities that only differ by names or values should be treated as duplicates.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Select file types to which the analysis should apply and select the checkboxes next to the constructs that you want to anonymize.
Apply the changes and close the dialog.
The dialog also allows you to completely exclude a language from both the duplicate analysis and the project analysis. If you disable a language on this page, this language will be hidden in the inspection settings.
Suppress the inspection
When you suppress the inspection, the code analysis engine doesn't highlight the problem found by this inspection in the specific piece of code (class, method, field, or statement).
Place the caret at the code element for which you want to suppress the inspection and press Alt+Enter.
Click the arrow
next to the Show all duplicates action and select the necessary suppress action.
For more information, refer to Suppress inspections.
Disable the inspection
When you disable the inspection, you turn it off. It means that the code analysis engine stops searching project files for the problem that this inspection is designed to detect.
Place the caret at the code element for which you want to disable the inspection and press Alt+Enter.
Click the arrow
next to the Show all duplicates action and select Disable inspection.
To re-enable the inspection, go to and select the checkbox next to Duplicated code fragment.
For more information, refer to Disable inspections.
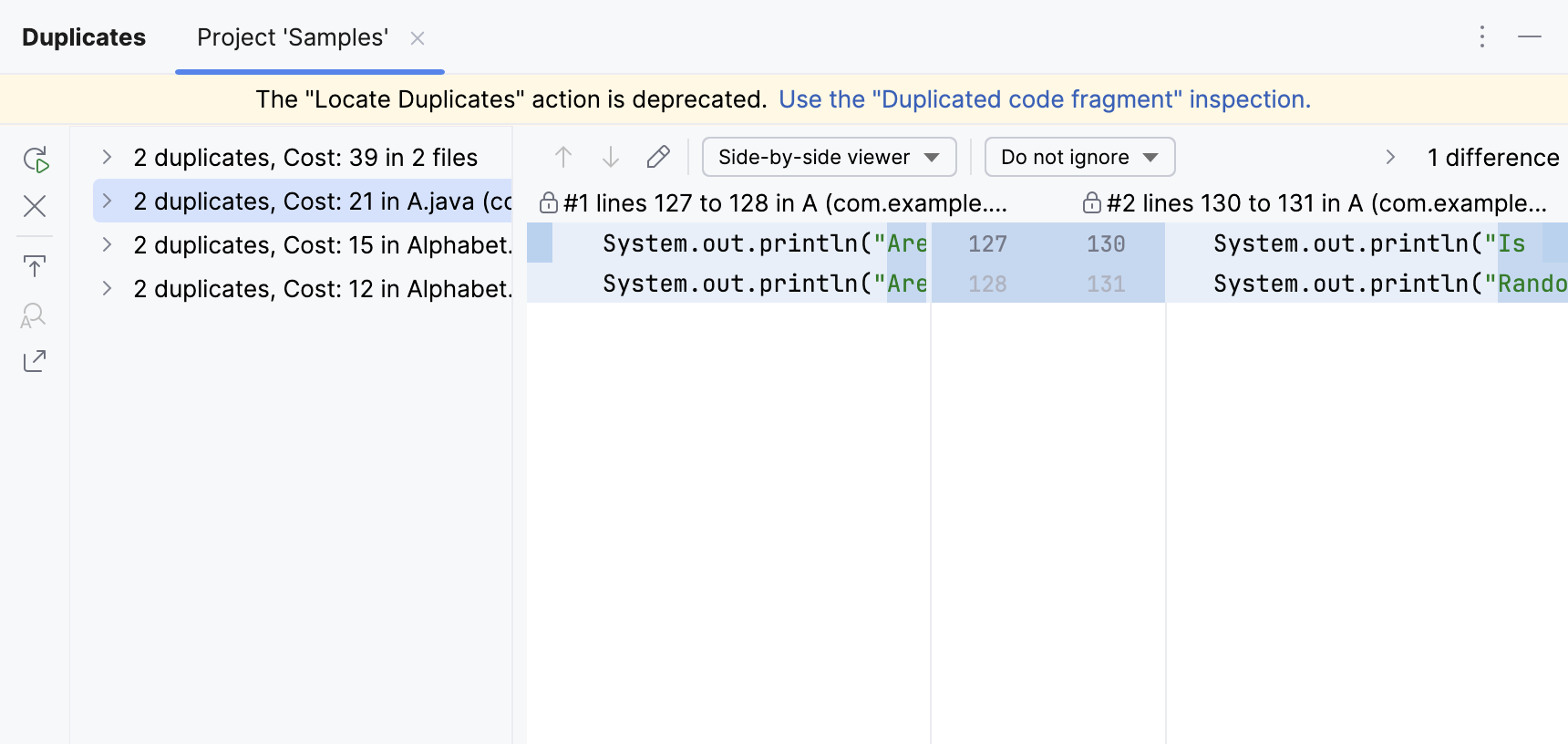
Locate duplicates manually (deprecated)
In the main menu, go to .
In the Specify Code Duplication Analysis Scope dialog, choose the analysis scope: the whole project, the current file, uncommitted files (for projects under version control), or a custom scope. You can also choose to include test sources in the analysis.
In the Code Duplication Analysis Settings dialog, select the languages that you want to analyze.
For each language, check the options to define the analysis preferences. For example, you can opt to request identical match for code fragments to be considered duplicates, or specify a certain limit below which the code constructs are not considered duplicates (for example, to avoid reporting each
ifconstruct in the source code).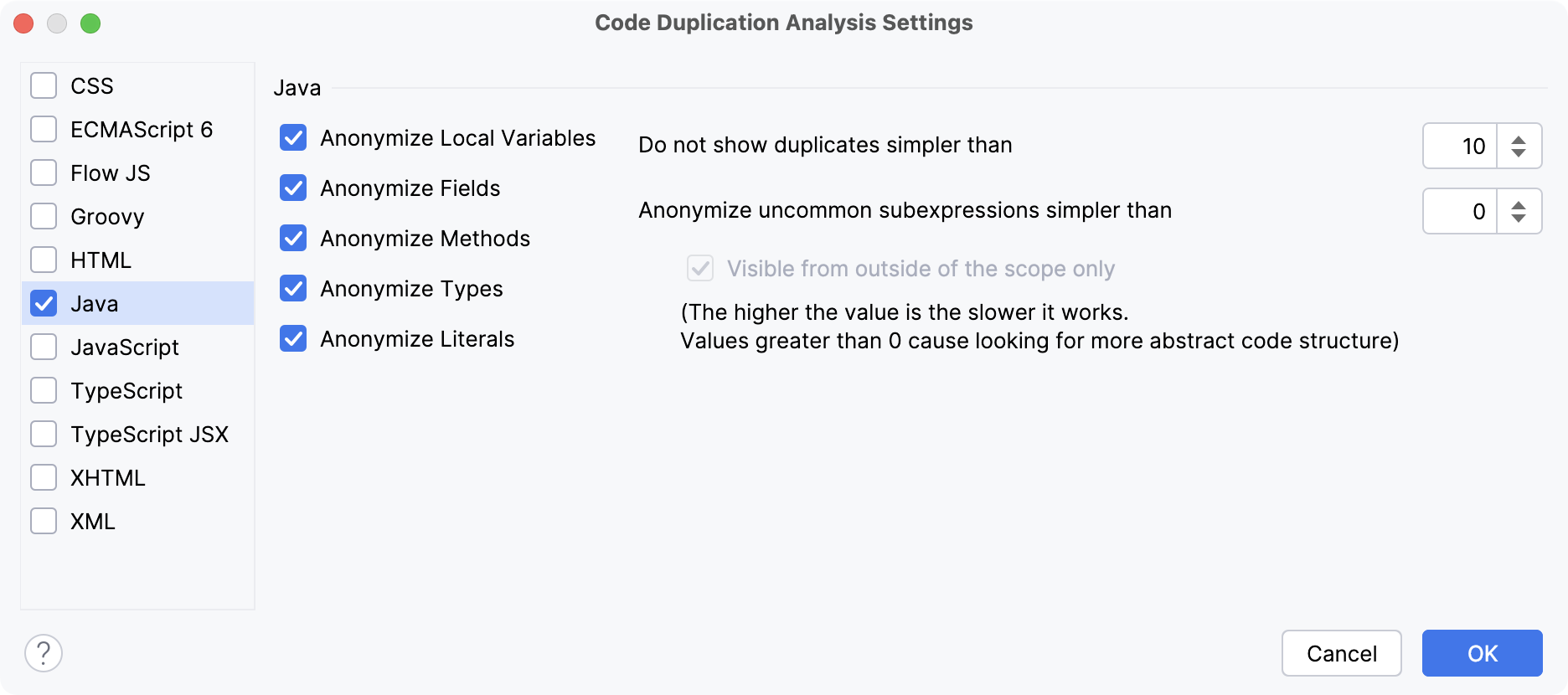
In the Duplicates tool window, explore the analysis results.
Specify Code Duplication Analysis Scope
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Whole project | Inspect the whole project. |
Module <name> | Inspect the module that is currently selected in the Project tool window Alt+1. |
File <name> | Inspect the file that is currently selected in the Project tool window or opened in the editor. |
Selected files | Inspect the files that are currently selected in the Project tool window. |
Uncommitted files | This scope is only available for the projects under version control. Inspect only the files that have not been committed to the version control system. |
Directory | Inspect the directory that is currently selected in the Project tool window. |
Custom scope | Inspect a custom scope of files. Select a pre-defined scope from the list, or click |
Include test sources | Inspect the test sources included in the analysis scope. |
Inspect injected code | Inspect pieces of code in other languages embedded in your code. |
Code Duplication Analysis Settings
Use this dialog to define the sensitivity of search and set the limitation that will help you avoid reporting every similar code construct. Your preferences are specified in a language-specific context.
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Java | To anonymize an element means to define whether identical entities that only differ by names or values should be treated as duplicates. Select elements to anonymize:
Configure duplicate parameters:
|
ActionScript ECMAScript 6 Flow JS Groovy JavaScript TypeScript TypeScript JSX | To anonymize an element means to define whether identical entities that only differ by names or values should be treated as duplicates. Select elements to anonymize:
Configure duplicate parameters:
|
CSS |
|
XHTML XML HTML |
|