Run/Debug Configuration: Gradle
You can run Gradle tasks using run configuration. The default options listed in such configuration are enough to run your task. If you want, you can also create an advanced configuration using additional options or adding more tasks and arguments.
Create a run/debug Gradle configuration
From the main menu, select Add Configuration. Alternatively, right-click any task in the Gradle tool window and select Modify Run Configuration.
Specify a name of your configuration in the Name field to quickly identify it when editing or running the configuration, for example, from the Run popup Alt+Shift+F10 or the Gradle tool window.
Specify where you want your configuration to run on. The default Local Machine option will run your configuration locally on your computer.
You can change the location of your run execution. For example, use SSH or Docker to run your target.
You can also run your target on WSL. If you need to configure a new target or change the existing configuration, click Manage targets and in the Run Targets dialog, add your changes. For more information, refer to Run targets.
If you need, specify Store as project file that saves the file with the run configuration settings, so you can share it with other team members. The default location is .idea/runConfigurations. However, if you do not want to share the .idea directory, you can save the configuration to any other directory within the project.
To change the location, select this option and click
and in the dialog that opens, add the new location.
If you don't need to specify anything in the Run field, the default tasks such as
helpand tasks specified in the Before build section. section will be executed. Alternatively, if you are creating a run configuration from the Gradle tool window, the task you have selected will be displayed in this field. However, you can specify additional external tasks and arguments for your run configuration. Use spaces to separate one task from another. If you want to see the available list of Gradle tasks and arguments, clickin the field.
Specify the location of your Gradle project.
You can either enter it manually or click
and point to the desired location in the dialog that opens. However, if you are creating a run configuration from the Gradle tool window, IntelliJ IDEA will display the name of your project automatically.
You can also click Gradle registered projects
icon to select an available Gradle module from the list of registered Gradle modules in your existing IntelliJ IDEA project.
If you need, you can specify a path to the build script file instead of the project path. This might be helpful if you have a custom build script to which you want to refer.
If you need, specify the environment variables that you want to use in you project.
The following default options are enabled, but you can click Modify options and use the Add Run Options list to add the new options or remove some default ones:
Open run/debug tool window when started - automatically opens the Run/Debug tool window when the configuration is executed and several debugger options
Debug Gradle scripts - enables breakpoints in the Gradle scripts.
This option is disabled when you execute your test using left gutter in the editor or the context menu. This is done to speed up your debugging process.
Add Run Options
The Add Run Options list lets you add more run options to the Run/Debug Configurations dialog or remove some of the default ones from it. The list is divided into various sections, so you can easily navigate through the available options.
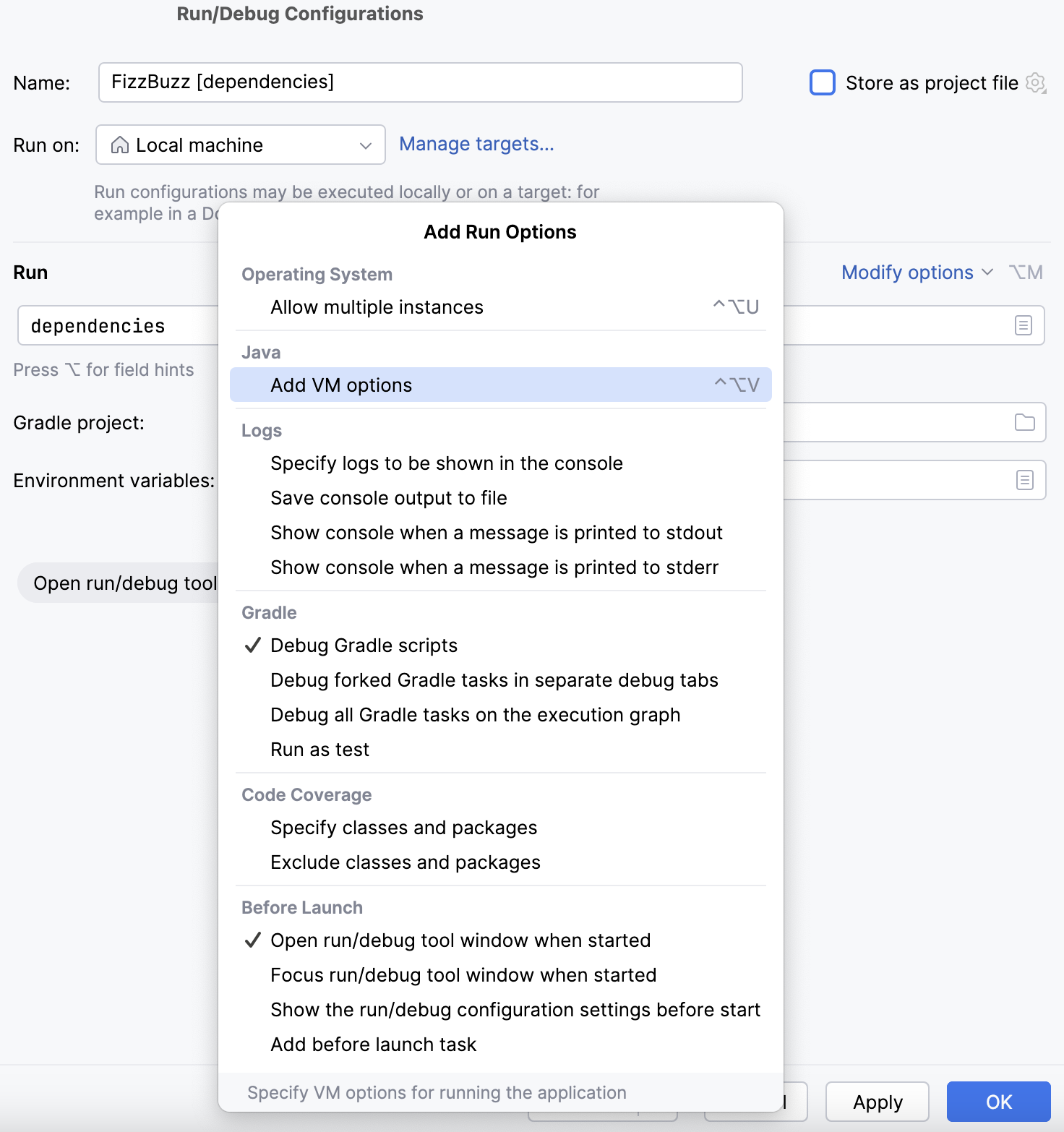
Operating System
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Allow multiple instances | Select this option to allow running multiple instances of this run configuration in parallel. By default, it is disabled, and when you start this configuration while another instance is still running, IntelliJ IDEA suggests stopping the running instance and starting another one. This is helpful when a run configuration consumes a lot of resources and there is no good reason to run multiple instances. |
Java
Item | Description |
|---|---|
VM options | Specify the options to be passed to the Java virtual machine when launching the application, for example, When specifying JVM options, follow these rules:
-Xmx1024m -Dspaces="some arg" -Dmy.prop=\"quoted_value\" -Dfoo=${MY_ENV_VAR}
Use code completion in this field: start typing the name of a flag, and the IDE suggests a list of available command line options. This works for The |
Logs
The following options are related to logging the execution of this configuration. For more information, refer to Logs.
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Specify logs to be shown in the console | Specify which log files to display while running the application. Click
For logs in the table, you can configure the following options:
|
Save console output to file | Save the console output to the specified location. Type the path manually or click the browse button and point to the desired location in the dialog that opens. |
Show console when a message is printed to stdout | Activate the console when the application writes to the standard output stream. |
Show console when a message is printed to stderr | Activate the console when the application writes to the standard error stream. |
Code Coverage
The following options are related to code coverage. For more information, refer to Code coverage.
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Specify classes and packages | In this table, specify classes and packages to be measured. Click |
Exclude classes and packages | Specify classes and packages that you want to exclude from coverage. Click |
Before Launch
In this area, you can specify tasks to be performed before starting the selected run/debug configuration. The tasks are performed in the order they appear in the list.
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Add before launch task | Enable this option to add one of the following available tasks:
|
Open run/debug tool window when started | Depending on the type of configuration, open the Run, Debug, or Services tool window when you start this run configuration. If this option is disabled, you can open the tool window manually:
|
Focus run/debug tool window when started | Focus on the run configuration tool window when the tests are running. |
Show the run/debug configuration settings before start | Show the run configuration settings before actually starting it. |
Gradle
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Debug all tasks on the execution graph | When you select this option, every task in the execution graph will be debugged. For example, all the dependent tasks of the task you are trying to debug. |
Debug forked Gradle tasks in separate debug tabs | Select this option to run a debugging process in a separate tab in the Debug tool window. |
Run as test | By default, this option is disabled. In such case, IntelliJ IDEA doesn't open the Run tool window and doesn't rerun tests tasks if they are up to date. However, if IntelliJ IDEA finds test tasks in the run configuration, those are highlighted in the Gradle tool window, IntelliJ IDEA doesn't rerun test tasks, but opens the Gradle tool window. The option becomes enabled when you trigger the test execution from the editor using In this case, IntelliJ IDEA opens the Run tool window and reruns the test tasks each time the execution is triggered even if the tests are up to date. This option might be helpful in controlling the rerunning process of the test tasks in your project. |