Create your multiplatform project
Here, you'll learn how to create and run your first Compose Multiplatform application using the Kotlin Multiplatform web wizard and Android Studio.
Create a project using the wizard
To begin, create a sample project. This is best achieved with the Kotlin Multiplatform web wizard:
Open the Kotlin Multiplatform wizard.
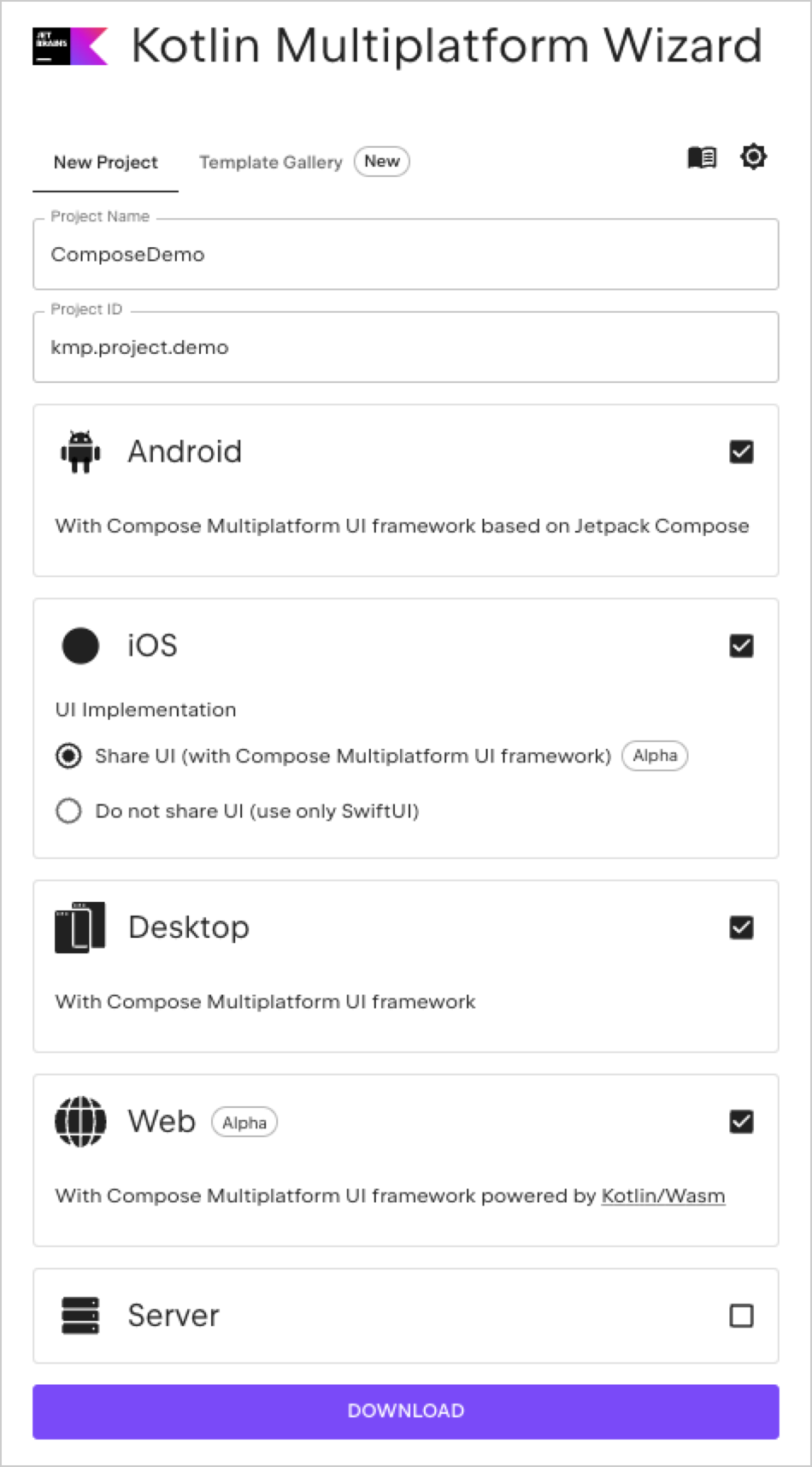
On the New project tab, change the project name to "ComposeDemo" and the project ID to "kmp.project.demo".
Select the Android, Desktop, and Web options.
If you're using a Mac, select iOS as well. Make sure that the Share UI option is selected.
Click the Download button and unpack the resulting archive.
Examine the project structure
Launch Android Studio.
On the Welcome screen, click Open, or select File | Open in the editor.
Navigate to the unpacked "ComposeDemo" folder and then click Open.
Android Studio detects that the folder contains a Gradle build file and opens the folder as a new project.
If you didn't select iOS in the wizard, you won't have the folders whose names begin with "ios" or "apple".
The default view in Android Studio is optimized for Android development. To see the full file structure of the project, which is more convenient for multiplatform development, switch the view from Android to Project:
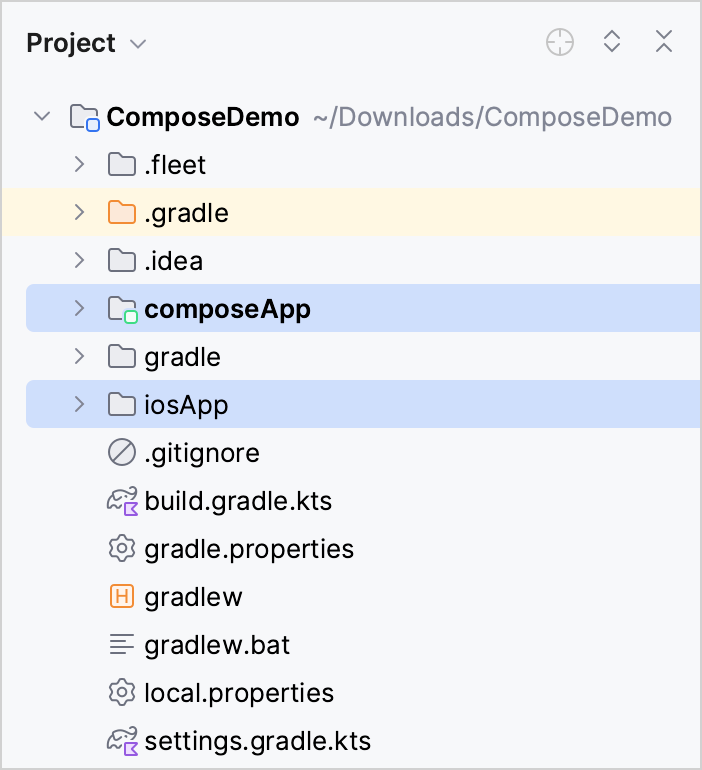
The project contains two modules:
composeApp is a Kotlin module that contains the logic shared among the Android, desktop, iOS, and web applications – the code you use for all the platforms. It uses Gradle as the build system that helps you automate your build process.
iosApp is an Xcode project that builds into an iOS application. It depends on and uses the shared module as an iOS framework.
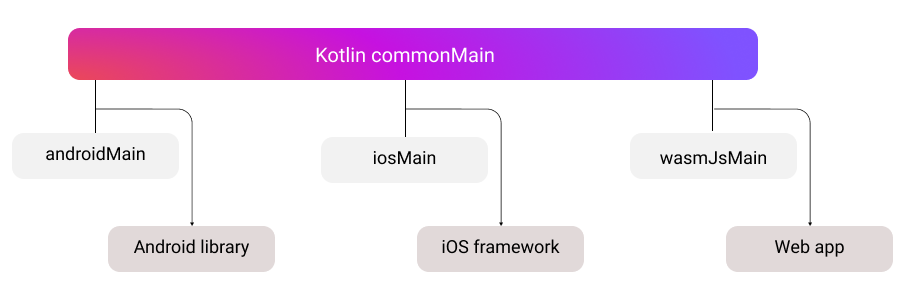
The composeApp module consists of the following source sets: androidMain, commonMain, desktopMain, iosMain, and wasmJsMain. A source set is a Gradle concept for a number of files logically grouped together, where each group has its own dependencies. In Kotlin Multiplatform, different source sets can target different platforms.
The commonMain source set uses the common Kotlin code, and platform source sets use Kotlin code specific to each target. Kotlin/JVM is used for androidMain and desktopMain. Kotlin/Native is used for iosMain. On the other hand, Kotlin/Wasm is used for wasmJsMain.
When the shared module is built into an Android library, common Kotlin code gets treated as Kotlin/JVM. When it is built into an iOS framework, common Kotlin code gets treated as Kotlin/Native. When the shared module is built into a web app, common Kotlin code gets treated as Kotlin/Wasm.
In general, write your implementation as common code whenever possible instead of duplicating functionality in platform-specific source sets.
In the composeApp/src/commonMain/kotlin directory, open the App.kt file. It contains the App() function, which implements a minimalistic but complete Compose Multiplatform UI:
Let's run the application on all supported platforms.
Run your application
You can run the application on Android, iOS, desktop, and web. You don't have to run the applications in any particular order, so start with whichever platform you are most familiar with.
Run your application on Android
Create an Android virtual device.
In the list of run configurations, select composeApp.
Choose your Android virtual device and then click Run: Android Studio will start the selected virtual device if it is powered down, and run the app.

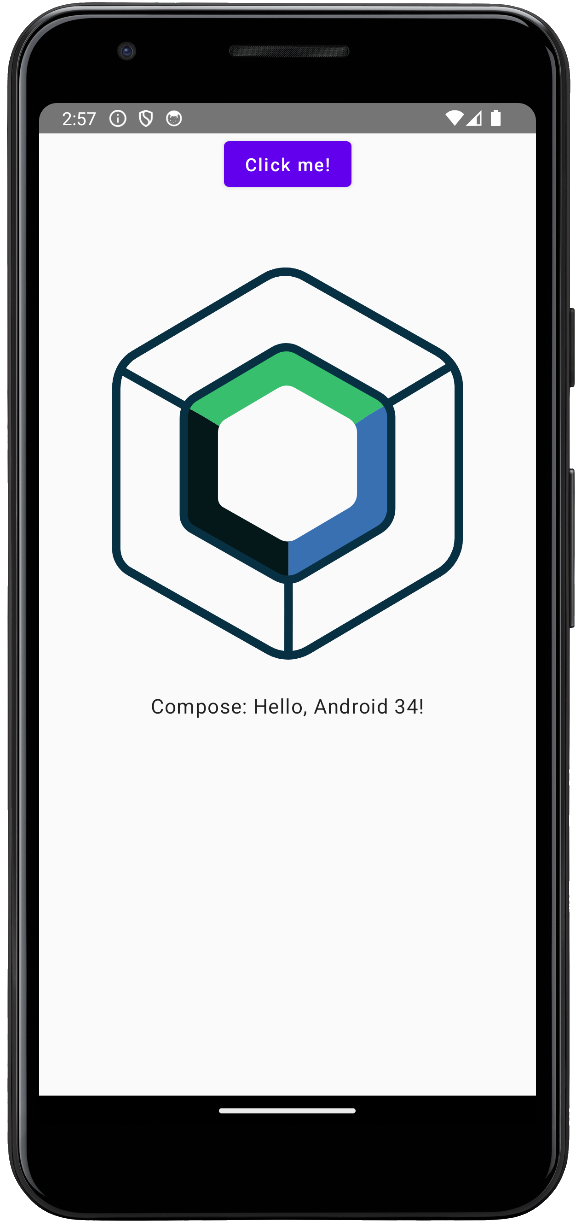
Run on a different Android simulated device
Run on a real Android device
Run your application on iOS
Launch Xcode in a separate window to complete the initial setup. If it's the first time you launch Xcode, you may also need to accept its license terms and allow it to perform some necessary initial tasks.
In Android Studio, select iosApp in the list of run configurations and click Run. By default, the run configuration will start a simulated device available in Xcode and run the app there. If you don't have an available iOS configuration in the list, add a new run configuration.


Run on a new iOS simulated device
If you want to run your application on a simulated device, you can add a new run configuration.
In the list of run configurations, click Edit Configurations.
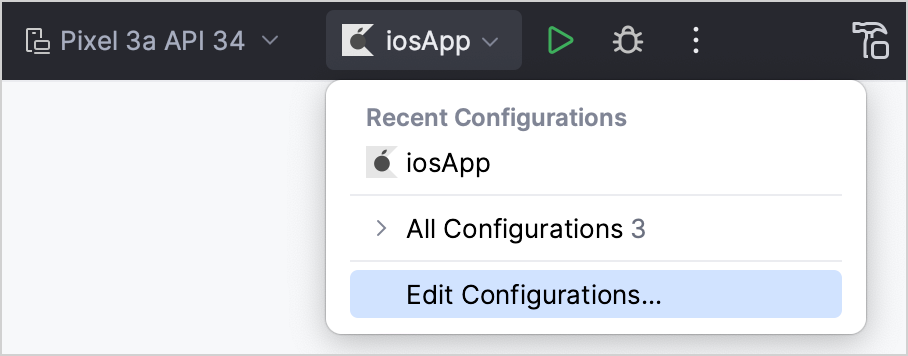
Click the + button above the list of configurations and then select iOS Application.
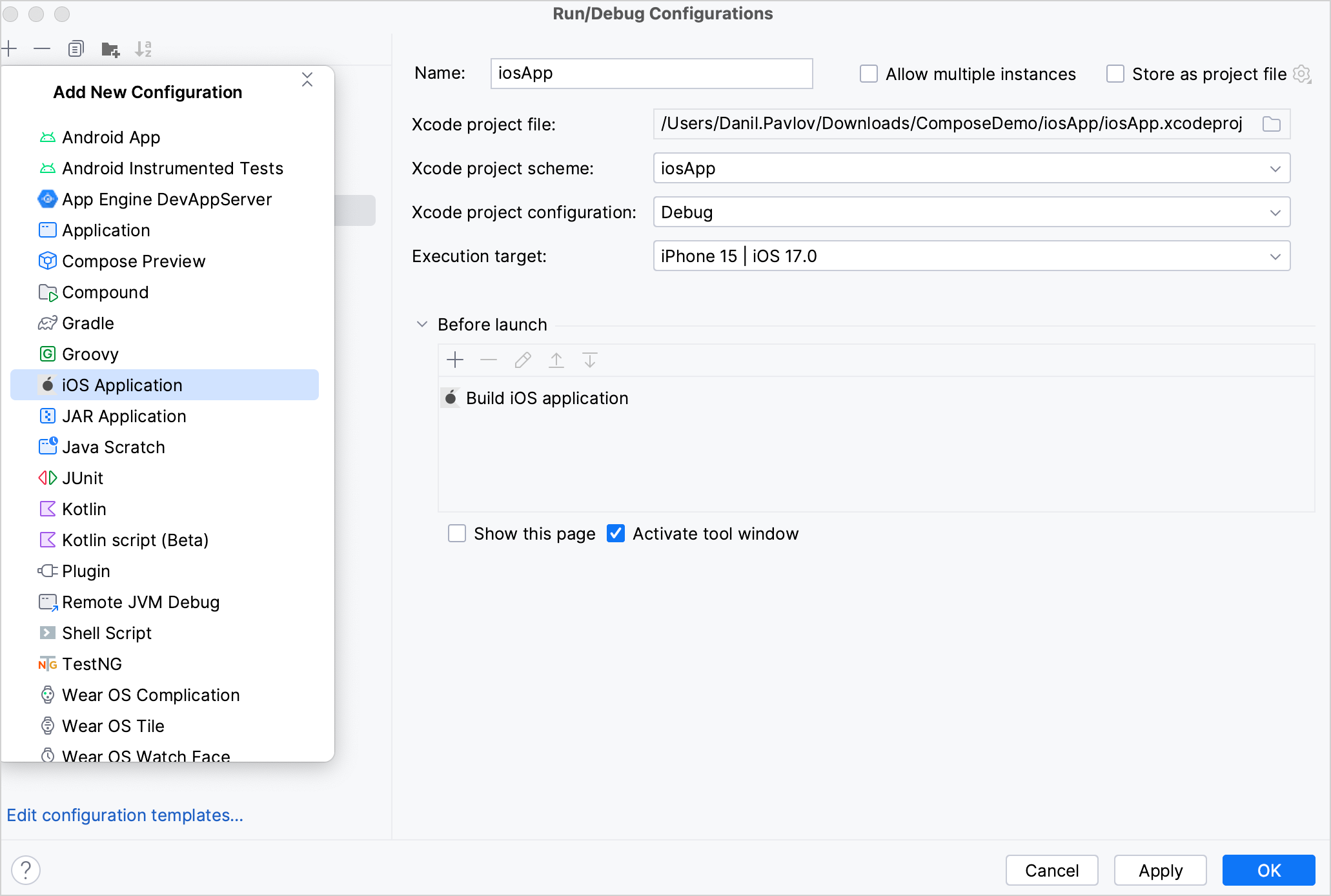
Name your configuration.
Select the Xcode project file. To do so, navigate to your project, for example, KotlinMultiplatformSandbox, open the
iosAppfolder, and then select the.xcodeprojfile.In the Execution target list, select a simulated device and then click OK.
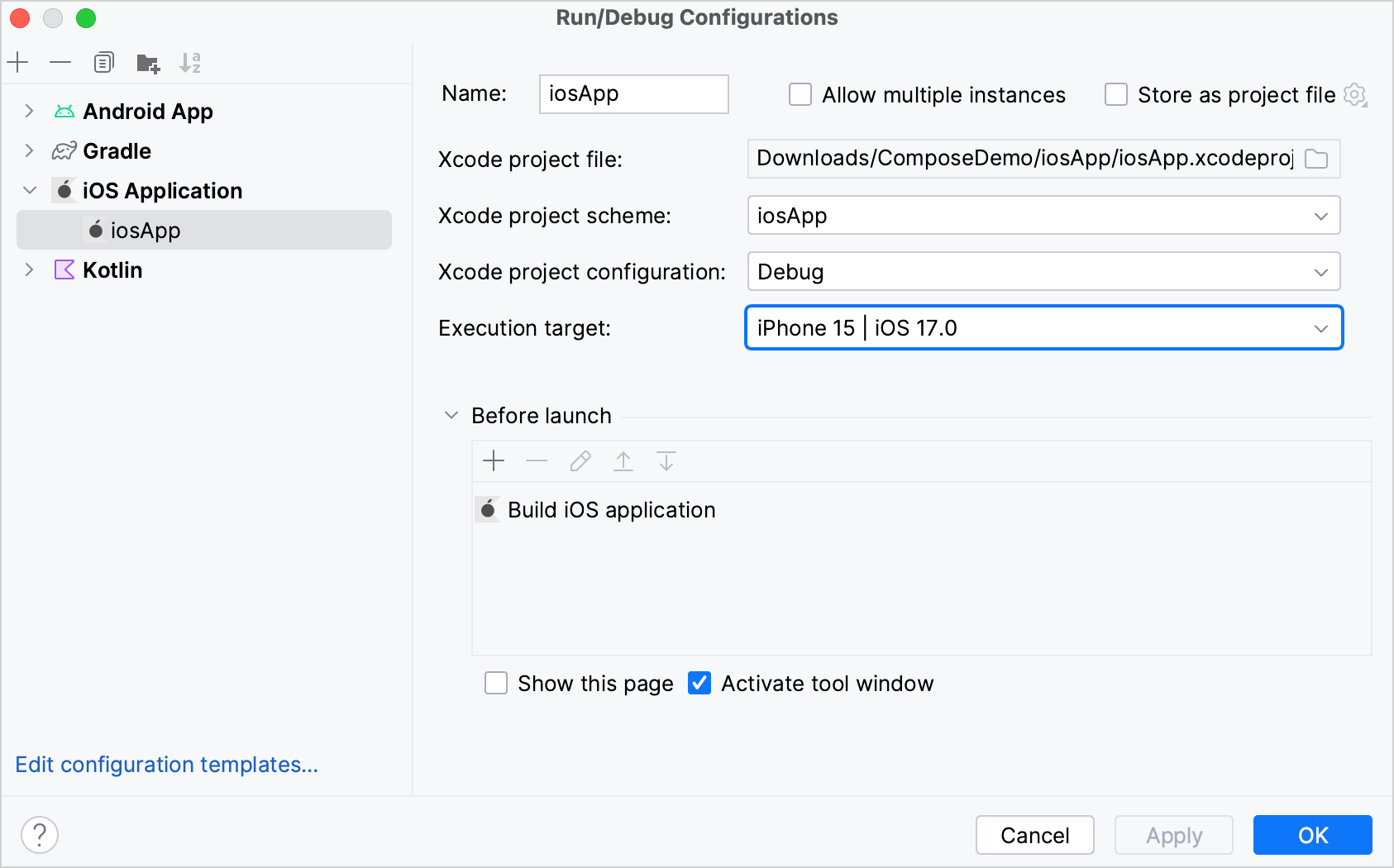
Click Run to run your application on the new simulated device.
Run on a real iOS device
You can run your multiplatform application on a real iOS device. Before you start, you'll need to set the Team ID associated with your Apple ID.
Set your Team ID
To set the Team ID in your project, you can either use the KDoctor tool in Android Studio or choose your team in Xcode.
For KDoctor:
In Android Studio, run the following command in the terminal:
kdoctor --team-idsKDoctor will list all Team IDs currently configured on your system, for example:
3ABC246XYZ (Max Sample) ZABCW6SXYZ (SampleTech Inc.)In Android Studio, open the
iosApp/Configuration/Config.xcconfigand specify your Team ID.
Alternatively, choose the team in Xcode:
Go to Xcode and select Open a project or file.
Navigate to the
iosApp/iosApp.xcworkspacefile of your project.In the left-hand menu, select
iosApp.Navigate to Signing & Capabilities.
In the Team list, select your team.
If you haven't set up your team yet, use the Add an Account option in the Team list and follow Xcode instructions.
Make sure that the Bundle Identifier is unique and the Signing Certificate is successfully assigned.
Run the app
Connect your iPhone with a cable. If you already have the device registered in Xcode, Android Studio should show it in the list of run configurations. Run the corresponding iosApp configuration.
If you haven't registered your iPhone in Xcode yet, follow Apple recommendations. In short, you should:
Connect your iPhone with a cable.
On your iPhone, enable the developer mode in Settings | Privacy & Security.
In Xcode, go to the top menu and choose Window | Devices and Simulators.
Click on the plus sign. Select your connected iPhone and click Add.
Sign in with your Apple ID to enable development capabilities on the device.
Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the pairing process.
Once you've registered your iPhone in Xcode, create a new run configuration in Android Studio and select your device in the Execution target list. Run the corresponding iosApp configuration.
Run your application on desktop
You can create a run configuration for running the desktop application as follows:
Select Run | Edit Configurations from the main menu.
Click the plus button and choose Gradle from the dropdown list.
In the Tasks and arguments field, paste this command:
desktopRun -DmainClass=MainKt --quietClick OK.
Now, you can use this configuration to run the desktop app in its own OS window:


Run your web application
Create a run configuration to run the web application:
Select Run | Edit Configurations from the main menu.
Click the plus button and choose Gradle from the dropdown list.
In the Tasks and arguments field, paste this command:
wasmJsBrowserRun -t --quietClick OK.
Now, you can use this configuration to run the web app:

The web application opens automatically in your browser. Alternatively, you can type the following URL in your browser when the run is finished:
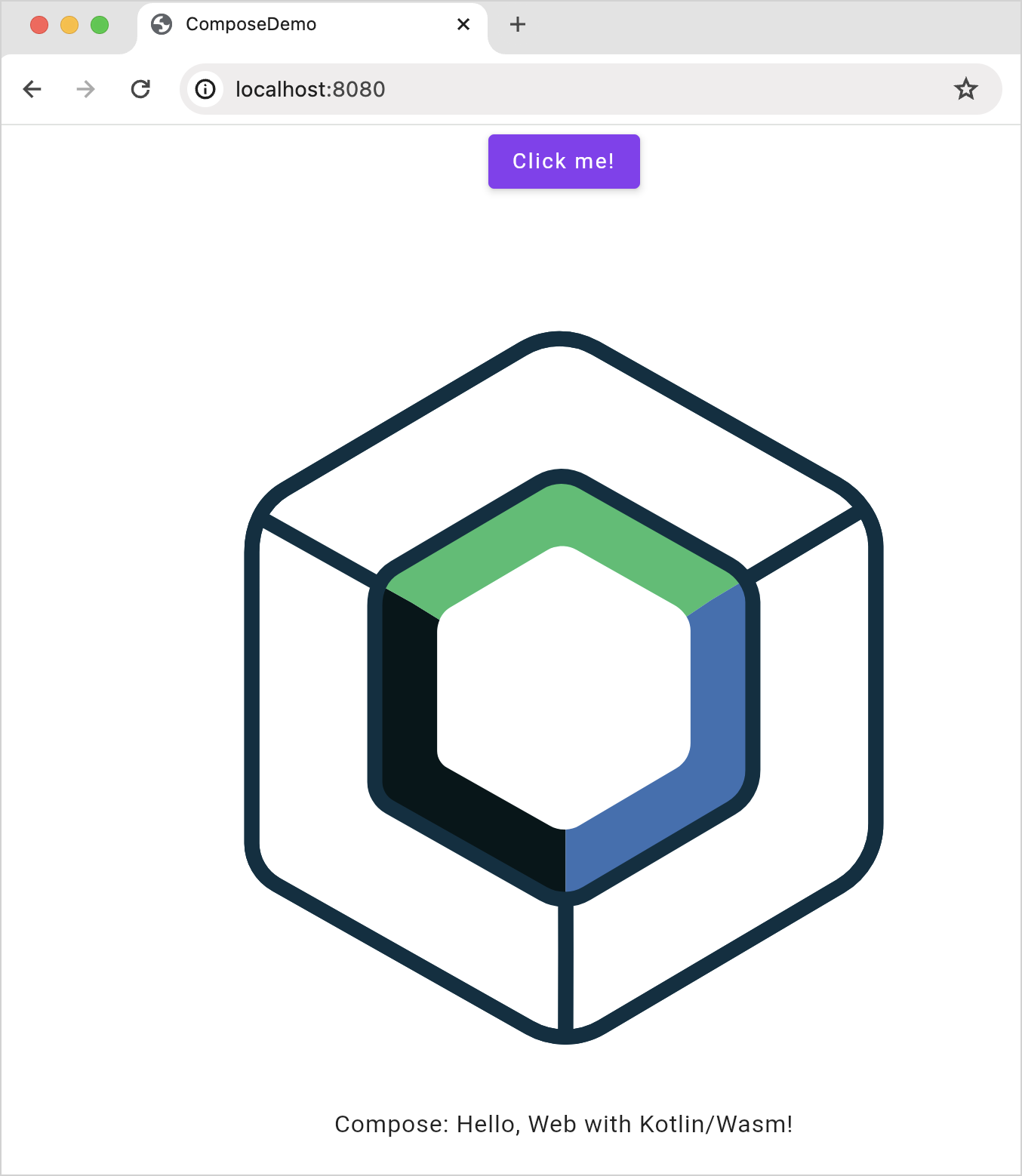
Next step
In the next part of the tutorial, you'll learn how to implement composable functions and launch your application on each platform.
Get help
Kotlin Slack. Get an invite and join the #multiplatform channel.
Kotlin issue tracker. Report a new issue.