Testing with PHPSpec
With PhpStorm, you can practice behaviour-driven development by running specifications using the PHPSpec toolset.
Before you start
Make sure the PHP interpreter is configured in PhpStorm on the PHP page, as described in Configuring Local PHP Interpreters and Configuring Remote PHP Interpreters.
Installing PHPSpec with Composer
On the context menu of composer.json, choose . Alternatively choose from the main menu.
- In the Manage Composer Dependencies Dialog that opens, select the
phpspec/phpspecpackage from the Available Packages list, possibly using the search field. The list shows all the available packages; the packages that are already installed are marked with a checkmark.Choose the relevant version from the Version to install list.
If necessary, expand the Settings hidden area and specify the advanced installation options. In the Command line parameters field, type the additional command line parameters.
Click Install.
Learn more about PHPSpec installation from PHPSpec Official website.
Integrating PHPSpec with a PhpStorm project
-
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), expand the node and select under .
On the Test Frameworks page that opens, click
 in the central pane and choose the configuration type from the list:
in the central pane and choose the configuration type from the list: 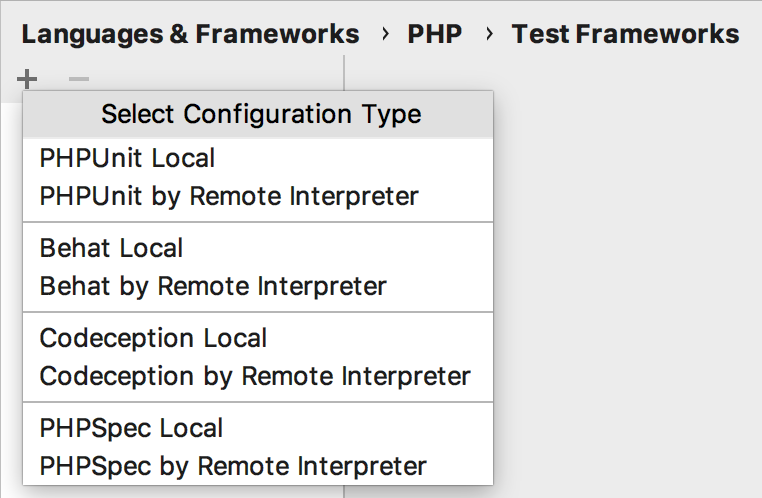
-
In local configurations the default project PHP interpreter is used, see Default project CLI interpreters for details.
-
To use PHPSpec with a remote PHP interpreter, choose one of the configurations in the dialog that opens:
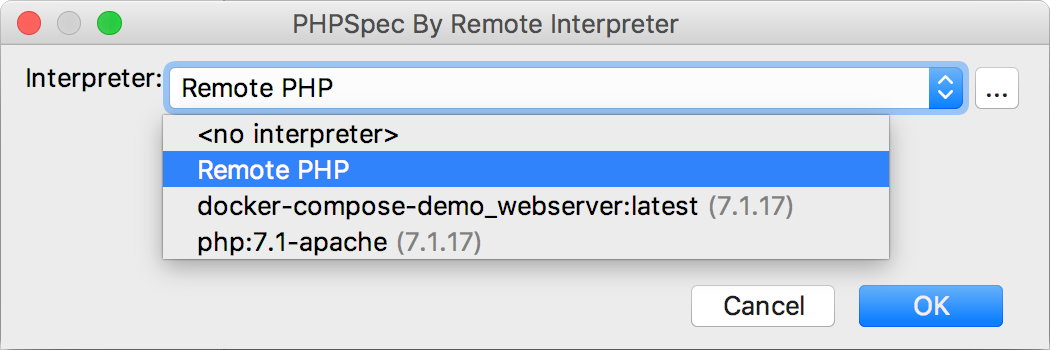
-
- In the Path to PHPSpec executable field, specify the location of phpspec. PHPSpec does not necessarily have to be installed under the current project root. Click
 next to the Path to PHPSpec directory or phar file field. PhpStorm detects the version of PHPSpec and displays it below the field.
next to the Path to PHPSpec directory or phar file field. PhpStorm detects the version of PHPSpec and displays it below the field. If no path to PHPSpec is specified for a Local interpreter, PhpStorm does not provide full support of PHPSpec, for example, it does not show suggestions for code completion and does not resolve references.
- In the Test Runner area, appoint the configuration .yml file to use for launching and executing specifications.
By default, PHPSpec looks for a phpspec.yml or a phpspec.yml.dist configuration file in the project root folder. You can appoint a custom configuration file.
Clear the Default configuration file checkbox to have PHPSpec use the phpspec.yml or phpspec.yml.dist configuration file from the project root folder. If no such file is found, test execution fails, therefore it may be more reliable to specify the configuration file explicitly.
- Select the Default configuration file checkbox to specify your own .yml configuration file. This file will be later used as default in all PHPSpec run/debug configurations.
In the field, specify the location of the configuration file to use. Type the path manually or click
 and choose the file in the dialog box that opens.
and choose the file in the dialog box that opens.
spec_prefixfrom the configuration file specified in the Default Configuration File field. The default value isspec. See PHPSpec Configuration: PSR-4 and PHPSpec Configuration: Spec and Source Location for details.
Generating a PHPSpec test for a class
-
Open the Create New PHP Test dialog by doing any of the following:
On the main menu, choose . Then, choose PHP Test | PHPSpec Spec from the context menu.
In the Project tool window, press Alt+Insert or right-click the PHP class to be tested and choose New | PHP Test | PHPSpec Spec.
-
In the editor of the PHP class to be tested, position the caret inside the definition of the class. Then, choose Go To | Test from the context menu or press Ctrl+Shift+T and select Create New Test from the pop-up menu. This way, you can generate a test for a PHP class defined among several classes within a single PHP file.
To create a test for a certain method, position the caret within the method declaration. The chosen method will be automatically selected in the Generate test methods for area of the Create New PHP Test dialog.
-
The Create New PHP Test dialog opens.
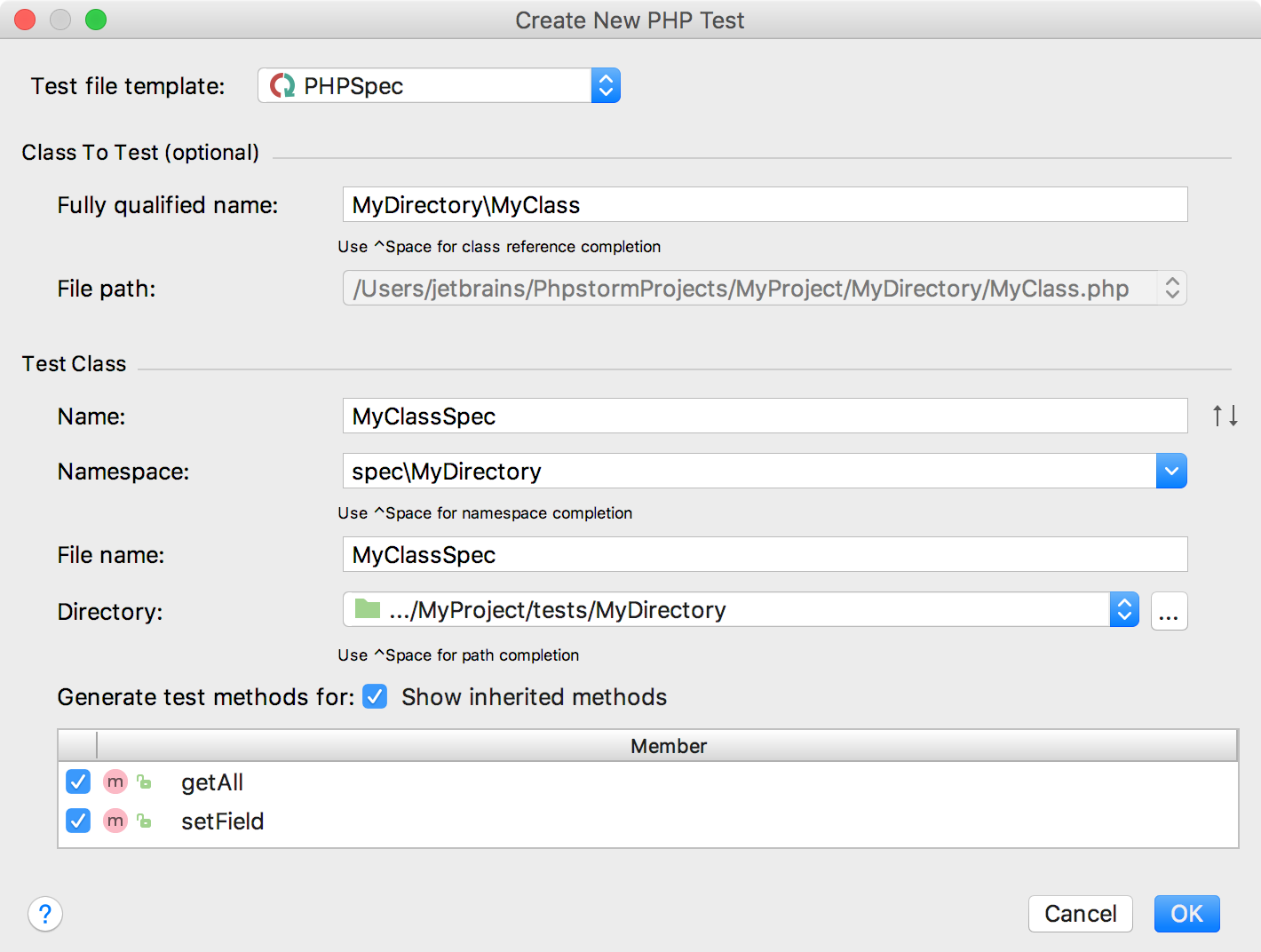
Provide the parameters of the generated test:
The test file template, that is, the template based on which PhpStorm will generate the test class. Make sure that PHPSpec is selected in the Test file template list.
The fully qualified name of the class to be tested, this name will be used to propose the Test Class Name. By default, the Name box displays the name of the class on which the test generation was invoked. To use completion, press Ctrl+Space.
The name of the test class. PhpStorm automatically composes the name from the production class name as <production class>Spec.php. The test class name is displayed in the Name field of the Test Class area.
-
The folder for the test class. By default, it is the folder that is marked as a test sources root. If no such folder is specified, the folder containing the production class is proposed instead.
To specify a different folder, click
 next to the Directory field and choose the relevant folder.
next to the Directory field and choose the relevant folder. - The production class methods to generate test method stubs for. In the Generate test methods for area, select the checkboxes next to the required production class methods. To include inherited methods from parent classes, select the Show inherited methods checkbox.
PhpStorm will automatically compose the test methods' names as
test<production method>. You can customize the code templates used for generating test method stubs on the Code tab of the File and Code Templates settings page.
Check, accept, or update the predefined settings and click OK to initiate the test generation.
When the test is ready, you can navigate back to the production class by choosing Navigate | Go to Test Subject. For details, see Navigating Between Test and Test Subject.
Running and debugging PHPSpec tests
For information about writing PHPSpec specifications, see the PHPSpec Documentation. To run or debug your tests, do one of the following:
To run or debug PHPSpec tests
- In the Project tool window, select the file or folder to run your tests from and choose Run '<file or folder>' or Debug '<file or folder>' on the context menu of the selection:
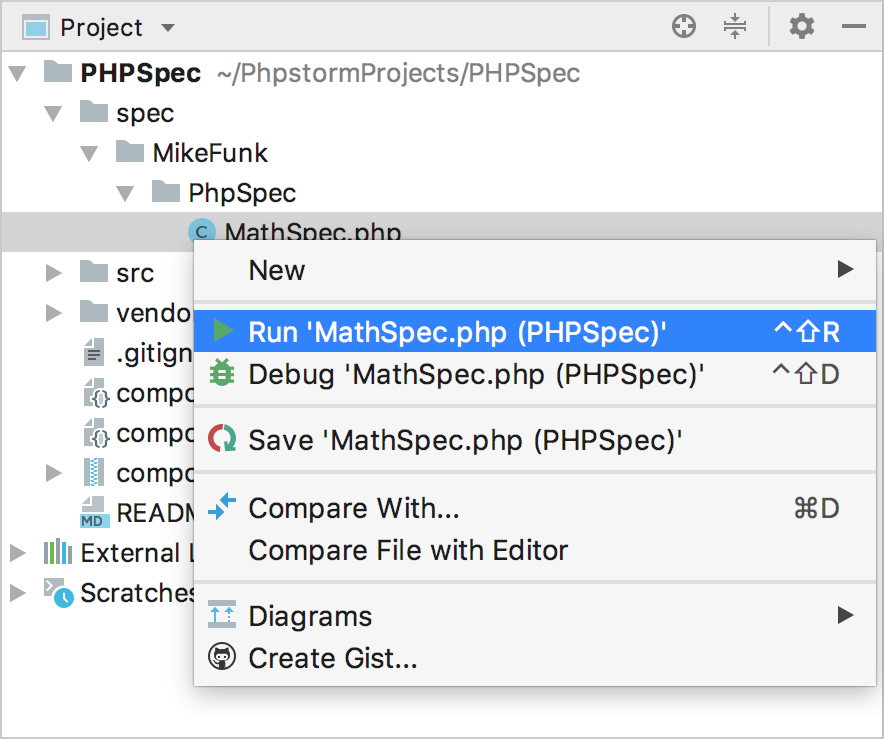
PhpStorm generates a default run configuration and starts a run/debug test session with it.
To save an automatically generated default configuration
After a test session is over, choose Save <default_test_configuration_name> on the context menu of the file or folder.
To run or debug tests through a previously saved run/debug configuration
Choose the required PHPSpec configuration from the list on the toolbar and click
 or
or  .
.
To create a custom run/debug configuration
In the Project tool window, select the file or folder with the tests to run and choose Create run configuration on the context menu. Alternatively, choose on the main menu, then click
 and choose PHPSpec from the list.
and choose PHPSpec from the list. In the Run/Debug Configuration: PHPSpec dialog that opens, specify the scenarios to run and customize the behavior of the current PHP interpreter by specifying the options and arguments to be passed to the PHP executable file.
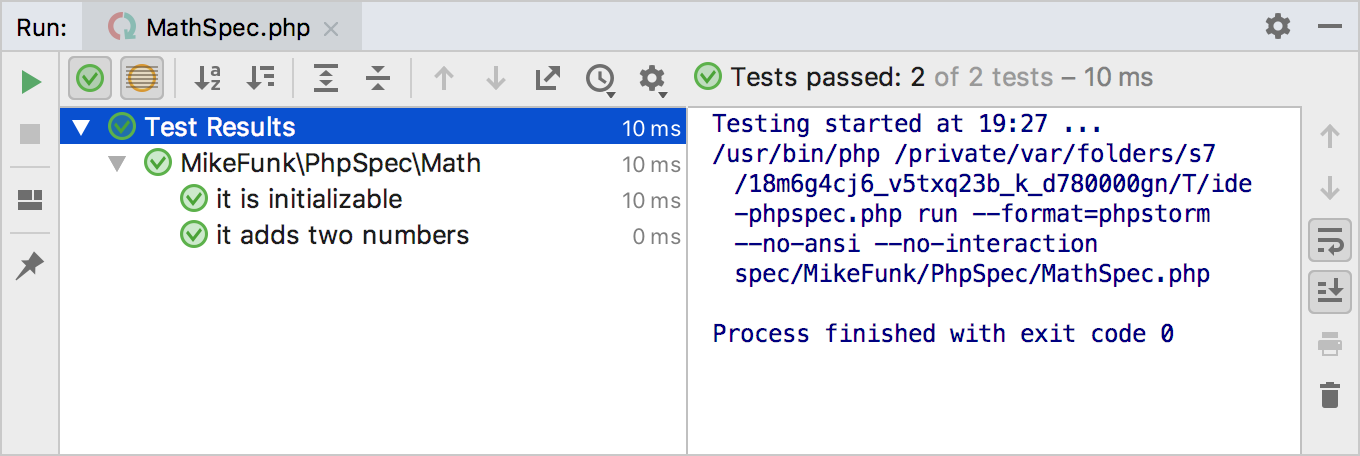
Monitoring test results
PhpStorm shows the tests execution results in the Test Runner tab of the Run Tool Window. The tab is divided into 2 main areas. In the left-hand area you can drill down through all unit tests to see the succeeded and failed ones. You can also filter tests, export results, and use the context menu commands to run specific tests or navigate to the source code.
The right-hand area displays the raw PHPSpec output: