Symfony
PhpStorm provides coding assistance and navigation facilities for developing applications with the Symfony framework.
Symfony support is provided by means of the Symfony Plugin. The source code for the plugin, as well as its issue tracker, can be found on GitHub.
Before you start
Before you start working with Symfony, make sure that the Symfony and PHP Annotations plugins are installed and enabled.
Enabling the Symfony Plugin for a project
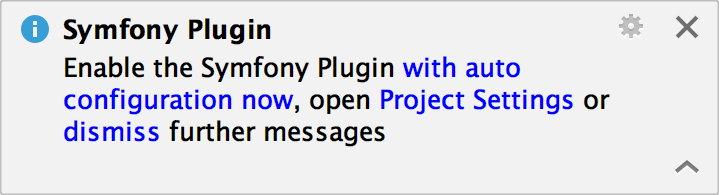
Having installed the Symfony plugin, you need to explicitly enable it for the project. After creating or opening a Symfony project, PhpStorm will display a notification message suggesting you enable the plugin.
Enable the Symfony Plugin for a project
-
Do any of the following:
-
Click the Enable the Symfony plugin with autoconfiguration link in the notification message.
-
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), navigate to and select the Enable Plugin for this Project checkbox.
-
Restart PhpStorm for the changes to take effect.
Specifying additional settings
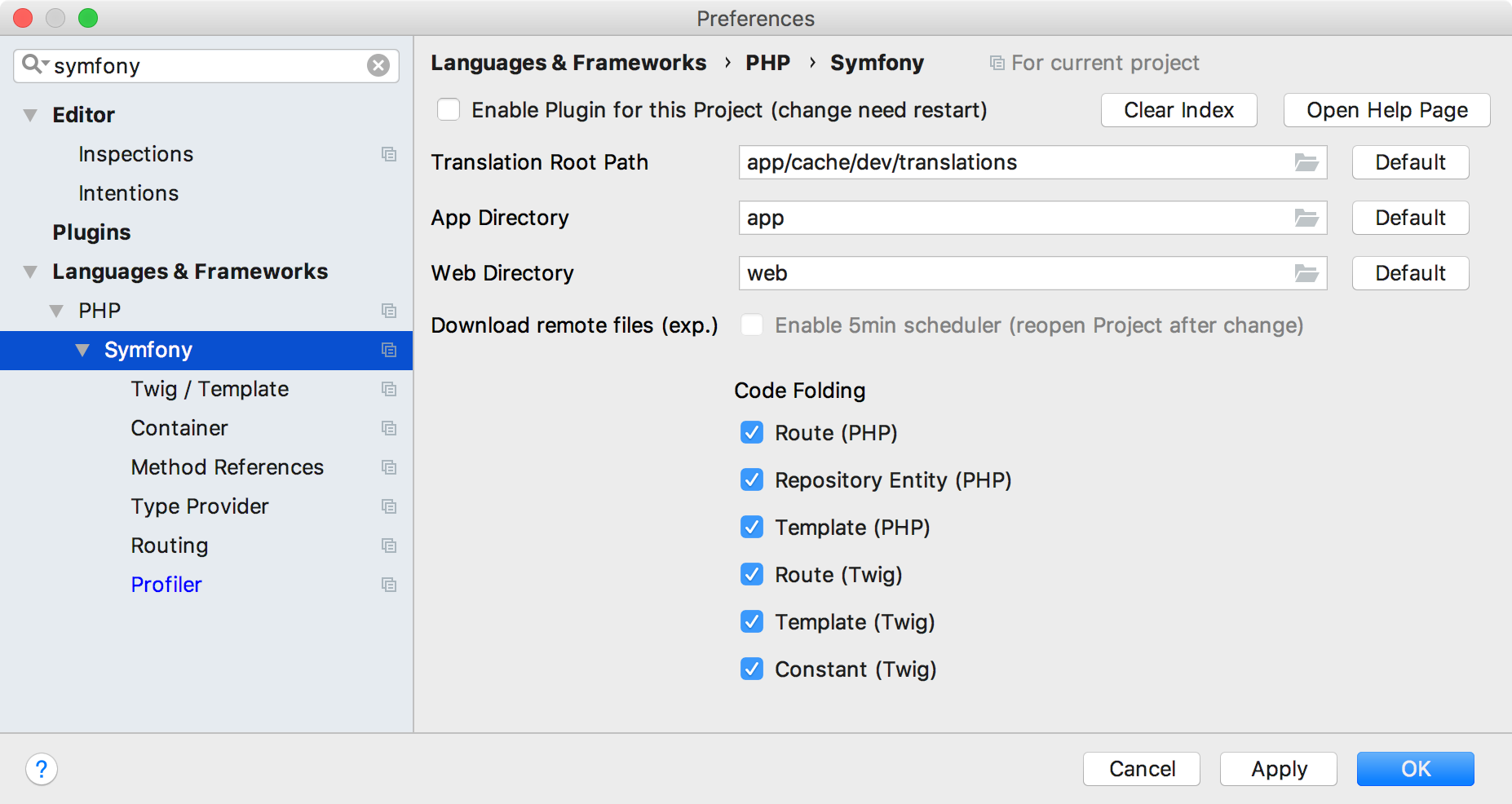
Depending on how the Symfony project is structured, you may have to change some additional settings under . When working with a Symfony application that follows the structure generated by, for example, the symfony/framework-standard-edition Composer project, the default paths and settings will work fine.
Note that the appDevDebugProjectContainer.xml and appDevUrlGenerator.php must be located under the Symfony's default path in order to work with all features the Symfony Plugin provides. It will use a fallback mechanism when these files cannot be found, but completion and navigation will be less precise in this case.
When using a non-default project structure, the following paths should be updated in the Symfony Plugin settings:
Translation Root Path: the path to the location where all translations are copied. This should be set to the translations path under the cache folder, so that all possible translations are discovered by the plugin.
App Directory: the path to the app directory.
Web Directory: the path to the web directory.
Symfony profiler
When the Symfony Plugin is enabled for a project, an additional region will be added to the PhpStorm status bar. Clicking Symfony in the status bar will open the popup menu with the related targets for the latest requests being made to our Symfony application.
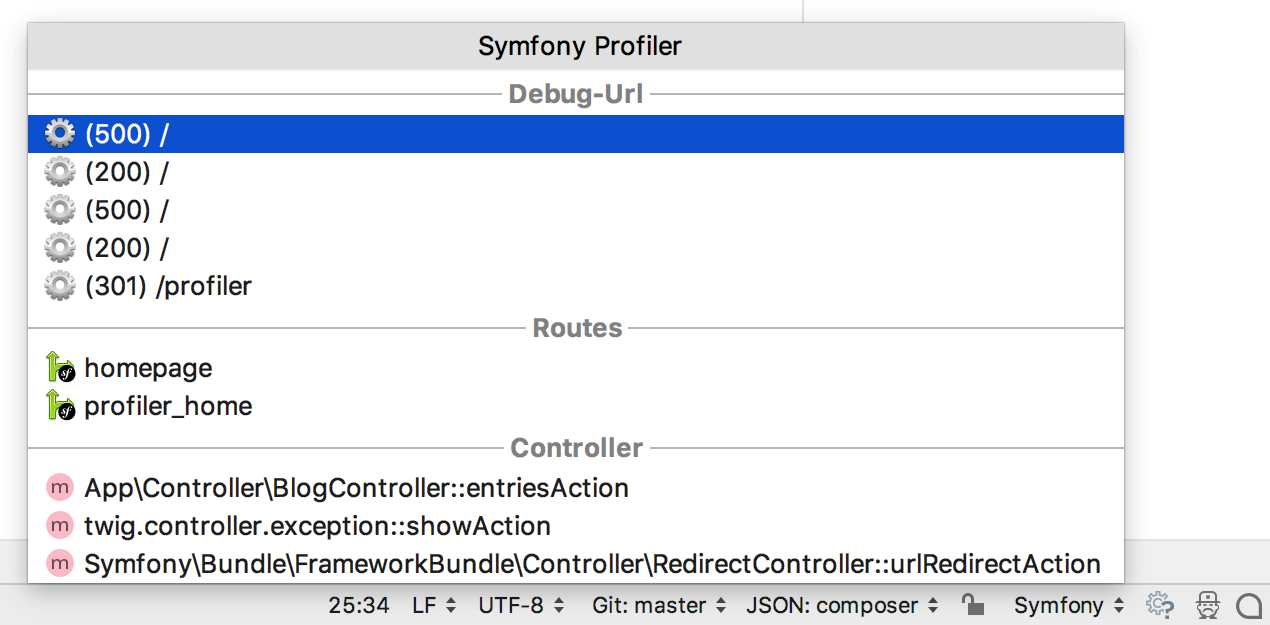
Navigate to a related target
-
Click the corresponding item in the profiler popup menu:
Debug URL: the Symfony profiler URL for the given request, for example, /app_dev.php/_profiler/355651.
Routes: the route registration in the application
Controller: the controller that was involved in creating a response.
Template: any of the templates related to a response.
Symfony Code Style
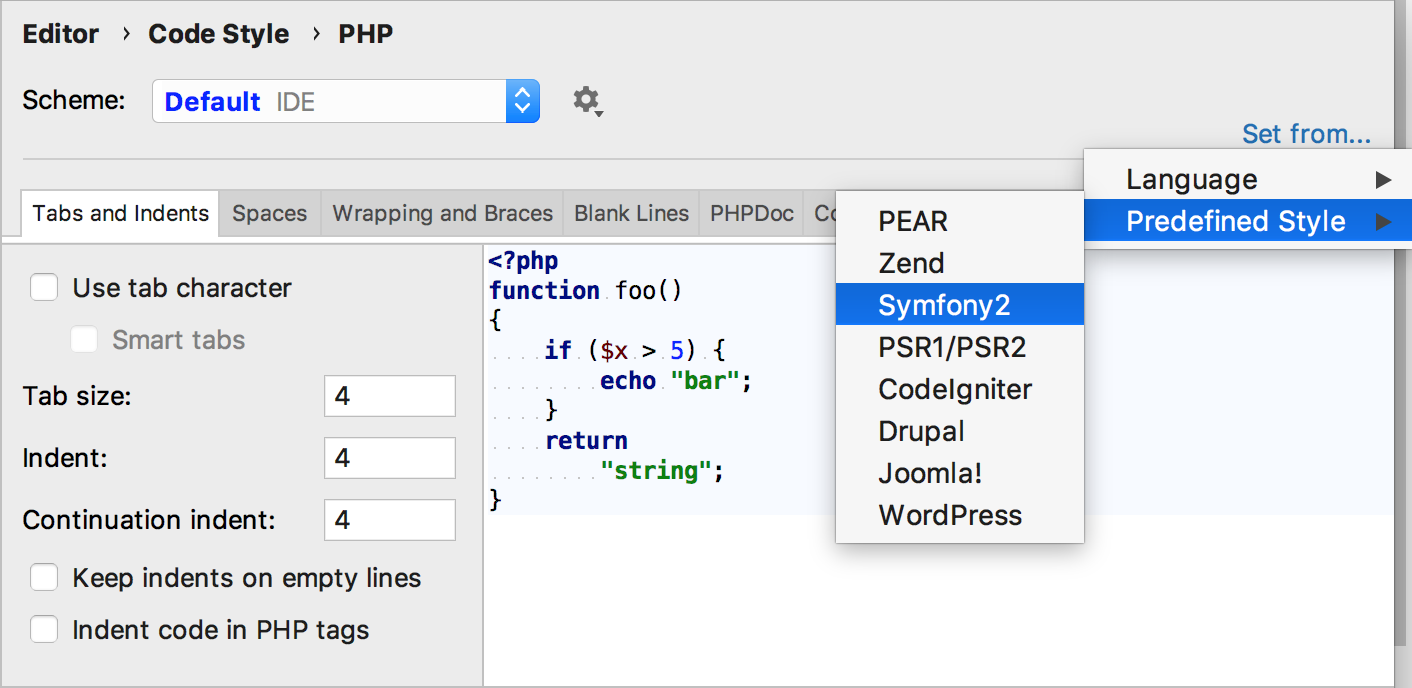
PhpStorm provides the built-in Symfony2 code style tailored for Symfony development.
Set the Symfony2 code style
-
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), navigate to .
-
Click the Set from... link in the upper-right corner and select the option from the popup menu.
Checking code against the Symfony coding standards
With PhpStorm, you can use the PHP Code Sniffer tool, which detects coding standard issues, in combination with Symfony coding standard, which provides a set of Symfony-specific standards to PHP Code Sniffer. This will ensure that your code is clean, consistent, and free of some common errors.
To get started, install PHP Code Sniffer using any technique described in Installing and configuring PHP Code Sniffer. Probably the easiest way is to install it with Composer.
Install PHP Code Sniffer
From the context menu of composer.json, choose . Alternatively choose from the main menu.
-
In the Manage Composer Dependencies Dialog that opens, select the squizlabs/php_codesniffer package from the Available Packages list, possibly using the search field.
Choose the relevant version from the Version to install list.
-
If necessary, expand the Settings hidden area and specify the advanced installation options. In the Command line parameters field, type the additional command line parameters. It is recommended to provide the
--dev, option: the package in this case is added to therequire-devsection of the composer.json file instead of the defaultrequiresection. Click Install.
Next, install Symfony coding standard, which will provide Symfony-specific standards to PHP Code Sniffer.
Install Symfony coding standard
From the context menu of composer.json, choose . Alternatively choose from the main menu.
-
In the Manage Composer Dependencies Dialog that opens, select the escapestudios/symfony2-coding-standard package from the Available Packages list, possibly using the search field.
Choose the relevant version from the Version to install list.
-
If necessary, expand the Settings hidden area and specify the advanced installation options. In the Command line parameters field, type the additional command line parameters. It is recommended to provide the
--dev, option: the package in this case is added to therequire-devsection of the composer.json file instead of the defaultrequiresection. Click Install.
The Symfony coding standard package will be installed, and the corresponding Symfony standard will be selected for the PHP Code Sniffer validation inspection automatically. If necessary, you can further customize the inspection on the page of the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S). See Configuring PHP Code Sniffer as a PhpStorm inspection for details.