Disable and suppress inspections
Some inspections may report problems that you currently do not want to see. In this case, you can disable or suppress them.
When you disable an inspection, you turn it off. It means that the code analysis engine stops searching project files for the problem that this inspection is designed to detect. Note that when you disable an inspection, you disable it in the current inspection profile; it remains enabled in other profiles.
Disable inspections
Disable an inspection in the settings
-
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), select .
Locate the inspection you want to disable, and clear the checkbox next to it.
Apply the changes and close the dialog.
Disable an inspection in the editor
You can quickly disable a triggered inspection directly in the editor.
Place the caret at the highlighted string and press Alt+Enter (or use the intention action
 ).
).Click
 next to the inspection you want to disable, and select Disable inspection.
next to the inspection you want to disable, and select Disable inspection.
Disable an inspection in the Results tool window
In the Inspection Results tool window (after running code analysis), right-click the inspection you want to disable and select Disable inspection.
Click
 to hide the disabled inspection alerts.
to hide the disabled inspection alerts.
Suppress inspections
When you suppress an inspection, the code analysis engine doesn't highlight the problem found by this inspection in the specific piece of code (class, method, or statement). You can also suppress all inspections in the current class.
Suppress an inspection in the editor
Place the caret at the highlighted string and press Alt+Enter (or use the intention action
 ).
).-
Click
 next to the inspection you want to suppress, and select the necessary suppress action.
next to the inspection you want to suppress, and select the necessary suppress action. 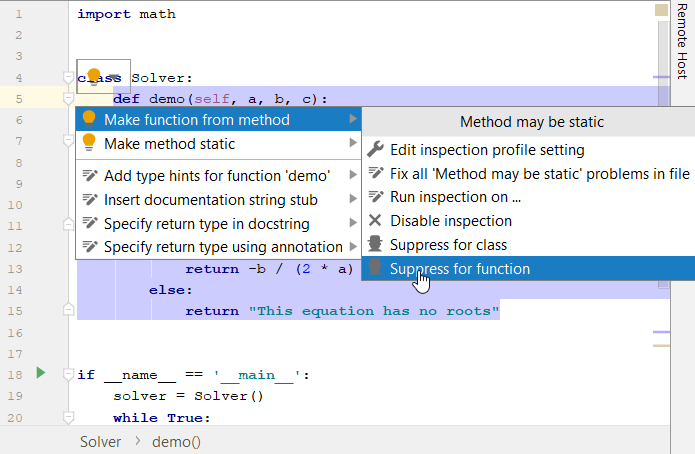
The inspection will be suppressed with special comments in the corresponding piece of code.
Suppress an inspection in the Results tool window
In the Inspection Results tool window (after running code analysis), right-click the inspection you want to suppress and select the necessary suppress action.
Change the highlighting level for a file
By default, PyCharm highlights all detected code problems. You can change this behavior for the file you are currently working with. Click ![]() in the status bar (bottom right-hand corner), and select one of these options:
in the status bar (bottom right-hand corner), and select one of these options:
 None — turn highlighting off.
None — turn highlighting off. Syntax — highlight syntax problems only.
Syntax — highlight syntax problems only. Inspections — (default) highlight syntax problems and problems found by inspections.
Inspections — (default) highlight syntax problems and problems found by inspections.
You can also change the highlighting level from the main menu. Select , or press Ctrl+Shift+Alt+H.
Suppressing comments
# noinspection PyPep8
# noinspection PyPep8Naming
# noinspection PyTypeChecker
# noinspection PyAbstractClass
# noinspection PyArgumentEqualDefault
# noinspection PyArgumentList
# noinspection PyAssignmentToLoopOrWithParameter
# noinspection PyAttributeOutsideInit
# noinspection PyAugmentAssignment
# noinspection PyBroadException
# noinspection PyByteLiteral
# noinspection PyCallByClass
# noinspection PyChainedComparsons
# noinspection PyClassHasNoInit
# noinspection PyClassicStyleClass
# noinspection PyComparisonWithNone
# noinspection PyCompatibility
# noinspection PyDecorator
# noinspection PyDefaultArgument
# noinspection PyDictCreation
# noinspection PyDictDuplicateKeys
# noinspection PyDocstringTypes
# noinspection PyExceptClausesOrder
# noinspection PyExceptionInheritance
# noinspection PyFromFutureImport
# noinspection PyGlobalUndefined
# noinspection PyIncorrectDocstring
# noinspection PyInitNewSignature
# noinspection PyInterpreter
# noinspection PyListCreation
# noinspection PyMandatoryEncoding
# noinspection PyMethodFirstArgAssignment
# noinspection PyMethodMayBeStatic
# noinspection PyMethodOverriding
# noinspection PyMethodParameters
# noinspection PyMissingConstructor
# noinspection PyMissingOrEmptyDocstring
# noinspection PyNestedDecorators
# noinspection PynonAsciiChar
# noinspection PyNoneFunctionAssignment
# noinspection PyOldStyleClasses
# noinspection PyPackageRequirements
# noinspection PyPropertyAccess
# noinspection PyPropertyDefinition
# noinspection PyProtectedMember
# noinspection PyRaisingNewStyleClass
# noinspection PyRedeclaration
# noinspection PyRedundantParentheses
# noinspection PySetFunctionToLiteral
# noinspection PySimplifyBooleanCheck
# noinspection PySingleQuotedDocstring
# noinspection PyStatementEffect
# noinspection PyStringException
# noinspection PyStringFormat
# noinspection PySuperArguments
# noinspection PyTrailingSemicolon
# noinspection PyTupleAssignmentBalance
# noinspection PyTupleItemAssignment
# noinspection PyUnboundLocalVariable
# noinspection PyUnnecessaryBackslash
# noinspection PyUnreachableCode
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
# noinspection PyUnusedLocal
# noinspection ReturnValueFromInit