Install, uninstall, and upgrade packages
PyCharm provides methods for installing, uninstalling, and upgrading Python packages for a particular Python interpreter. It means that each project has its own set of packages, which is considered a best practice for Python dependency management. By default, PyCharm uses pip to manage project packages. For conda environments, you can use the conda package manager.
In PyCharm, you can preview and manage packages in the Python Packages tool window and in the Python interpreter settings.
Manage packages in the Python Packages tool window
The Python Packages tool window provides the quickest and neat way to preview and install packages for the currently selected Python interpreter. This tool window is enabled by default, and you can open it by clicking Python Packages on the left. At any time you can open it using the main menu: .
The Python Packages tool window shows installed packages and the packages available in the PyPI and conda package repositories. Use the search field to filter the list of the available packages.

You can preview the package documentation in the documentation area, or click the Documentation link and open it in a browser.
Install packages
Start typing the package name in the search field of the Python Packages tool window. The matching packages are displayed.
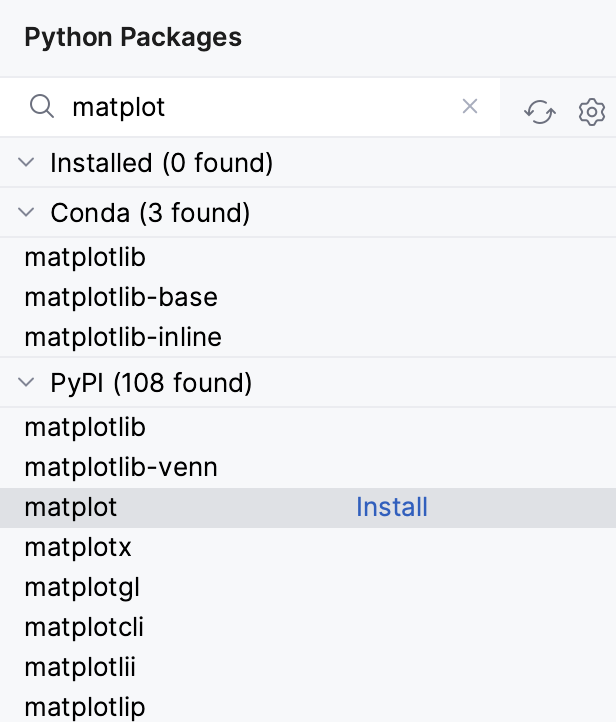
If the current Python interpreter is a conda virtual environment, the packages available in the conda package repository are also displayed.
Select the package and then do one of the following:
Click Install next to the package name and choose the version.
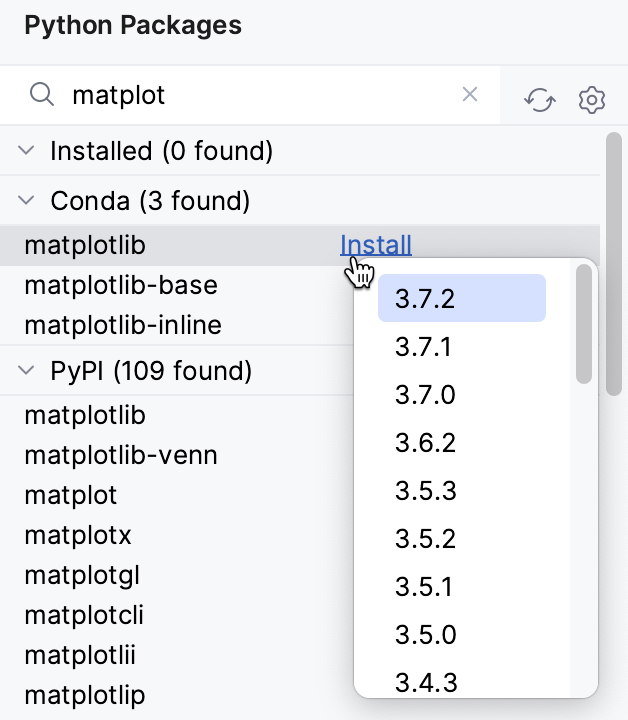
Choose the version from the list of available versions and click Install.

You can use the
pip installcommand-line options during the installation:Right-click next to the package name and select Install with Options.
In the dialog that opens, enter the required options and click OK.
Packages installed with
condaorpipare marked with the corresponding icons.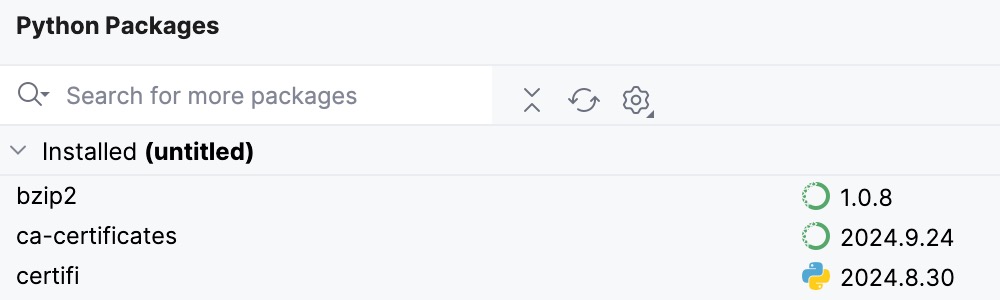
If a popup with an error message appears, refer to the Troubleshooting guide for a solution.
Manage package repositories
To specify a custom repository, for example devpi or a private PyPi server, click
Settings next to the search field.
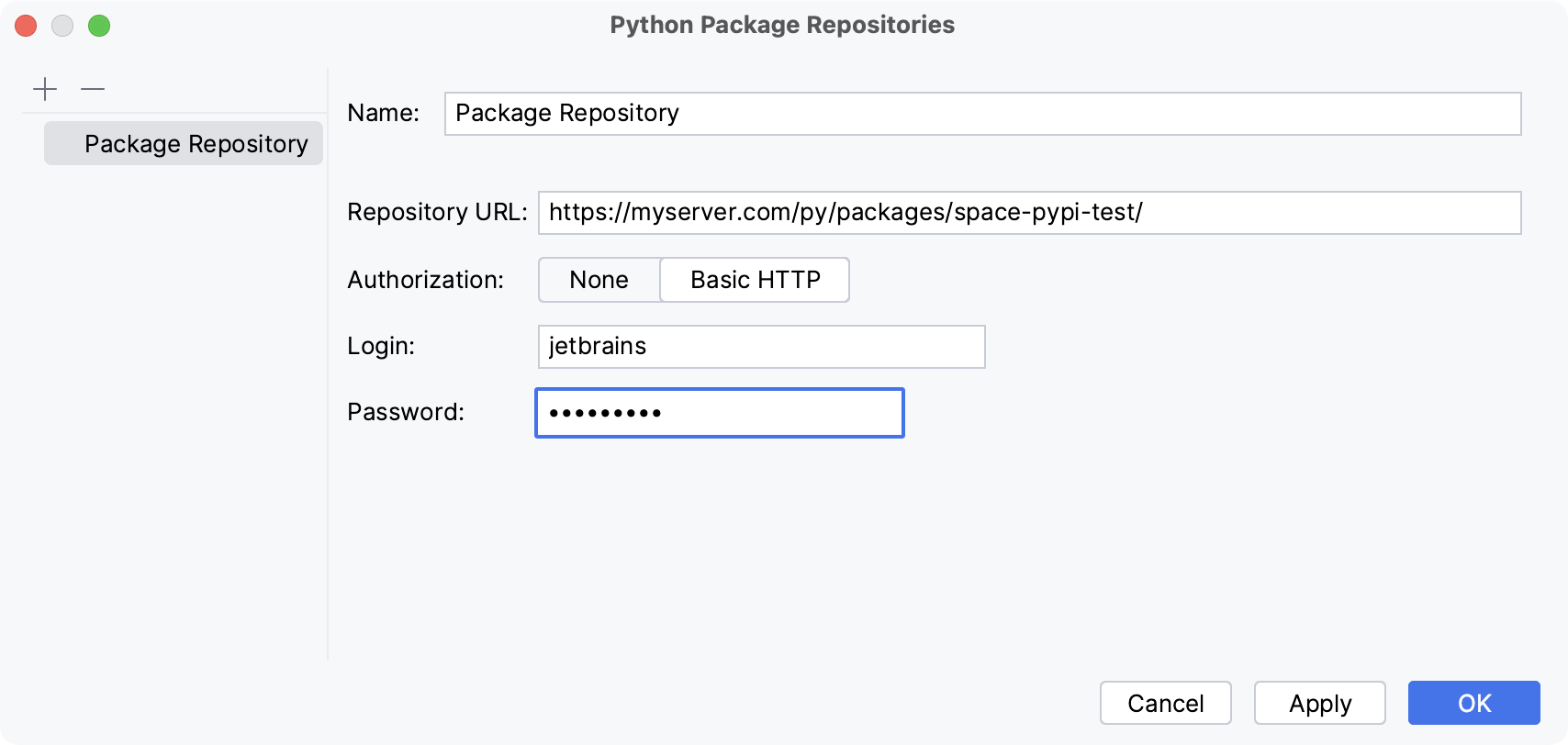
In the Python Packages Repositories dialog, click
Add. If no authorization is required, for example, in the case of a local repository, type the repository URL and click OK.
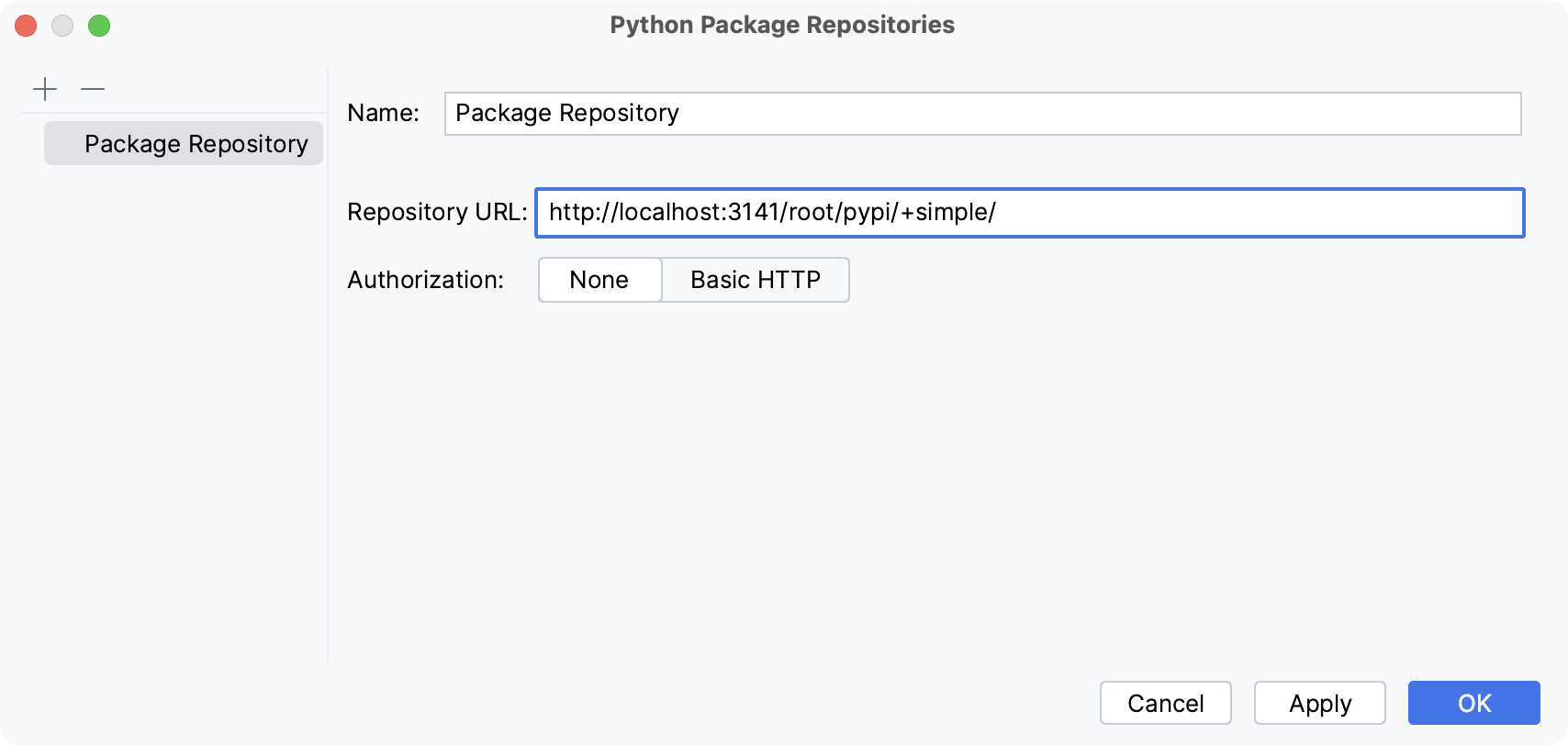
If you want to install Python packages from a repository that requires HTTP authorization, click Basic HTTP and type the repository URL and the login credentials. Click OK to complete the task.
Install packages from Version Control System
Click the Add Package link on the Python Packages toolbar and select From Version Control.
Specify a path to the target git repository. For more information about supported path formats, refer to pip documentation.
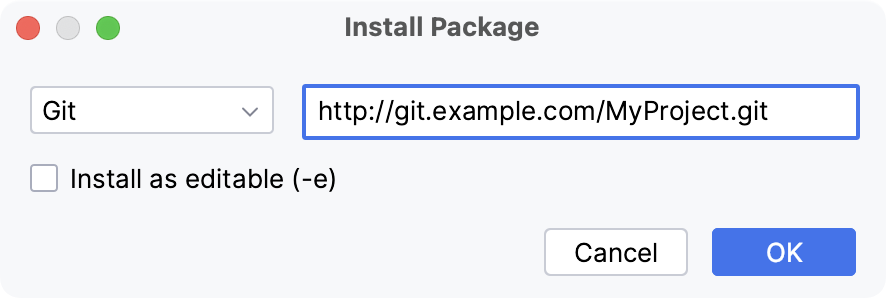
Select Install as editable (-e) if you want to install the package in the editable mode (for example, setuptools develop mode).
Install packages from disk
Click the Add Package link on the Python Packages toolbar and select From Disk.
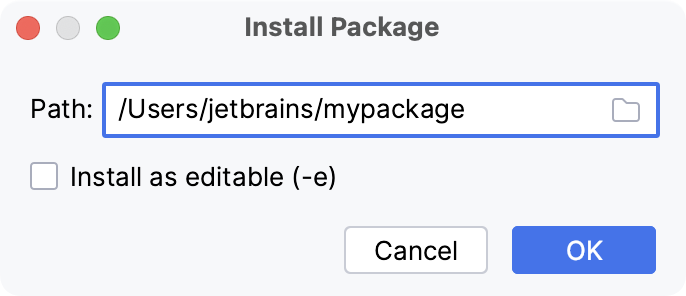
Specify a path to the package directory or an archive (zip or whl).
Select Install as editable (-e) if you want to install the package in the editable mode (for example, setuptools develop mode).
Upgrade packages
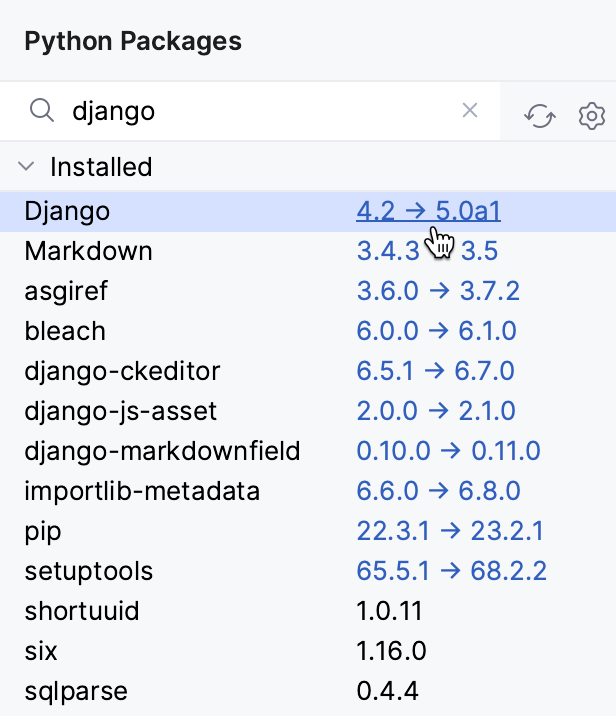
If a newer version of the package is available, a link with the current version and the newest version is displayed next to the package name. Click the link to upgrade the package to the latest version.
If a popup with an error message appears, refer to the Troubleshooting guide for a solution.
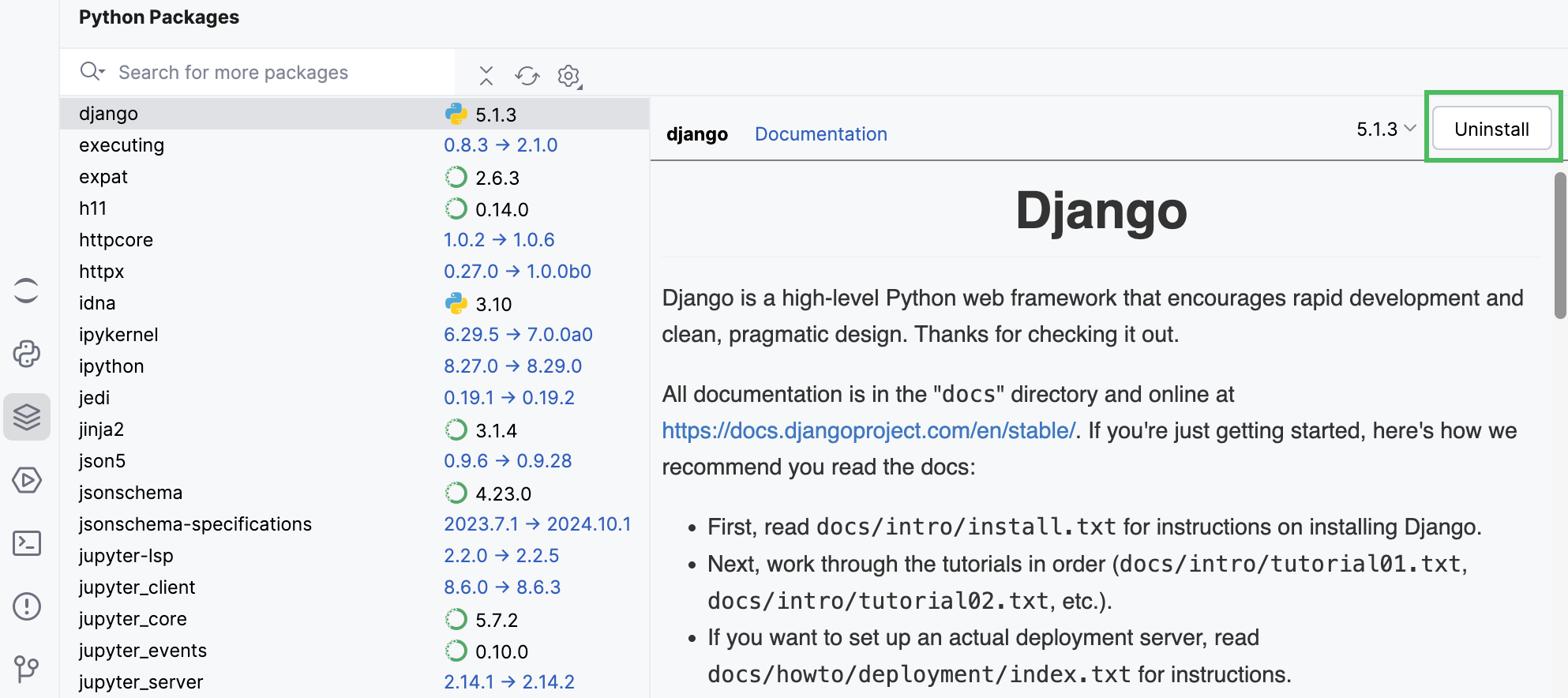
Uninstall packages
To delete an installed package, click Uninstall next to the package version.
Manage packages in Python interpreter settings
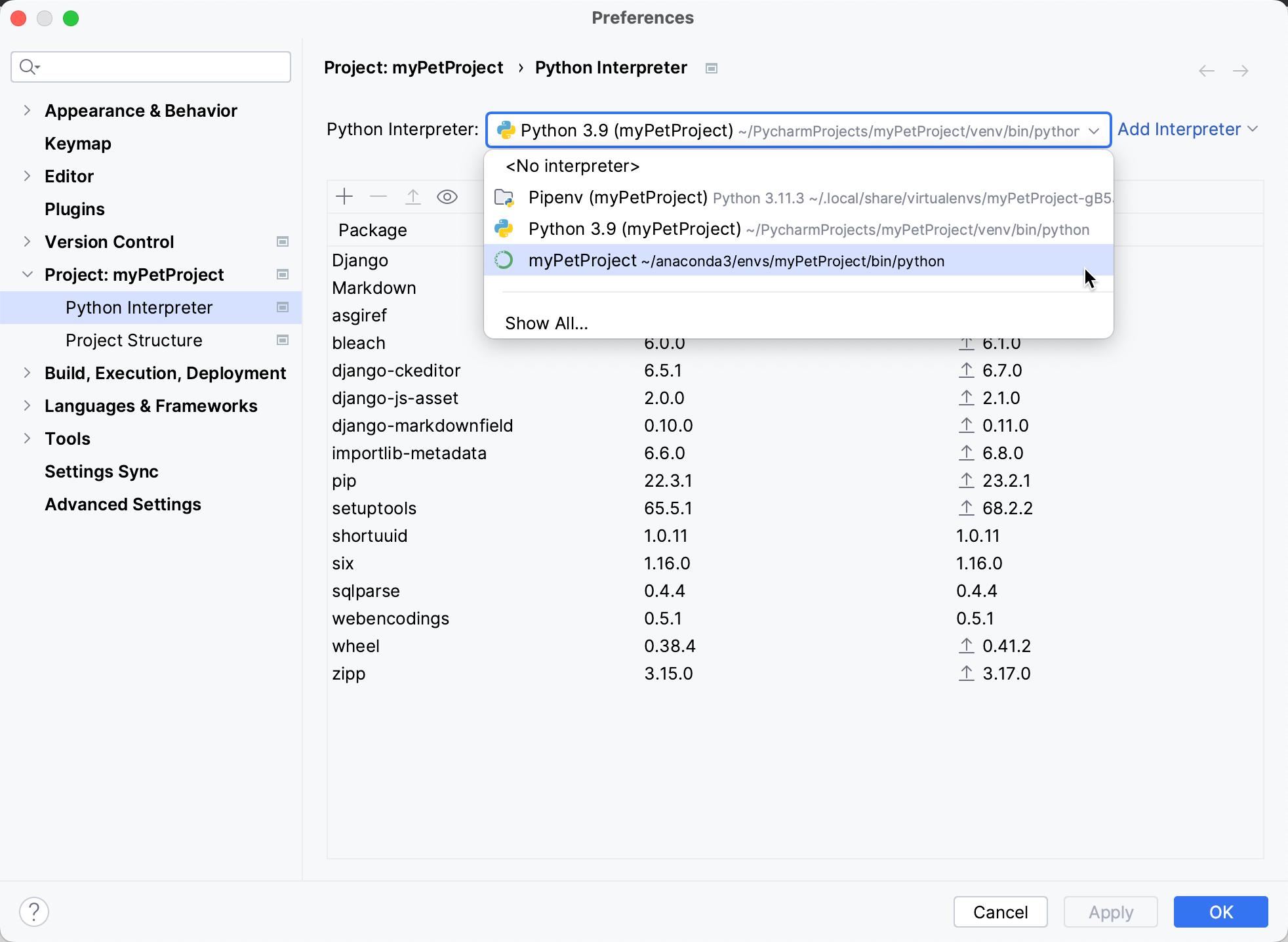
To manage Python packages for a project Python interpreter, go to or select Interpreter Settings in the Python Interpreter selector. Then select the interpreter in the Python Interpreter field.
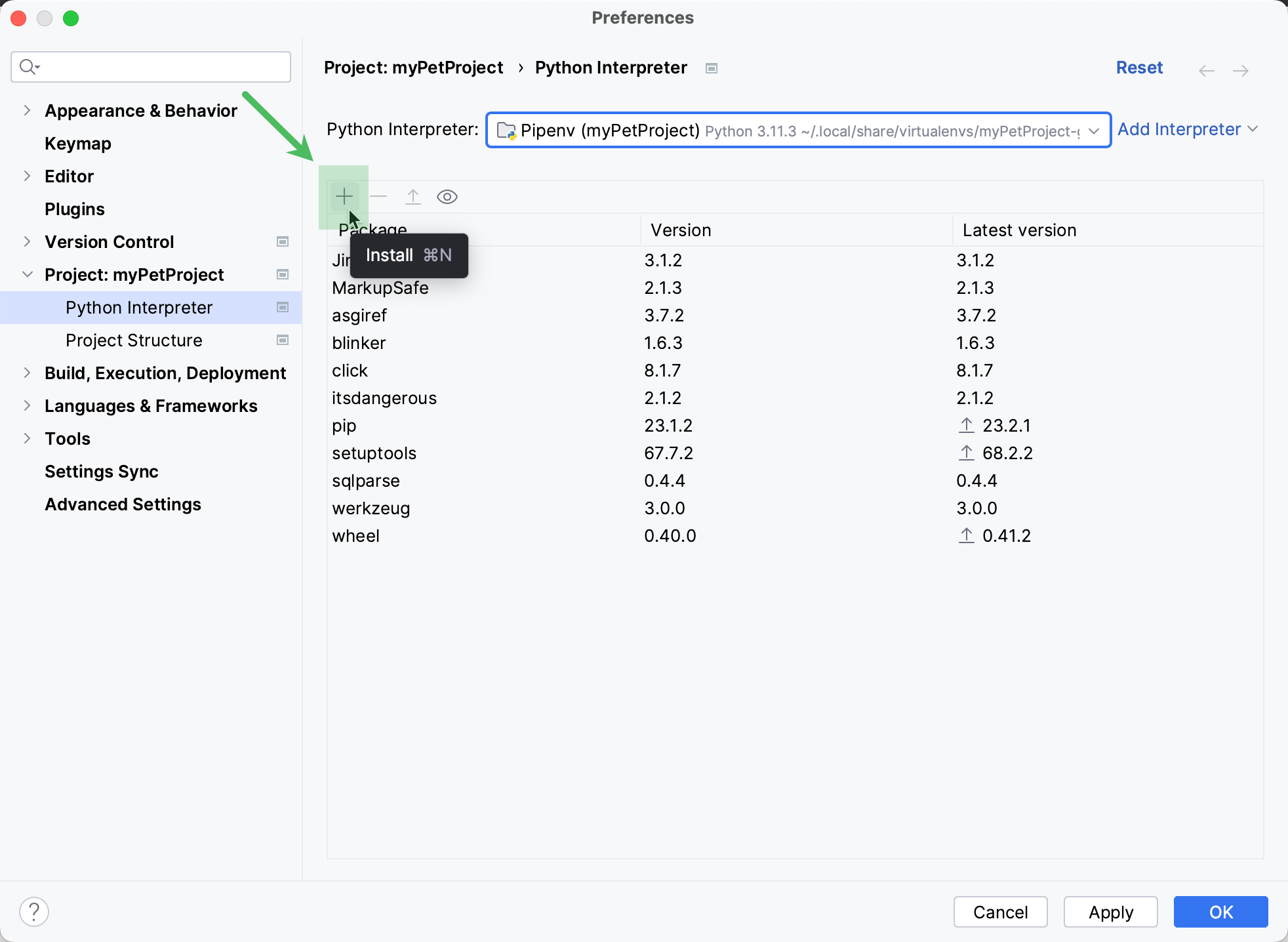
Install packages
Click the
Install on the toolbar.
In the Available Packages dialog that opens, type the name of the package in the search field.
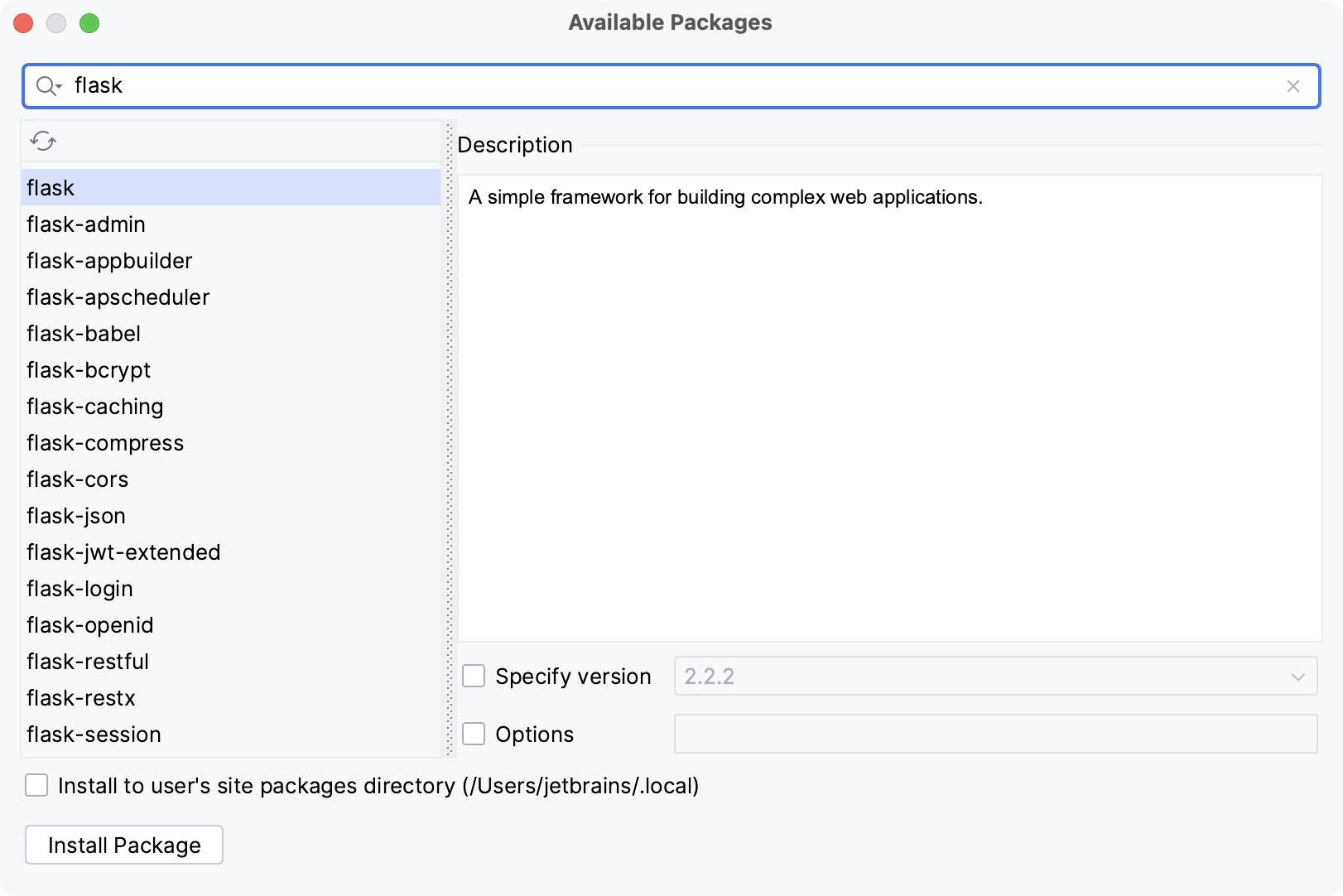
If required, select the following checkboxes:
Specify version: if this checkbox is selected, you can select the desired version from the list. By default, the latest version is installed.
Options: If this checkbox is selected, you can type the
pip installcommand-line options in the text field.Install to user's site packages directory <path>: If this checkbox is disabled (by default), the package will be installed into package directory of the current interpreter. If the checkbox is enabled, the package will be installed into the mentioned directory. This option is available only for conda environments.
Select the package and click Install Package.
If a popup with an error message appears, refer to the Troubleshooting guide for a solution.
Install packages from conda package repository
If you select a Python interpreter with the configured conda environment, the Use Conda Package Manager toggle appears in the packages area toolbar.
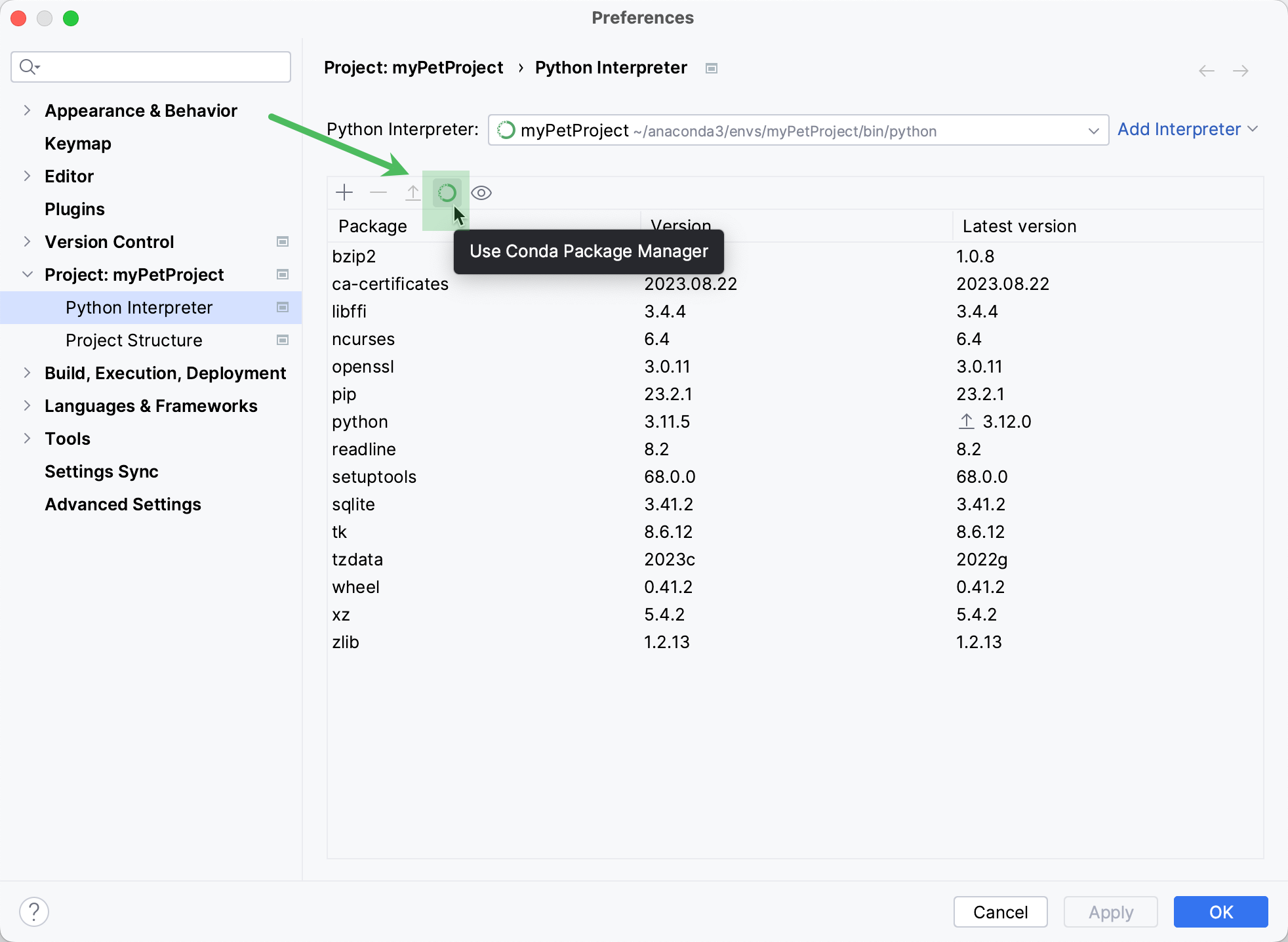
Use this toggle to install and upgrade packages from the conda package repository. This toggle is enabled by default for conda environments.
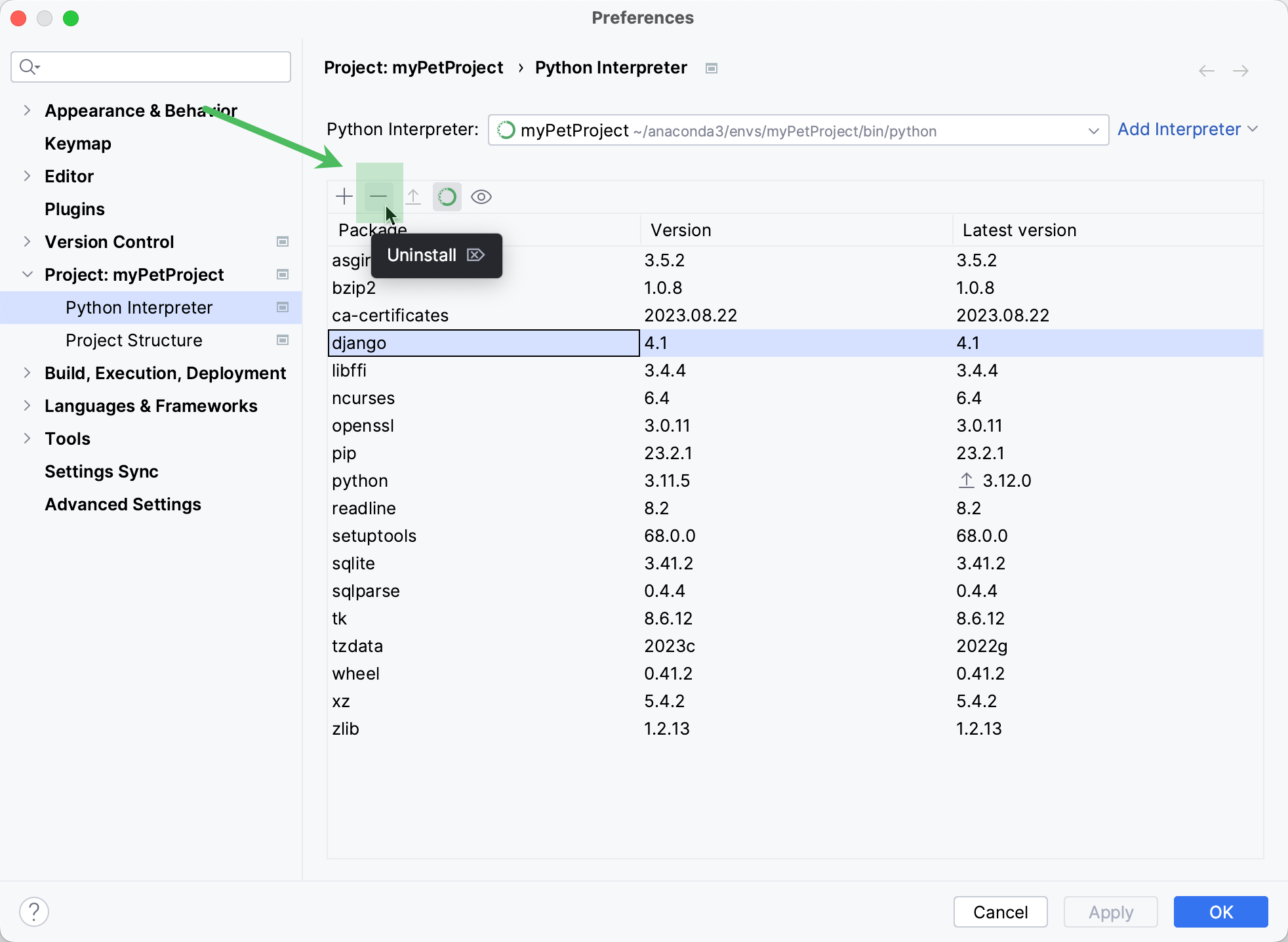
Uninstall packages
In the list of packages, select the packages to be uninstalled.
Click
Uninstall on the toolbar.
PyCharm tracks the status of packages and recognizes outdated versions by showing the currently installed package version (column Version), and the latest available version (column Latest version). When a newer version of a package is detected, PyCharm marks it with the Upgrade icon.
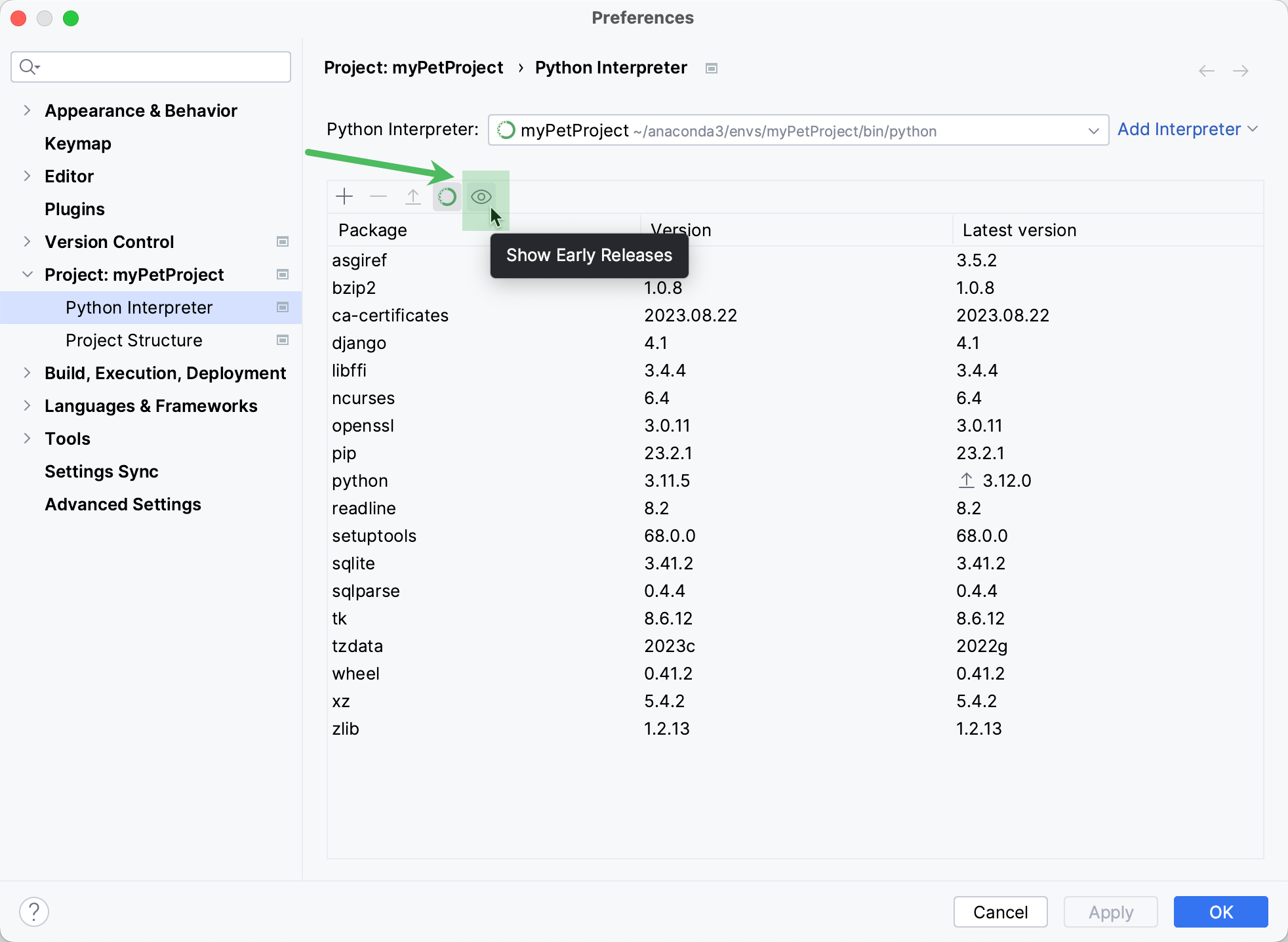
By default, the Latest version column shows only stable versions of the packages. If you want to extend the scope of the latest available versions to any pre-release versions (such as beta or release candidate), click Show early releases.
Upgrade packages
In the list of packages, select the package to be upgraded.
Click
Upgrade on the toolbar.
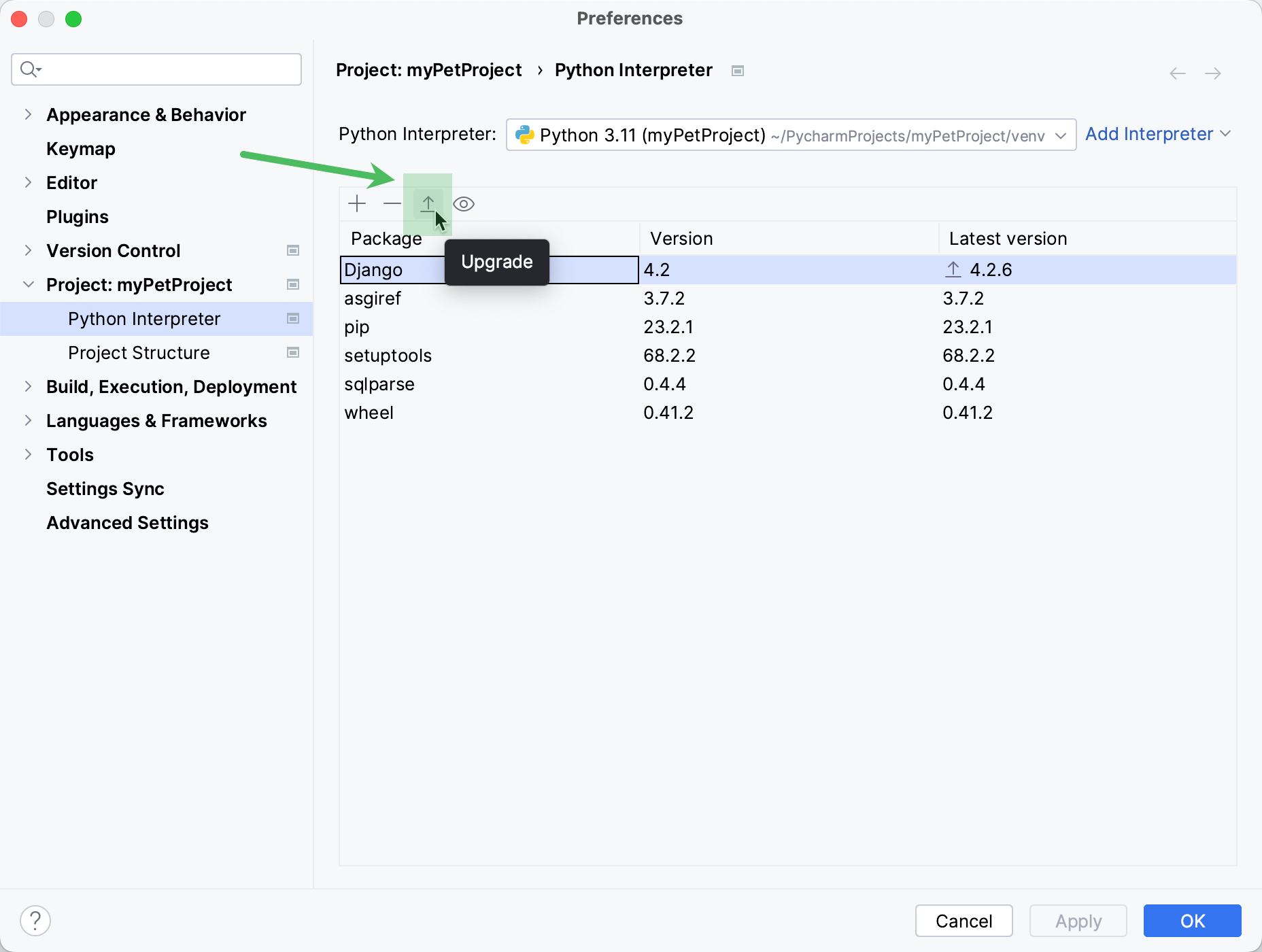
The selected package will be upgraded to the latest available version.
Click OK to complete upgrading.
If you're accustomed to installing packages from the command line, you can proceed with your workflow using the Terminal.
Reuse installed packages
Create a new virtual environment and install packages that you want to be used in other projects. Then you can specify this virtual environment as a Python interpreter for the target project and all the needed packages will be available.
In the Terminal window execute the following command:
pip freeze > requirements.txtThen add the created
requirements.txtfile to the target project and PyCharm will prompt you to install the packages listed in the file.