Attaching to Local Process
On this page:
Introduction
PyCharm makes it possible to attach to a Python process, while running a Python script launched either outside of PyCharm, or inside PyCharm, but NOT in the debug mode.
Prerequisites for Ubuntu users
If you are using PyCharm on Ubuntu (or probably, on some other Linux distribution), upon the first attempt to attach to the local process you can get the ptrace: Operation not permitted. error message. To disable it and enable attach to the local process feature, do the following:
- To disable this restriction temporarily, enter the command:
echo 0 | sudo tee /proc/sys/kernel/yama/ptrace_scope - To disable this restriction permanently, open the file
/etc/sysctl.d/10-ptrace.conffor editing and change the linekernel.yama.ptrace_scope = 1tokernel.yama.ptrace_scope = 0. To apply the changes, entersudo service procps restartor restart your system, at your choice.
You can find more details here.
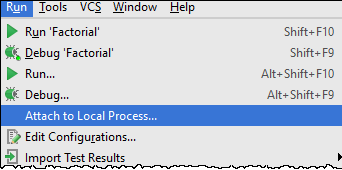
Attaching to local process
To attach to a local process, follow these general steps:
- Launch the process intended for debugging. You can do it from operating system or using the PyCharm terminal.
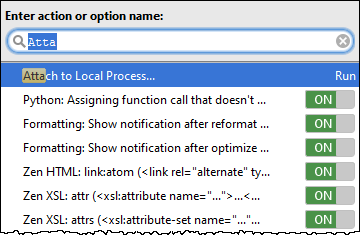
- To find the process to attach to, do one of the following:
- From the list of available processes that appears, select the desired process. Simplify your search by typing the first letters of its name or PID

- Proceed with debugging the same way as you usually do it in PyCharm (set breakpoints, step through, pause and resume the process, evaluate expressions etc.)
- When finished, detach the process: select the or click the Stop the process button
 of the Debug Tool Window .
of the Debug Tool Window .
See Also
Reference:
Last modified: 26 July 2017