Run/Debug Configuration: Node.js
Create:
The following Node.js versions are supported in PyCharm 2023.3 and later:
Node.js 22 - the Active Long Term Supported (LTS) version
Node.js 24 - the current version
Learn more from Supported Node.js versions.
In this dialog, create configurations for starting the debugger together with your Node.js applications on your computer.
Before you start
Download and install Node.js.
Install the Node.js plugin on the Settings | Plugins page, tab Marketplace, as described in Installing plugins from JetBrains Marketplace.
Configuration tab
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Node runtime | In this field, specify the Node.js runtime to use. This can be a local or remote Node.js runtime or a Node.js on Windows Subsystem for Linux. Select a runtime from the list or click |
Node parameters | In this field, type the Node.js-specific command-line options to be passed to the Node.js executable file. The most common options are:
For a full list, refer to Node.js command-line options. |
Working directory | In this field, specify the working directory of the application. By default, the field shows the project root folder. |
JavaScript file | In this field, specify the path to the main file of the application that starts it (for example, bin/www for Express applications). If you are going to debug CoffeeScript, specify the path to the generated JavaScript file with source maps. The file can be generated externally or through compilation using File Watchers. For more information, refer to Debugging CoffeeScript. |
Application parameters | In this field, type the Node.js-specific arguments to be passed to the application on start through the process.argv array. |
Environment variables | In this field, specify the environment variables for the Node.js executable file, if applicable. Click Browse
The definitions of variables are displayed in the Environment variables read-only field with semicolons as separators, for example:
|
Docker container settings | This read-only field shows port and volume bindings. Click 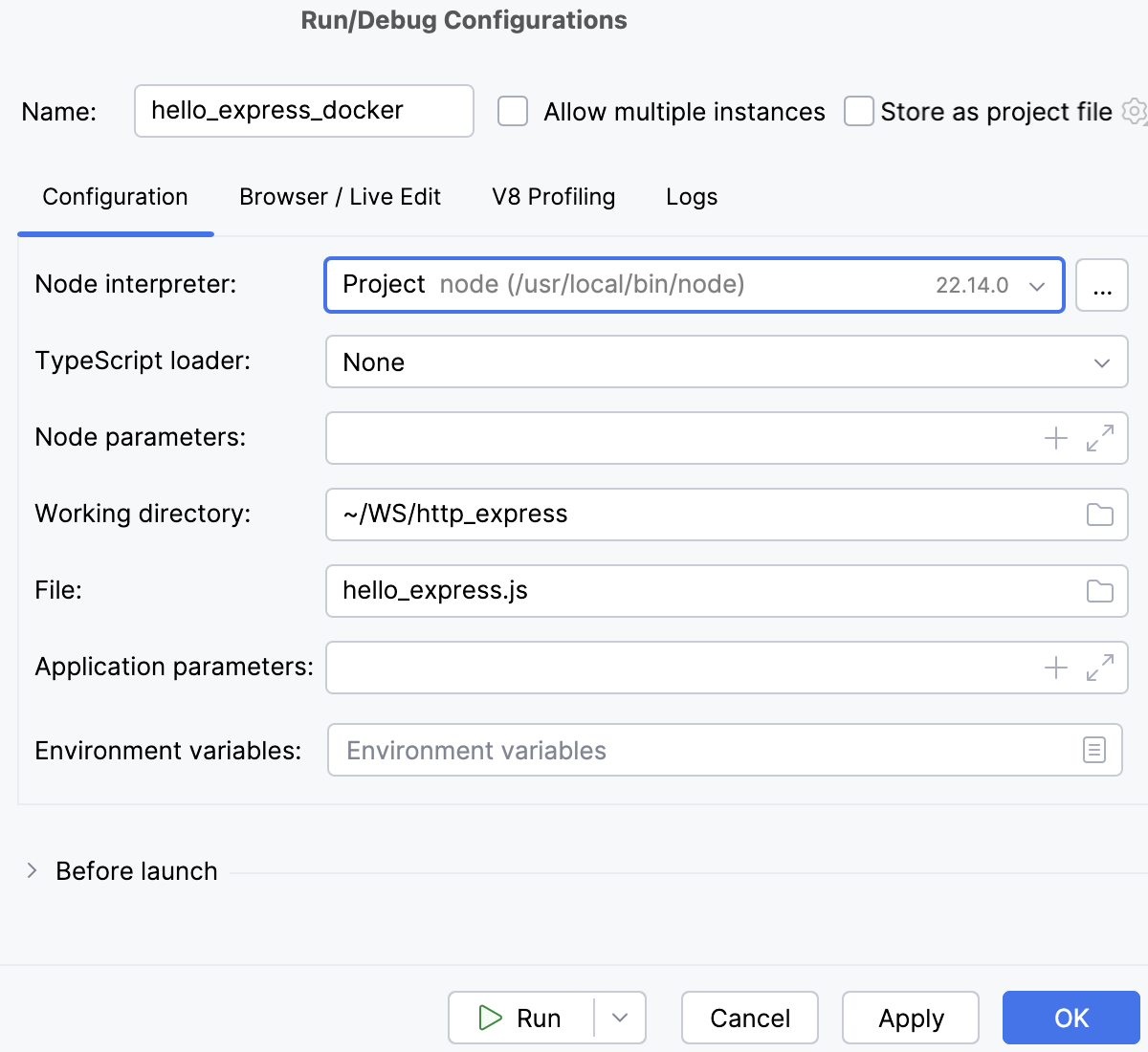 |
Docker Compose | In this area, specify the commands and options to be passed to Docker Compose. Accept the default settings or click Check the Command Preview. |
Browser / Live Edit tab
In this tab, configure the behaviour of the browser and enable debugging the client-side code of the application. This functionality is provided through a JavaScript Debug run configuration, so technically, PyCharm creates separate run configurations for the server-side and the client-side code, but you specify all your settings in one dedicated Node.js run configuration.
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Open browser | In the field in this area, specify a project HTML file to create a correct URL to this file according to the project root to be started on the built-in web server. For example, if you choose project_root/inner_folder/index.html the resulting URL will be http://localhost:63342/project_root/inner_folder/index.html. If you select the After Launch checkbox, the browser will open this page automatically after the application starts. Alternatively you can view the same result by opening the page with this URL address in the browser of your choice manually. |
After launch | Select this checkbox to automatically open the browser. From the list, select the browser to use:
|
with JavaScript debugger | Select this checkbox to enable debugging the client-side code in the selected browser. |
V8 Profiling tab
In this tab, enable V8 CPU and memory profiling.
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Record CPU profiling info | Select this checkbox to start logging the CPU profiling data when the application is launched. The controls in the area below become enabled. Specify the following:
|
Allow taking heap snapshots | Select this checkbox if you are going to run memory profiling. |
Logs tab
In this tab, enable showing information produced by a logging tool like morgan in the Console tab of the Run tool window. For more information, refer to Managing logs when running a Node.js app.
Common settings
When you edit a run configuration (but not a run configuration template), you can specify the following options:
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Name | Specify a name for the run configuration to quickly identify it among others when editing or running. |
Allow multiple instances | Allow running multiple instances of this run configuration in parallel. By default, it is disabled, and when you start this configuration while another instance is still running, PyCharm suggests stopping the running instance and starting another one. This is helpful when a run configuration consumes a lot of resources and there is no good reason to run multiple instances. |
Store as project file | Save the file with the run configuration settings to share it with other team members. The default location is .idea/runConfigurations. However, if you do not want to share the .idea directory, you can save the configuration to any other directory within the project. By default, it is disabled, and PyCharm stores run configuration settings in .idea/workspace.xml. |
Toolbar
The tree view of run/debug configurations has a toolbar that helps you manage configurations available in your project as well as adjust default configurations templates.
Item | Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|---|
Alt+Insert | Create a run/debug configuration. | |
Alt+Delete | Delete the selected run/debug configuration. Note that you cannot delete default configurations. | |
Ctrl+D | Create a copy of the selected run/debug configuration. Note that you create copies of default configurations. | |
The button is displayed only when you select a temporary configuration. Click this button to save a temporary configuration as permanent. | ||
Move into new folder / Create new folder. You can group run/debug configurations by placing them into folders. To create a folder, select the configurations within a category, click Then, to move a configuration into a folder, between the folders or out of a folder, use drag or To remove grouping, select a folder and click | ||
Click this button to sort configurations in the alphabetical order. |
Before launch
In this area, you can specify tasks to be performed before starting the selected run/debug configuration. The tasks are performed in the order they appear in the list.
Item | Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|---|
Alt+Insert | Click this icon to add one of the following available tasks:
| |
Alt+Delete | Click this icon to remove the selected task from the list. | |
Enter | Click this icon to edit the selected task. Make the necessary changes in the dialog that opens. | |
Alt+Up Alt+Down | Click these icons to move the selected task one line up or down in the list. The tasks are performed in the order that they appear in the list. | |
Show this page | Select this checkbox to show the run/debug configuration settings prior to actually starting the run/debug configuration. | |
Activate tool window | By default this checkbox is selected and the Run or the Debug tool window opens when you start the run/debug configuration. Otherwise, if the checkbox is cleared, the tool window is hidden. However, when the configuration is running, you can open the corresponding tool window for it yourself by pressing Alt+4 or Alt+5. |