Creating a Flask Project
Flask project in intended for productive development of the Flask applications. PyCharm takes care of creating the specific directory structure, and settings.
To create a Flask project, follow these steps
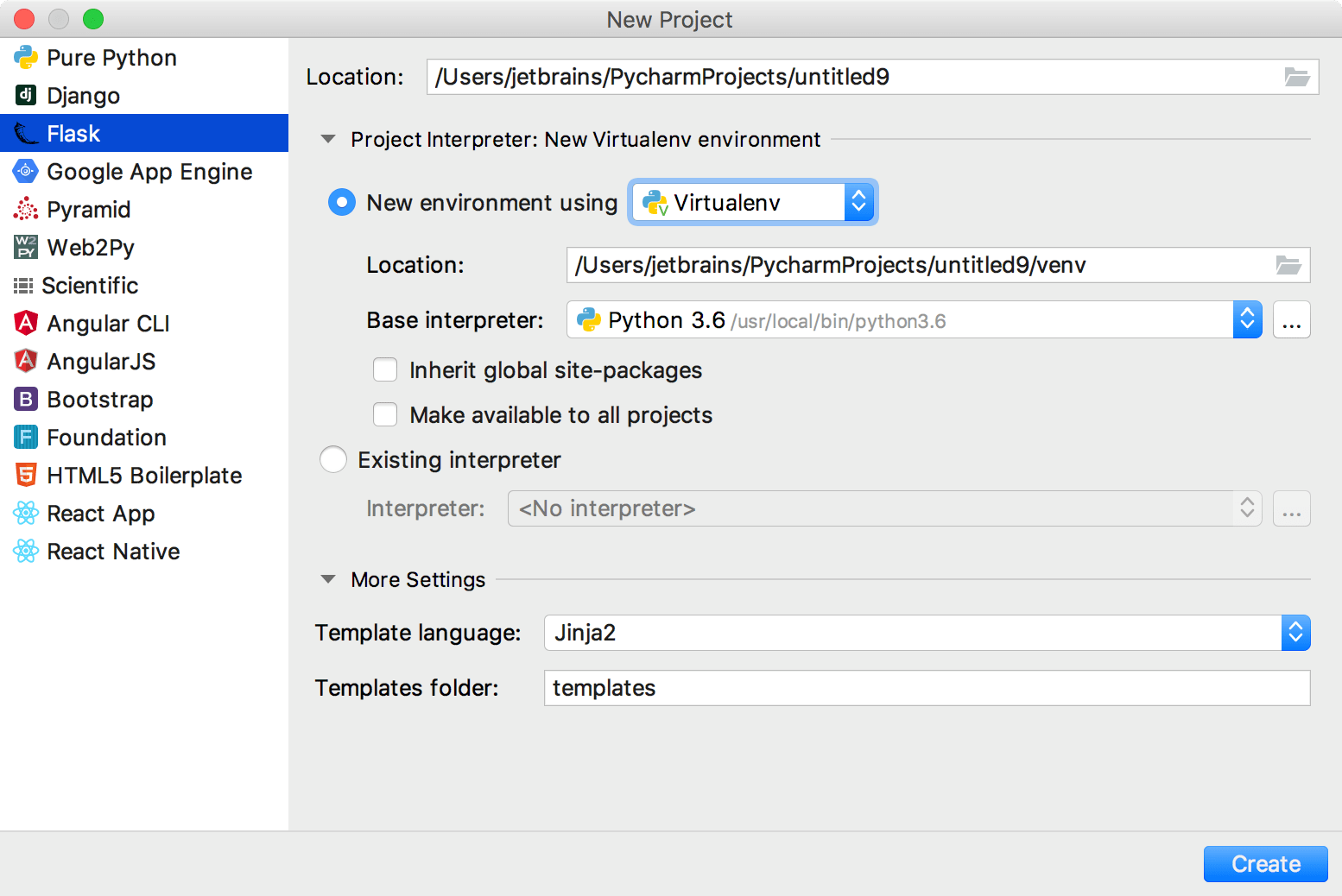
From the main menu, choose , or click the New Project button in the Welcome screen. New Project dialog opens.
-
In the New Project dialog, do the following:
Specify project type Flask.
Specify project location.
-
Next, click
 to expand the Project Interpreter node, and select the new environment or existing interpreter, by clicking the corresponding radio-button.
to expand the Project Interpreter node, and select the new environment or existing interpreter, by clicking the corresponding radio-button.The following steps depend on your choice:
-
New environment using: if this option has been selected, choose the tool to be used to create a virtual environment. To do that, click the list and choose Virtualenv, Pipenv, or Conda.
Next, specify the location and base interpreter of the new virtual environment. If necessary, click the Inherit global site-packages and Make available to all projects check boxes.
When you configure a project Python interpreter, you need to specify the path to the Python executable in your system. So, before configuring a project interpreter, you need to ensure that you've downloaded Python and installed it in your system and you're aware of a path to it. You can create several project interpreters based on the same Python executable. This is helpful when you need to create different virtual environments for developing different types of applications. For example, you can create one virtual environment based on Python 3.6 to develop Django applications and another virtual environment based on the same Python 3.6 to work with scientific libraries.
Existing interpreter: if this option has been selected, choose the desired interpreter from the list, or (if the desired interpreter is not found), click
 and choose the interpreter. See Configure a Python interpreter for details.
and choose the interpreter. See Configure a Python interpreter for details.
-
-
Click
 (More Settings), and specify the following:
(More Settings), and specify the following: From the list, select the template language to be used.
In the Templates folder field, specify the directory where the templates will be stored, and where they will be loaded from. You can specify the name of the directory that doesn't yet exist; in this case, the directory will be created.
Click Create.
You can run the created application by right-clicking app.py and choosing Run 'Flask Project(app.py)'. Preview the run results.
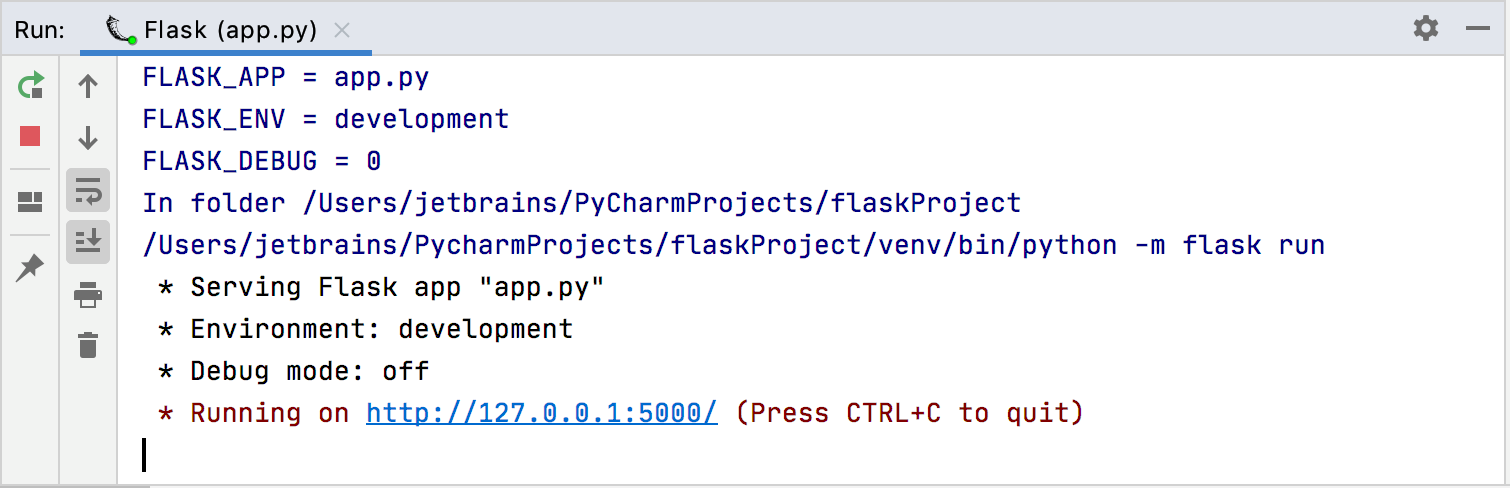
Note that the application was run with the following Flask specific variables:
-
FLASK_APP=app.py– Defines an entry point of the Flask application - the target instance of theFlaskclass. When extending your Flask application and adding more modules and files, you might need to pass some non-defaultFLASK_APPvalues. You can pass a module name, a path to the target Python file, or any combination of modules, scripts, andFlaskclass instances, for example,FLASK_APP=access_management.access:app2, where:access_management– the module nameaccess– the target file in the moduleapp2– theFlaskclass instance inaccess.
For more information about the
FLASK_APPvariable, refer to Flask CLI documentation. FLASK_ENV=development– Sets one of possible environments.FLASK_DEBUG=0– Controls the built-in Flask debug mode. With this mode enabledFLASK_DEBUG=1, the development server will be automatically reloaded on any code change enabling continuous debugging. For more information about Flask debugger, refer to Flask Debug Mode.
You can change Flask specific variables by editing the corresponding parameters of the Flask Server Run/Debug configuration.
Support for Flask in PyCharm is managed by the corresponding option in the project (Ctrl+Alt+S).