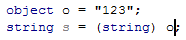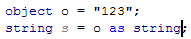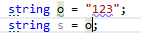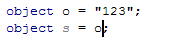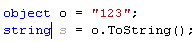Examples of quick-fixes
Quick-fixes are available in a variety of circumstances, which is too large to be listed. ReSharper provides a total of more than 1200 quick-fixes in all supported languages. Here we will show how to use them using a small selection of situations:
Type mismatch
Whenever the type of an expression cannot be implicitly cast to the type applicable to the expression context, ReSharper detects this error and highlights it in the editor. After placing the caret at the highlighted error and pressing Alt+Enter, you can choose a quick-fix from the following list:
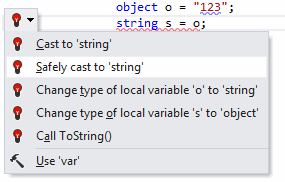
The effects of applying the proposed quick-fixes are illustrated in the table below.
Quick-fix | Effect |
|---|---|
Cast to | |
Safely cast to | |
Change type of | |
Change type of | |
Call |
Undefined variable
Whenever ReSharper detects an undefined variable in your code, the error is highlighted. After placing the caret at the highlighted error and pressing Alt+Enter you will be presented with the following list of quick-fixes:
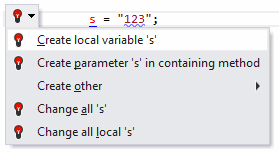
The effects of applying the proposed quick-fixes are illustrated in the table below.
Quick-fix | Effect |
|---|---|
Create local variable | A new local variable |
Create parameter | A new parameter is added to the method signature:  |
Create other | Opens a sub-menu where you can choose to create a field or a property in the corresponding class. For example, if you choose to create a field, a new private field 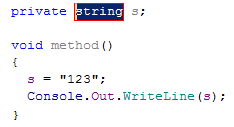 |
Change all | If you choose Change all, the following suggestion displays: 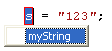 Type the new name only once; ReSharper changes all the other occurrences of the undefined variable: |
Undefined method call
Whenever ReSharper detects a call to an undefined method in your code, the error gets highlighted. After placing the caret at the highlighted error and pressing Alt+Enter, ReSharper displays the following list of quick-fixes:
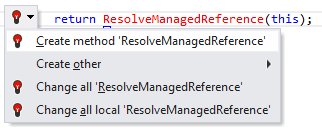
After applying a quick-fix, the code gets modified as shown in the following table:
Quick-fix | Effect |
|---|---|
Create method | This quick-fix declares a new method with the signature derived from the method call, benefiting developers who prefer top-down programming. In our example, ReSharper creates the following declaration, correctly guessing the return type:  ReSharper also suggests applicable types and a name for the parameter of the new method: 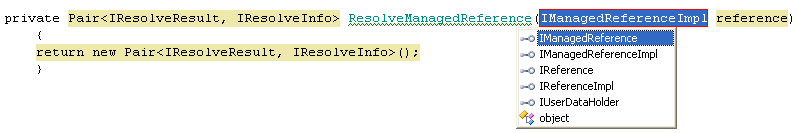 |
Create other | This sub-menu includes other quick-fixes involving creation of auxiliary code. For example:
|
Change all | Similarly to the corresponding quick-fix for undefined variables, this quick-fix allows you to quickly replace all occurrences of the symbol |
Forgotten method return
If a method is expected to return a value but you forgot to provide a return statement, ReSharper warns you about that by highlighting the closing bracket of the troublesome method. After placing the caret at the highlighted error and pressing Alt+Enter you will be presented with the following quick-fixes:
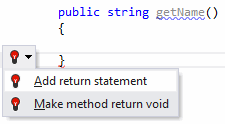
Quick-fix | Effect |
|---|---|
Add return statement | After the quick-fix is applied, ReSharper adds a |
Make method return void | After the quick-fix is applied, ReSharper replaces the initial return type of the method with |
Missing Using directives
Whenever you have a type name in your code that cannot be resolved because you forgot to write a corresponding using directive in your file, a small popup suggests to import the type:

Press Alt+Enter, and the appropriate using directive will be inserted. Should there be multiple types with the matching name, you will be asked to choose the one you wish to use (For more information, refer to Importing Namespaces).
If you chose not to import a required namespace when the popup was displayed, or if you disabled Show the 'Import missing references' popup in editor on the page of ReSharper options Alt+R, O, you can import a type at any time by placing the caret at the type, pressing Alt+Enter and choosing the corresponding quick-fix.
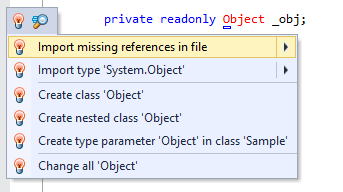
You may want some types or namespaces not to be suggested, for example, if you have something similar to a system type in your solution, say MyFramework.MyCollections.List, but you are not actually using it. To exclude such items from the suggestions, add them to the Exclude from import and completion list on the page of ReSharper options Alt+R, O.
The format of the entries is Fully.Qualified.Name, Fully.Qualified.Name.Prefix*, or *Fully.Qualified.Name.Suffix. Generic types are specified as List`1.
Missing async modifier
If you have a method that contains the await operator, but that is not defined as asynchronous, ReSharper detects such mismatch and offers to fix this problem using the corresponding quick-fix.
Before: |  |
Applying the quick-fix: | 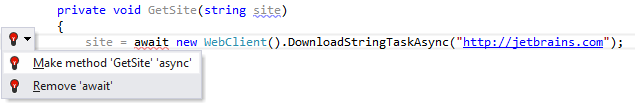 |
After: | 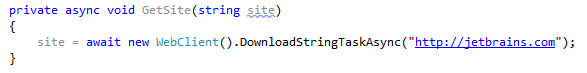 |
Converting a loop to a LINQ expression
With C# 3.0 and LINQ, developers are able to write data-intensive code more easily by directly describing their intent to the compiler. ReSharper detects code that can be rewritten using LINQ syntax and offers to perform the conversion automatically:
Before: |  |
Applying the quick-fix: | 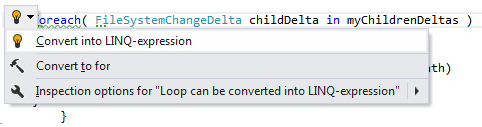 |
After: |  |
Migrating to IEnumerable in method parameters and returns
ReSharper scans your code base to detect methods that can safely return and accept IEnumerable instead of a more specific type such as Array, List, or ArrayList:
Before: | 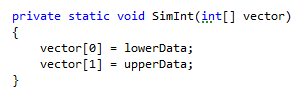 |
Applying the quick-fix: | 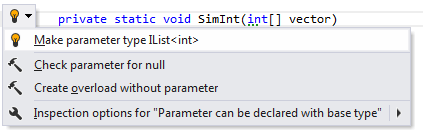 |
After: | 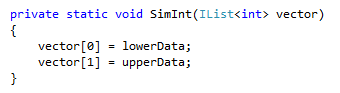 |
Converting assignment statements to object initializers
ReSharper provides both a context action and a quick-fix to convert assignment statements into object initializers. The context action lets you add field assignments to an initializer one-by-one, whereas the quick-fix adds them all in one go. Here's how the quick-fix works:
Before: | 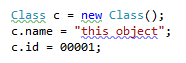 |
Applying the quick-fix: | 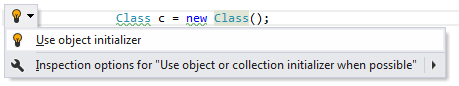 |
After: |
|
Converting static method invocation to extension method call
When you invoke an extension method as a traditional C# static method, ReSharper helps you quickly comply with standard extension method call practices:
Before: | |
Applying the quick-fix: | 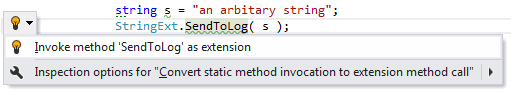 |
After: |
Converting anonymous method to lambda expression
ReSharper suggests converting anonymous methods to lambda expressions. The reverse functionality is provided as a context action.
Before: |
|
Applying the quick-fix: | 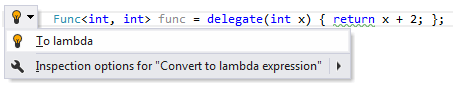 |
After: |
|
Converting to auto-property
ReSharper makes it quick to convert traditional, private field-based properties to automatic properties implemented in C# 3.0. For more information, refer to Use auto-properties.
Before: | 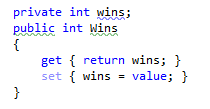 |
Applying the quick-fix: | 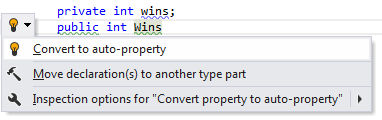 |
After: |
|
Making type parameter invariant
When a usage of a type parameter violates its variance, ReSharper suggests to make the parameter invariant:
Before: |  |
Applying the quick-fix: | 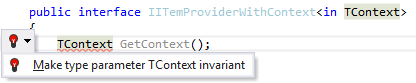 |
After: |  |