Speeding up ReSharper (and Visual Studio)
There are two major sources of performance problems with ReSharper installed in Visual Studio:
- Your system does not meet the requirements. In this case, we suggest you to upgrade your system as the first step of dealing with the problems.
We constantly make sure that ReSharper works fine on modern hardware and with medium- and large-size solutions without any tweaking. We believe that Visual Studio developers are working towards the same things.
By trying to speed up ReSharper on outdated hardware by disabling some features, you deprive yourself of great tools that can speed up your development performance. - Visual Studio and ReSharper, which share the same 32-bit process push your system to its limits. Often, this is reported to happen on large-size solutions and when ReSharper is installed to Visual Studio 2015.
In this case, provided your system meets the requirements, the check-list below will help you fix performance problems in most cases.
A significant time (up to several minutes) taken for opening a large solution for the first time is not a sign of a problem. ReSharper builds and caches a model of the solution, which is then used in almost all of its features - not only for code analysis, but also for navigation and search, code completion, unit testing and more.
Subsequent openings of this solution will not result in any significant delays because the indexing results are already cached on your hard drive.
Note that because ReSharper processes assembly annotations at the very first start, any subsequent start will be faster even if you clean up ReSharper caches.
In this topic:
- Try this first
- Hardware check-list
- Recommended system software adjustments
- Visual Studio
- ReSharper
- Known Performance Problems
- Known Compatibility Problems
Try this first
The most common causes of performance problems could be eliminated with the following actions:
- If you do not use solution-wide analysis, disable it or consider disabling warnings in solution-wide analysis. Even if it is disabled, you can find all code issues in your solution at any time by running code inspection for the whole solution. To configure solution-wide analysis, go to .
- In Visual Studio options, go to : select None for the source control plug-in. This will turn off Git or another VCS provider and improve overall performance.
- Review Visual Studio settings and disable features that you do not use.
Hardware check-list
- Make sure there is no hardware interrupts and DPCs (usually caused by bad drivers and/or virtualization).
- Make sure your hard drive is not fragmented.
- Make sure the pagefile is at least 1GB.
- Make sure you have at least 15% free disk space (MFT fragmentation/running out of space risk).
- Make sure you have at least 4GB RAM free.
- Storing the solution and ReSharper caches on an SSD would help, while a RAMDisk would not make a big difference.
Recommended system software adjustments
- Use a Windows version currently supported by Microsoft
- Keep Windows updated
- Use 64-bit operating system
- Add the devenv.exe, msbuild.exe and your code folder to the ignore list of Windows Defender (and other antivirus software).
- Stop unnecessary services and processes
Visual Studio
Before starting to tweak Visual Studio settings, check that the most recent Visual Studio update / service pack / hot fixes are installed.
Configuring Visual Studio preferences
Open Visual Studio options () and configure the preferences as follows:
- : disable Automatically adjust visual experience based on client performance, disable Enable rich client visual experience, enable Use hardware graphics acceleration if available. These adjustments will reduce UI lags and improve overall performance.
- : select None for the source control plug-in. This will turn off Git or another VCS provider and improve overall performance.
- : choose to show empty environment at startup and disable downloading content. Turning off the start page and the news channel might save some time on startup.
- : disable Save AutoRecover information. This will reduce disk operations.
- : disable Track changes. This will reduce disk operations.
- : disable Show annotations over vertical scroll bar. This will reduce editor lags.
- : disable CodeLens. This will improve overall performance.
- : disable Just-In-Time Debugging for Script. This will speed up build and debug.
- : disable Web Forms Designer. This will reduce UI and editor lags.
- : disable XAML Designer. This will reduce UI and editor lags.
- : disable all auto-formatting preferences. If you use ReSharper's formatting assistance, this will prevent your code from being reformatted twice and reduce editor lags.
- : if you use File Structure window, then you probably don't use the navigation bar on top of the editor and you can safely disable it on this options page.
- : disable synchronization of settings. This will improve overall performance.
Configuring Roslyn
In most of reported performance problems, ReSharper was installed in Visual Studio 2015. This is no surprise: when your Visual Studio solution grows large, two code analysis engines (ReSharper and Roslyn) working simultaneously can reach the memory limit of the 32-bit process that they share.
Although there is no official way to disable Roslyn, you can check out this article to find some alternative solutions.
You can also take a look at Roslyn performance considerations for large solutions.
Other Visual Studio adjustments
- Uninstall unused packages and extensions from Visual Studio
- If you are not working on some projects, you can unload them from Visual Studio and reload them back when needed. Right-click on the project or a solution folder in the Solution Explorer and choose Unload Project or Unload Projects in Solution Folder - this will improve overall performance.
ReSharper
Before starting to tune up ReSharper, check that you are running the latest version, and if not, consider updating.
Configuring ReSharper preferences
ReSharper provides plenty of different features, and if necessary, you can disable most of them in ReSharper options. So the general rule here is: if you have any performance problems, disable features you do not use.
Open ReSharper options () and configure the preferences as follows:
- : on this options page, you can disable various aspects of code inspection. Here is what you can disable, starting from minimum disabled features:
- In Visual Studio 2015 and later versions, clear the Do not show Visual Studio bulb... check box. This will prevent ReSharper from triggering Roslyn analyzers and thus will reduce CPU usage.
- If you do not use solution-wide analysis, disable it or consider disabling warnings in solution-wide analysis. Even if it is disabled, you can find all code issues in your solution at any time by running code inspection for the whole solution.
-
If there is any source code in your solution that you do not need to analyze, add the corresponding files and folders to the ignore list.
You can add the the current file to the ignore list by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Alt+8. Pressing the shortcut again will re-enable the inspection for this file. If you want to bind a different shortcut for this operation, look for the
ReSharper_EnableDaemoncommand in Visual Studio option. - The ultimate step is to clear the Enable code analysis check box. This will disable the design-time inspection, but you will still be able to run code inspection in the desired scope when you need it.
- : here you can disable ReSharper features that you do not use. For example, clearing the Unit Testing check box will disable all ReSharper unit testing features and save some memory.
- : in the Store solution caches in: selector, choose 'System TEMP' or any custom folder. If your solution is not under a VCS, you can also choose 'Solution folder'. It is not recommended to choose 'User local settings folder' (%LOCALAPPDATA%) The problem with this folder is that Visual Studio's directory watcher is triggered each time ReSharper writes to this folder, which happens very often.
- : you may need to configure this if you experience slowdowns on typing. Similarly to code inspection, you can disable specific parts of ReSharper IntelliSense or turn it off completely and fall back to native Visual Studio's IntelliSense. Here is what you can disable, starting from minimum disabled features:
- : disable Auto-format on semicolon and Auto-format on closing brace to avoid reformatting code while typing; also disable Correct common language-specific typos, which will turn off some typing assist features. Clearing these check boxes will speed up typing.
- : disable Highlight current line, Highlight matching delimiters. This might reduce the chance of UI and editor lags.
- : disable ReSharper extensions that you do not use.
- : enable ReSharper build. ReSharper's incremental build can considerably reduce build time, especially for large solutions.
- : here you can disable the context actions that are not helpful to you.
- : if you work with JavaScript and have some performance problems, do not enable the Analyse properties' context when inspecting code option.
- : here you can add C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, CSS, HTML and JSON files, folders and wildcards to be treated either as 'skipped' or 'library'. ReSharper will completely ignore 'skipped' files, and treat 'library' files as read-only – indexed for navigation, but no inspections, quick-fixes and refactorings.
- : on this page, you can disable automatic language injections that are of no interest to you.
Do not overuse complex UI controls
- Close unused unit tests sessions.
- Close unused type, project, and assembly dependency diagrams.
- If you enable solution-wide analysis, you can close the Errors/Warnings in Solution window as you will see the number of errors/warnings in the status bar anyway.
Other adjustments
- To speed up expanding code templates, you can turn off the Reformat and Shorten qualified references options for templates that you use:
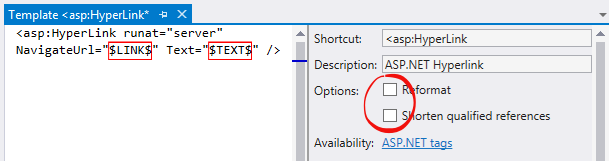
- Close Process Explorer window when you do not use it.
If nothing helps
If you've tried out everything described above and the performance is still down, you can temporarily disable ReSharper and check whether it was the cause of the slowdown. To disable/enable ReSharper, go to and click Suspend Now/Resume Now.
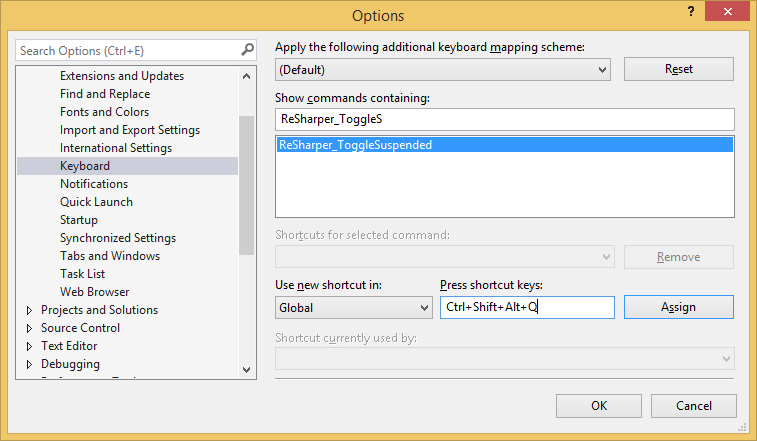
If suspending ReSharper helps improve the performance but you still want to use it occasionally for code analysis, code cleanup or reformatting code, you might want to have a shortcut that quickly switches ReSharper on and off. Here is how to do it: go to and find the ReSharper_ToggleSuspended command, then press a shortcut of your choice and click Assign.
Known Performance Problems
If you have recently updated ReSharper and observe performance degradation with solutions that were opened with previous versions, you can attempt to speed thing up by clearing the ReSharper caches and deleting the solution .suo file.
To clear the caches, go to and click Clear Caches.
Known Compatibility Problems
Other Visual Studio extensions
Major compatibility issues have been observed with the following products:
- DevExpress CodeRush/Refactor Pro (incompatible)
- Telerik JustCode (incompatible)
- Whole Tomato Visual Assist
- Productivity Power Tools
Performance degradation has been observed with the following products:
There are also reports on Web Essentials contributing to low performance while editing .cshtml files. If you're affected by this problem, consider going to and setting Auto-format HTML on Enter to False.
Parallels Desktop for Mac
If you're running Visual Studio in a Windows virtual machine on your Mac using Parallels Desktop, ReSharper IntelliSense lists might be very slow to render.
If this occurs in your setup, consider switching from Coherence mode to Full Screen mode. For guidelines on switching between the two modes, please see this Parallels Knowledge Base entry.