Exploring Type Hierarchy
Ctrl+Alt+H
ReSharper_TypeHierarchyBrowse
With ReSharper, you can investigate the inheritance hierarchy of types. You can see both base types and inheritors of the selected type and navigate to any of them with a mouse click. For any node in the hierarchy, you can view all or only polymorphic members in the preview pane.
To investigate hierarchy
- Open the desired type in the editor or expand it in the Solution Explorer, and place the cursor on the type or a type member.
- Press Ctrl+Alt+H or choose in the main menu.
- Examine type hierarchy in the dedicated tab that adds to the Hierarchy window.
Some symbols in the tree are displayed in a bold font. It means that they inherit directly from the type being examined.
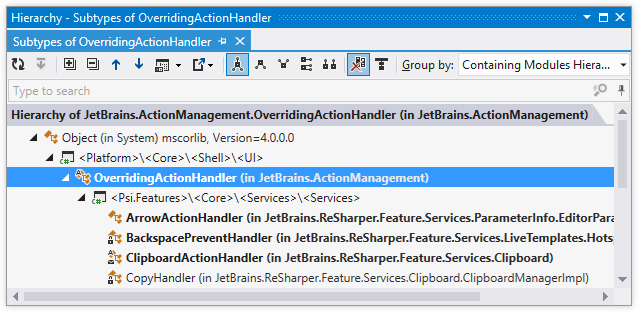
Hierarchies can be rather complicated, making it difficult to find one particular symbol, especially when you have doubts about its name and place in the hierarchy. In such case you can start typing a part of symbol's name or its CamelHumps abbreviation and ReSharper narrows down the set of elements in the window: 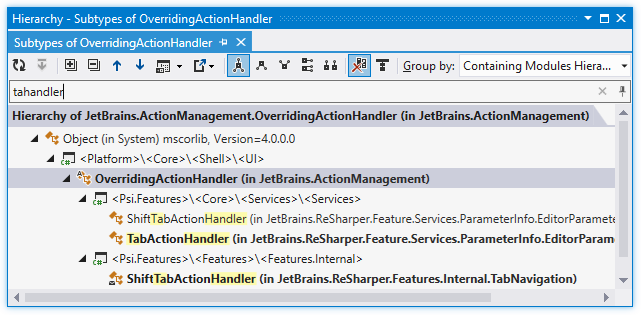
You can also visualize the current hierarchy on the type dependency diagram by clicking the Show on Diagram ![]() on the toolbar.
on the toolbar.
To rebuild a hierarchy for an intermediate node
- In the hierarchy tree view, select the desired node.
- Click Base on This
 on the toolbar or choose the corresponding command in the context menu of the selection.
on the toolbar or choose the corresponding command in the context menu of the selection.
To preview members of a type selected in the hierarchy
- Select a type in the hierarchy.
- Click Show Members
 on the toolbar or press Ctrl+P. The members preview pane displays at the bottom of the window:
on the toolbar or press Ctrl+P. The members preview pane displays at the bottom of the window: 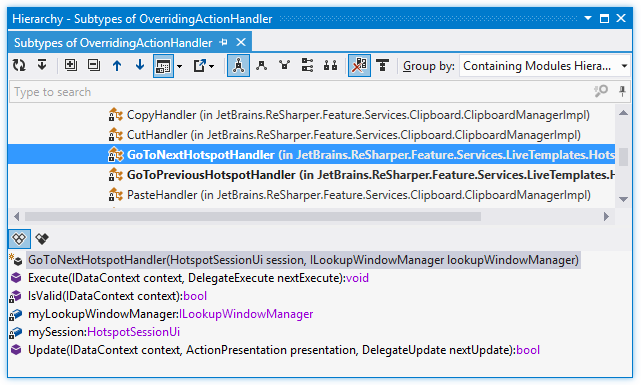
- You can move the preview pane to the right of the window by clicking the down arrow next to Show Members
 on the toolbar and selecting Right.
on the toolbar and selecting Right. - You can also preview either all members of a type, or just those that are polymorphic. To switch between these two modes, use the All Instance Members
 and Only Polymorphic Members
and Only Polymorphic Members  buttons at the top of the preview pane.
buttons at the top of the preview pane.
This feature is supported in the following languages and technologies:
The instructions and examples given here address the use of the feature in C#. For details specific to other languages, see corresponding topics in the ReSharper by Language section.