Configuring Project-Specific Properties
ReSharper_EditProjectItemProperties
The main set of ReSharper preferences (configured in the ReSharper | Options dialog) apply either globally or per solution. There are also some preferences that can be configured for each project or folder separately. These preferences are available in the Project Item Properties popup, which you can invoke by selecting Edit project item properties from the context menu of the project in the Solution Explorer.
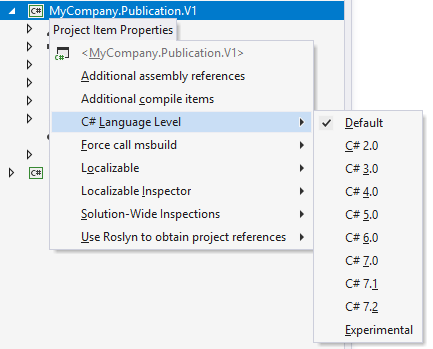
Similarly to other ReSharper settings, project-specific properties can be saved in two files: [ProjectName].csproj.DotSettings (intended for common preferences, like C# version) and [ProjectName].csproj.DotSettings.user (intended for personal preferences, like local path mapping). If necessary, you can share the common preferences with your team by putting the [ProjectName].csproj.DotSettings file under source control.
When you edit project-specific settings from the UI, they are saved in the [ProjectName].csproj.DotSettings file.
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Namespace provider | Only available on folders. By default, ReSharper assumes that the namespace each class appears in matches its location in the project. The 'root' namespace for the project is defined in the project properties: 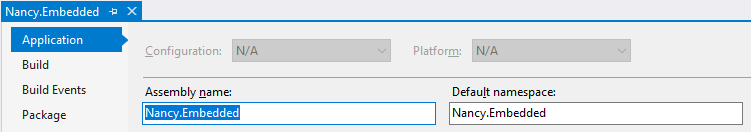 As a result of the above, all code elements at the project level are expected to appear in the Namespaces are made deeper with the introduction of folders. In the example below, a folder called 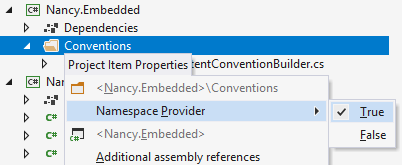 A folder which is not a Namespace Provider will not influence the namespace of elements it contains, and ReSharper will analyze and refactor the related code the accordingly. |
Additional assembly references | If your project references some assemblies in a custom way, ReSharper may not be able to find them and therefore cannot correctly analyze this project. |
Additional compile items | If your project includes files in a custom way, ReSharper may not be able to find them and therefore cannot correctly analyze this project. |
C#/VB Language Level | Use this selector to choose the language version. The Default value means that ReSharper automatically detects the language version based on the project settings. Depending on the selected language version, ReSharper's code inspection detects code issues and suggests improvements relevant to the selected version. |
Force call MsBuild | Use this option to retrieve module references via MsBuild. For example, this may be helpful if there are COM API references and the project is opened in an older Visual Studio version, without Roslyn support. |
Custom pageParseFilterType handling | This property is only available for web projects. |
Localizable | This preference defines whether to perform localization inspection. If the Default value is selected, the inspection is only performed if there is at least one resource file in the project. The Yes and No values allow enabling/disabling this inspection explicitly. |
Localizable inspector | This preference defines the algorithm that ReSharper uses to detect localizable strings; Optimistic or Pessimistic. If the Pessimistic algorithm is chosen, ReSharper looks for localizable strings in all elements, except those which have the attribute |
Path mapping | This property is only available for web projects. |
Solution-Wide Inspections | This preference defines whether the Solution-Wide Code Inspections should be enabled in the project. The On and Off values allow enabling/disabling this inspection explicitly. The Internal symbols only value partly enables this inspection for types and type members with the internal access. |
Use Roslyn to obtain project references | Starting from Visual Studio 2015, ReSharper retrieves project references via Roslyn. If some references are not resolved correctly, you can disable this option so that the references are retrieved via COM API. |