Localization inspections and quick-fixes
ReSharper provides a number of code inspections that help you localize your application by detecting localizable strings, problems with resources and so on, in resource files and resource usages in code files. These inspections detect localization issues in design time in the open documents and allow you to find localization issues in specific scope up to the entire solution.
In design time, detected issues are highlighted to draw your attention. To resolve the highlighted issues, ReSharper provides a number of resource-specific quick-fixes.
'Element is localizable' inspection
This inspection detects hard-coded string literals and suggests moving them to resource files. If the same string is already defined in resources, ReSharper will suggest replacing the literal with the existing resource entry.
As not every string needs to be moved to resources and localized, ReSharper provides several ways to configure this inspection. When the 'Element is localizable' inspection is enabled, it works according to the flow chart below. Each step in the algorithm is explained under the chart.
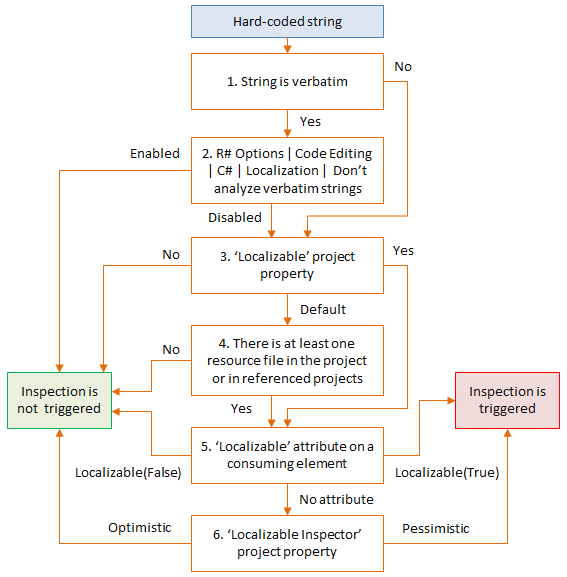
Verbatim strings are prefixed with
@, for example@"Hello world"By default, verbatim strings are ignored by the localization inspection, but you can change it using the Don't analyze verbatim strings option on the page of ReSharper options Alt+R, O.
The Localizable project property defines how to treat strings in a project. To change this property, right-click the project in the Solution Explorer, select Edit project item properties, and then choose Localizable > [Default | Yes | No].
If the current project or any other project that it references contains at least one resource file (.resx), ReSharper will consider the project as localizable by default.
Further configuration is possible for specific functions and properties that can consume string values by marking them with
LocalizableAttribute, which lets you explicitly enable[Localizable(true)]or disable[Localizable(false)]the localization inspection on the consumed strings.Note that symbols could be marked with this attribute via external annotations. For example, external annotations are used to mark
Console.WriteLinewith[Localizable(true)].The Localizable Inspector project property defines how to treat string literals that are not consumed by any member marked with
LocalizableAttribute— Optimistic algorithm will ignore such strings, Pessimistic will flag them as localizable.To change this project property, right-click the project in the Solution Explorer, select Edit project item properties, and then choose Localizable Inspector > [Optimistic | Pessimistic].
The easiest way to disable localization inspection for the current project is to press Alt+Enter over a highlighted string in the editor and use the corresponding command in the action list:
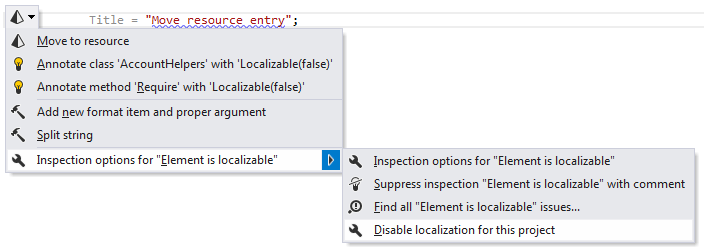
This command sets the Localizable property in the current project to No.
Quick-fixes for localization issues
If a quick-fix is available for a code issue detected with localization inspection, ReSharper displays the corresponding action indicator on the left of your caret. You can press Alt+Enter or click the indicator icon to see the list of available actions, To apply a desired action, click it or select it in the list and press Enter.
Here are some quick-fixes for localization inspections:
Move to resource
This quick-fix invokes Move to Resource refactoring to move localizable string to a resource file. It is available when a string is highlighted with a curly underline.
Use resource entry instead of literal
If ReSharper detects that some string literal is already defined in resources, it suggests to replace the string with the corresponding resource usage:
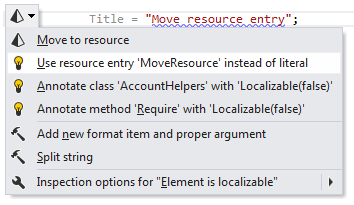
After applying this quick-fix, the string is replaced with the resource usage.
Annotate type with 'Localizable(false)'
This group of quick-fixes lets you add [Localizable(false)] attribute to the selected type or member to suppress the 'Element is localizable' inspection for all usages of this symbol.
Create resource file
If a resource filename is used in a code file, but you haven't created the resource file yet, ReSharper can do it for you. It highlights the resource filename in red and suggests the corresponding quick-fix:
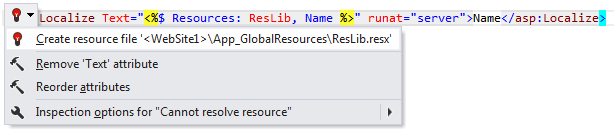
After applying the quick-fix, the missing resource file is created.
Create resource item
If a resource name is used in a code file, but you haven't declared this resource yet, ReSharper can do it for you. It highlights the resource name in red and suggests the corresponding quick-fix:
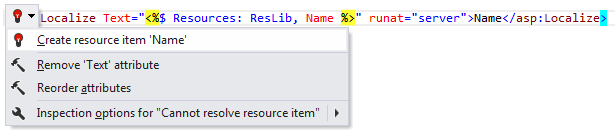
After applying the quick-fix, the missing resource declaration is added in the resource file.
Declare resource entry
If there are several cultures organised in a culture hierarchy, and there is a resource entry that is declared in a culture-specific resource file but is not declared in the default culture, ReSharper highlights the resource declaration and suggests the corresponding quick-fix:
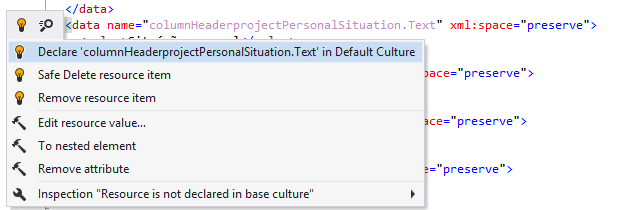
After applying the quick-fix, resource declaration is inserted into the default culture where you can replace its value with a new one.
Override resource entry
If there are several cultures organised in the culture hierarchy and there is a resource entry, which is declared in the default culture but is not overridden in one or more other cultures, ReSharper highlights the name of resource and suggests the corresponding quick-fix(es):
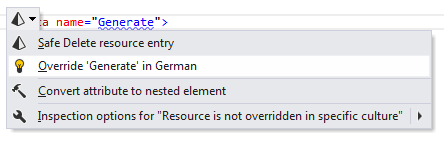
After applying the quick-fix, resource declaration(s) is inserted into the culture-specific resource file(s) where you can specify correct values.
Remove resource entry
ReSharper suggests this quick-fix in the following cases:
A resource entry has equal values in neutral and specific cultures;
There are two or more declarations with the same resource name;
There are several cultures organised in the culture hierarchy and there is resource entry that is declared in specific culture, but is not declared in default culture.
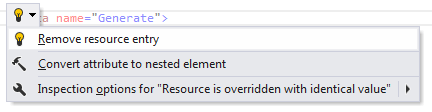
After applying the quick-fix, resource declaration is removed from the current resource file.
Remove redundant resource entry type
Specifying the string type for a resource entry is redundant because it is the default resource entry type. ReSharper will suggest removing the redundant attribute:
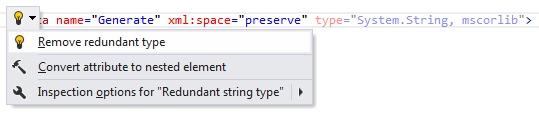
Safe delete
If there are several cultures organised in the culture hierarchy and there is a resource entry, which is declared in the default culture but is not overridden in culture-specific resource files, ReSharper highlights the name of the resource suggests this quick-fix:
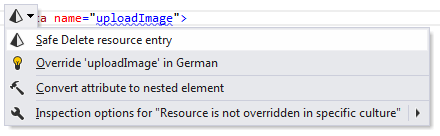
After applying this quick-fix, follow the steps of the Safe Delete Resource refactoring.