Code Syntax Style: Optional Member Qualifiers
In C#, you can qualify instance members with this keyword, and qualify static members with type name or a base type name. These qualifiers help you disambiguate members hidden by local variables or method parameters. In all other cases, these modifiers are optional, and you can decide for yourself whether to use them or not. With ReSharper, you can configure your preferences for using optional modifiers and enforce these preferences.
ReSharper helps you adjust optional member qualifiers in the existing code and takes your preferences into account when it produces new code with code completion and code generation features, applies code templates and performs refactorings.
Enforce style preferences for optional member qualifiers
By default, ReSharper treats all optional member qualifiers as redundant and suggests removing them.
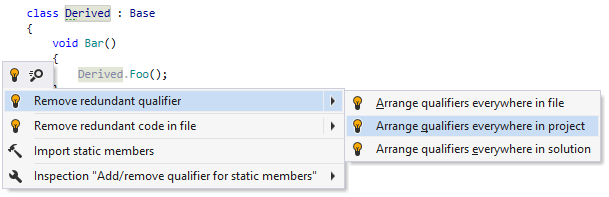
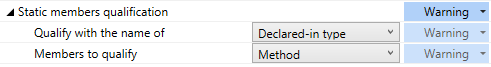
If you prefer to use optional qualifiers, you need to specify it explicitly as described below. For example, you may prefer to qualify static methods with the type where they are declared:
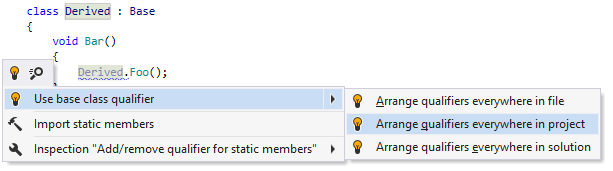
As soon as you change the preferences, ReSharper will treat the same code differently and suggest the corresponding corrections:
Another option to enforce preferences for member qualifiers in a bulk mode is code cleanup. You can either run code cleanup with one of the built-in profiles Full Cleanup or Reformat & Apply Syntax Style, or create and run a custom profile solely targeted at your specific task as described below.
Apply preferences for member qualifiers with custom Code Cleanup profile
Select from the main menu or press Alt+R O.
Go to the cleanup profiles settings page: .
Create a new profile as described in the Create a new custom cleanup profile section. In the Selected profile settings section for the new profile, tick the Arrange qualifiers checkbox. Optionally, you can enable other code cleanup tasks in this profile.
Click Save in the Options dialog to apply the modifications and let ReSharper choose where to save them, or save the modifications to a specific settings layer using the Save To list. For more information, see manage and share resharper settings.
Select the scope where you want to enforce your preferences:
Set the caret anywhere in the file to enforce your preferences to the file.
Select one or more items in the Solution Explorer to enforce your preferences in the files under these nodes and their child items.
Do one of the following:
Press Control+Alt+F or choose from the main menu .
Right-click anywhere in the text editor or right-click the selection and choose Cleanup Code in the context menu.
In the Code Cleanup dialog that opens, select the newly created profile .
Click Run. ReSharper will enforce your preferences in the selected scope.
If you want to apply preferences for member qualifiers without opening the Code Cleanup dialog to choose a profile, you can bind the created profile to the silent cleanup and run it by pressing Control+Shift+Alt+F. You can also create a custom cleanup profile that would combine applying the preferences with other code style tasks.
To apply preferences for optional member qualifiers together with all other formatting and syntax style rules to the selected code block, Alt+Enter and choose .
You can adjust optional member qualifiers every time you save changes in a file to make sure that your edits always comply with your code style.
Automatically adjust optional member qualifiers on saving changes
Select from the main menu or press Alt+R O.
Go to the cleanup profiles settings page: .
Select your custom Code Cleanup profile and click Set as default (the default profile is also used for silent cleanup).
Go to the options page and select Automatically run cleanup when saving a file.
Optionally, you can restrict automatic cleanup to specific files by a file mask. You can also select Only changed parts of file to make sure that cleanup is applied to the code affected by your changes, and the rest of the code in the file is not modified.
Click Save in the dialog to apply the modifications and let ReSharper choose where to save them, or save the modifications to a specific settings layer using the Save To list. For more information, see manage and share resharper settings.
The next time you finish editing and save the file (Ctrl+S) or all files (Ctrl+Shift+S), ReSharper will clean up the affected files using the selected profile. If the default cleanup profile is not selected, ReSharper will prompt you choose one of the profiles.
Configure preferences of optional member qualifiers
Your member qualifiers style preferences are saved using the mechanism of layer-based settings. Among other things, this mechanism allows you to maintain different preferences for different solutions as well as to keep these preferences under a VCS and automatically share them with your team members.
Go to the page of ReSharper options (Alt+R, O).
Modify settings in the Instance member qualification and Static member qualification categories according to your coding practices/standards.
The Notify with selectors in the right column allow you to set severity levels of code inspections detecting code that differs from your preferences.
Click Save in the Options dialog to apply the modifications and let ReSharper choose where to save them, or save the modifications to a specific settings layer using the Save To list. For more information, see manage and share resharper settings.
This feature is supported in the following languages and technologies: