Context Actions
Alt+Enter
Context actions are code transformations helpers available right in the editor. In contrast to quick-fixes, context actions do not aim to resolve a problem or improve your code, instead, they allow you to quickly introduce minor changes like changing access modifiers, generating code that checks for null, convert 'foreach' to 'for', etc.
Rider provides hundreds of context actions in all supported languages. You can find the full list in the context actions reference.
Applying context actions
As soon as a context action becomes available for the current caret position, Rider displays the corresponding action indicator ![]() to the left of the caret. Sometimes however, Rider provides several contextually available features for the current caret position. In this case, the action indicator corresponding to the action with the highest priority is shown, and all other actions only appear when you expand the action list by clicking on the action indicator or pressing Alt+Enter Context actions have the lowest priority, therefore, they often appear at the bottom of the action list:
to the left of the caret. Sometimes however, Rider provides several contextually available features for the current caret position. In this case, the action indicator corresponding to the action with the highest priority is shown, and all other actions only appear when you expand the action list by clicking on the action indicator or pressing Alt+Enter Context actions have the lowest priority, therefore, they often appear at the bottom of the action list:
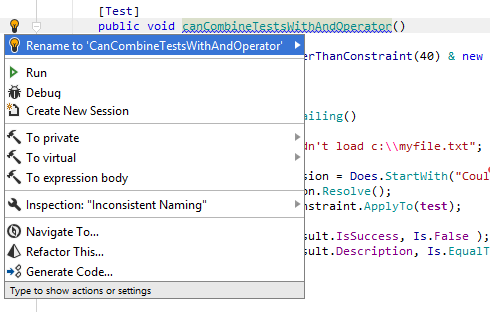
In most cases, a context action is applied immediately. However, some actions require user interaction to chose how exactly they transform your code. In these cases, a Hot Spot Session is deployed in the editor, where you can select one of the suggested values or provide your own values in the active input positions.
For example, here is what happens when you apply the Iterate collection via 'foreach' context action:
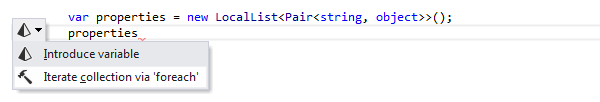
After creating the foreach statement, a hot spot session helps you complete editable parameters of the generated statement:
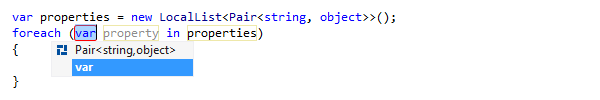
To complete the hot spot session:
- If Rider suggests some values for the current parameter, use Up and Down arrow keys to navigate through the list of suggested values, or just type in a desired value.
- Press Tab or Enter to accept the value and move to the input position of the next parameter. If this is the last parameter, the hot spot session completes and the caret moves to the end position defined for the session.
- Press Shift+Tab to move the input focus to the input position of the previous parameter.
- Press Esc to exit the hot spot session. In this case, all session parameters will be initialized with default values.
Applying context actions in wider scope
Some context actions can automatically find and change similar code items in a larger scope - in the current file, in the current project or in the whole solution. These context actions work the same as Fix in Scope. For example, you can move all types from the current file to new matching files:
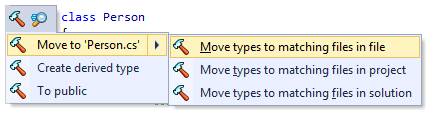
The full list of context actions that can be applied in wider scopes includes:
TypeScript
C#
- Add another accessor
- Add block braces to switch section statements
- Add name to argument
- Convert expression body member to statement body
- Convert integer literal to binary form
- Convert integer literal to hexadecimal form
- Convert integral literal to decimal form
- Convert string interpolation to 'string.Format' call
- Fully qualify reference to type, static member or namespace
- Insert digit separators in integer literal
- Insert digit separators in real literal
- Insert generic method invocation type arguments
- Invoke extension method as static
- Join attributes into single section
- Move type to another file to match its name
- Qualify static members imported via 'using static' directive
- Remove #region, #endregion directives (see Adding and Removing #region Blocks)
- Remove argument name
- Remove digit separators from numeric literal
- Remove redundant parenthesis (see Code Syntax Style: Optional Parentheses)
- Replace array initializer with expression
- Replace explicit type specification with 'var' when inferred type would remain the same
- Replace 'var' with explicit type declaration
- Specify enum member values
- Split attributes into separate sections