Configuring Remote Interpreters via Vagrant
Besides that, make sure that the following prerequisites are met (outside of RubyMine):
- Oracle's VirtualBox is installed on your computer.
- Vagrant is installed on your computer, and all the necessary infrastructure is created.
- The parent folders of the following executable files are added to the system PATH variable:
vagrant.batorvagrantfrom your Vagrant installation. This should be done automatically by the installer.VBoxManage.exeorVBoxManagefrom your Oracle's VirtualBox installation.
- The required virtual boxes are created.
Configuring remote Ruby interpreter via Vagrant
To configure a remote Ruby interpreter
- In the Ruby SDK and Gems page of the Settings/Preferences dialog box, click
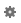 next to Project Interpreter field.
next to Project Interpreter field. - From the drop-down list, choose .
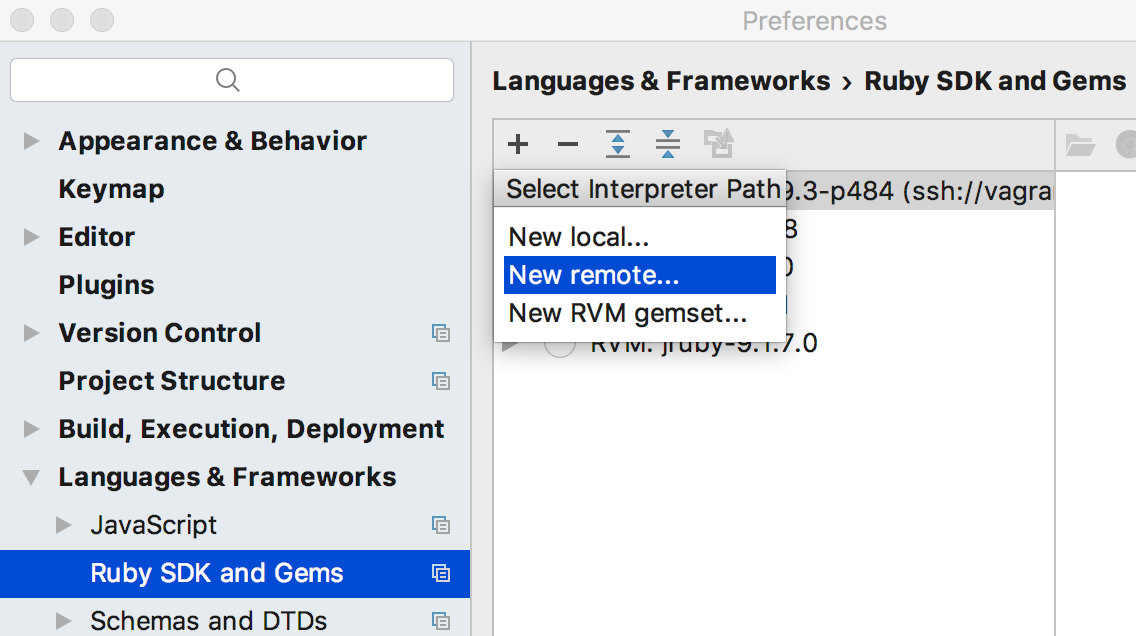
The dialog box Configure Remote Ruby Interpreter opens.
- In the left-hand pane of the dialog box, click Vagrant:
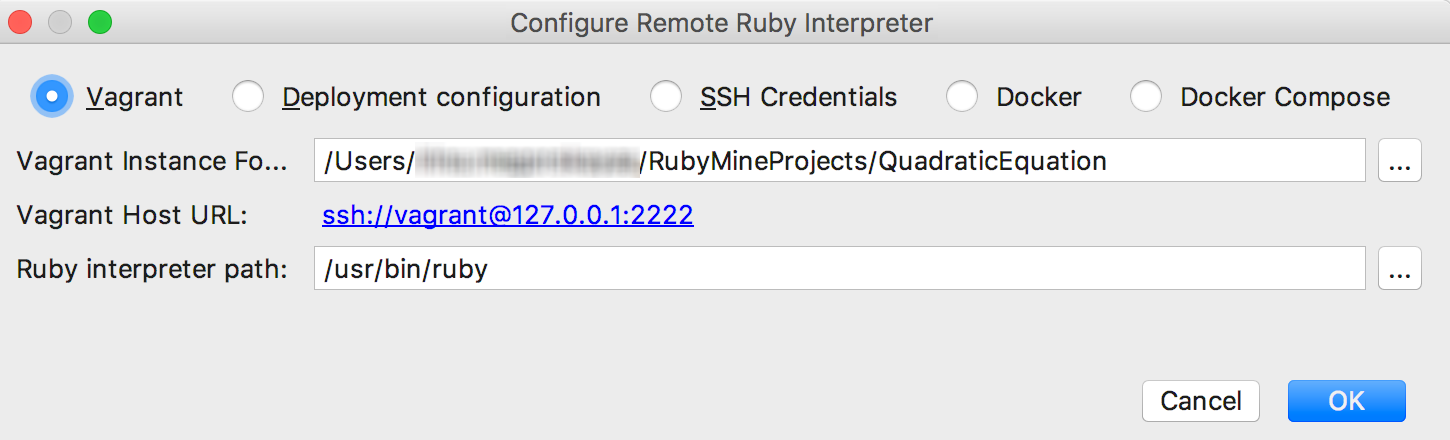
In this case, the remote server settings are taken from the vagrant configuration file, defined in the page Vagrant.
- Click the browse button
 next to the field Vagrant instance folder, and specify the desired Vagrant instance folder.
next to the field Vagrant instance folder, and specify the desired Vagrant instance folder. This results in showing the link to Vagrant host URL.
- The Ruby interpreter path field displays the path to the desired Ruby executable. You can accept default, or specify a different one.
- Click OK in the Configure Remote Ruby Interpreter dialog box.
- Back in the Ruby SDK and Gems page, if necessary, configure the path mappings:
- Click
 :
: 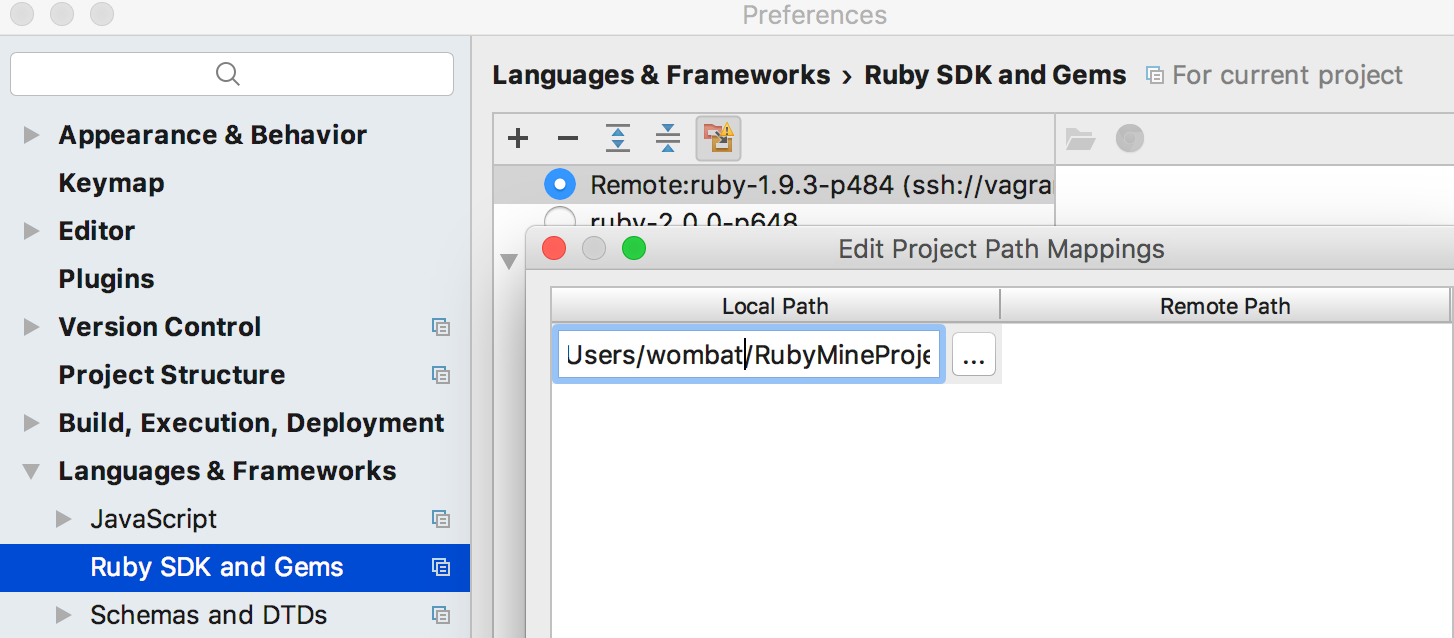
- In the dialog box that opens add (
 ) or delete (
) or delete ( ) path mappings as desired.
) path mappings as desired.
- Click
Adding a Vagrant box
In the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S), click Vagrant page under the Tools node, and there (if necessary) click ![]() to add a virtual box.
to add a virtual box.
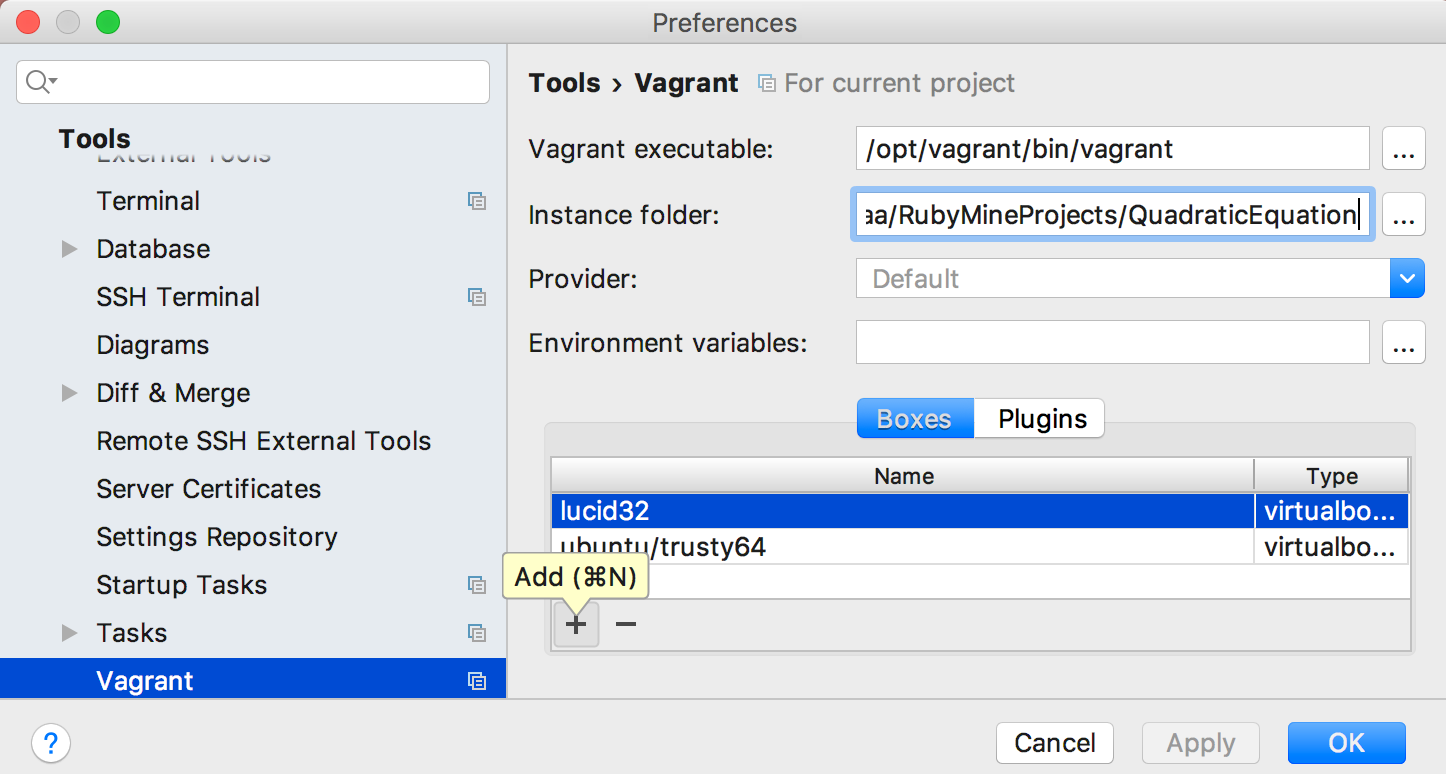
In the Add Vagrant Box dialog box, specify the name of the new box, and its URL. Then click OK and take your time. The new box is added to the list of available boxes.
By default lucid32 is proposed to be installed, but it has no ruby on it, so in this case you'll need to add ruby. Here we will connect by SSH and install ruby manually.
Launching a Vagrant box
On the main menu, point to , and click to perform init command. From the dialog box that opens, select the particular Vagrant box you want to work with:
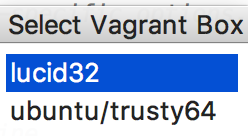
After that, the init command is executed:
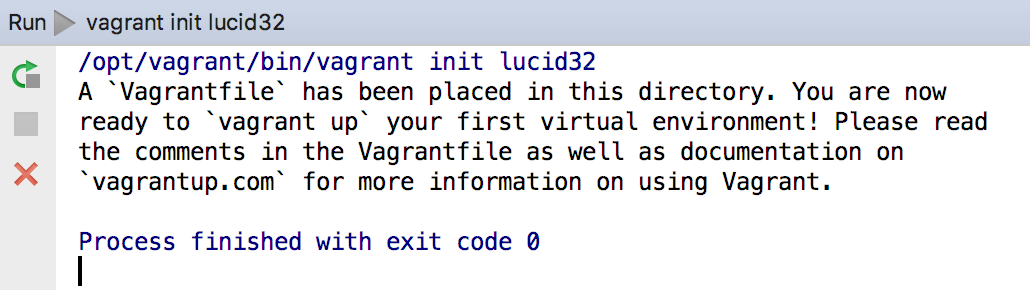
The Vagrant configuration file Vagrantfile is created. Next, you have to perform the vagrant up command. To do that, point to on the main menu, and that choose .
The command vagrant up is executed and shows its output in the Run tool window:
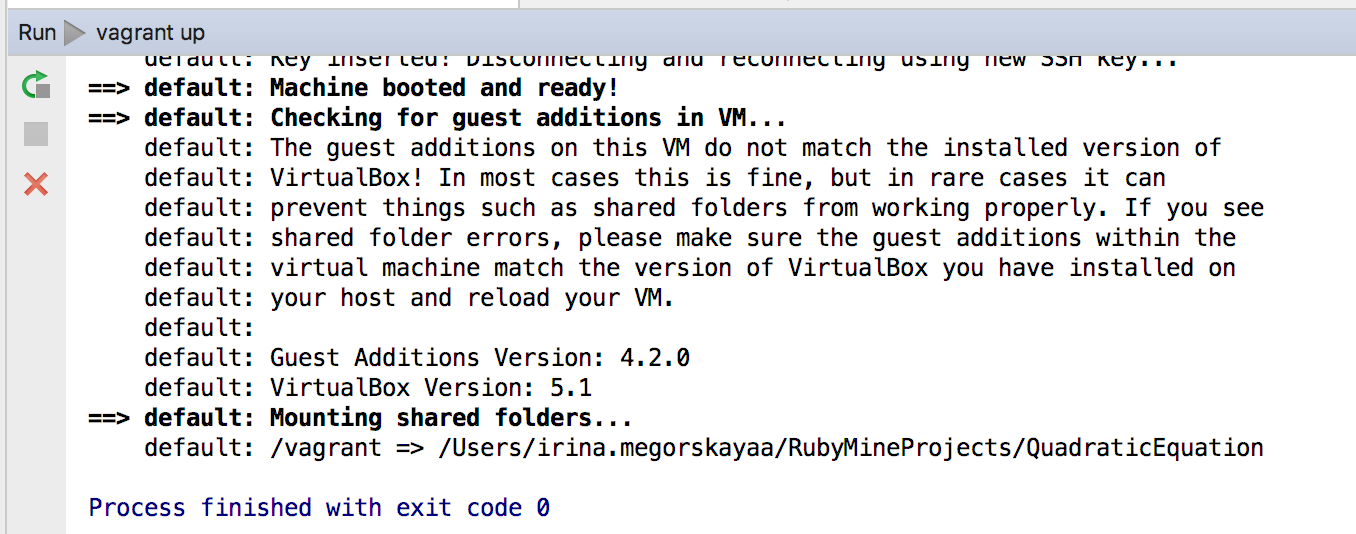
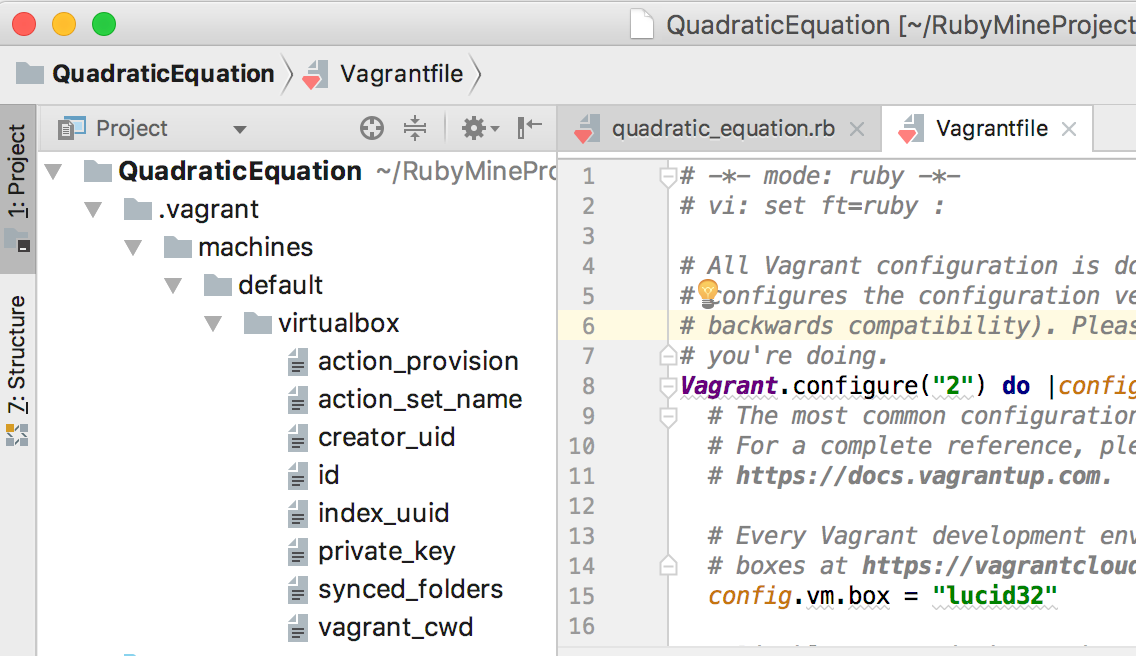
Note the .vagrant folder in the project structure:
Installing Ruby
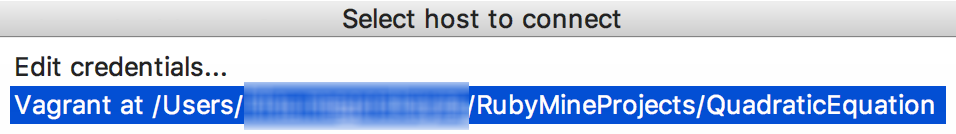
Now we can connect to the Vagrant Box via SSH and install ruby manually, for example using rvm. In this case on the main menu choose . You'll be suggested to choose host from the list - and our Vagrant will be in the list:
Configuring remote interpreter via Vagrant
Having added a Vagrant box and performed Vagrant-specific commands, it's time to configure a remote interpreter. This is how it's done...
To configure a remote interpreter via Vagrant, follow these steps:
- Open the Settings/Preferences dialog box again (
 on the main toolbar), and click the page Ruby SDK and Gems. Here you can select one of the existing interpreters, but what if none of the them meets your needs? Then click
on the main toolbar), and click the page Ruby SDK and Gems. Here you can select one of the existing interpreters, but what if none of the them meets your needs? Then click  and choose :
and choose : 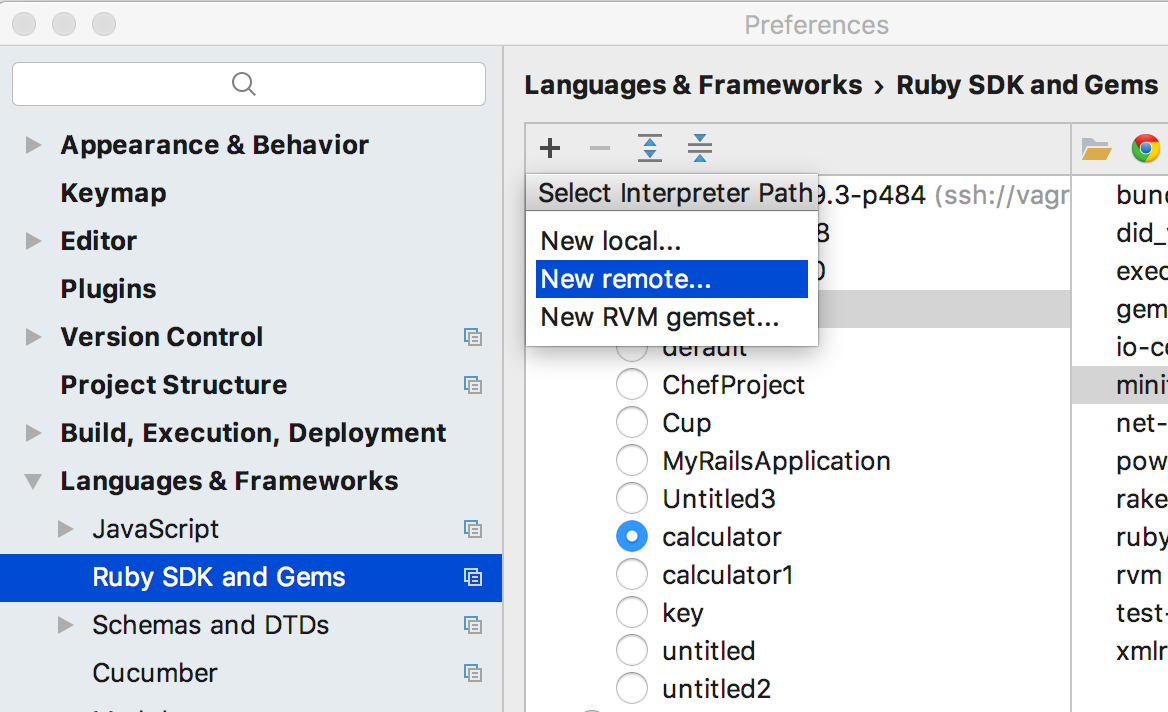
The dialog box Configure Remote Ruby Interpreter opens.
- In this dialog box, click the radio button Vagrant:

In this case, the remote server settings are taken from the vagrant configuration file, defined in the Vagrant page.
The Ruby interpreter path field displays the path to the desired Ruby executable. You can accept default, or specify a different one. When adding an rvm-based remote interpreter, it's important to specify the gem set in the Ruby interpreter path.
- In the Configure Remote Ruby Interpreter dialog box, click OK. The configured remote interpreter is added to the list so we can choose it and apply the changes.