Modify source code of database objects
Enable the Database Tools and SQL plugin
This functionality relies on the Database Tools and SQL plugin, which is bundled and enabled in RubyMine by default. If the relevant features are not available, make sure that you did not disable the plugin.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Open the Installed tab, find the Database Tools and SQL plugin, and select the checkbox next to the plugin name.
RubyMine tracks changes that you make to objects that store their source code in the database. These objects might be triggers, procedures, functions, views, or other objects. Every modification that you make to these objects in the editor is saved as a local version of the object source code.
Updating source code
RubyMine retrieves the information about a database during the introspection process. This information is used to show the objects in the Database tool window, display their DDL, suggest them during completion, and in other features for coding assistance.
You can update the source code of database objects directly by editing their DDL and submitting your changes. The IDE will generate a migration script and execute it in the database.
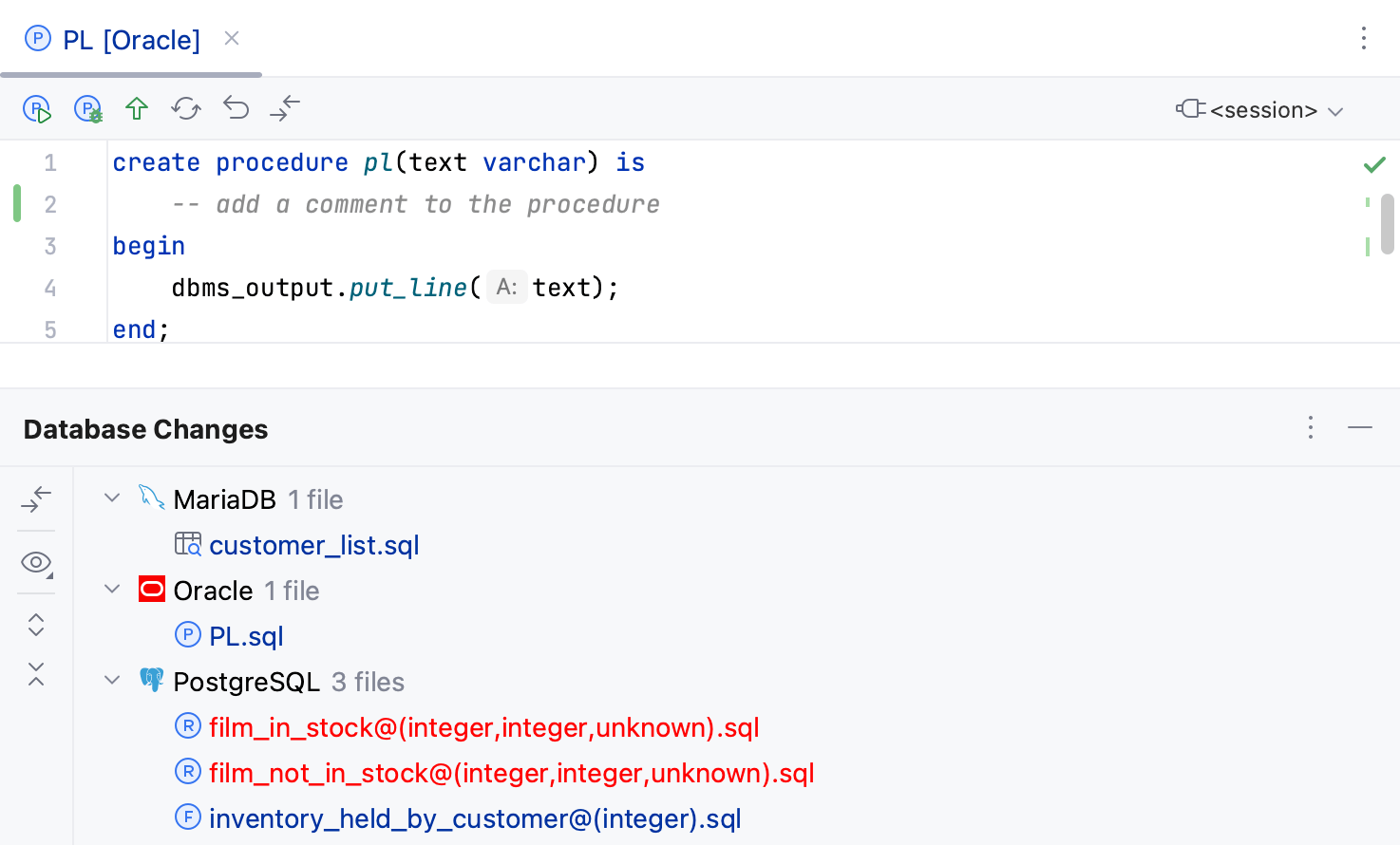
The Database Changes tool window displays a summary of all your changes.
Load source code for a data source
RubyMine retrieves the source code for a data source during the introspection. You can manage this process in the data source properties.
Open data source properties by doing one of the following:
On the Database tool window toolbar, click
Data Sources.
Press Shift+Enter.
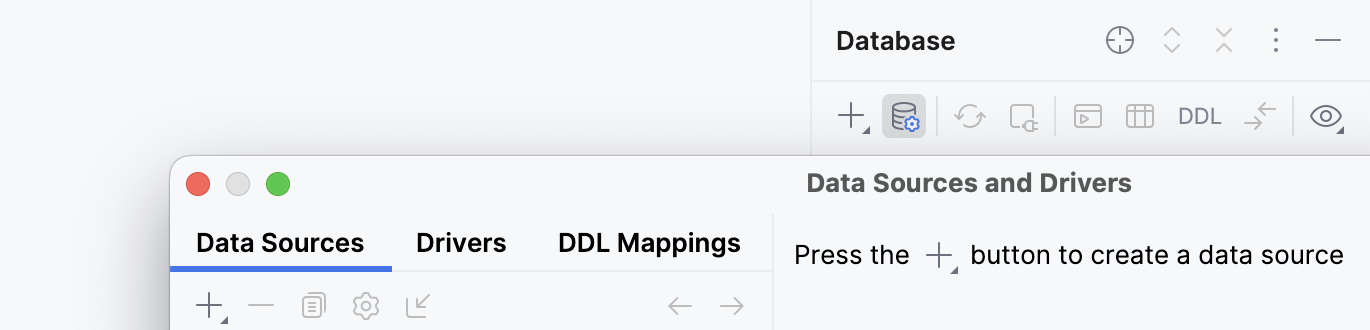
Select one or more data sources for which you want to download source code.
Right-click the selection and navigate to . You can select between the following options:
None: do not download source code.
Except System Schemas: download source code for all the objects except for system schemas.
All Schemas: download all the available source code.
Edit source code of an object
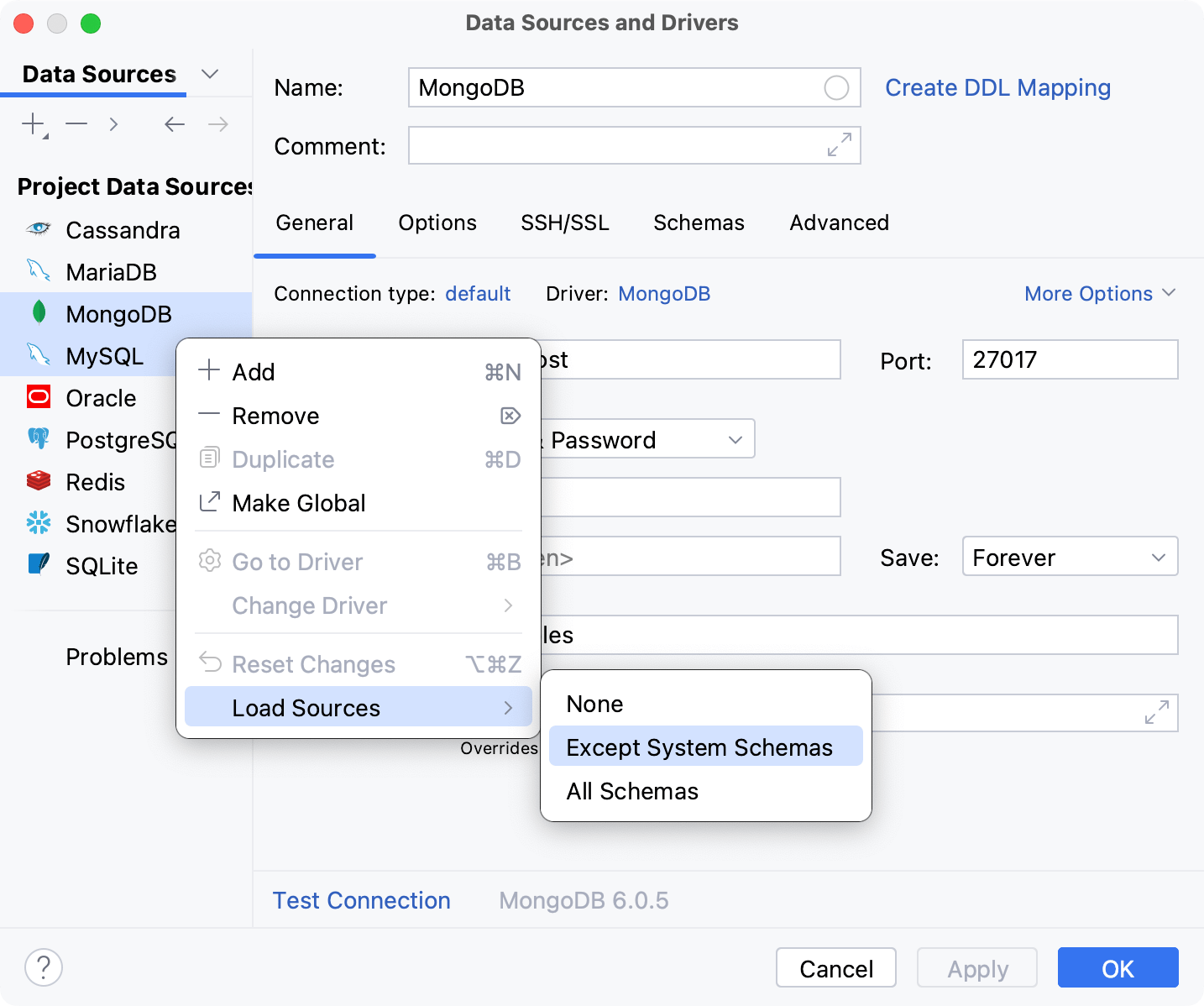
You can update the source code of database objects by directly editing their DDL CREATE scripts and submitting your changes in the editor. The IDE will generate a migration script with your changes, prompt you to verify it, and then execute it in the database.
Right-click an object and select . Alternatively, press Ctrl+B.
Make changes to source code.
(Optional) In the Database Changes tool window (), double-click the modified object to open the Diff Viewer and verify your changes.
Click the Submit button (
).
When you click the Submit button (
) in the Database Changes tool window, you see the Migration dialog. The Migration dialog displays a migration script for the object.
In the Object Migration dialog, verify that the migration script is correct and click OK.
A migration script is code that changes the entire database or a part of it. You can use migration scripts to add or remove a column, upgrade the database version, or change column properties.
RubyMine can automatically generate a migration script, but you have to check it before running.
See all the changes in source code
Select from the main menu.
See the difference between modified and stored versions
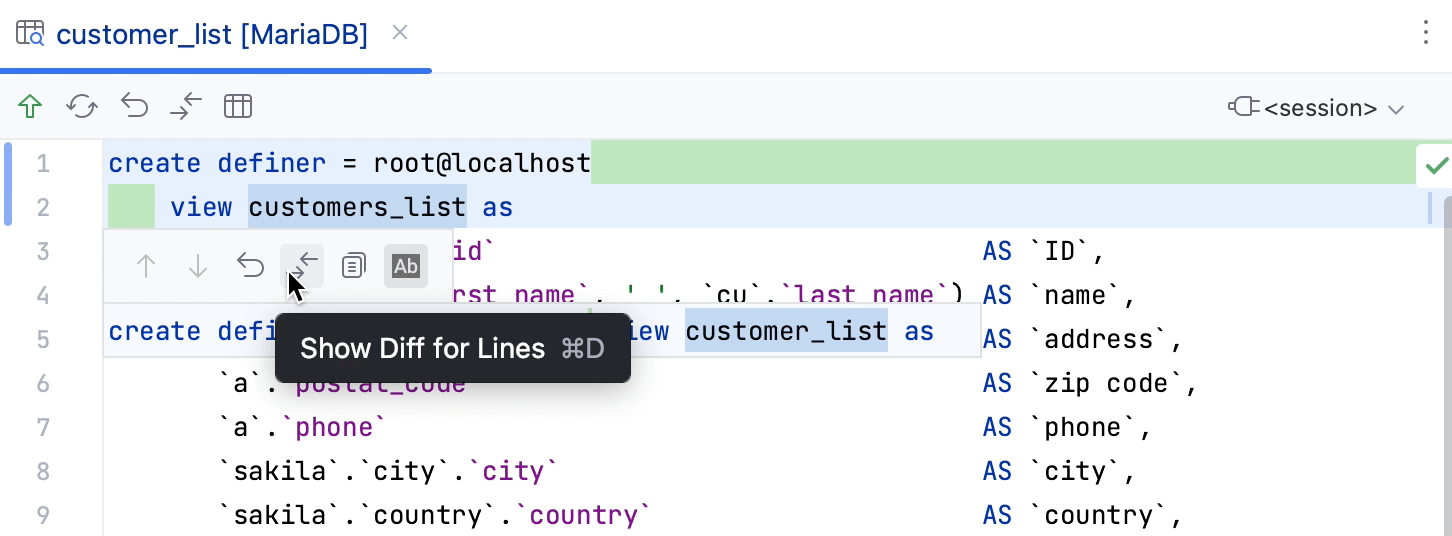
When you edit the source code of any object, RubyMine tracks changes and highlights them in the gutter. For example, add a comment line to a routine or a trigger function. The added line becomes highlighted. If you click the highlighted line in the gutter, a small toolbar is displayed with the Show Diff for Lines button. You can click the Show Diff for Lines button (
) to see the difference between the code that you added and the one from source code.
In the Database Changes tool window (), double-click the modified object to open the Diff Viewer and verify your changes.
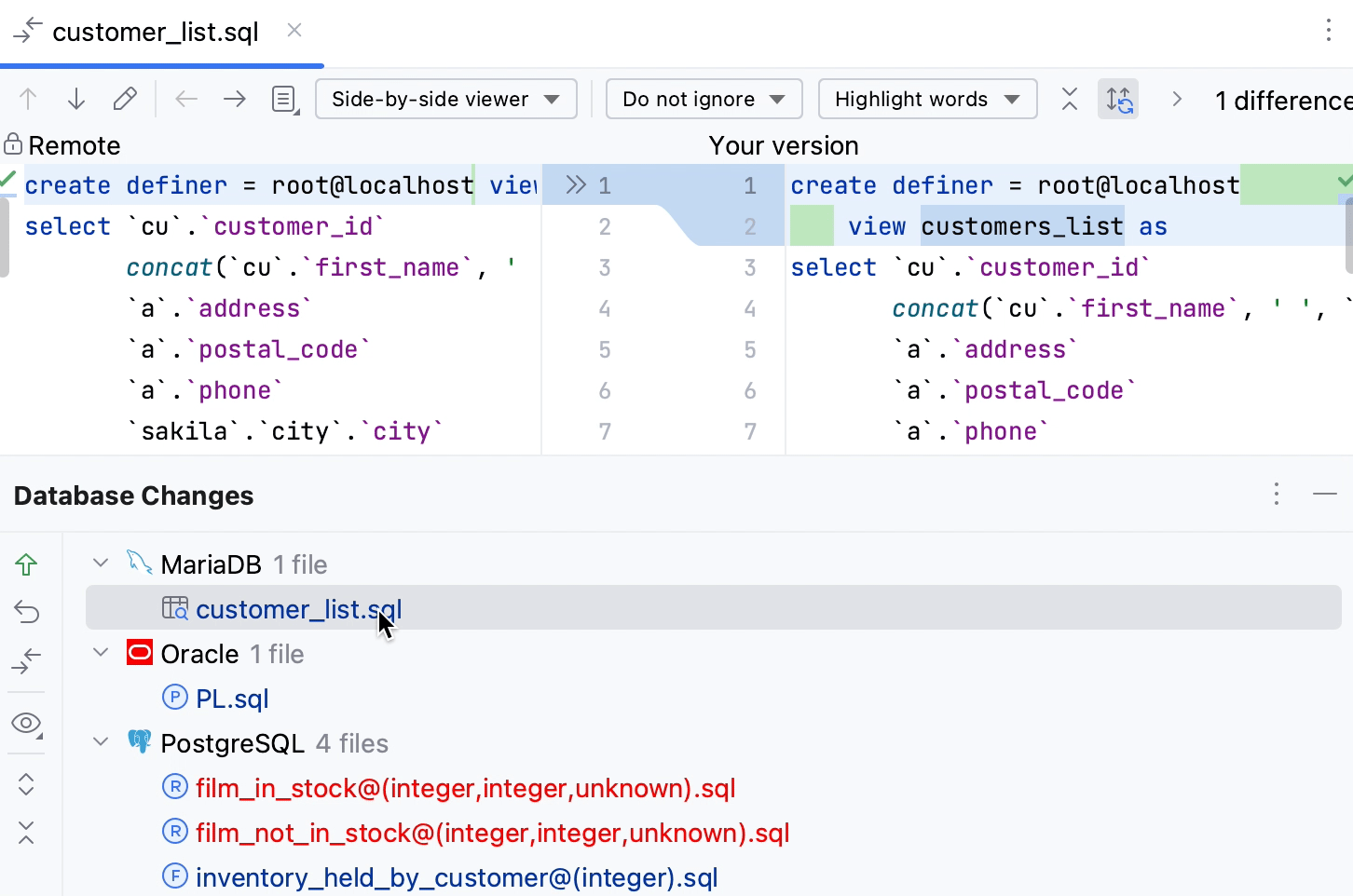
Outdated cached objects
RubyMine caches the source code of all the objects from the database to provide fast coding assistance and navigation. If an object that you opened was updated from a third-party location, you will see a notification that the cached object differs from the source code of the same object in the database.
If you see this warning in the IDE, you can select between the following actions:
Synchronize: fetch changes from the database and update the cached local object.
Disable check: disable this notification.
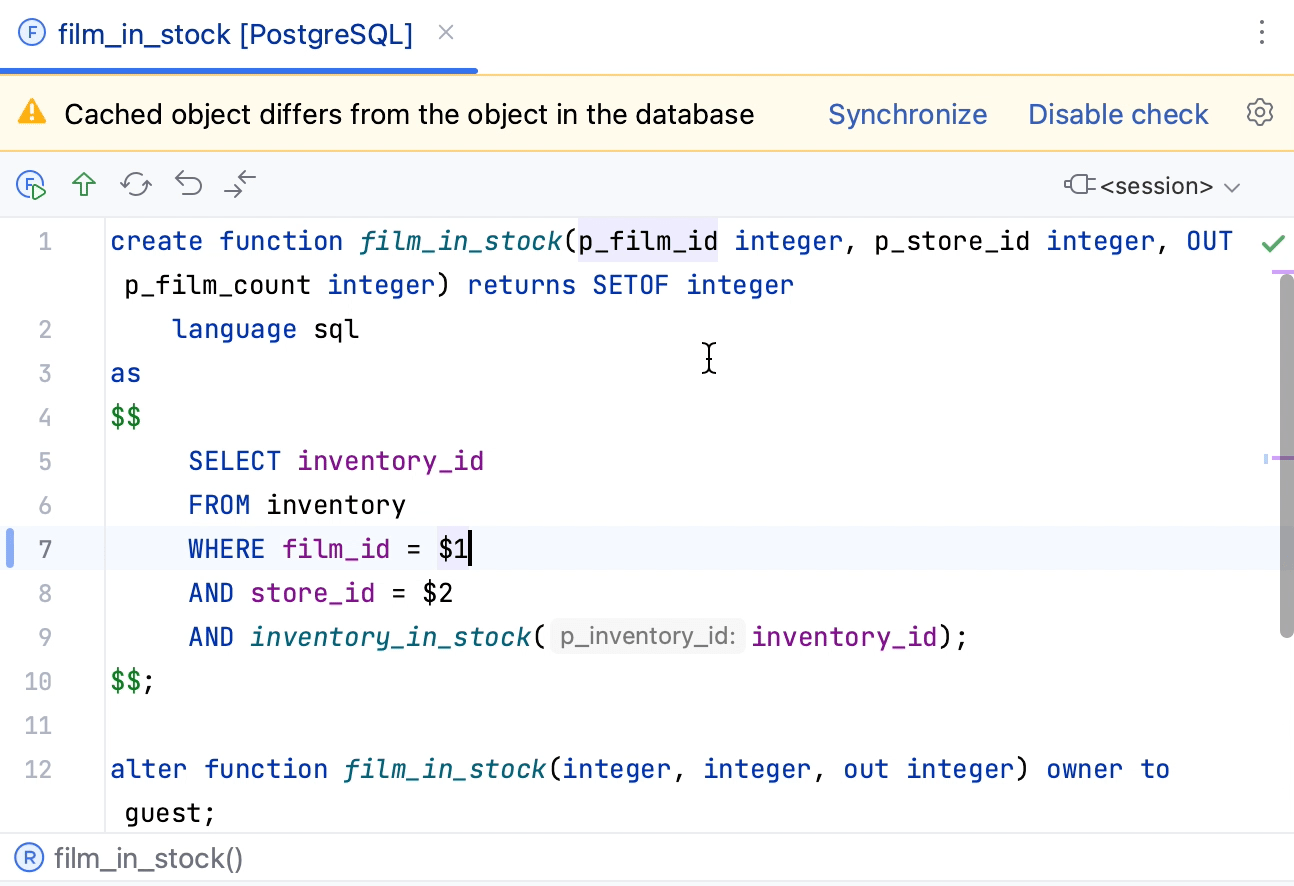
Also, there might be a conflict between your version of the object source code and the one in the database. For example, when you have modified the same source code as someone else and pressed Submit (Ctrl+K).
You can forcefully replace the source code of the object in the database (Force Refactoring) or synchronize the object state and then proceed with changes (Abort Refactoring and Synchronize).
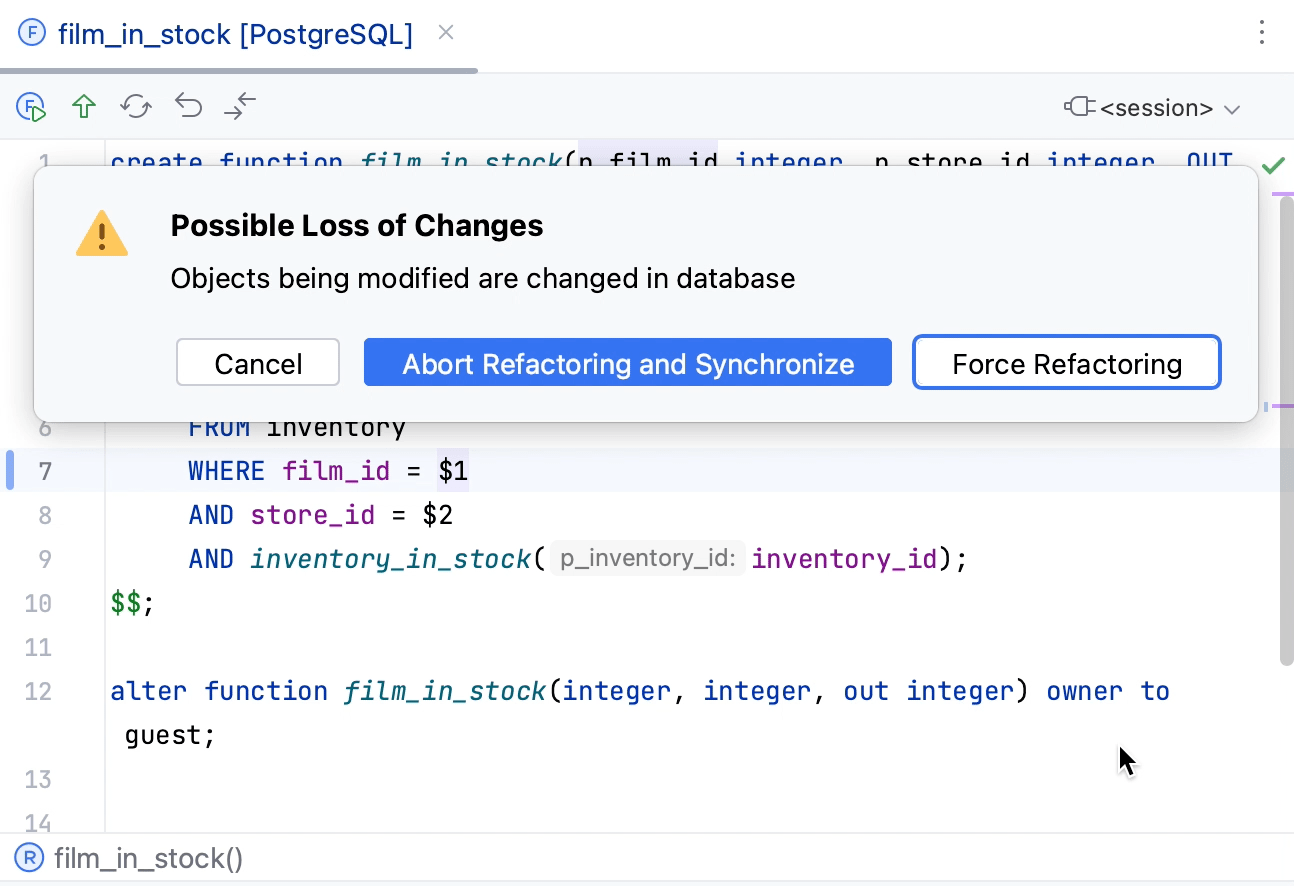
If you selected Abort Refactoring and Synchronize, RubyMine stops the submit operation and fetches changes from the database (similar to pressing Synchronize Ctrl+F5). If the conflict still exists, you will see the following notification.
In this notification, you can select between the following options:
Revert local changes: roll back all your changes and replace them with the version from the database.
Keep local changes: use your changes and overwrite changes in the database.
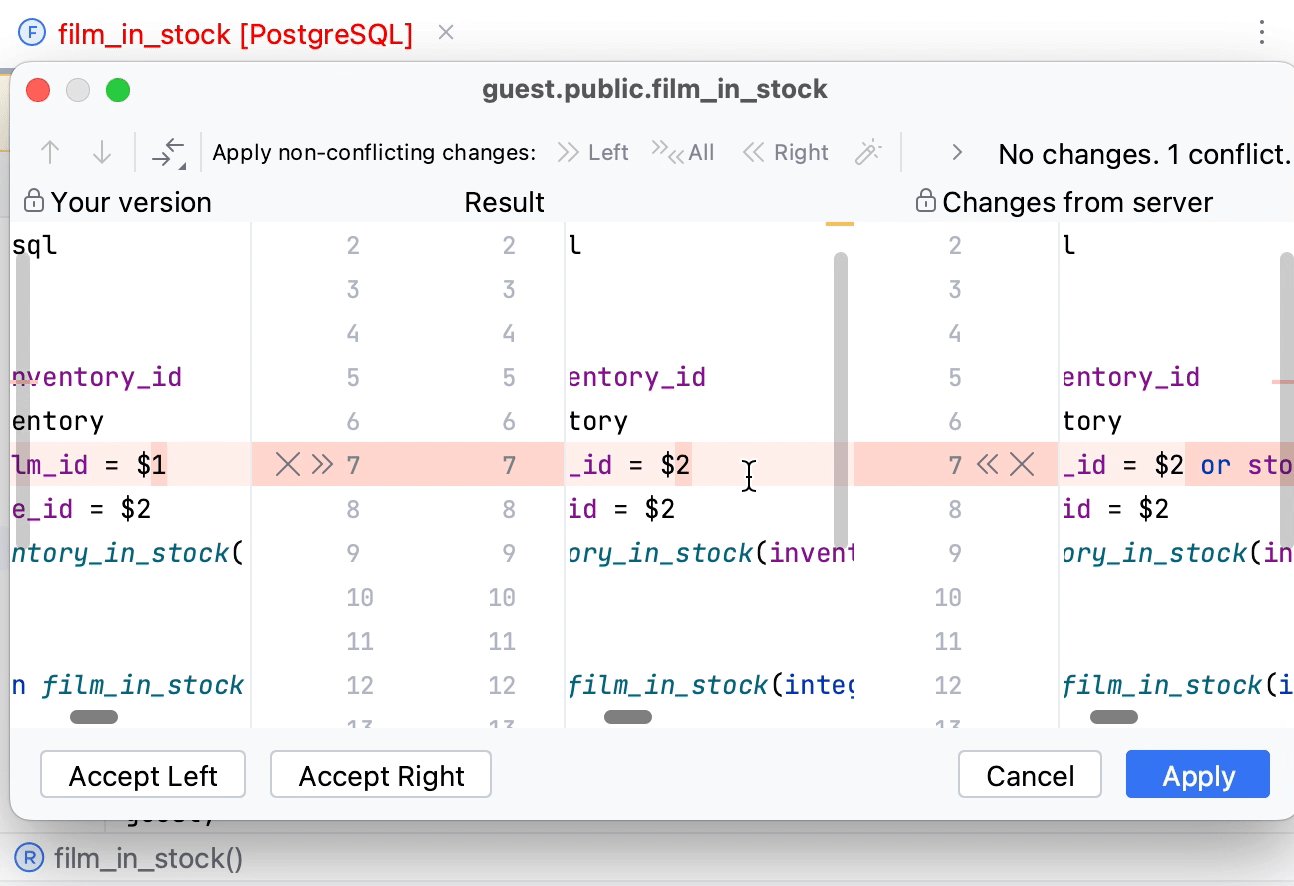
Merge: display the diff dialog to merge two versions of the object source code.
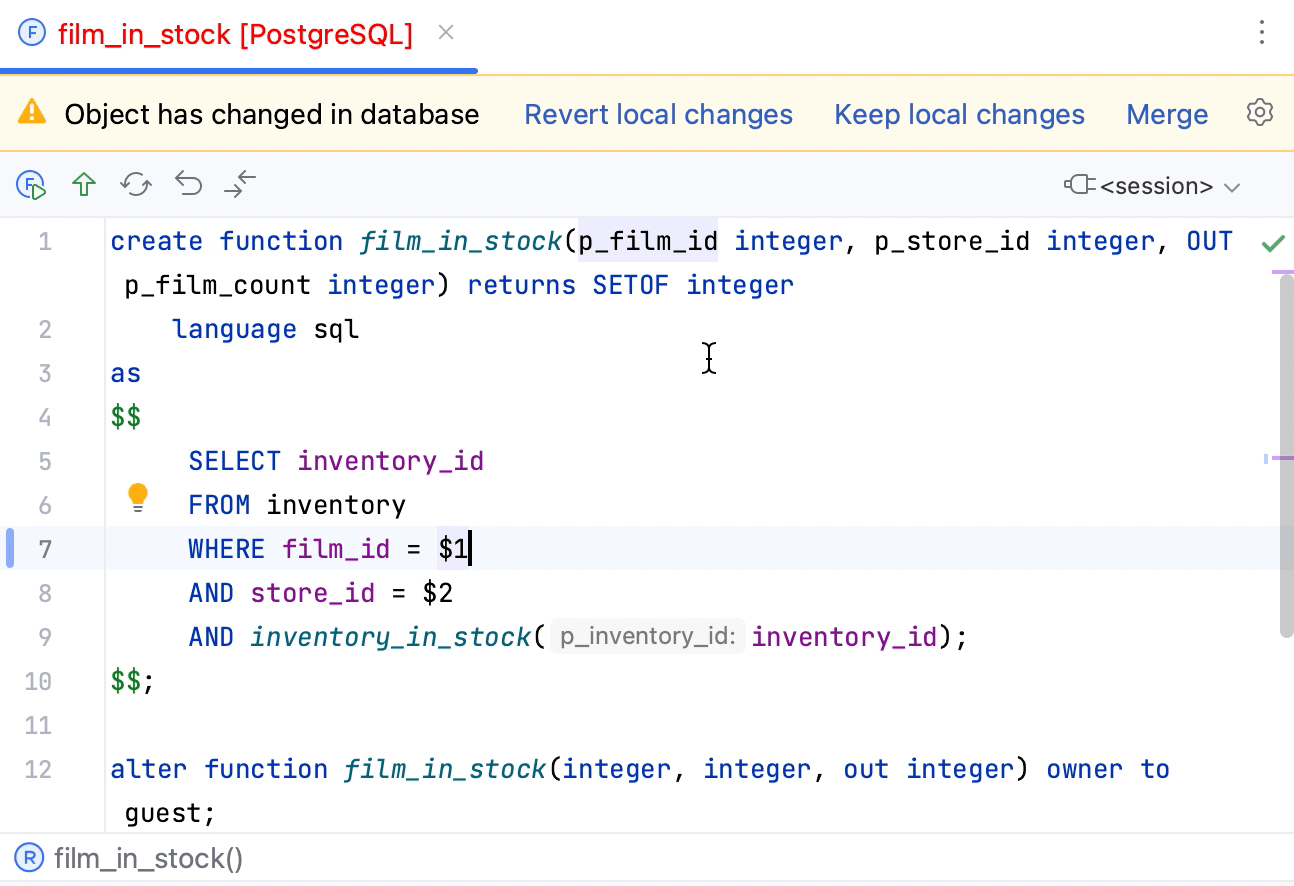
Colors of the object state
By default, all the objects are displayed in black. It means that the current state of an object source code does not differ from the source code of the same object on a server.
If the source code of the object has been changed but there are no conflicts with the object source code on a server, the object is displayed in blue.
If there are conflicts in the source code of a local object and the same object on a server, the object is displayed in red. If you open such an object in the editor, you will see a notification about conflicts.
For example, in the following screenshot, the get_customer_balance function is modified but contains no conflicts, the film_in_stock function was modified and conflicts with the source of the same function on a server, other objects are not modified.