Branching and Quality Protection
Choosing the right branching strategy for your team is important because it can have a significant impact on the development process, including how safe it is to introduce code changes, how often new features are released, and how quickly changes can be delivered to the production environment.
Some common strategies include:
- Git flow
This strategy is useful for teams that have a clear release process and need to keep the production environment stable.
The
mainbranch is for production code only.The
developbranch is for development code.featurebranches are created from the develop branch.releaseandhotfixbranches are created from themainbranch.
- GitHub flow
This strategy emphasizes collaboration, frequent releases, and a streamlined development process.
The
mainbranch is for production code only.Development is done in separate
featurebranches and then merged into themainbranch when ready.Pull requests are used for code review and to discuss changes before merging.
Releases are cut from the
mainbranch and tagged for easy versioning.
- Trunk-based development
This strategy requires strict discipline and collaboration among developers to maintain a stable trunk branch.
All code is committed to a single branch, usually called
trunk.The trunk branch is always production-ready.
Development work is done directly on the
trunkbranch.No long-lived
featurebranches.Before pushing the changes, developers perform a full "pre-integrate" build (compile, unit tests, etc.) on their local machines.
After the changes are already in
trunk, there could be a "post-integrate" code review.
Each strategy has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on the specific needs of your team. Although, SpaceCode is suited for almost any flow, we recommend that you consider employing a strategy that is native to SpaceCode — SpaceCode Git Flow as it allows you to unlock the full potential of SpaceCode quality protection features.
SpaceCode Git flow
SpaceCode Git flow is similar to GitHub flow, with a greater emphasis on the safety of making changes to the main branch and the ability to scale to large projects and teams. In JetBrains, we use this flow for many of our products, including JetBrains SpaceCode itself.
The main concepts of the SpaceCode Git flow are listed below. You can consider these as your to-do list. Though most of the items are optional, the more you get, the closer you will be to the best and safest flow possible.
- Protected branches
A single
mainbranch is always production-ready. Themainbranch is protected – direct commits are not allowed.- Feature branches and merge requests
When creating a
featurebranch, always do this from the up-to-datemainor, if required, from another feature branch. To merge changes from yourfeaturebranch tomain, you must create a merge request.- Merge requests and quality gates
Before the changes can be actually merged, a merge request must pass through quality gates (set of conditions). There are two quality gates, each is optional:
Approval in a turn-based code review: After commenting on the changes, the reviewer passes the turn to the author. The author then applies the comments and feedback to the code, making any necessary revisions. Once the revisions are made, the author adds new commits to the code review and passes the turn back to the reviewer. The process continues until the review is finally approved by the reviewer(s).
The reviewer can be assigned automatically based on the code owners feature – the
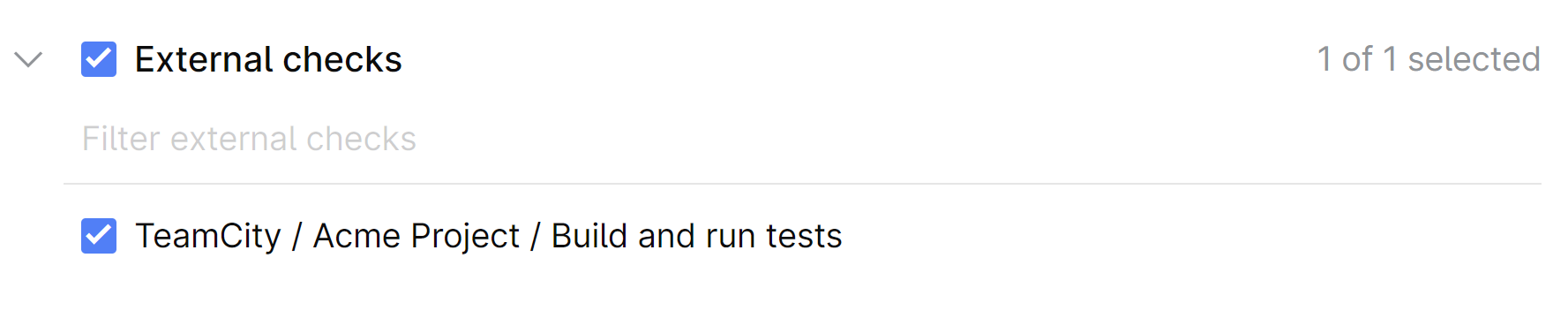
CODEOWNERSfile outlines who owns certain paths or files in a repository.An external check, which passes if an external service approves the merge request by sending an HTTP API request to SpaceCode. For example, this could be an external CI/CD service like JetBrains TeamCity.
- Safe merge
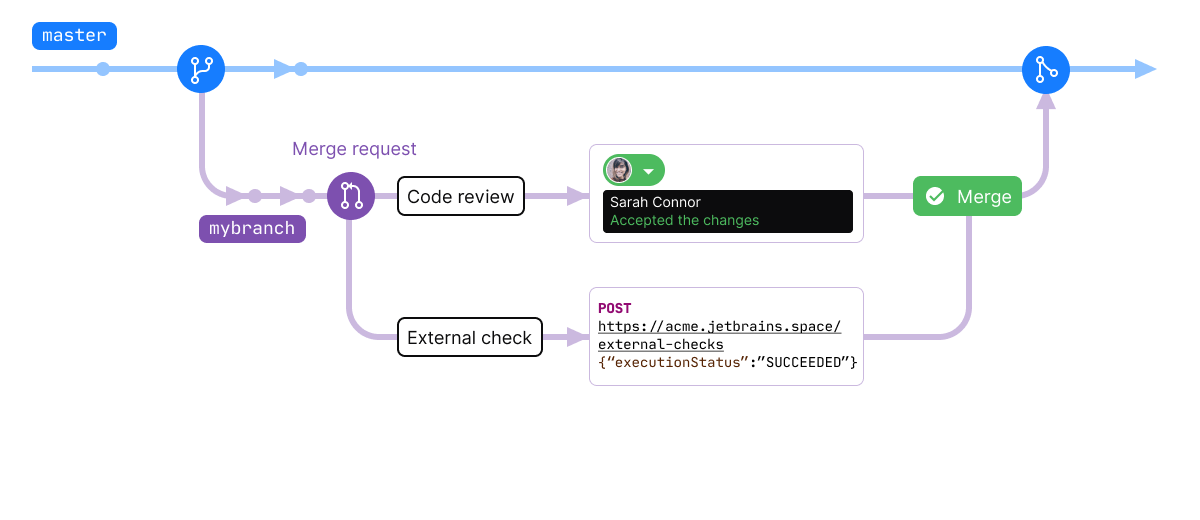
Safe merge is an additional safety step before finally merging changes from a
featurebranch tomain. Based on the merge request changes, SpaceCode creates a temporary merge commit with the latest changes from bothmainandfeaturebranches. This commit has its ownrefand can be used to perform the required quality checks, e.g., an Automation job or a TeamCity build that compiles the project and runs tests. If the checks are successful, the changes fromfeatureare finally merged tomain.You can use safe merge instead of or in addition to the 'green build' quality gate. Learn how to set up safe merge
- Release branches
If the project implies some public releases, you should use
releasebranches created from the up-to-datemain. If required, last minute changes are cherry-picked frommainto a particularreleasebranch.
Tutorial. Set up SpaceCode Git flow for your project
The best part about SpaceCode Git flow is that you can easily employ it for your existing project even if you don't currently use JetBrains SpaceCode.
Suppose:
You have a project hosted on GitHub (or another Git hosting).
You use JetBrains TeamCity for CI/CD purposes.
You signed up for SpaceCode
Here's how you can switch to the SpaceCode Git flow.
Step 1. Mirror your existing Git repository
In this tutorial, we assume that you have an existing Git repository hosted somewhere. In fact, this could be any Git hosting, but for the sake of simplicity, let it be GitHub. Now, our goal is to create its mirror in SpaceCode.
First, create a project. On the top right, click
 and choose Project:
and choose Project: 
Give your project a name and click Create.
Next, add a new repository. Navigate to your new project:
And click New repository at the bottom of the page.
In the New repository window:
Choose Import a repository.
Specify your GitHub repository URL and its name in SpaceCode.
Turn on Mirror changes from external repository.
Under Authentication, choose Token and click Get a new token to get an access token from GitHub. Once you get it, paste the token to the text field.
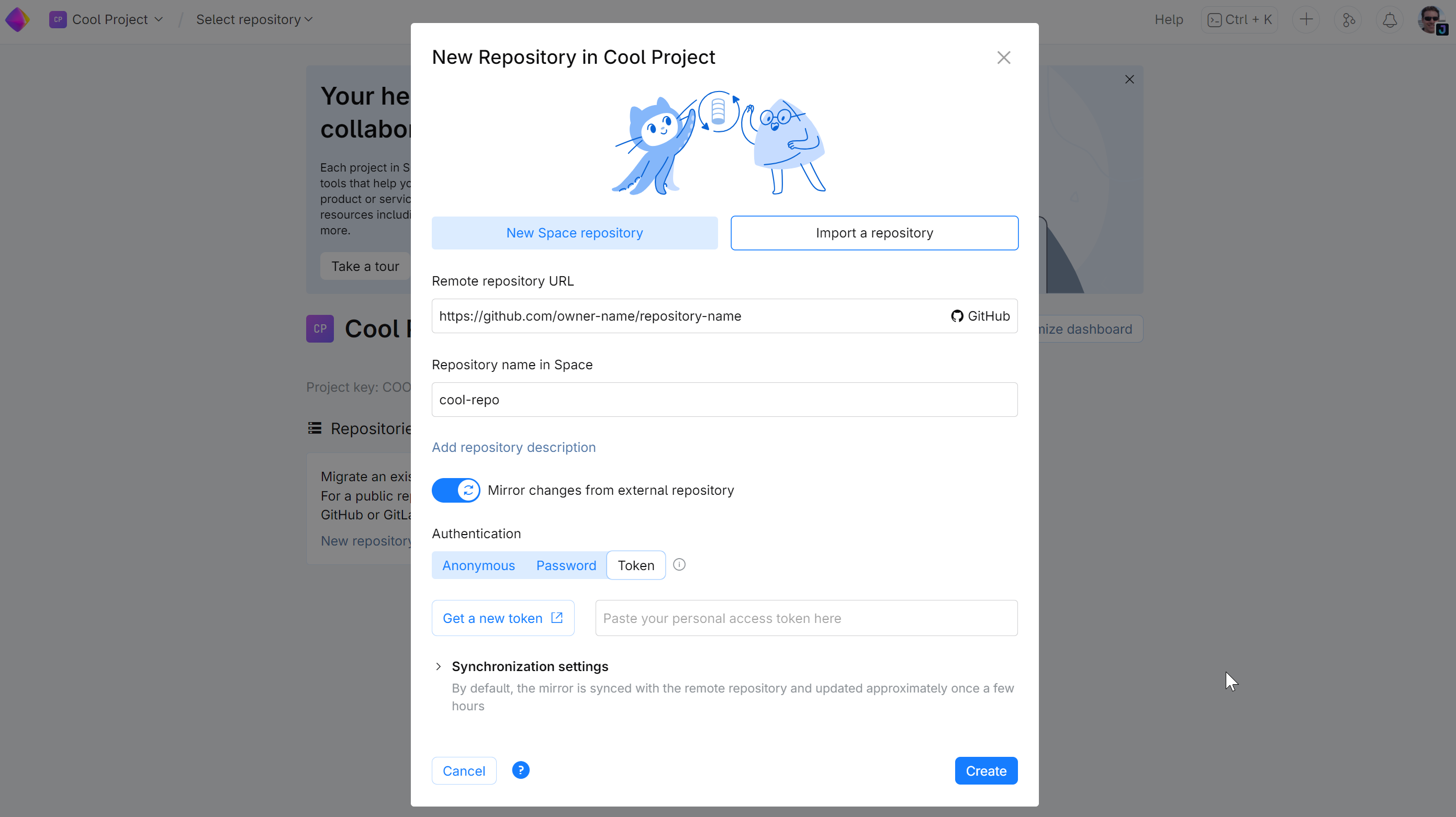
Click Create.
Important! Ensure all developers have switched to the new Git remote (the mirror in SpaceCode). Otherwise, all repository restrictions we apply in the further steps won't make any sense.
Done! We now have a working mirror of your repository in SpaceCode. The commits you push to the SpaceCode mirror will be delivered to the GitHub repository and vice versa.
Step 2. Protect the main branch
The next step is to protect the main branch from direct commits. After doing this, the only way a change can make it to main is through a merge request.
Navigate to your repository and open its Settings.
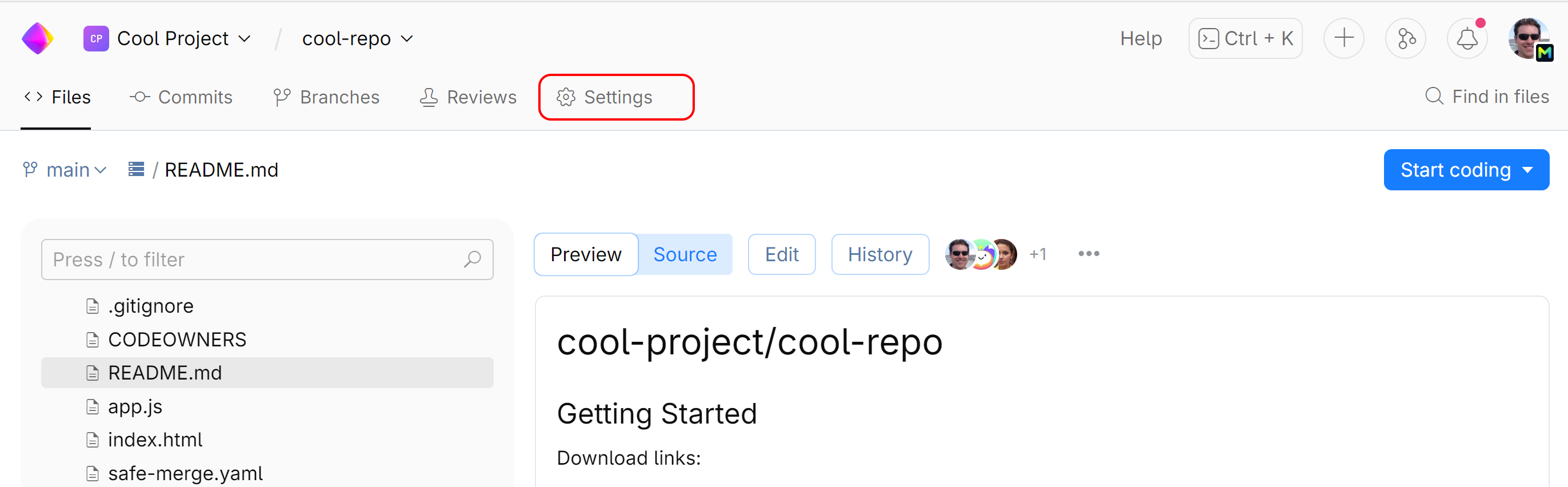
On the left sidebar menu, choose Protected Branches, then click New rule.
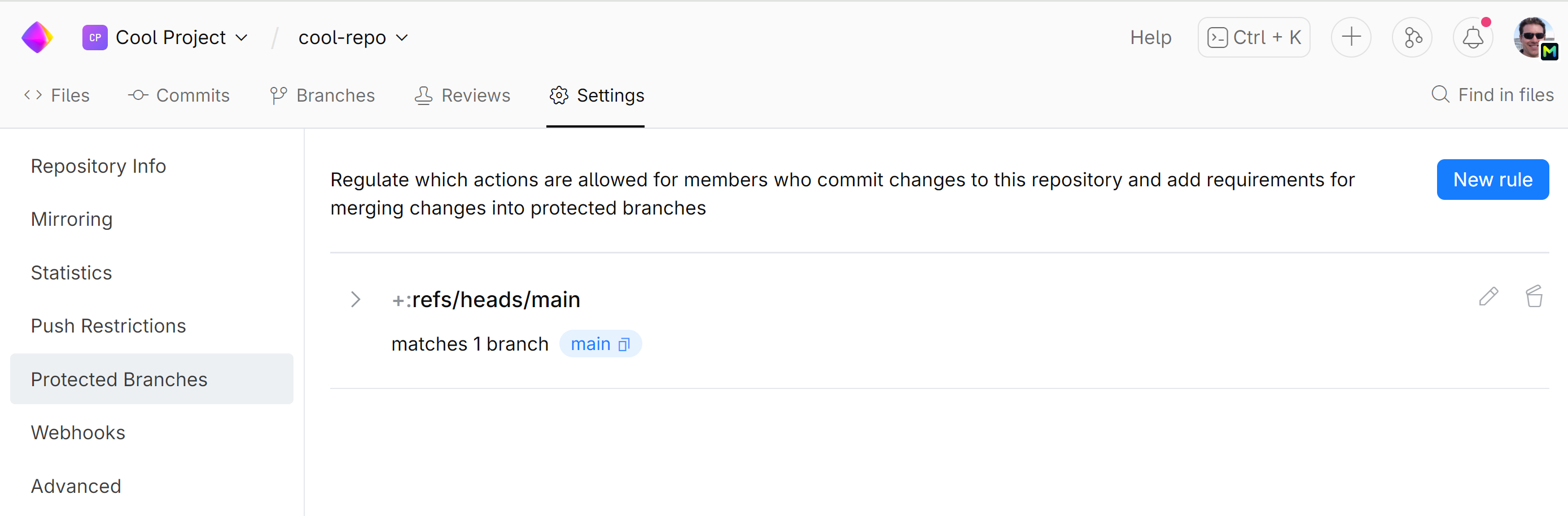
In the New Branch Protection Rule window:
Add
+:mainto Branch name patterns. This is the pattern that allows SpaceCode to determine to which branches it must apply the rule.Check that Push and Force push under the Regulated actions are set to Nobody.
Click Save.
Done! Nobody is allowed to push or force push commits to the main branch of our project. The only way to push to main now is to use merge requests.
Step 3. Add obligatory code reviews and code owners
One of the main ways to ensure code quality is introducing merge requests – a developer must make an explicit request to merge their changes to a protected branch. Before being merged, the changes must pass through the so-called quality gates. The first quality gate we set up in this tutorial is an obligatory code review – your colleagues must review and approve the code changes before they can be merged into main.
To simplify assignment of a right person for a code review, you can employ the code owners feature. This is a CODEOWNERS file that assigns the particular files and directories to the corresponding team members. After a code review is created, SpaceCode automatically assigns a reviewer based on CODEOWNERS.
To add a code review quality gate
Navigate to the repository and open its Settings.
On the left sidebar menu, choose Protected Branches, then edit the previously created rule.
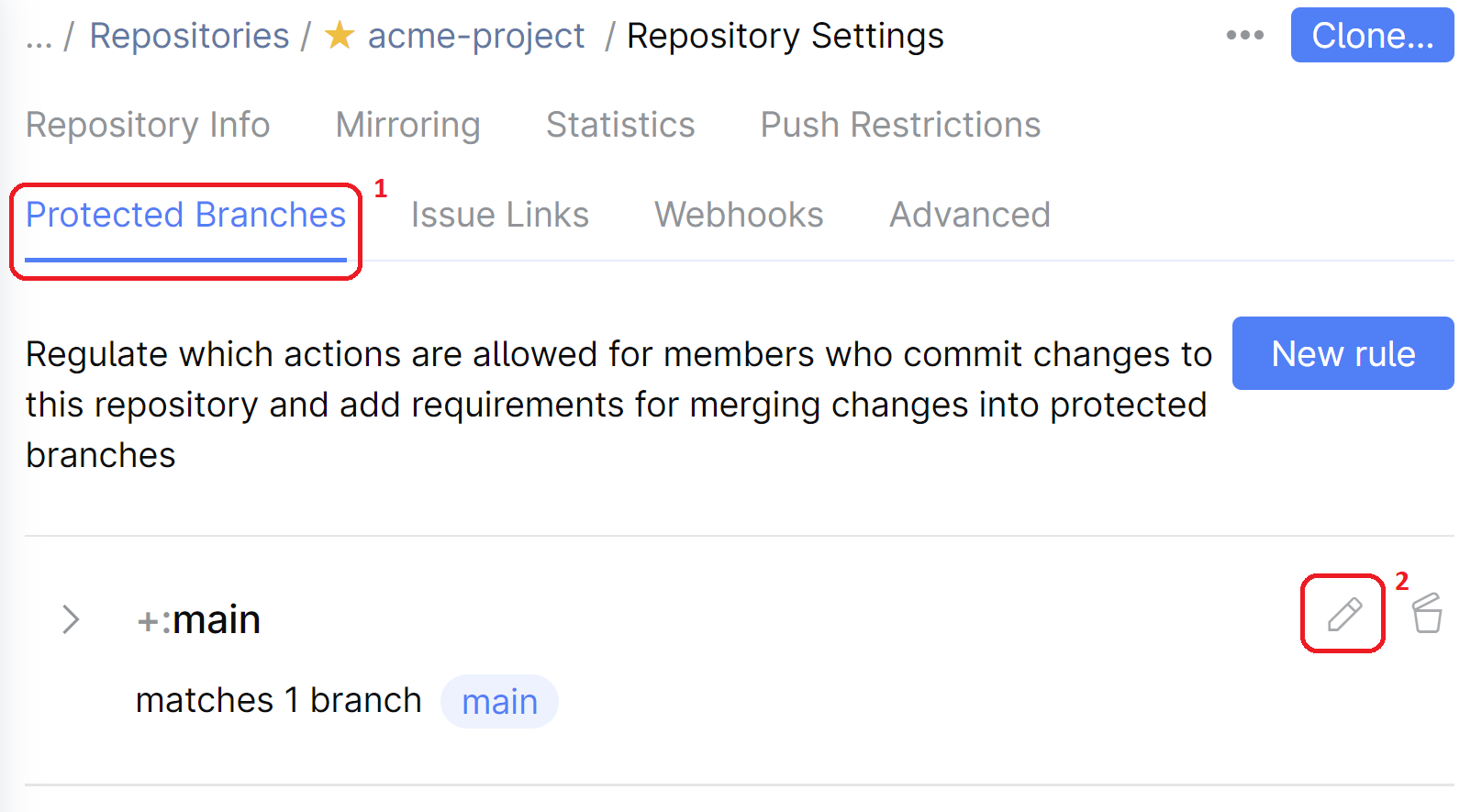
Under Quality Gates for Merge Requests, turn the switch On.
In Requirements, open Approvals and specify the required reviewers in the From field. This could be a particular user or a user group. In the require ... approval field, specify how many approvals are enough. For example:
From Project Member require 2 approval: a merge request must be approved by at least 2 project members (any members).
From Project Admin, John Doe require 1 approval: a merge request must be approved either by John or by any user with the Project Admin role.
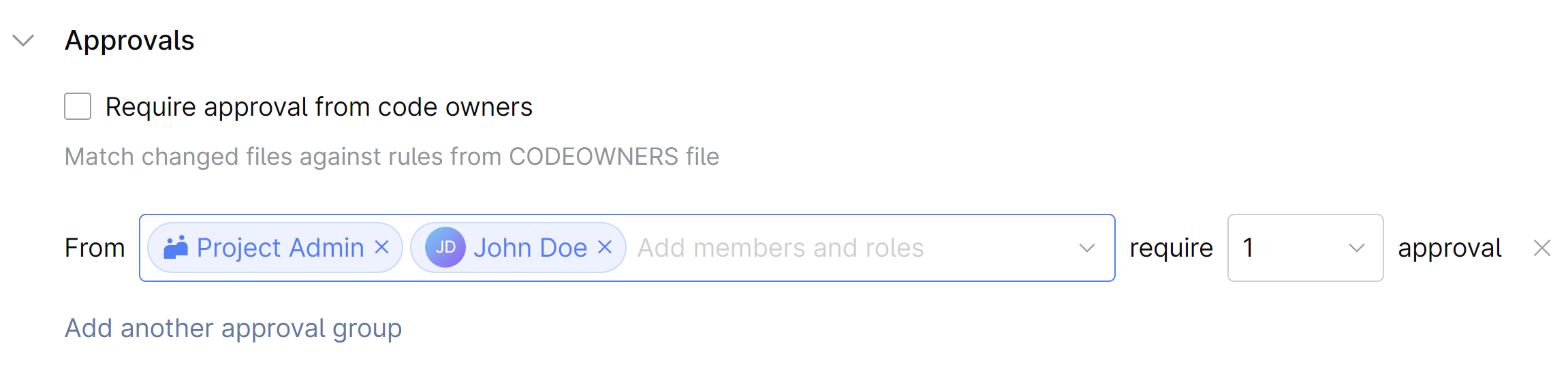
To add code owners
In your project repository, create a
CODEOWNERSfile. The file must be located either in the project root or in the.spacedirectory.Important! The
CODEOWNERSfile must be on the target branch of the merge request. So, if you protect themainbranch, theCODEOWNERSfile must be located in themainbranch as well.In the
CODEOWNERSfile, assign specific parts of the code base to specific users or user groups. For example:# John handles Gradle files *.gradle John.Doe # Sarah handles the source code src Sarah.Connor # CODEOWNERS file is for Project Admins CODEOWNERS "Project Admin"For more information about the file syntax, refer to Code Owners.
In the repository settings, open Protected Branches, then edit the previously created rule.
If Quality Gates for Merge Requests are not yet enabled, turn them On.
In Requirements, open Approvals and select the Require approval from code owners checkbox.
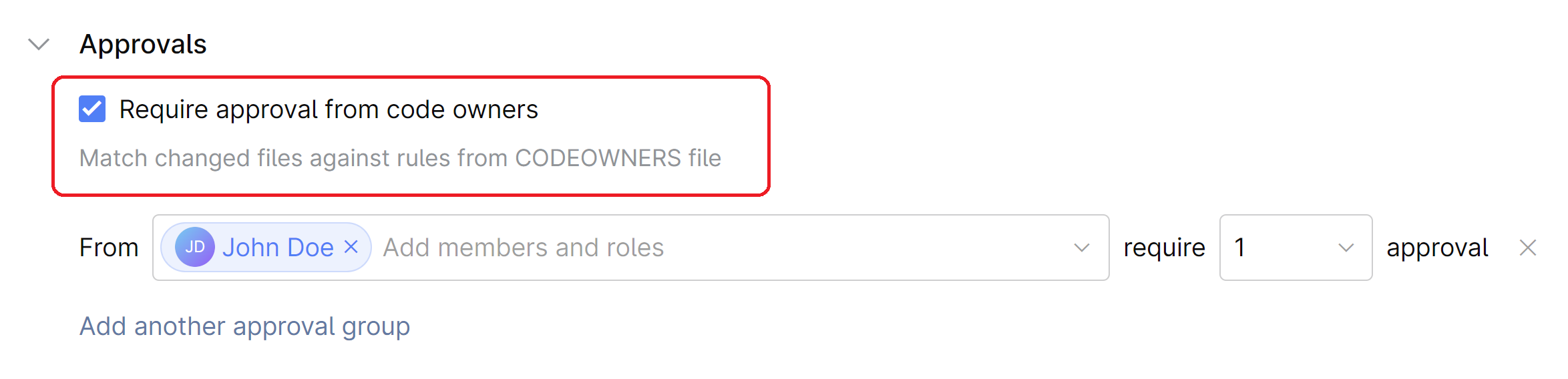
Done! Now, a merge request will require an obligatory code review.
Important: the reviewers you add via the From field and the reviewers assigned based on the CODEOWNERS file do not exclude, but complement each other. Approval is required from all reviewers specified in From and CODEOWNERS.
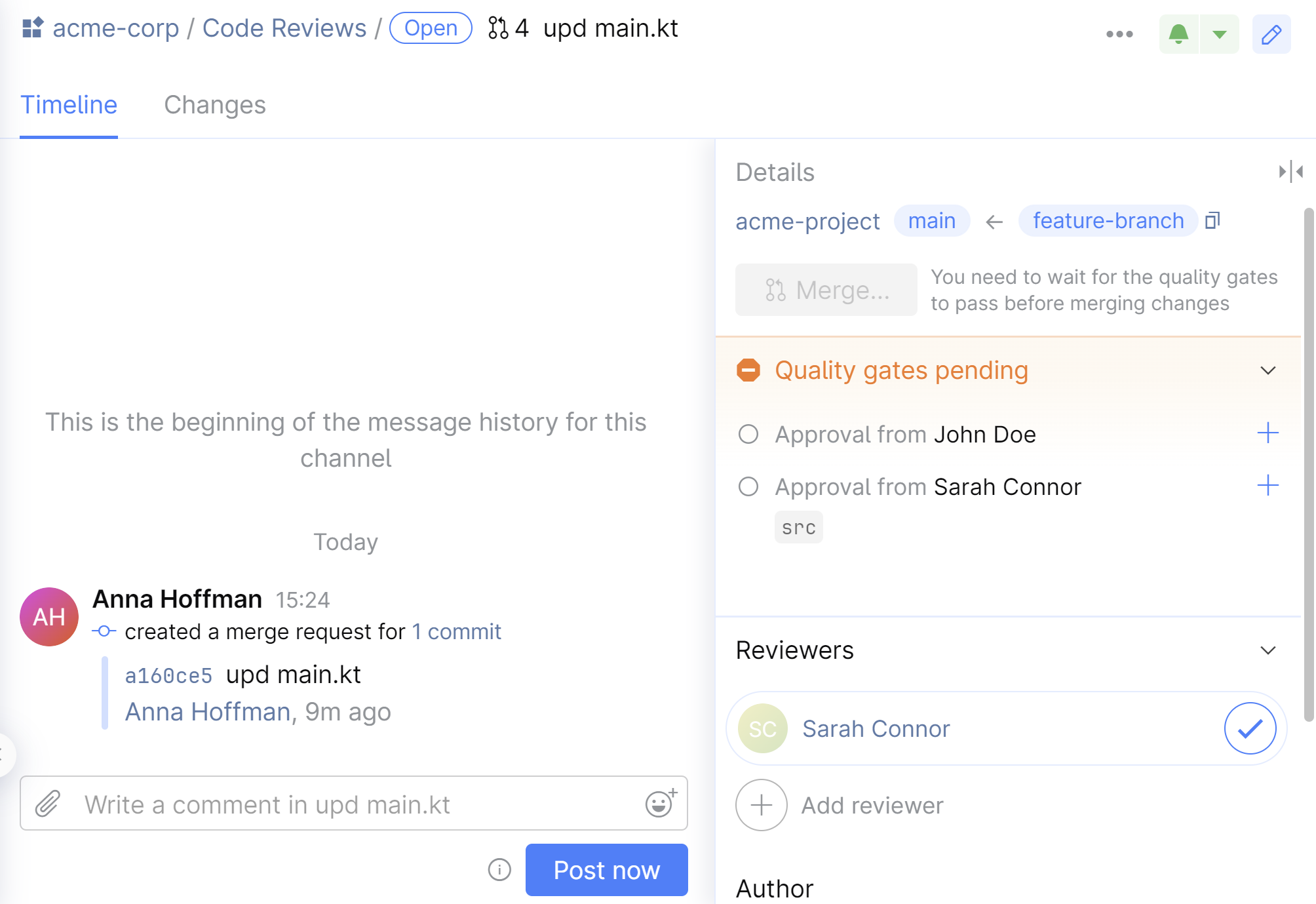
Step 4. Connect your CI/CD server to SpaceCode
In this tutorial we assume that you use JetBrains TeamCity for CI/CD. Now, we need to connect our repository to a respective TeamCity project to receive external check statuses from TeamCity's Commit Status Publisher.
Please follow the TeamCity Integration Guide to set up a connection.
As soon as your CI/CD server is connected to SpaceCode, we're ready to use it for the 'green build' requirement.
Step 5. Add the 'green build' quality gate
One more quality gate that ensures code quality is the 'green build' requirement. The changes are allowed to be merged into main only if a CI/CD server can successfully build the source branch (the one that contains the changes, e.g., a feature branch). In this step, we'll show how you can do this for TeamCity.
Done! After you complete this step, it won't be possible to merge a change until the corresponding CI/CD build is successfully finished.
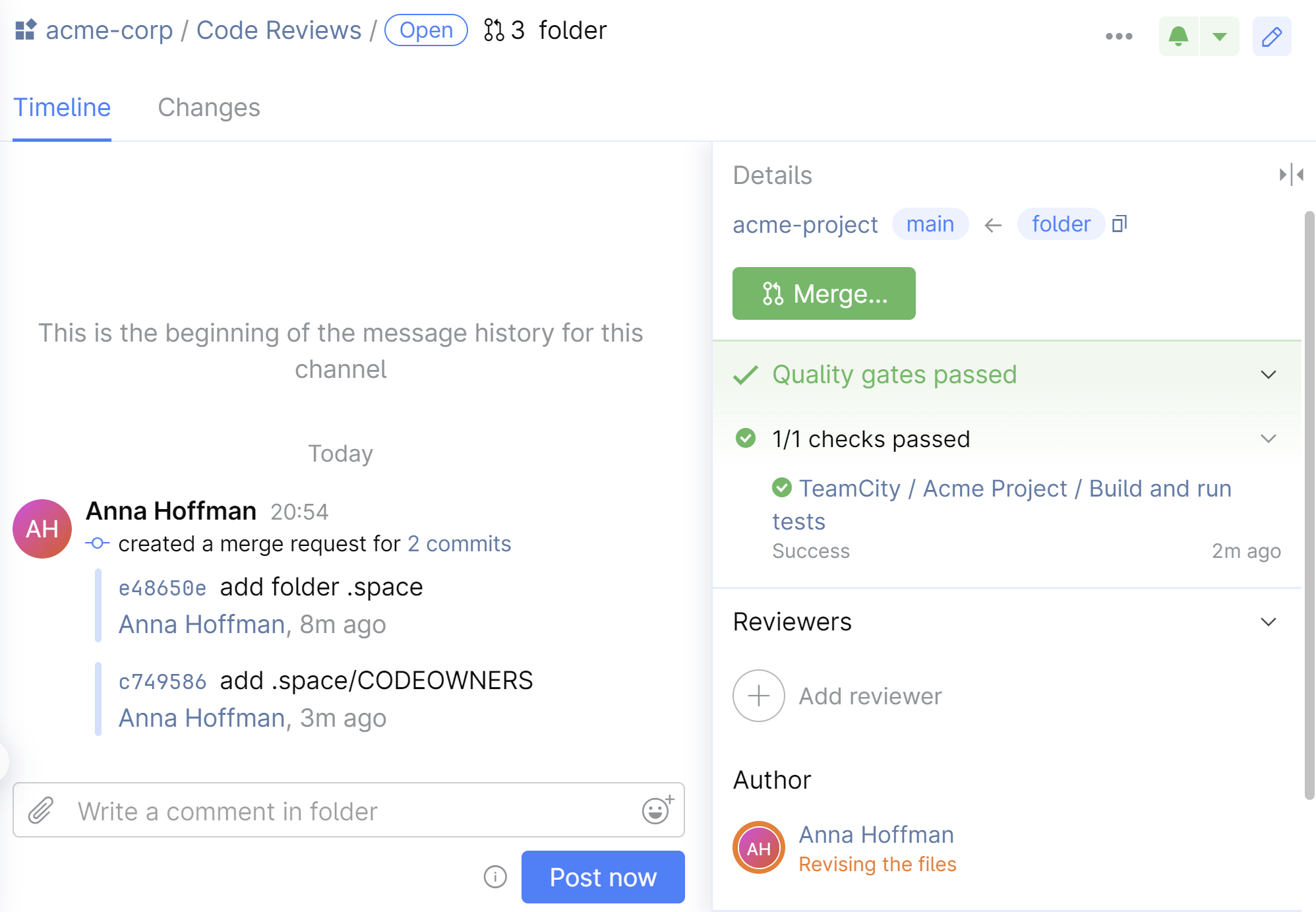
Step 6. Set up 'safe merge'
In projects with large number of merge requests, it makes sense to prefer the Safe Merge feature over a simple 'green build' quality gate. Safe merge creates a temporary merge commit with the latest updates from your main and feature branches, and then testing it with Automation jobs or TeamCity builds. This is important because while you were working on a feature branch, the main branch could have received changes that conflict with your work. By using safe merge, you can catch these conflicts before actually merging the branches.
Let's start by adding a new branch specification to the project's VCS root in TeamCity. We must do this because TeamCity monitors only the
refs/heads/*branches by default, but SpaceCode creates temporary merge commits inrefs/merge/<merge-request-name>/safe-merge.In TeamCity, open project settings, then VCS Roots.
Edit the VCS root, namely, in Branch specification, add the line
+:(refs/merge/*)

Now, we should create a JSON file that will configure safe merge settings. The exact file location doesn't matter. The main requirement is that you must create the file in the target repository. In our example, it's
main.Create the file and edit its content. In our case, we need a simple configuration that will specify the TeamCity server settings and the build configuration that must be run during safe merge:
// If you want to use this example in a real JSON file, delete all comments first! { // Safe Merge version number. Should be "1.0" "version": "1.0", // What to do it build fails. // This setting is helpful for builds with flaky tests. "retry-policy": { // How many build attempts are allowed "num-retries": 3, // Use the same temporary merge commit on a retry // or create a new one "reuse-merge": true }, "builds": [ { "teamcity": { // Build configuration ID // You can get it in build config settings "configuration": "AcmeProject_BuildAndRunTests", // Name of your TeamCity connection // Only required if you have one then one connection set up "connection": "MyTeamCityIntegration" } } ] }For details on configuration syntax, refer to the safe merge documentation.
Open the repository settings.
On the repository settings page, go to Protected Branches, then edit the previously created rule.
Turn Safe Merge On and click Select under Configuration file.
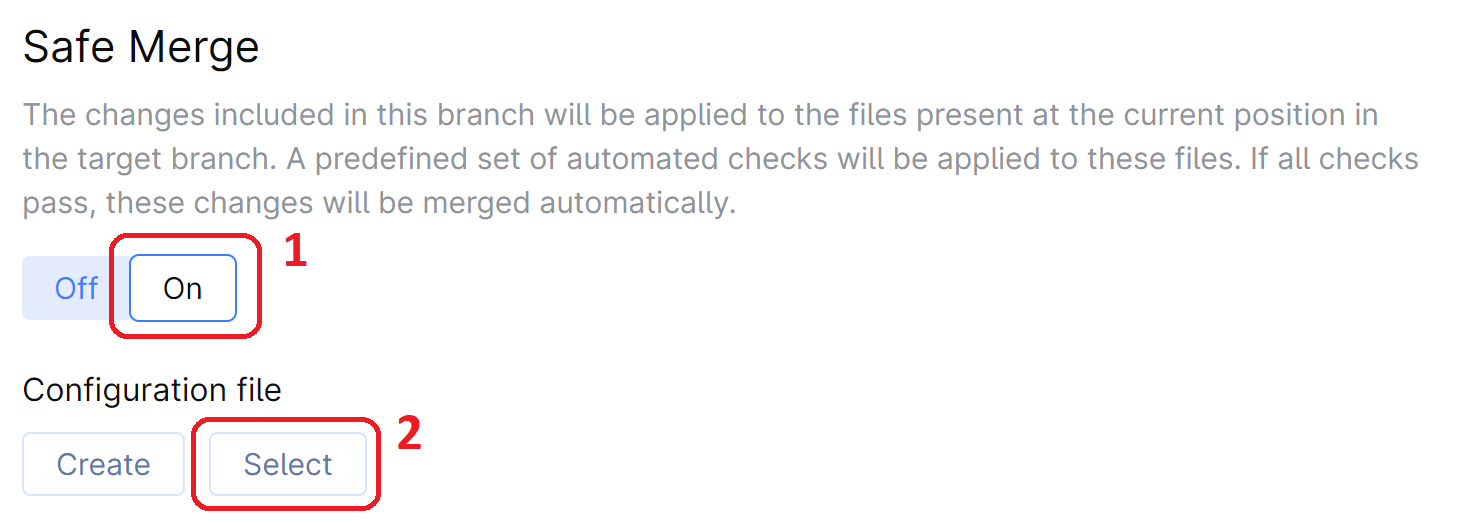
Select the file and click Save.
That's it! The safe merge feature is enabled for your project. Now, the Merge button in a merge request will change to Safe merge. Clicking it will create a temporary merge commit and run the CI/CD build we've specified in the JSON file. If the build is successful, this will end up with merging the changes into the main branch. If you want only to run the build without actually merging the changes, click Dry run.
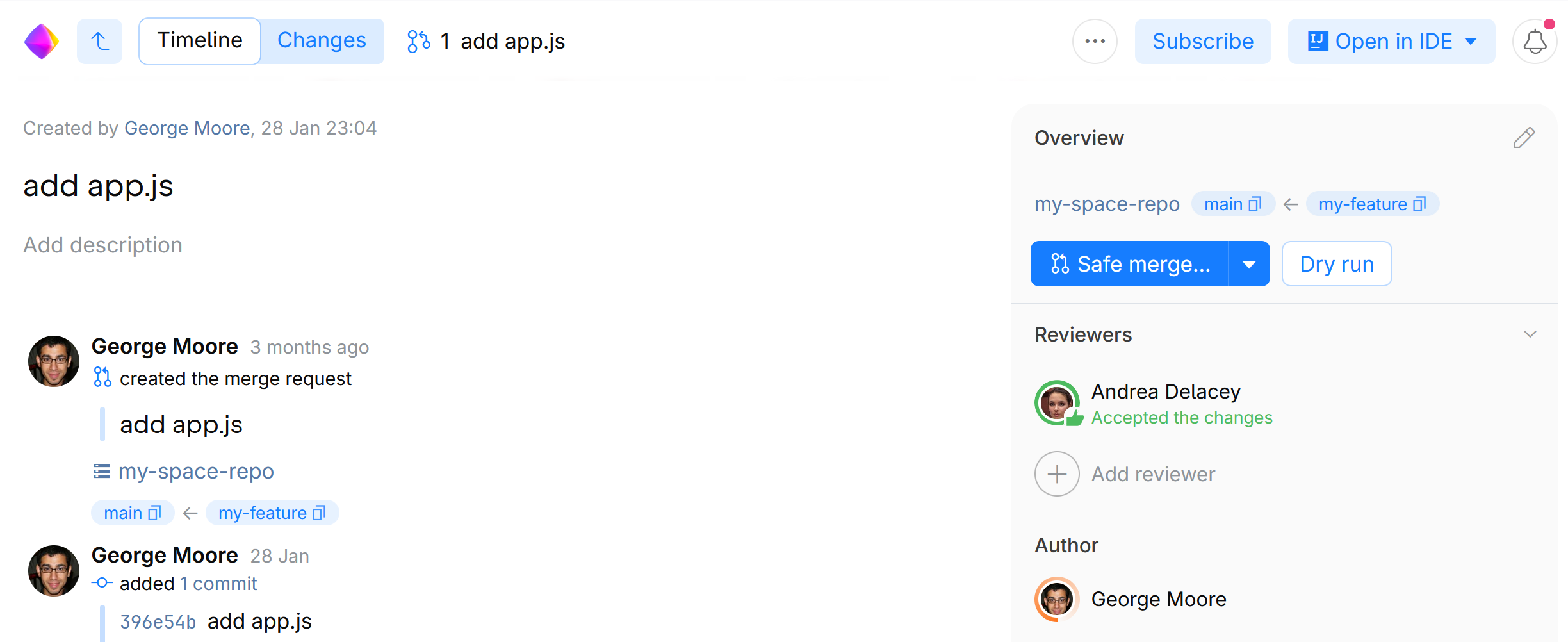
Conclusion
We believe that SpaceCode Git flow addresses the challenges of large projects and teams and guarantees that code changes are thoroughly reviewed and tested before being merged. Though, this tutorial is a good starting point, it's obvious that every project is different and the final flow configuration may require some adjustments to fully meet your needs.