Introduce JavaScript modern practices
From this article, you will learn how WebStorm-provided coding assistance helps you follow key best practices in modern JavaScript for cleaner, more maintainable, and more performant code.
When dealing with old codebases, you may encounter outdated patterns and practices. WebStorm helps you by highlighting such patterns and suggesting quick fixes.
Declare variables with let and const
let and const provide block-scoping, which is more predictable and reduces unexpected errors that can happen when declaring variables with var, which is function-scoped.
Although var declarations may be used on purpose, in old code it can result from the old approach.
WebStorm detects usages of var and suggests replacing it with let or const.
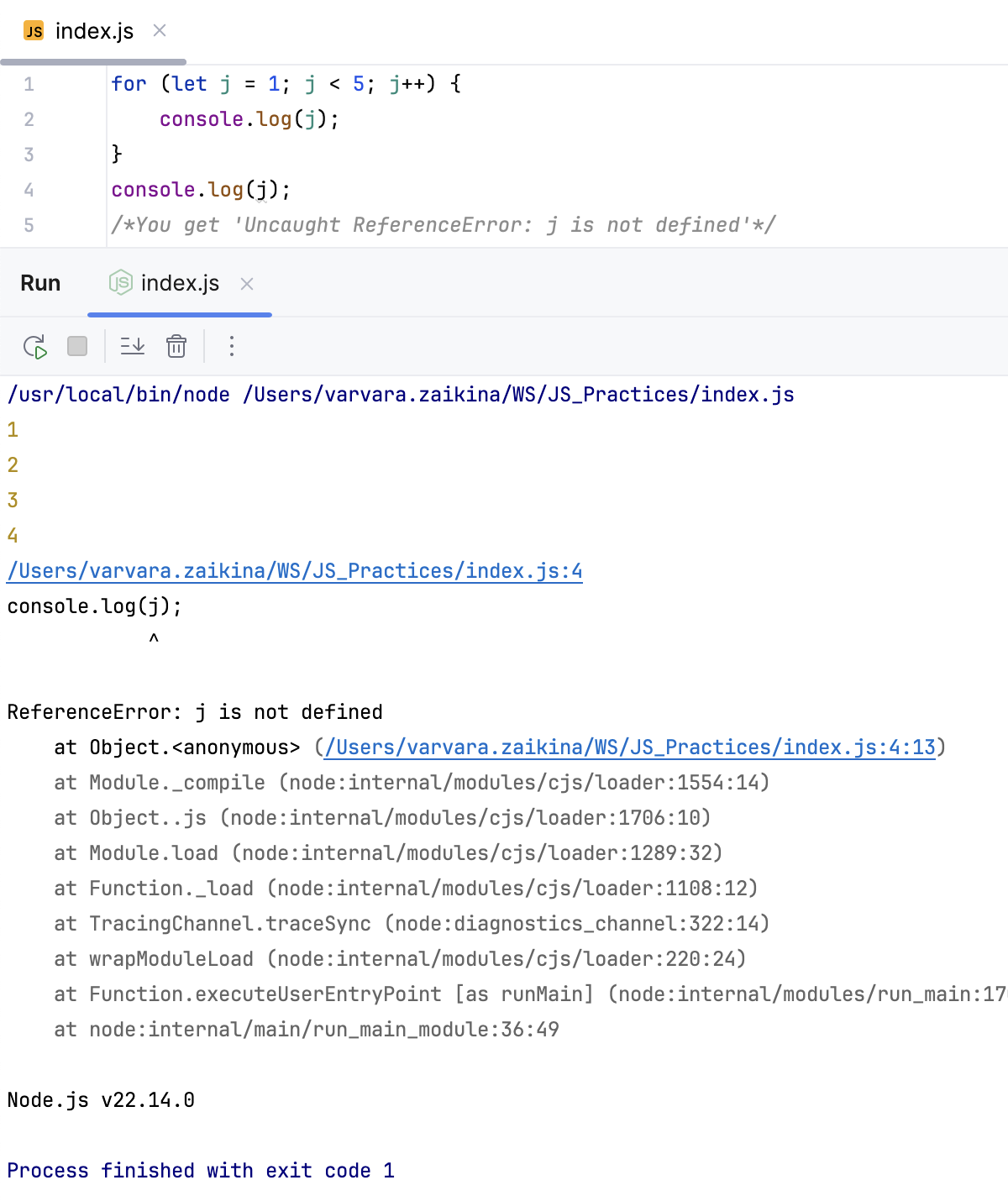
Hover over a highlighted
vardeclaration and click the Convert to const link.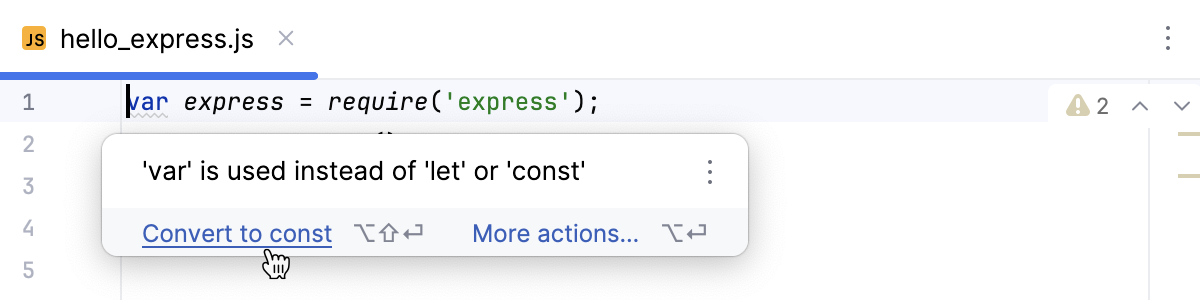
Place the caret at a
vardeclaration, press Alt+Enter, and select Convert to let or Convert to const from the popup list.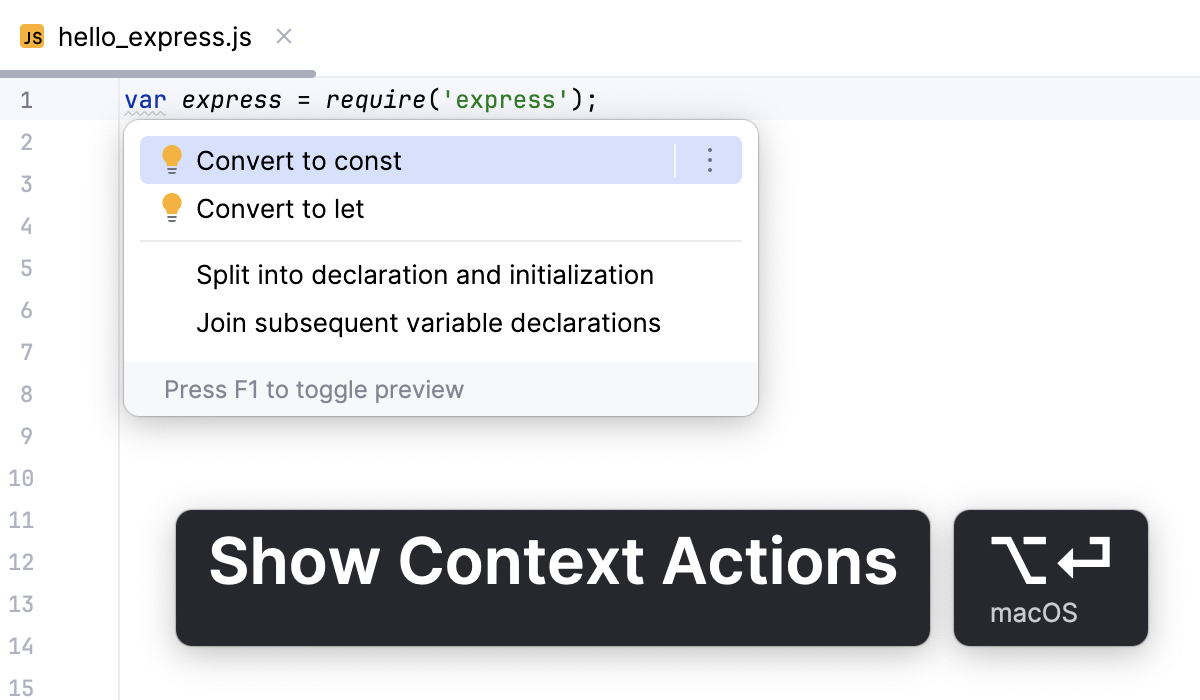
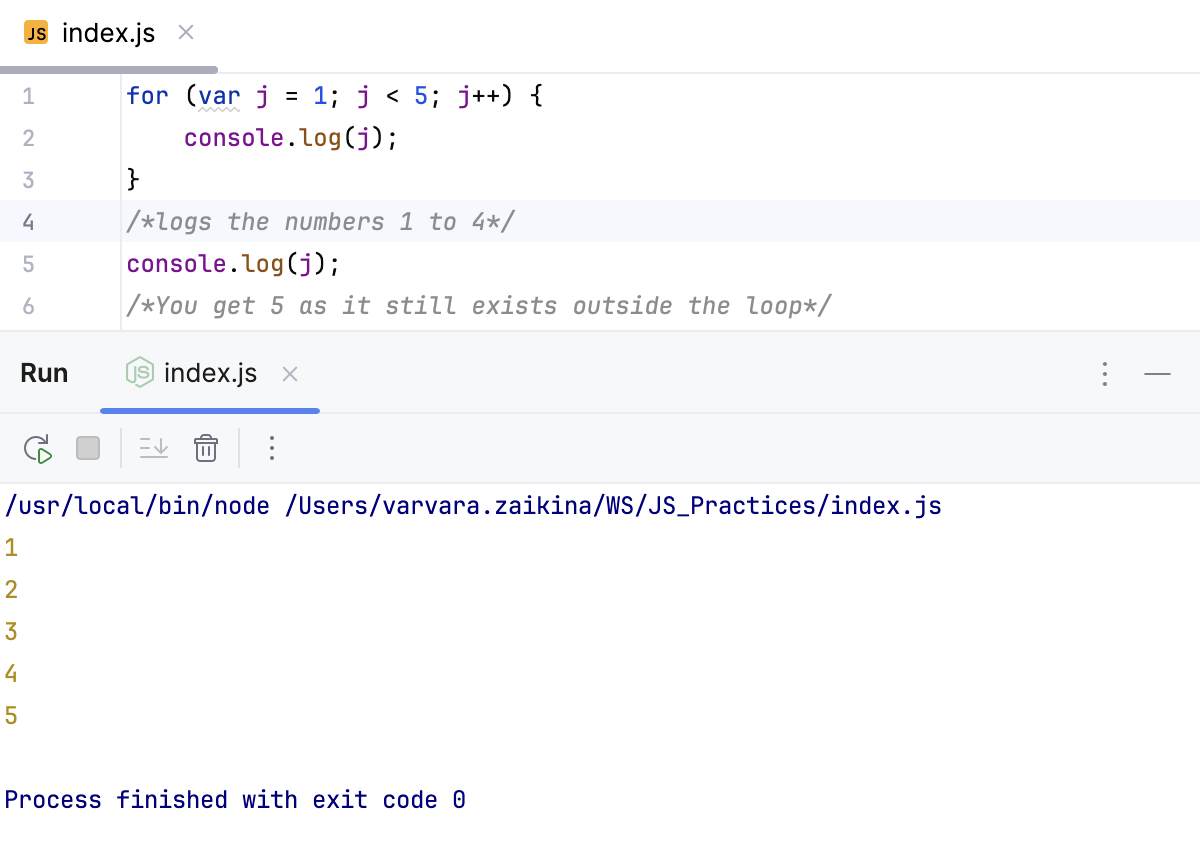
Example
Use Classes instead of Function: prototype
Although in many old codebases you may run into the function prototype approach for emulation of classes, it is recommended that you use classes because they have much cleaner syntax.
WebStorm suggests a refactoring that you can invoke with a Convert to class context action.
Place the caret at the name of the function to be converted and press Alt+Enter.
From the list, select Convert to class.
In the Refactoring Preview, review the suggested updates and click Refactor, when ready.
Use arrow function expressions
Arrow functions provide a more concise syntax, automatically bind the this context, which can be particularly helpful in class methods where this can easily get lost.
With WebStorm, you can introduce an arrow function using a dedicated context action.
Place the caret inside an anonymous function and press Alt+Enter.
From the popup list, select Convert to arrow function.
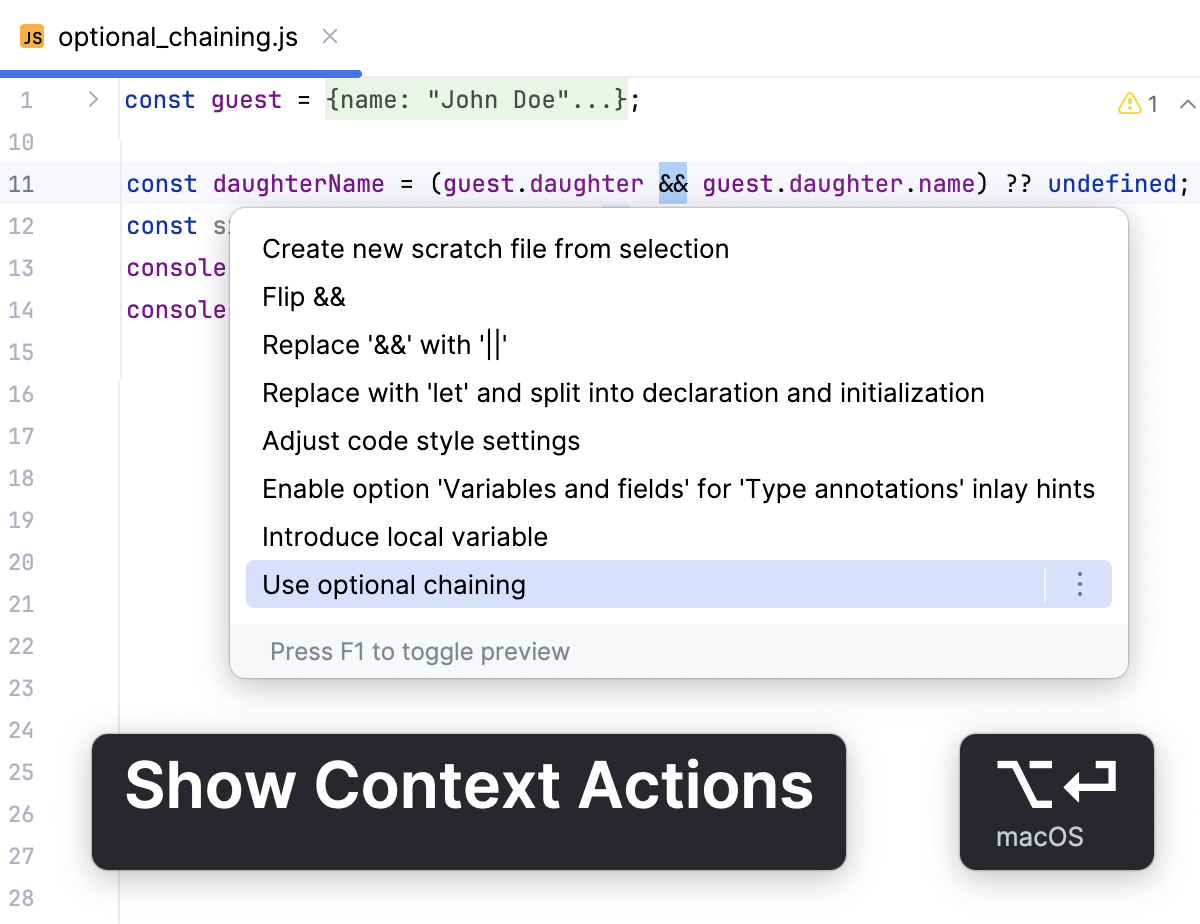
Use optional chaining
The optional chaining operator (?.) automatically checks whether a property, an array element, or a method exists before attempting to access it. If any part of the chain is null or undefined, it returns undefined rather than throwing an error. Without optional chaining, this check requires verbose and repetitive code.
WebStorm suggests a context action to introduce a ?. operator.
Place the caret at an expression to be converted and press Alt+Enter.
From the popup list, select Use optional chaining.
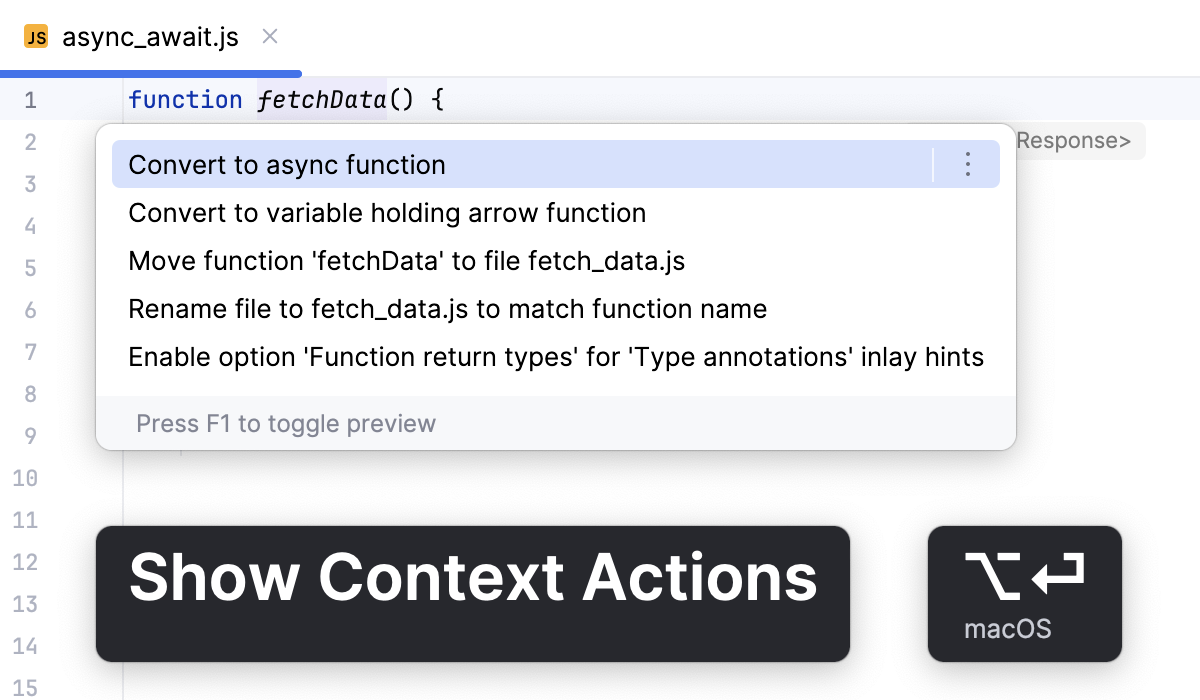
Use async/await syntax
The async/await syntax simplifies working with asynchronous operations by removing the need for chaining .then() and .catch(). It makes your code more readable, more maintainable, and easier to follow, especially when dealing with multiple async calls.
With WebStorm, you introduce the async/await syntax into your code via the Convert to async function context action.
Place the caret at a function to introduce the
async/awaitsyntax to and press Alt+Enter.From the popup list, select Convert to sync function.
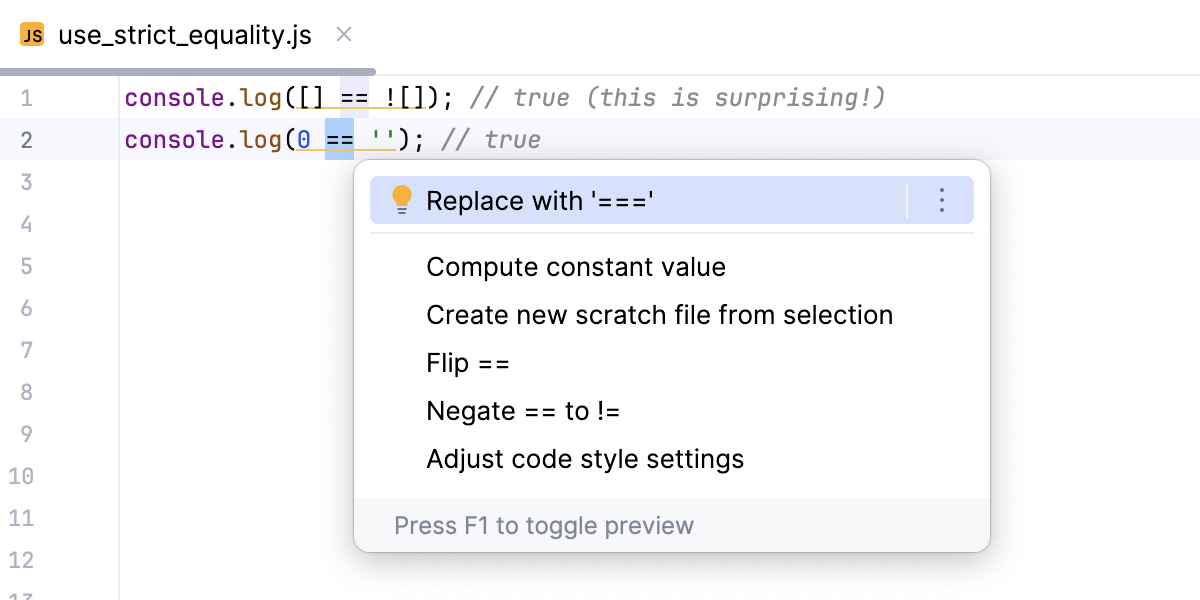
Use strict equality (===)
Using strict equality (===) instead of loose equality (==) leads to more predictable and reliable behavior because strict equality does not perform type coercion but compares both value and type directly.
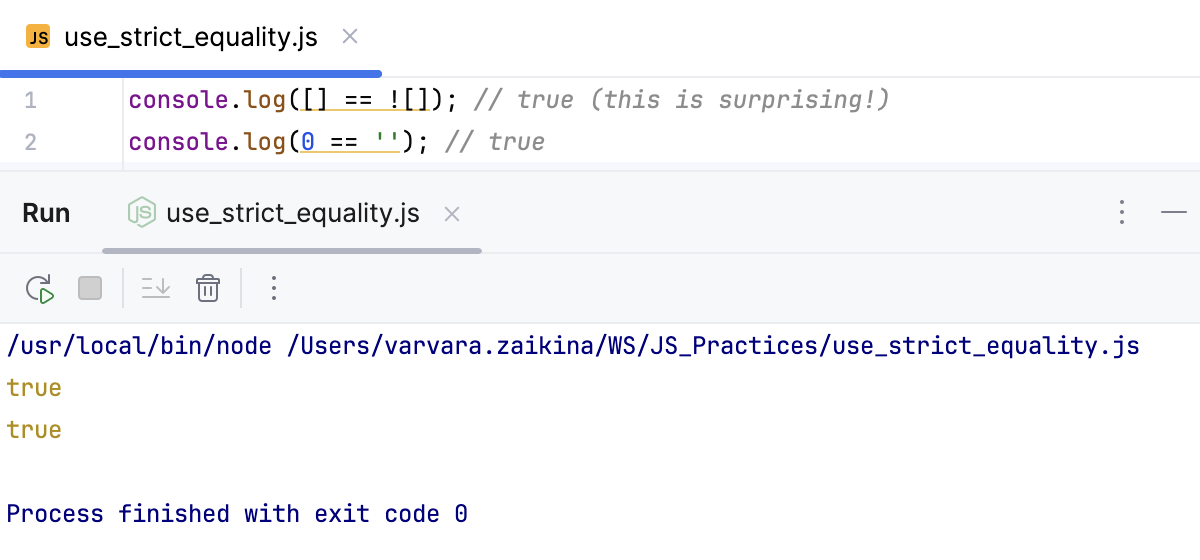
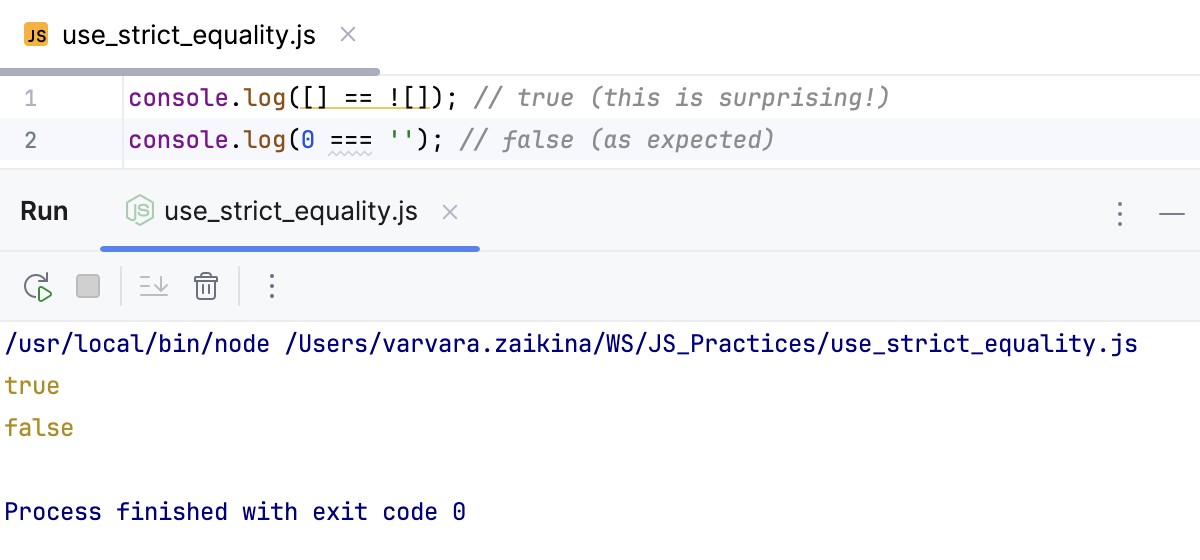
WebStorm detects potential problems that using the loose equality may cause, highlights unreliable code fragments, and suggests a quick fix.
Hover over a highlighted loose equality and click Replace with '==='.
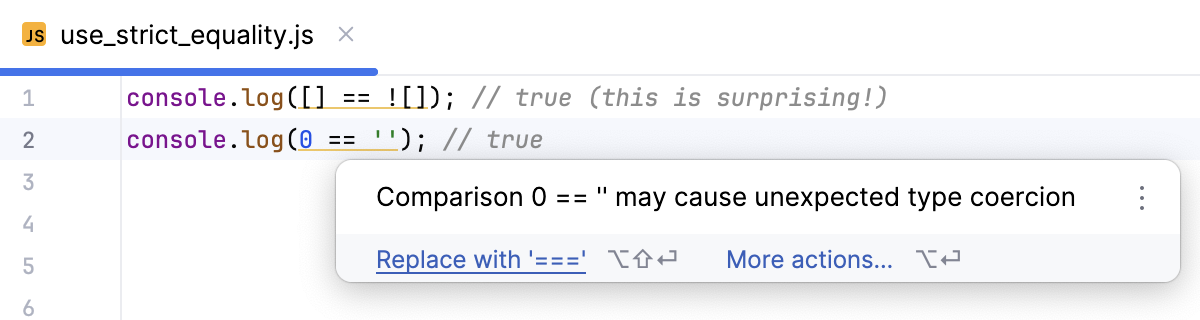
Place the caret at a
===equation, press Alt+Enter, and select Replace with '===' from the popup list.