Import from GitHub
The import from GitHub lets you migrate issues, comments, users, and other data from a GitHub repository to YouTrack.
A setup wizard navigates you through the import configuration process. It prompts you to enter the connection settings and lets you map a project in YouTrack to a repository in GitHub. If your repository has a custom set of fields for issues, you can edit the import script in YouTrack directly.
Import Details
If the GitHub database contains references to entities that do not exist in YouTrack yet, they are created. The YouTrack user account you use to run the import should have permissions to create all imported entities. We recommend using an account with a System Admin role or the Low-level Admin Write permission to run the import.
Here is the list of entities that are imported from GitHub and their mapping to YouTrack entities:
Entity in GitHub | Entity in YouTrack |
|---|---|
Repository | Project |
Issues | Issues |
Comments | Comments |
Users | Users |
Custom fields | Custom fields |
Attachments | Attachments |
Markdown files ( | Knowledge base articles |
HTML files ( | Knowledge base articles |
reStructuredText files ( | Knowledge base articles |
Repository collaborators | Project team members |
Set up an Import from GitHub
Before you add a new import configuration, you need to create a personal access token that will grant access to the repository in GitHub. Then you can use the token for authorization when setting up the import in YouTrack.
Create an Access Token in GitHub
To set up import of issues from GitHub, first, you need to create a personal access token for the GitHub account that you use to access issues in GitHub repository.
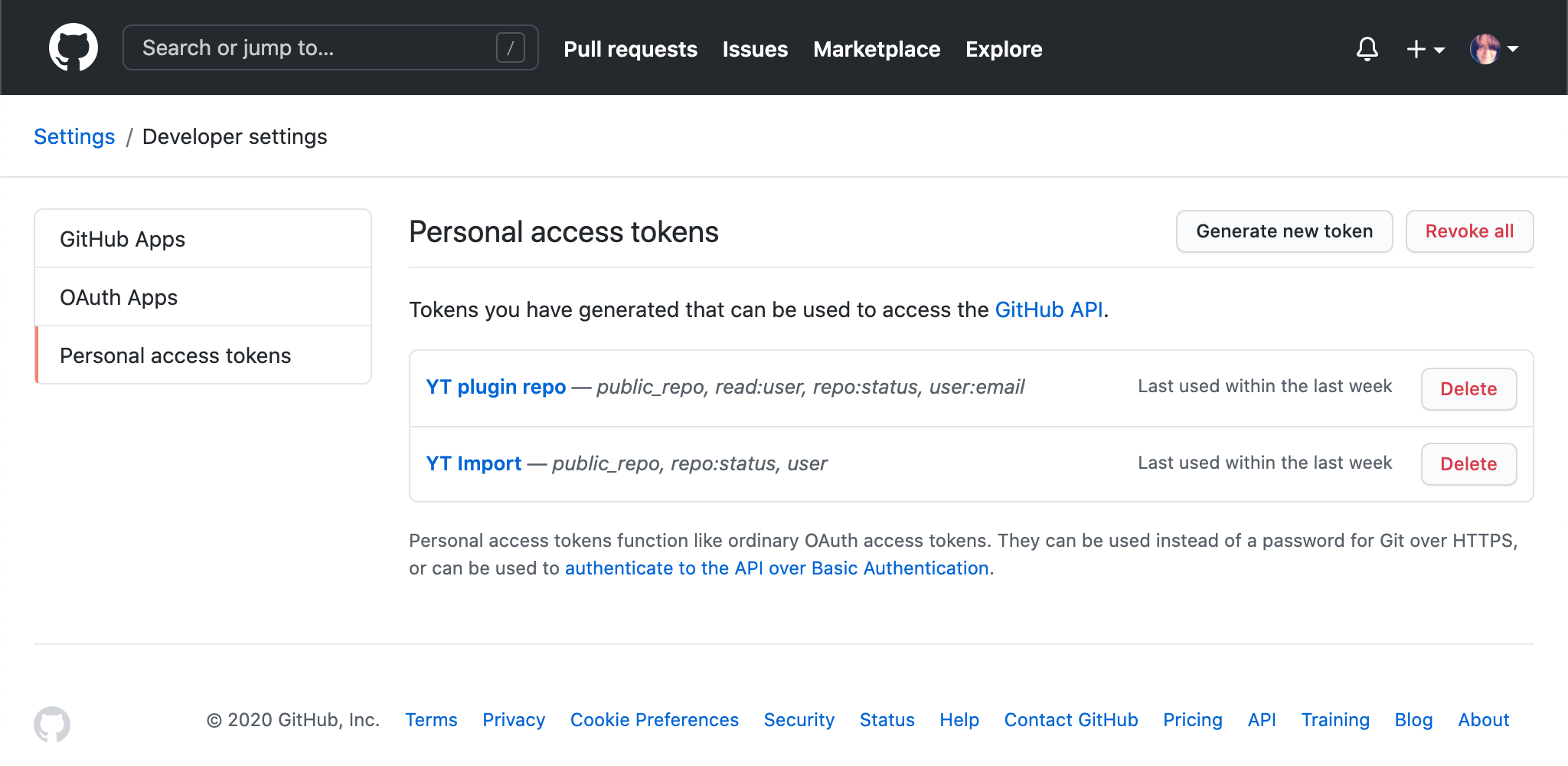
To create a personal access token in GitHub:
Log in to GitHub with an account that is granted administrative permissions.
In the upper-right corner of any page, click your profile photo, then click Settings.
In the left sidebar, click Developer settings, then Personal access tokens.
Click Generate new token, and provide a description for the token.
Set the expiration date for the token if necessary.
Select the scopes for the token.
We recommend to use the following minimal set of scopes for the token to import GitHub issues depending on the repository type:
repo:repo:statuspublic_repo
user:read:useruser:email
repo:To import issues from a private repo, you need to enable the complete set or thereposcopes.user:read:useruser:email
Click Generate token.
The new personal access token is added to the list.
For more details on creating personal access tokens in GitHub, refer to the GitHub documentation.
Configure an Import from GitHub in YouTrack
The setup wizard guides you through the setup process.
To configure an import from GitHub:
From the Administration menu, select .
Click New import to open the setup dialog.
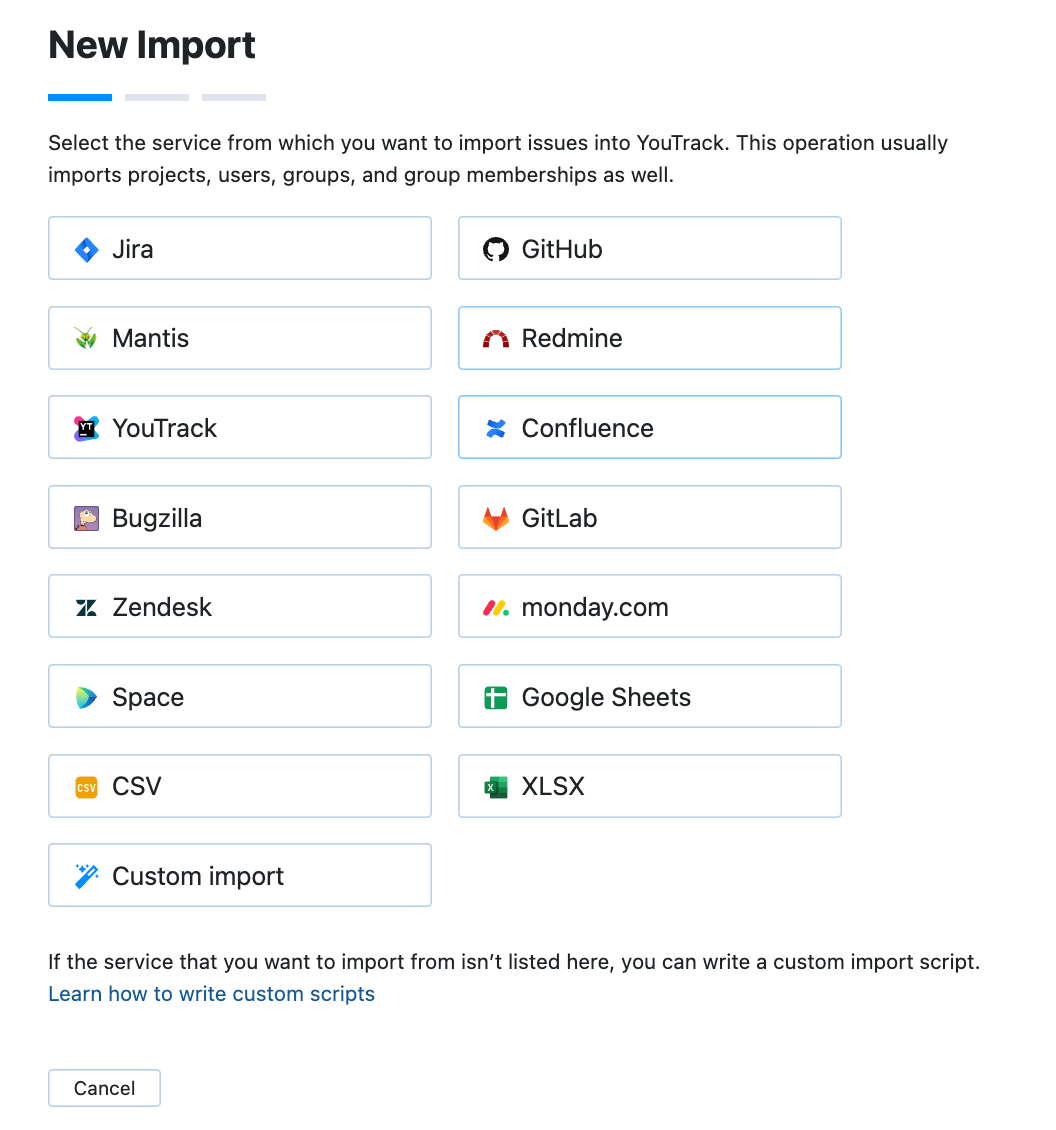
Select GitHub.
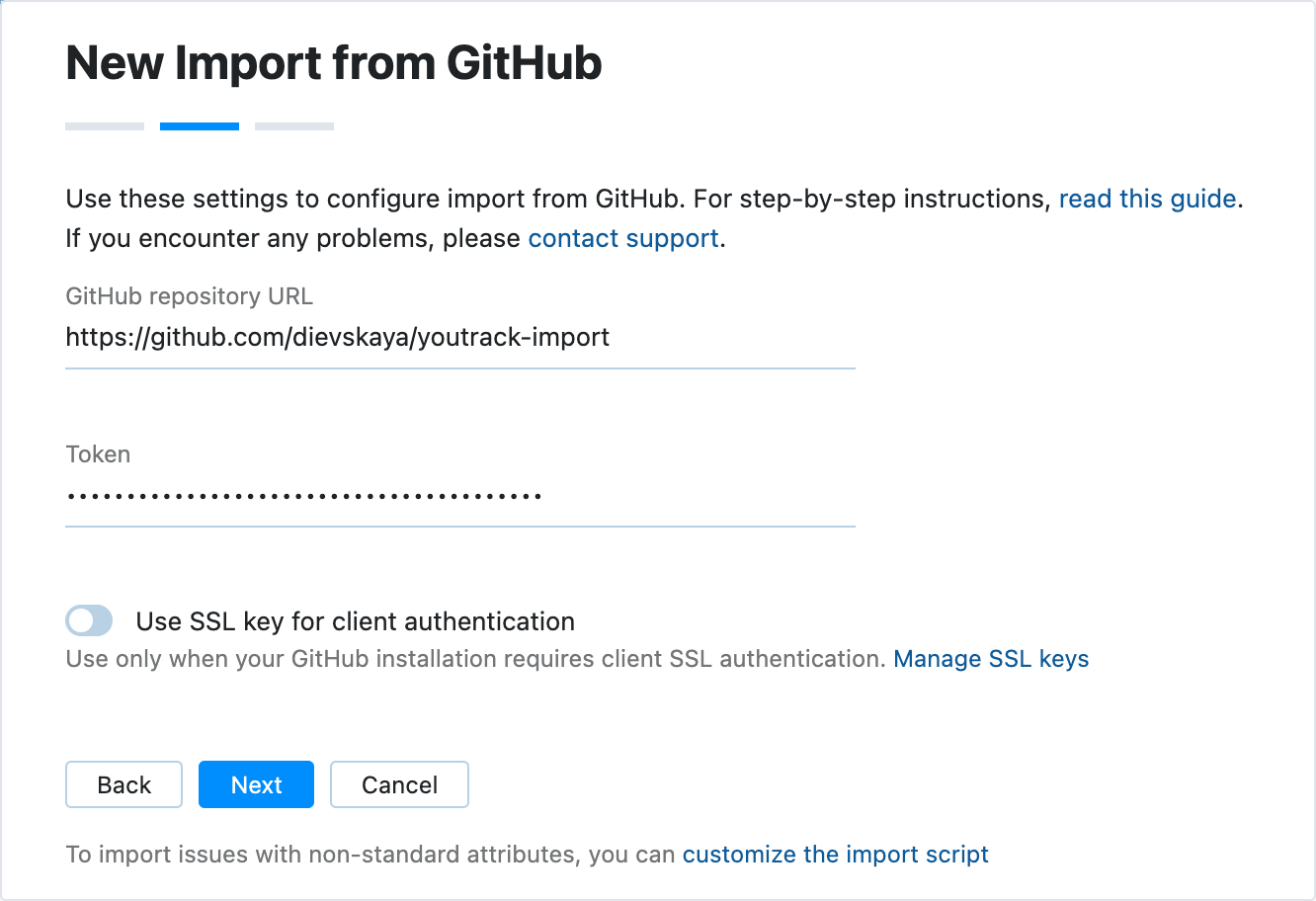
Configure the import settings:
Setting
Description
GitHub repository URL
Enter the URL of the target repository. Since it's not a clone URL, do not include the
.gitsuffix.Token
The personal access token that you have generated in GitHub for the user account that you use to access the target issues.
If required by your GitHub installation, enable the Use SSL key for client authentication option.
When done, click Next.
Review the settings that you have provided.
Select the target project for the import. For more details about the project mapping configuration, see Project Mapping.
Optionally, enable the Continuous import toggle. When enabled, YouTrack will periodically poll the GitHub repository and import updated and new issues that were created since the last sync.
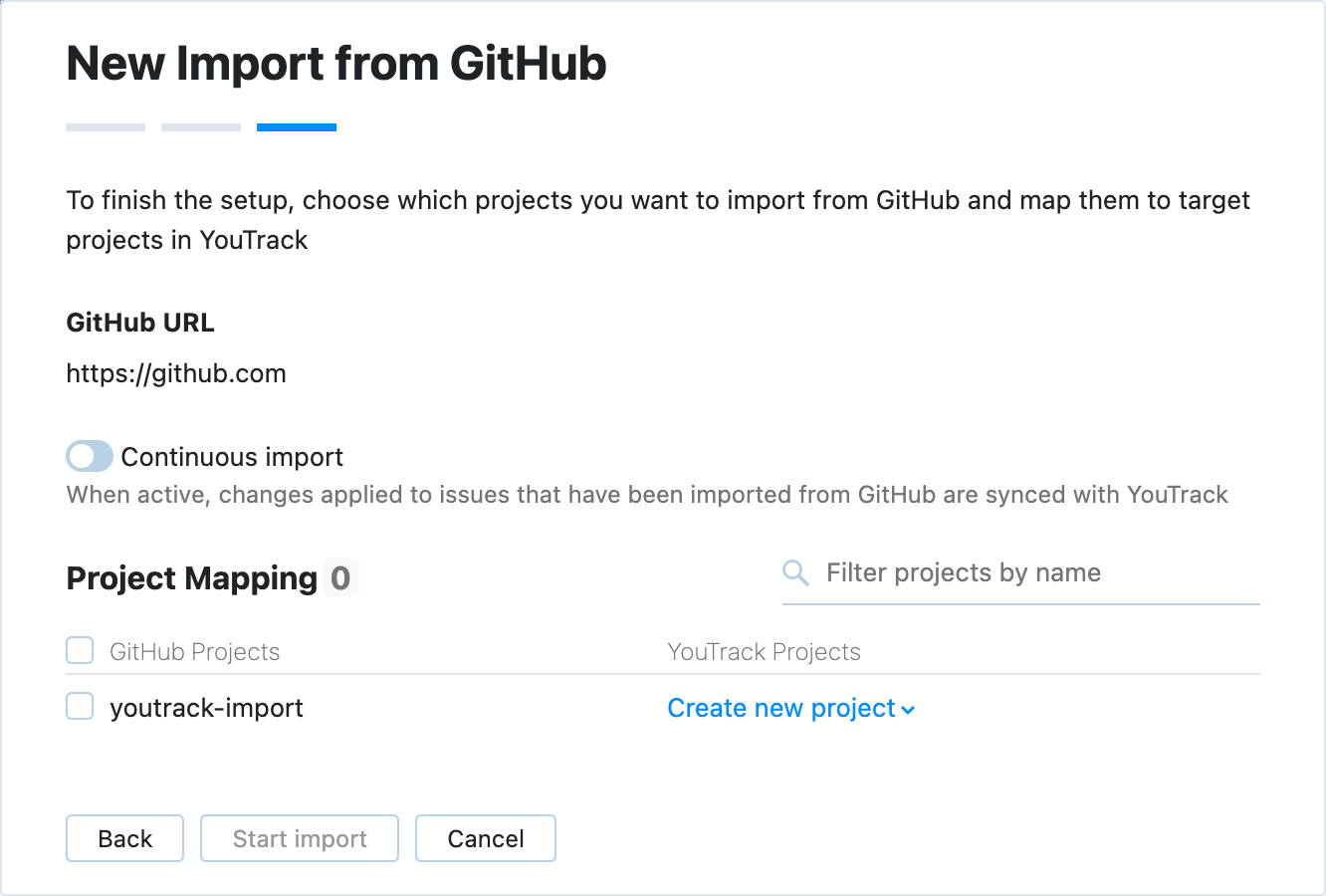
When done, click Start import.
YouTrack will import found issues, articles, and users into the target YouTrack project.
If the Continuous import option is enabled, YouTrack will periodically check the target GitHub repository for updated and new issues.
When you have set up an import, it is shown in the imports list. To view configuration and import details, select an import configuration in the list.
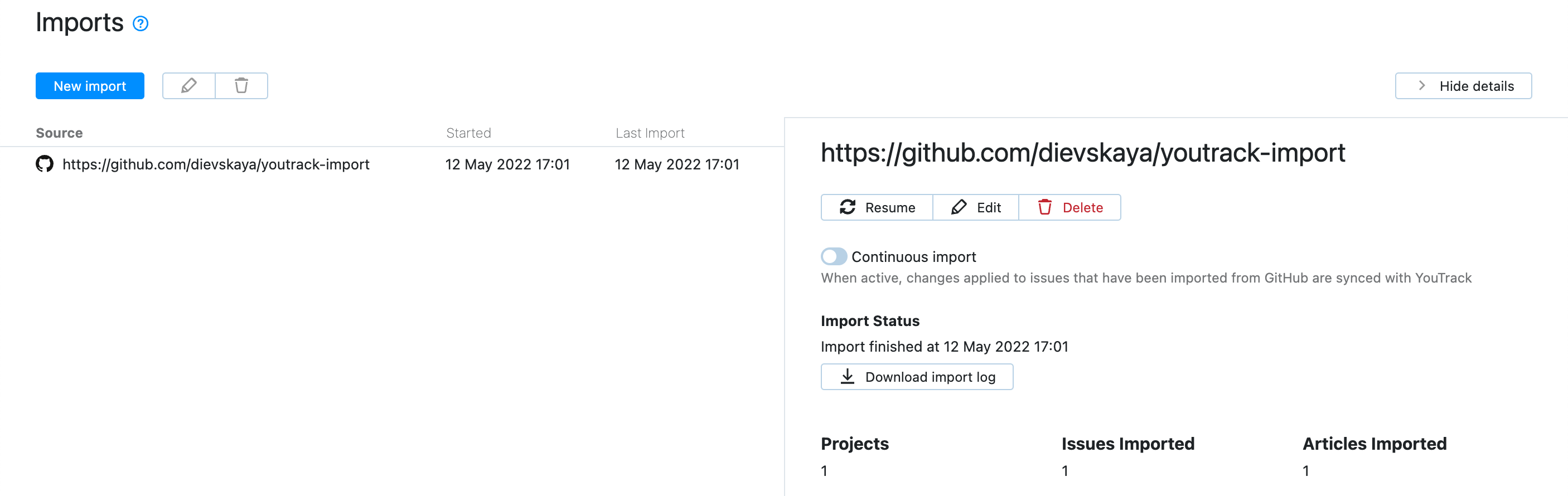
In the details sidebar, YouTrack shows import status and details on the data that was imported. Click the Resume button in the toolbar to explicitly start polling for changes and importing updates from the target GitHub repository.
You can also download the import log file to study and investigate when needed.
Project Mapping
On the final step of the import setup, you can choose whether to create a new project for the import or import data into an existing project in YouTrack.

To configure project mapping:
Select the target YouTrack project.
YouTrack checks for existing YouTrack projects with corresponding names. If it finds a YouTrack project with the same name as the GitHub repository, YouTrack suggests it as the target project.
If there is no existing YouTrack project with the corresponding name, YouTrack suggests creating a new one.
If you want to change the target project, select another option from the corresponding dropdown on the list.
Click Start import to finalize import setup and start import.
Import starts.
Import Options
After the initial import, the following controls are available in the sidebar:

Control | Description |
|---|---|
Resume | Immediately imports any changes made in the connected GitHub repository after the previous import. |
Edit | Opens the integration settings page in edit mode. Use this option to connect to a different GitHub repository, update the login credentials, or update project mapping. |
Delete | Deletes the current import settings. Projects, issues, comments, users, and groups that were imported from the connected GitHub repository are not affected. If you delete the import settings and connect to the same GitHub repository, the issues are re-imported into the existing project with new issue IDs. |