What’s new in IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3
IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3 delivers major performance and usability improvements, including faster startup, easier installation of theme and keymap plugins, enhanced VCS workflows, and adds support for microservices frameworks, MongoDB and more.
Better Performance
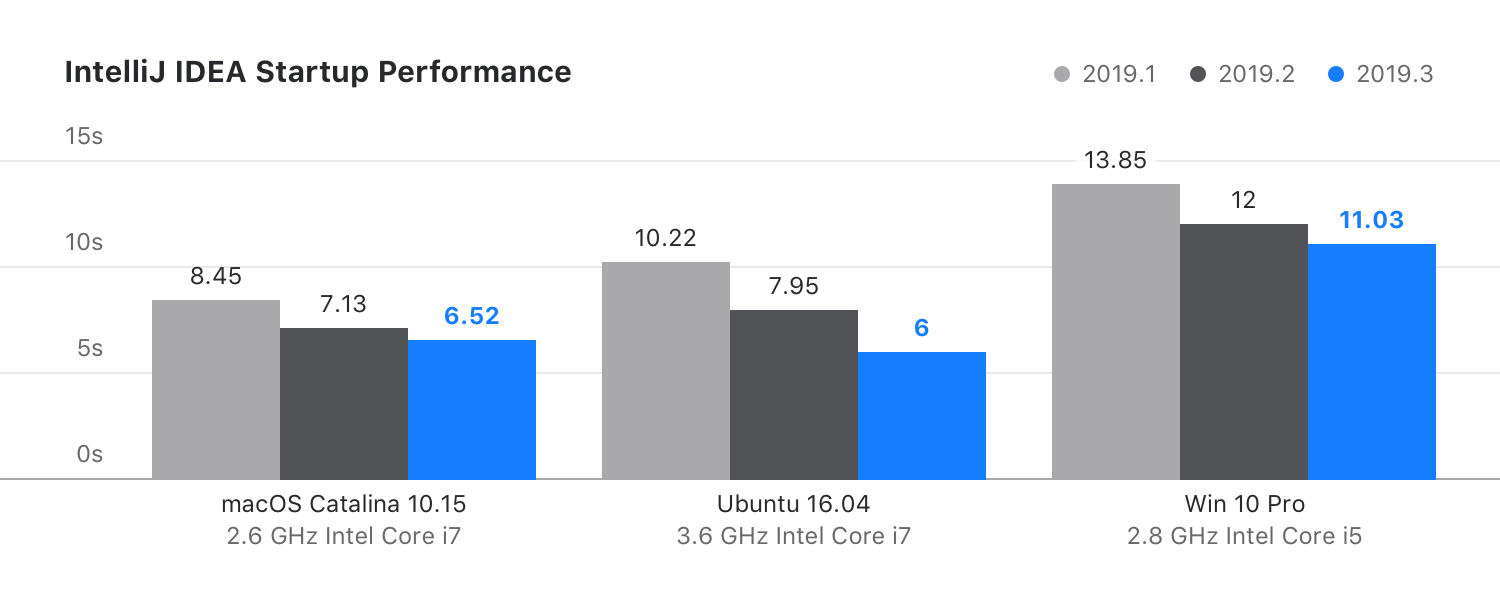
Faster startup
One of the major performance improvements in this release is that startup times are shorter than ever. We have introduced substantial architectural changes to parallelize some of the tasks the IDE performs at startup so that they are not performed sequentially.
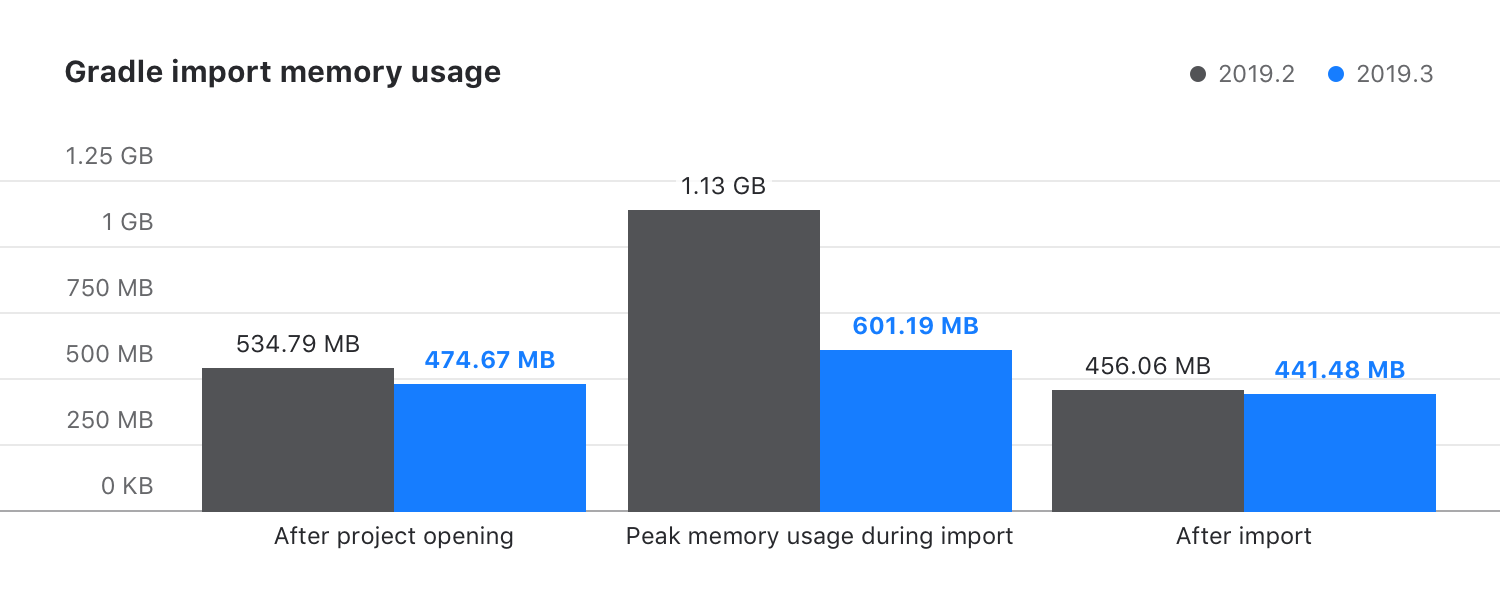
Reduced memory consumption
In IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3, we have optimized performance to reduce peak memory consumption when importing large Gradle projects.
Responsive UI
We have managed to fix over 1600 UI freeze reports you’ve submitted to us. Apart from these, we’ve fixed issues with editing POM.xml files in Maven projects, where completion suggestions are now displayed without any delays. Other fixes have resulted in faster processing of VCS status updates in large projects, better handling of ignored files, faster rendering of the project tree, better performance when working with a large number of editor or debugger tabs, and more speedups.
Better Java performance
This release brings lots of improvements for Java type inference, which not only fix various editor freezes but also speed up Java type inference for long method call chains. The ‘Join Lines’ action works faster when applied to multiple lines. You’ll also experience accelerated highlighting for Java code, especially when it comes to methods with generic var-args into which dozens of arguments are placed.
Better Kotlin performance
IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3 bundles Kotlin 1.3.60, which provides some impressive speedups such as faster highlighting in the editor.
Improved Usability
Faster startup
One of the major performance improvements in this release is that startup times are shorter than ever. We have introduced substantial architectural changes to parallelize some of the tasks the IDE performs at startup so that they are not performed sequentially.


Reduced memory consumption
In IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3, we have optimized performance to reduce peak memory consumption when importing large Gradle projects.
Smooth scrolling
A small but very valuable improvement we’ve made is to scrolling, which is now much smoother when done using the mouse wheel.
Automatic configuration of imported Maven or sbt projects
Now, when you import, create, or open an sbt or Maven project, IntelliJ IDEA will automatically set it up for you, so you no longer need to configure the settings manually.
Reworked behavior of context actions
In the intention actions dialog, the IDE now shows all available intention actions by default, even after you’ve chosen an action and closed the dialog.
Feature Polish
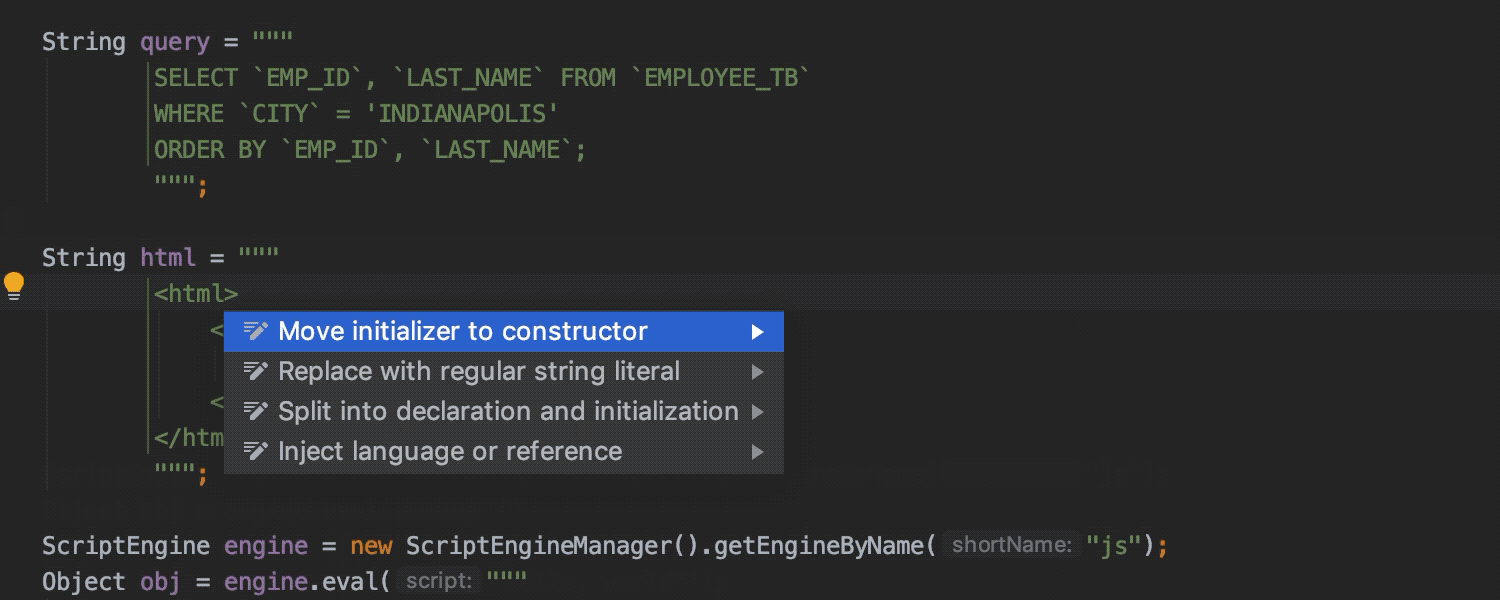
Extended support for Java 13 features
We’ve extended support for Java 13 text blocks: they are formatted automatically when inserting a third quote.
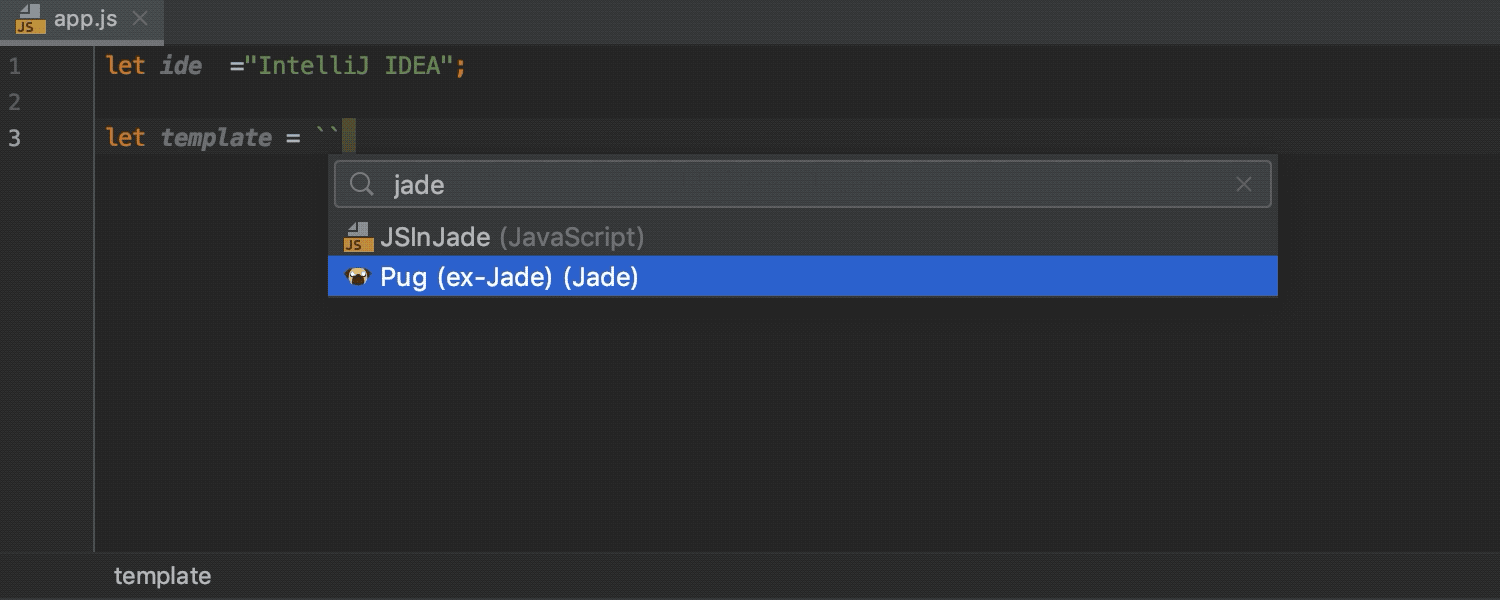
More template languages can be injected
With IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3, you can inject more template languages into your code, specifically Pug (ex-Jade), Handlebars, EJS, and Slim.
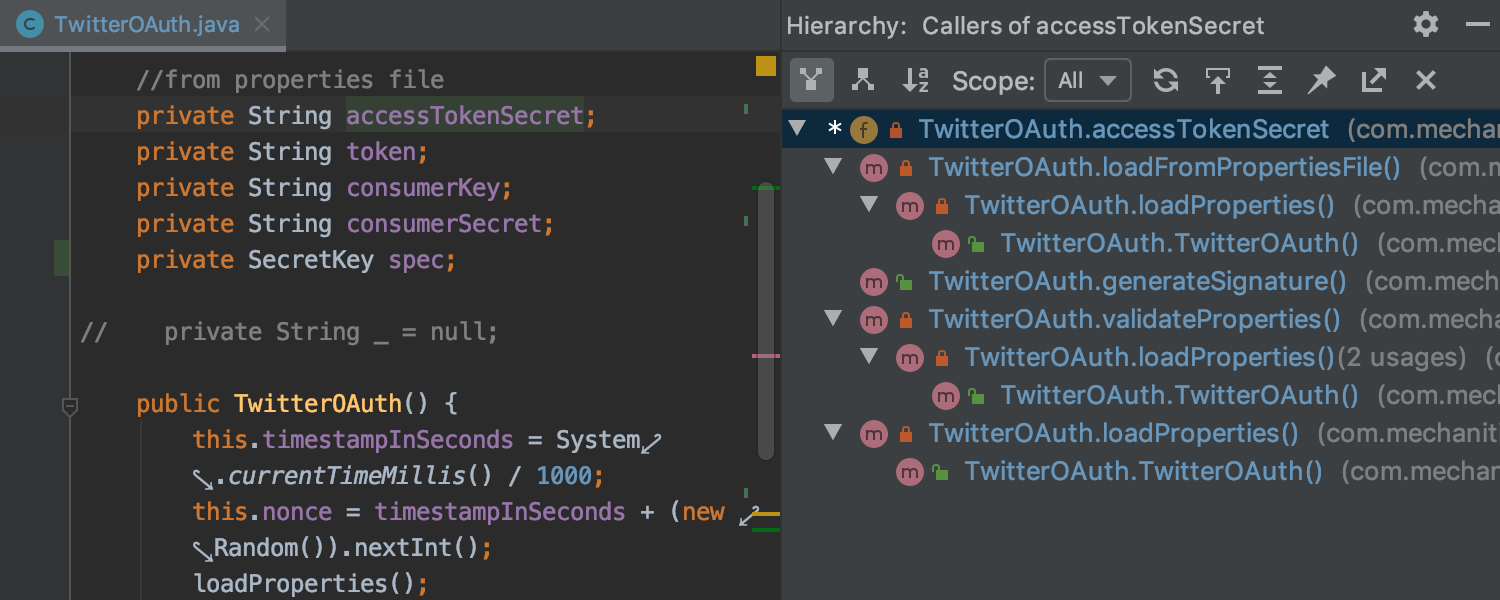
New ‘Field Call Hierarchy’ action
There’s now a simple way to view the hierarchy of a selected field by calling the new ‘Field Call Hierarchy’ action with Ctrl+Alt+H.
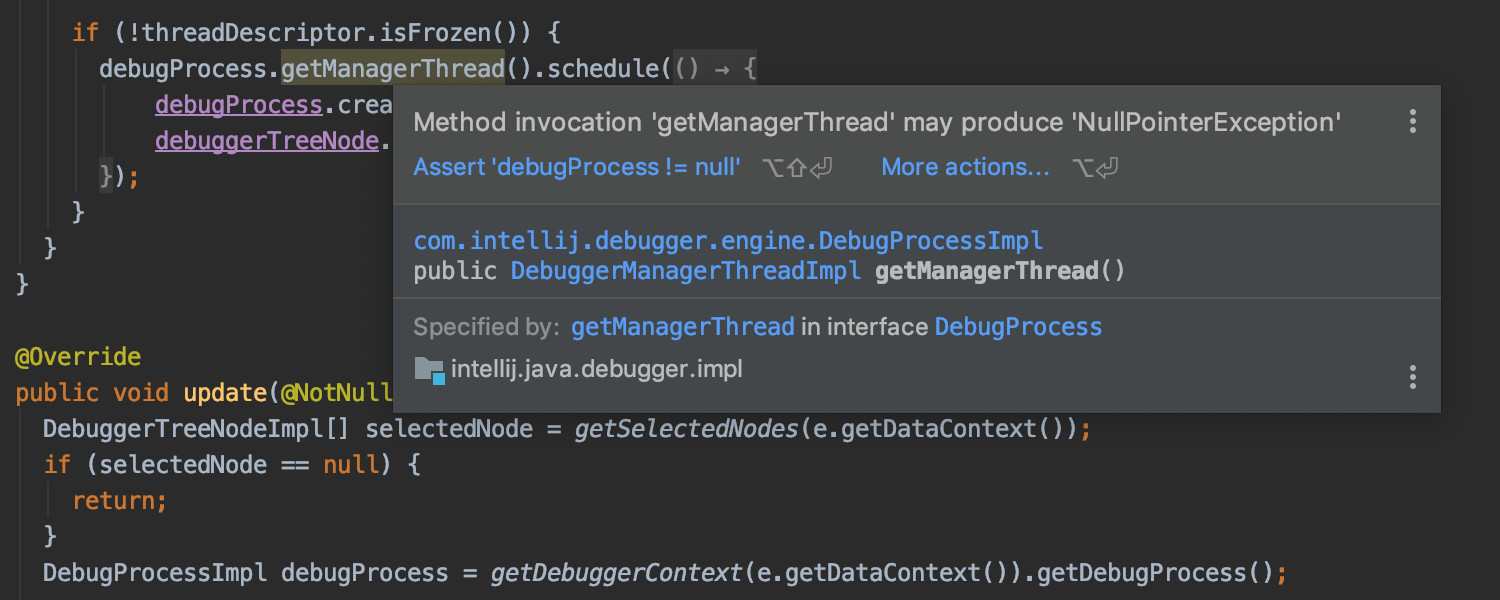
Unified popup for errors and documentation
When you hover the mouse over a symbol highlighted by an inspection, now you can have the popup also display the error, in addition to showing code reference information. To enable this, select ‘Show quick documentation on mouse move’ in Settings/Preferences | Editor | General.
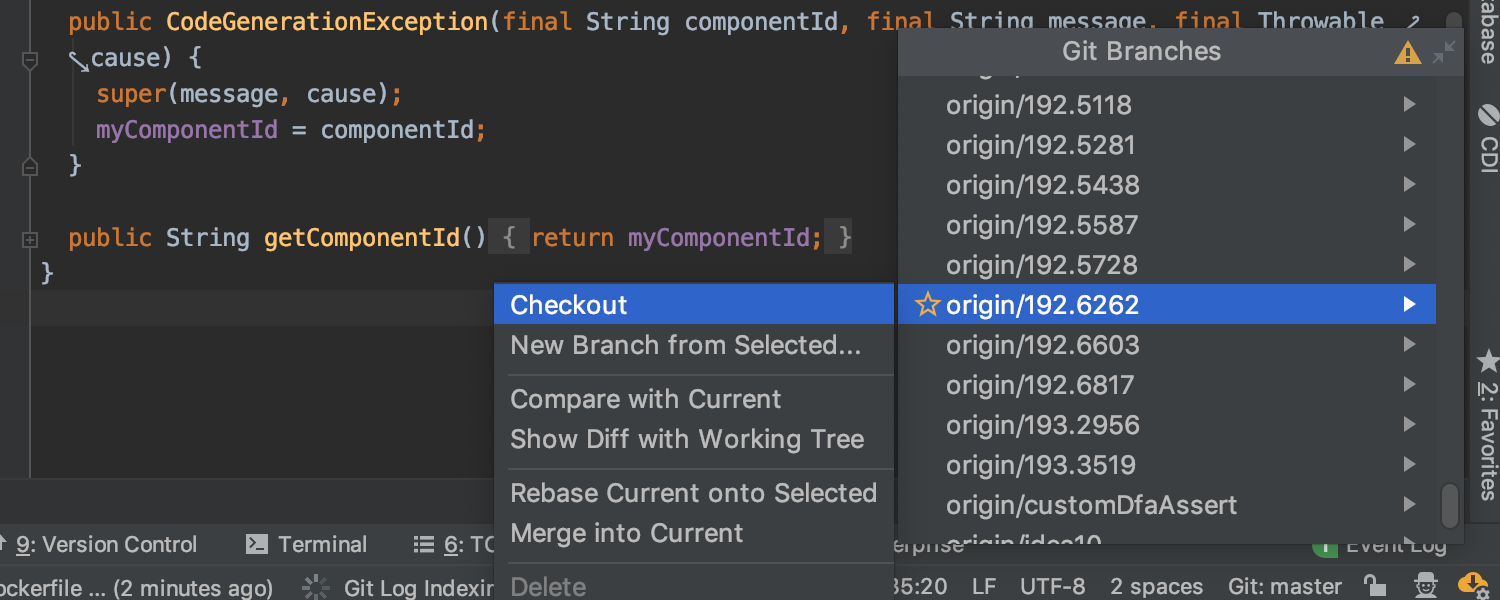
Improved Git checkout workflow
To eliminate confusion, the newly renamed ‘Checkout’ action called on a remote branch now creates a new local branch, checks it out, and sets tracking to the upstream. We’ve also added a ‘New Branch from Selected’ action for local and remote branches, which creates a new local branch and checks it out, but doesn’t set tracking to any remote branch.
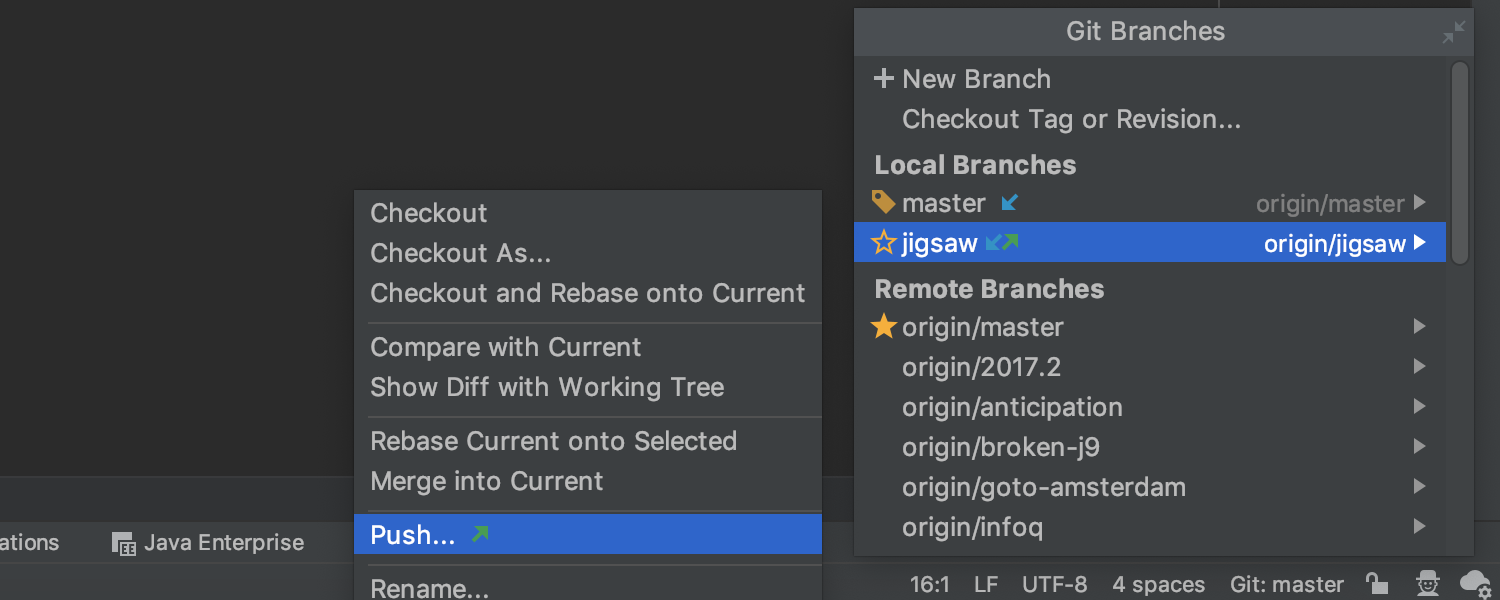
A simpler way to push branches
Another time-saver you’ll be glad to discover is that you no longer need to check out a branch to push it – you can simply select a branch in the Git branches popup and push it from there.
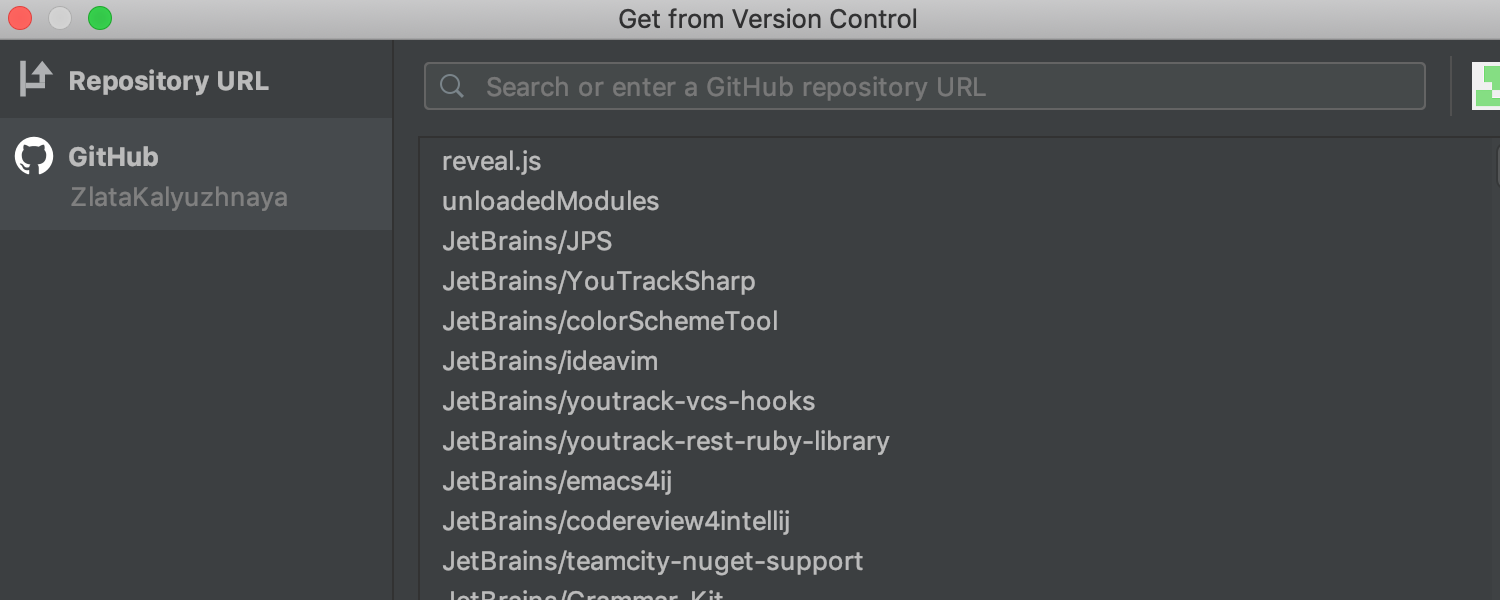
Unified ‘clone’ experience
We’ve reworked the ‘Clone’ dialog to unify the UI for getting projects from different VCS hosting services. If you’re already logged in to your VCS, the IDE displays a list of available repositories that you can choose from, so you no longer need to enter a repository URL.
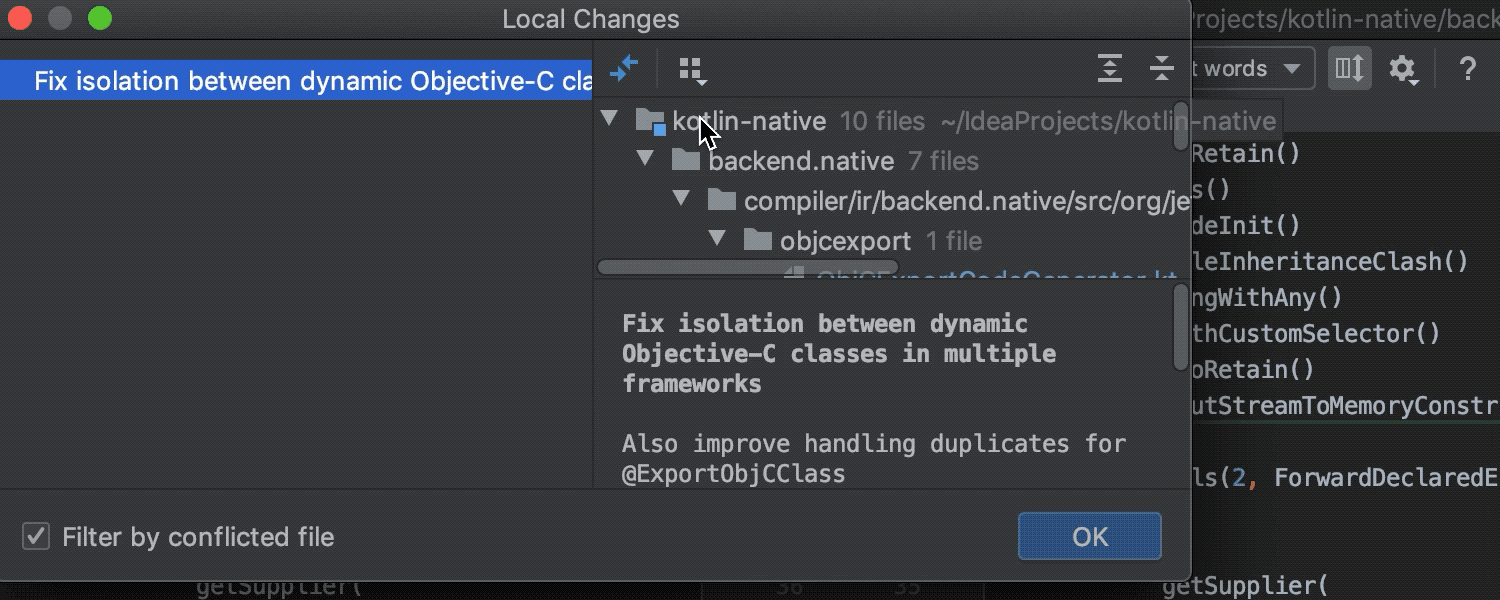
More insight into merge conflicts
Now when a conflict occurs during a merge, rebase, or cherry-pick operation, you can get more information about the source of the changes displayed in the Merge dialog. Simply click the ‘Show Details’ link to get the list of commits that led to the resulting code state.
New Frameworks and Technologies



Microservices frameworks support Ultimate
To help keep your IntelliJ IDEA projects technologically relevant, version 2019.3 adds initial support for Micronaut, Quarkus, and Helidon. You can enjoy full coding assistance, navigation, inspections, find usages, and other goodies if you employ a microservice-based architecture for your Java projects.
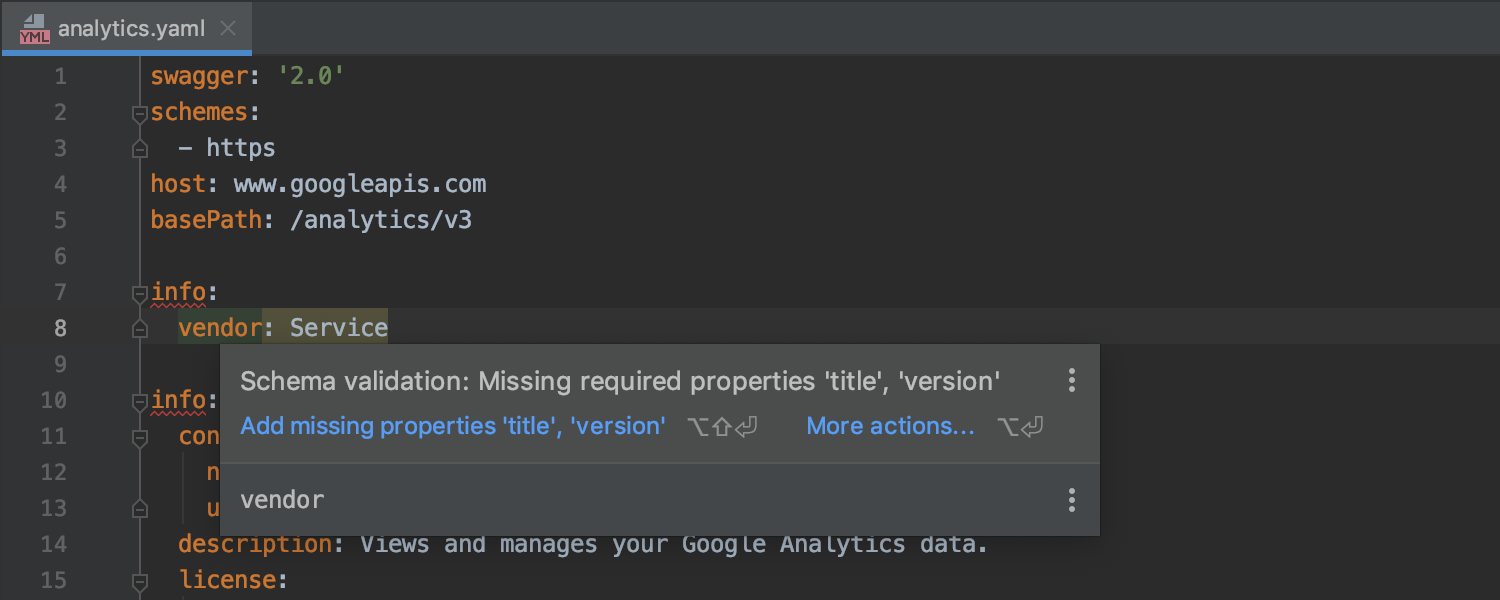
OpenAPI and Swagger support Ultimate
We’ve introduced support for Swagger v2 and OpenAPI v2, which provides validation by schema, as well as code completion, navigation, find usages, and the Rename refactoring in YAML/JSON files containing API descriptions.
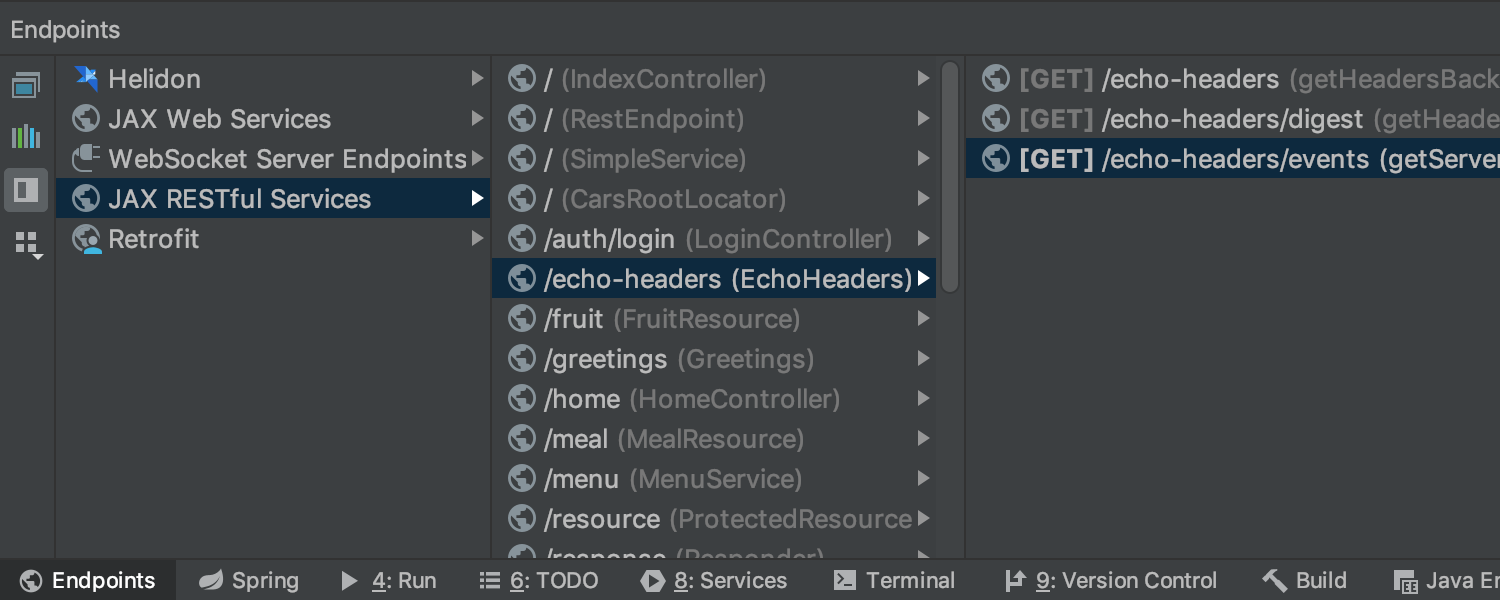
New Endpoints view Ultimate
The brand-new ‘Endpoints’ tool window provides an aggregated view of both client and server APIs used in your project for HTTP and Web Socket protocols. What is more, you can extend the view to all projects currently opened in IntelliJ IDEA.
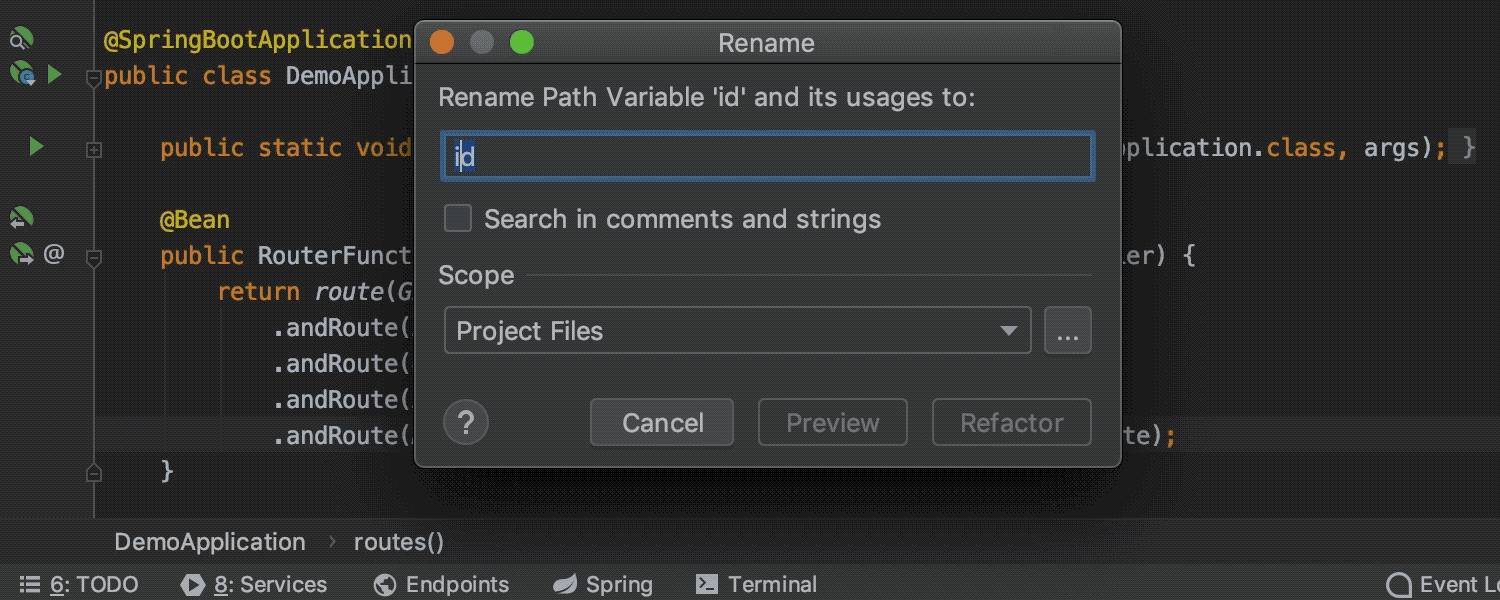
Spring Web Flux support Ultimate
View the full list of Web Flux URL mappings in the MVC view in the Spring tool window, navigate between them, and benefit from coding assistance, search, and the Rename refactoring for URLs and URL segments.
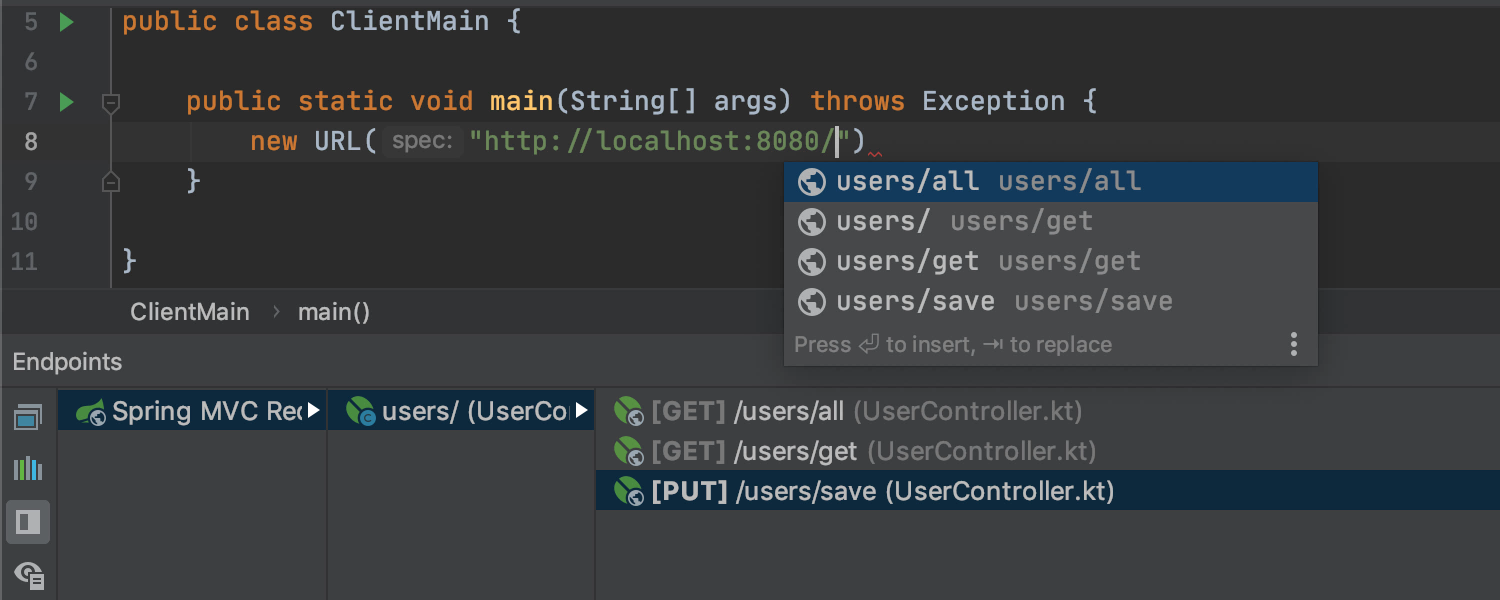
Java HTTP Clients support Ultimate
IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3 brings URL support in the following Java HTTP client APIs: java.net.{URI/URL}, Retrofit v2, OkHttp v3, and Injectable URL reference. Coding assistance, navigation, find usages – everything you’re used to in Java is now available for HTTP clients.



Project Reactor support Ultimate
Take advantage of inspections for Java and Kotlin Reactor projects, which report thread-blocking method calls detected in code fragments where a thread should not be blocked. The IDE will also warn you about the potential return of null from lambda operators of Flux and Mono methods. On top of that, there’s a dedicated Reactor debug mode that provides a helpful view of the reactive stack frames and intermediate variable values.



MongoDB support Ultimate
IntelliJ IDEA 2019.3 comes with long-awaited MongoDB support. After you’ve added a MongoDB data source, view collections and fields in the database explorer, run queries, and review query results. We’re going to extend MongoDB support in future releases.
What’s Fixed
- The IDE can now detect the directory to which Gradle was installed through Homebrew.
- The UI has been improved so it’s now easier to manually set the Gradle home directory.
- IntelliJ IDEA now supports password storing via KWallet on Linux.
- For JavaFX projects, the IDE can display an FXML file with the embedded Scene Builder in the Scene Builder tab.
- The ‘Authentication Required’ dialog for SVN doesn’t keep popping up anymore when the SVN server is not reachable.
- We’ve fixed issues related to performing the ‘git update’ operation with rebase.
- The IDE now displays a progress bar when indexing the Git log.
- You can now choose whether you want to see when a change was authored or the commit timestamp in the file history view and in VCS annotations.
Plus fixes for 1679 issues affecting a total of 3904 votes!