Cucumber.js
Cucumber.js is a test framework for behavior-driven JavaScript development. Cucumber.js tests are written in the human-readable Gherkin language and are stored in feature files that have the feature extension. WebStorm integrates with Cucumber.js and recognizes features written in Gherkin, so you can run Cucumber.js test right from the IDE.
Before you start
To work with Cucumber.js versions 6.0.0+, make sure you are using WebStorm 2020.3.1 or later.
Make sure you have Node.js on your computer.
Make sure the Cucumber.js and Gherkin required plugins are enabled on the Settings | Plugins page, tab Installed. For more information, refer to Managing plugins.
Install Cucumber.js
In the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) , type one of the following commands:
npm install cucumberfor local installation in your project.npm install -g cucumberfor global installation.npm install --save-dev cucumberto install Cucumber.js as a development dependency.
See also Cucumber.js demo on the Cucumber.js official website.
Create test definitions
With WebStorm, you can write step definitions both in JavaScript and in TypeScript. WebStorm detects and highlights the steps where definitions are missing and suggests a quick-fix to generate them.
Place the caret at the step without a definition, press Alt+Enter, and select Create step definition or Create all step definitions.
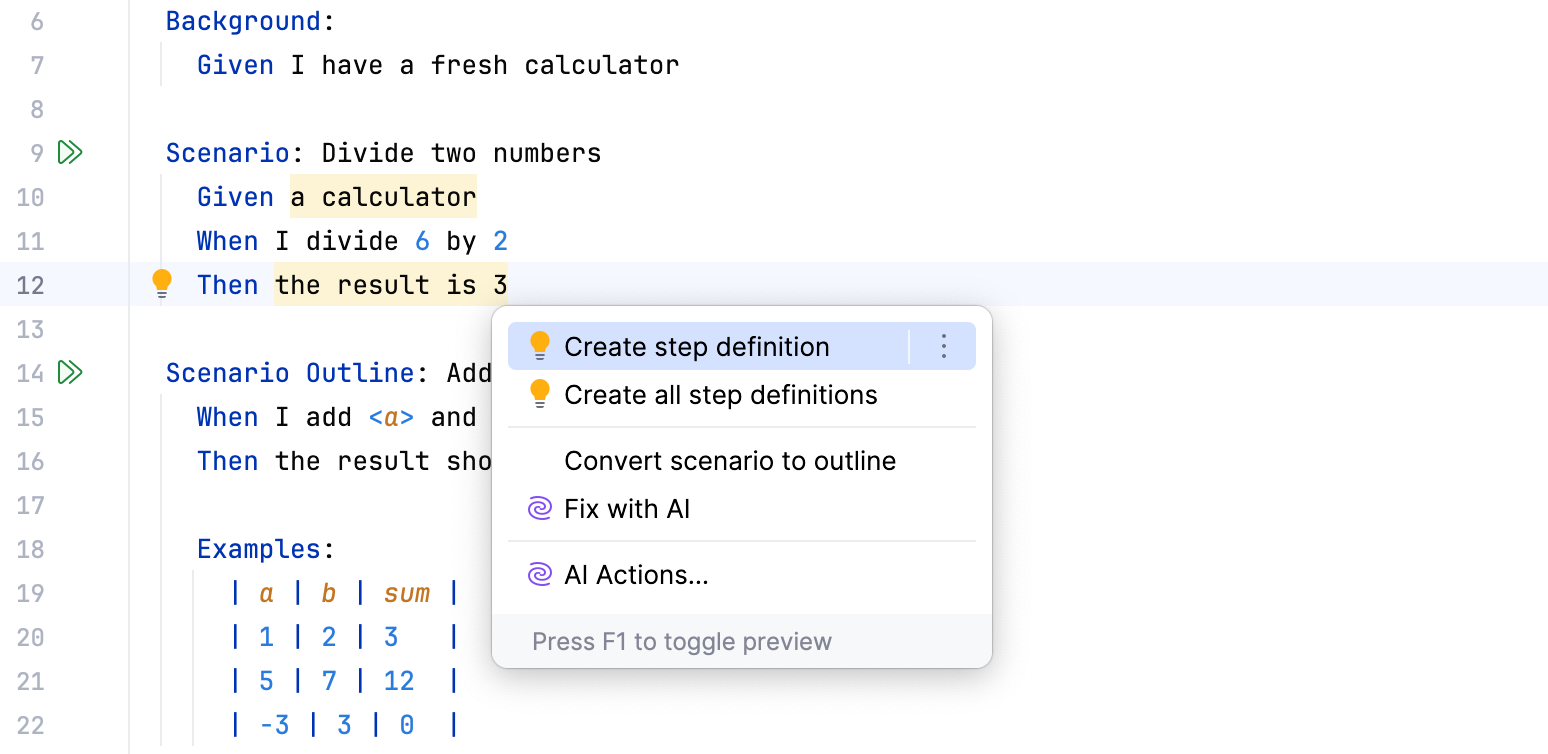
Alternatively, hover over the step and use the links in the popup.

In the dialog that opens, specify the name for the new file and the language to write the definitions in.
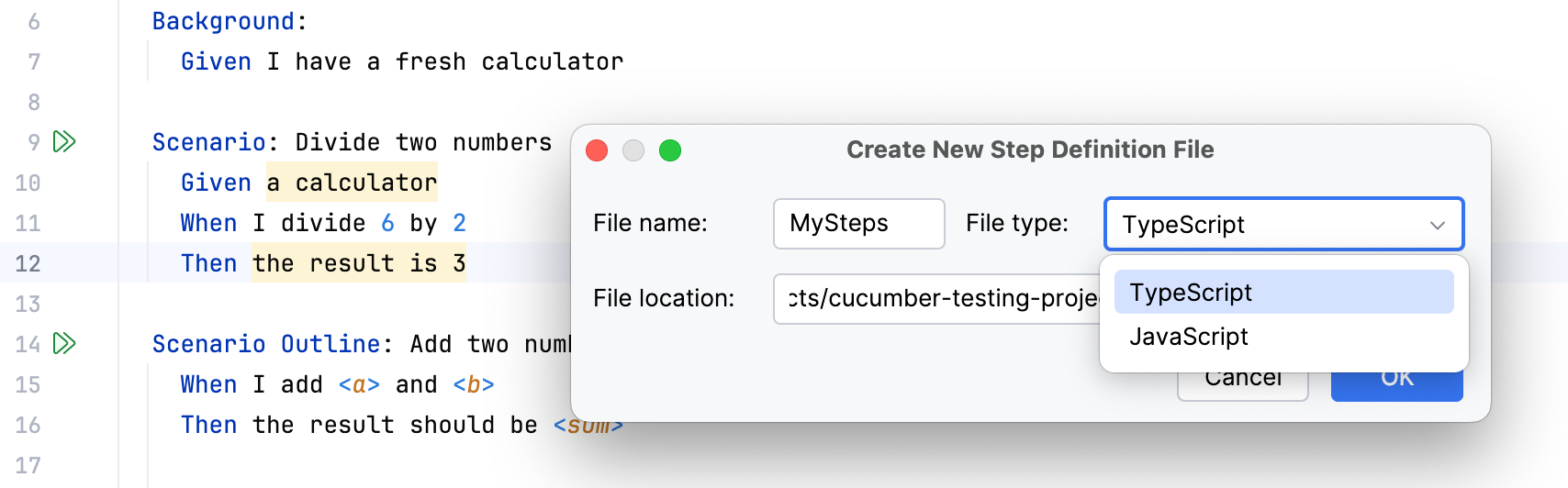
If such file already exists, WebStorm displays a popup where you have to select a file to add the definition to or choose to create a new file.
Run tests
Cucumber.js tests are launched only through a run/debug configuration.
Create a Cucumber.js run configuration
Open the Run/Debug Configuration dialog ( in the main menu), click
in the left-hand pane, and select Cucumber.js from the list. The Run/Debug Configuration: Cucumber.js dialog opens.
In the Feature file or directory field, specify the tests to run. Type the path to a specific .feature file or to a folder, if you want to run a bunch of features.
Specify the Node.js runtime to use.
If you choose the Project alias, WebStorm will automatically use the project default interpreter from the Node runtime field on the JavaScript Runtime page . In most cases, WebStorm detects the project default runtime and fills in the field itself.
You can also choose another configured local or remote interpreter or click
and configure a new one.
For more information, refer to Configuring remote Node.js runtimes, Configuring a local Node.js runtime, and Using Node.js on Windows Subsystem for Linux.
In the Cucumber package field, specify the path to the folder where the cucumber package is stored.
Specify the working directory of the application. By default, the Working directory field shows the project root folder. To change this predefined setting, specify the path to the desired folder.
Optionally:
In the Name Filter field, type the name of a specific scenario to run instead of all the scenarios from the feature file or directory.
Specify the command-line arguments to be passed to the executable file, such as
-r--require LIBRARY|DIR,-t--tags TAG_EXPRESSION, or--coffee. For more information, refer to native built-in help available through thecucumber-js --helpcommand.In the Environment variables field, specify the environment variables for your application.
Run tests via a run configuration
Select the Cucumber.js run/debug configuration from the list of configurations and click
in the list or on the toolbar.

Monitor test execution and analyze test results in the Test Runner tab of the Run tool window. For more information, refer to Explore test results.
Run tests from a test file
To run a single test, open the test file in the editor, place the caret at the scenario to run, and then select from the context menu.
To run all tests from a single test file, open the test file in the editor or select it in the Project tool window and choose from the context menu.
In either case, WebStorm creates a run/debug configuration which you can save and use later.
Debug tests
Set breakpoints where necessary.
Debug tests via a run configuration
Select the Cucumber.js run/debug configuration from the list of configurations and click
in the list or on the toolbar.

Monitor test execution and analyze test results in the Test Runner tab of the Run tool window. For more information, refer to Explore test results.
Debug tests from a test file
To debug a single test, set the breakpoints where necessary, place the caret at the scenario to debug, and then select from the context menu.
To debug all tests from a single test file, open the test file in the editor or select it in the Project tool window and choose from the context menu.
In either case, WebStorm creates a run/debug configuration which you can save and use later.
Run and debug tests written in TypeScript
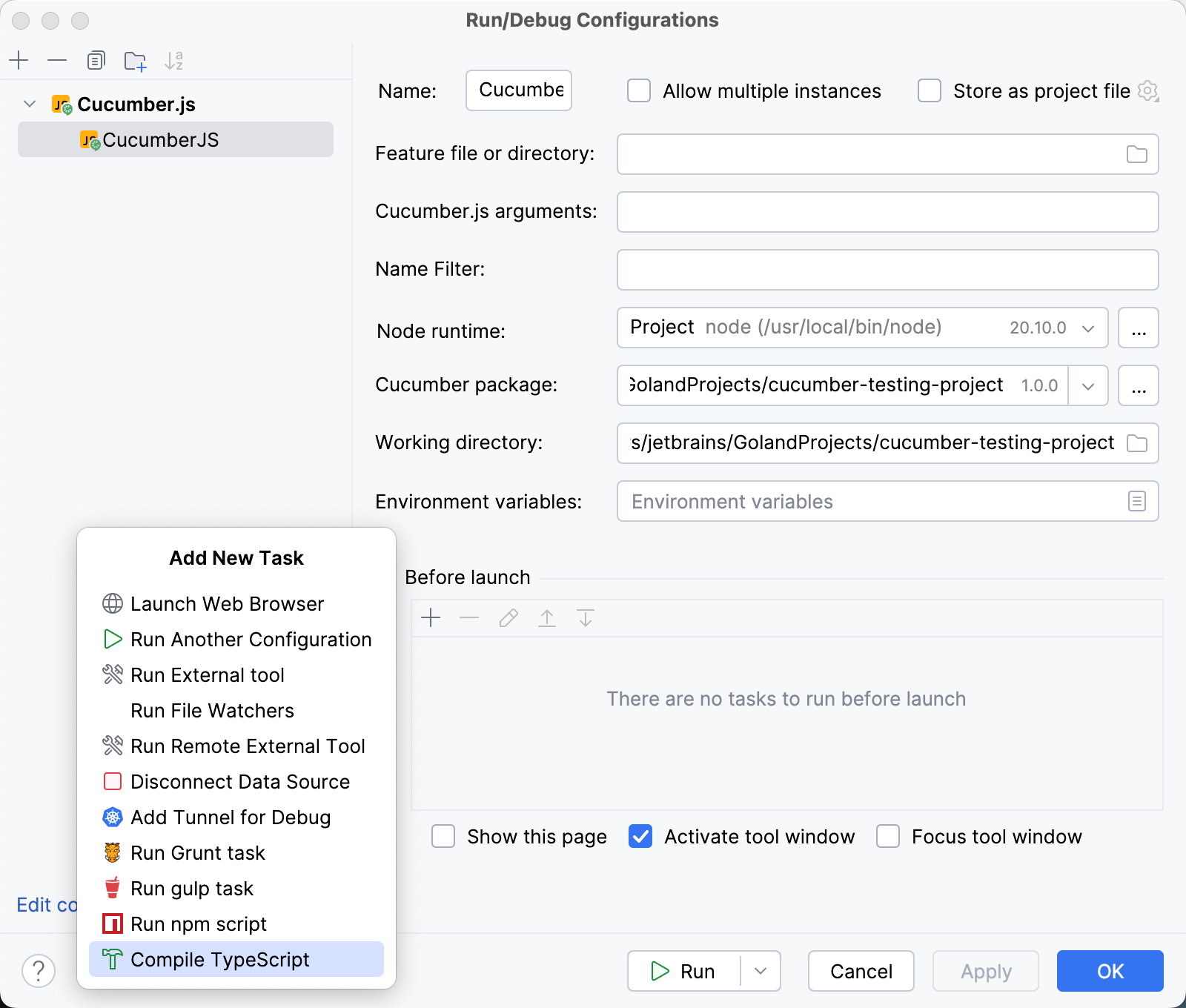
Create a Cucumber.js run/debug configuration as described above.
In the Before launch area, click
, select Compile TypeScript from the list, and then specify the tsconfig.json file to use. WebStorm will run the TypeScript compiler with this tsconfig.json before running Cucumber.js.
To debug tests written in TypeScript, open your tsconfig.json and set
"sourceMap": trueto enable source maps.
Navigation
With WebStorm, you can jump between a file and the related test file or from a test result in the Test Runner Tab to the test.
To jump between a test and its subject or vice versa, open the file in the editor and select or from the context menu, or just press Ctrl+Shift+T.
To jump from a step in a .feature file to the step definition, press and hold Ctrl, hover over the step, and click the step when it turns into a link.
To jump from a test result to the test definition, click the test name in the Test Runner tab twice, or select from the context menu, or just press F4. The test file opens in the editor with the caret placed at the test definition.
Configure syntax highlighting
You can configure Cucumber.js-aware syntax highlighting according to your preferences and habits.
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to .
Select the color scheme, accept the highlighting settings inherited from the defaults or customize them as described in Colors and fonts.