Multi-Cluster Installation to Amazon EKS
This guide describes how to install the CodeCanvas application to a Kubernetes cluster hosted in AWS EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service). It implies that the database and object storage services are hosted in AWS, namely, in RDS and S3.
The multi-cluster installation implies that the CodeCanvas application and dev environment infrastructure are deployed to separate Kubernetes clusters. Learn more
I. Pre-installation steps
Before installing CodeCanvas, complete the following prerequisites.
1. Set up PostgreSQL database
CodeCanvas requires a PostgreSQL database for the CodeCanvas application data.
Install PostgreSQL server (versions 12.2–15.12 are supported). The server must be accessible from the CodeCanvas application cluster, e.g., you can create a pod with the server in the same cluster.
Create a dedicated database for the CodeCanvas application.
Ensure that the database server is up and running before proceeding with the installation.
2. Create AWS S3 bucket
Create an AWS S3 bucket to store CodeCanvas and user data.
3. Prepare CodeCanvas application cluster
The CodeCanvas application cluster hosts the CodeCanvas application and related services. Learn more about the CodeCanvas architecture
Amazon EKS cluster
Set up an Amazon EKS cluster for the CodeCanvas application that meets the following requirements:
Requirement
Description
Helm
Version 3.8.0 or later
Kubernetes
Version 1.29 or later
Cluster nodes
At least four nodes with Linux OS (x86_64). Recommended min resources: 4 CPU cores and 8GB memory
Namespace
Create a dedicated namespace for the CodeCanvas application (replace
NAMESPACE_PLACEHOLDERwith an actual namespace name):kubectl create namespace NAMESPACE_PLACEHOLDERIngress controller
Install an Ingress controller compatible with your Kubernetes setup. In this guide, we use the ingress-nginx controller.
4. Configure DNS and TLS
Domain name
Register a domain name for the CodeCanvas instance, e.g.,
codecanvas.example.com.DNS zones
Install ExternalDNS in the CodeCanvas application cluster to manage DNS records.
TLS certificates
Install cert-manager in the CodeCanvas application cluster to manage TLS certificates issued by Let's Encrypt.
Subdomains
Configure subdomains for the CodeCanvas application components. The configuration in
custom.values.yamlsupposes the following DNS domain naming scheme:EXTERNAL_DOMAIN_PLACEHOLDER– the main domain for the CodeCanvas application that serves the main administrative UI and REST API. For example,codecanvas.example.comcomputeservice.EXTERNAL_DOMAIN_PLACEHOLDER– the subdomain that serves thecompute-serviceREST API. It is an internal domain customarily accessed only by dev environment pods.gateway.EXTERNAL_DOMAIN_PLACEHOLDER– serves thegateway-relayservice (Relay server). It is an external domain accessed by user IDE clients.
5. Set up IAM roles and permissions
To grant CodeCanvas access to a storage bucket in AWS, you can use either static credentials or IAM roles for service accounts (IRSA). We recommend using IRSA.
Configure the IRSA role for the CodeCanvas application service account. CodeCanvas requires write permission to the bucket. For details on how to set up IRSA, refer to the AWS documentation.
6. (Optional) Configure the SMTP server
CodeCanvas uses the SMTP server to send various emails to users, for example, invitation links during the user creation, email verification, and other notifications. If you want to enable this functionality, ensure you have an SMTP server accessible from the CodeCanvas application cluster.
II. Install CodeCanvas
1. Create custom.values.yaml
Create a custom.values.yaml and copy the snippet below to it. You will replace placeholders with actual values in the next steps.
2. Assign an AWS IRSA role to the CodeCanvas application
In custom.values.yaml, replace CODECANVAS_IRSA_ARN with the actual ARN of the AWS IRSA role that the CodeCanvas application should use.
3. Specify external domain
In custom.values.yaml, replace EXTERNAL_DOMAIN_PLACEHOLDER with the domain name you've registered for your CodeCanvas instance.
4. Set up cert-manager
In custom.values.yaml, replace CERT_MANAGER_NAME_PLACEHOLDER with the name of cert-manager used in your cluster.
5. Specify database settings
The CodeCanvas installation implies that you use an external PostgreSQL database. Though you can use any PostgreSQL database, we recommend using Amazon RDS.
5.1 Obtain credentials
Get the credentials for the database user that has permissions to create, read, update, and delete all entities in the schema.
5.2 Create a database secret
A database secret is used to secure access to the PostgreSQL database.
In
custom.values.yaml, replaceDB_SECRET_NAME_PLACEHOLDERwith the name of the secret that will be created. For example,codecanvas-db-secret-ext.Create a
codecanvas-db-secret.yamlfile and copy the snippet below to it.apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret type: Opaque metadata: name: "DB_SECRET_NAME_PLACEHOLDER" namespace: "NAMESPACE_PLACEHOLDER" stringData: DB_HOST: "CODECANVAS_DB_HOST_PLACEHOLDER" DB_NAME: "CODECANVAS_DB_NAME_PLACEHOLDER" DB_PASSWORD: "CODECANVAS_DB_PASSWORD_PLACEHOLDER" DB_PORT: "CODECANVAS_DB_PORT_PLACEHOLDER" DB_USERNAME: "CODECANVAS_DB_USERNAME_PLACEHOLDER"Replace the following placeholders:
DB_SECRET_NAME_PLACEHOLDERwith the name of the secret that will be created. It should match the name incustom.values.yamlyou've specified earlier. For example,codecanvas-db-secret-extNAMESPACE_PLACEHOLDERwith your Kubernetes namespaceCODECANVAS_DB_PASSWORD_PLACEHOLDERwith a password for theCODECANVAS_DB_USERNAME_PLACEHOLDERuserCODECANVAS_DB_HOST_PLACEHOLDERwith the PostgreSQL hostnameCODECANVAS_DB_PORT_PLACEHOLDERwith the PostgreSQL port
Run:
kubectl apply -f codecanvas-db-secret.yamlYou can now delete the
codecanvas-db-secret.yamlfile or keep it based on your organization's secret management policies.
6. Specify object storage settings
This installation implies that you use an AWS S3 bucket for storing user data.
You should authorize CodeCanvas to access your S3 object storage in one of two ways: using static credentials or IAM roles for service accounts (IRSA). We recommend using IRSA.
In custom.values.yaml, replace the following placeholders:
CODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_REGION_PLACEHOLDERwith the AWS region where the bucket is located (e.g.,eu-west-1)CODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_BUCKET_PLACEHOLDERwith the name of the S3 bucket created for CodeCanvas
To set up authorization in your S3 object storage with static credentials, you should create an object storage secret and provide a username and password.
In
custom.values.yaml, replace the following section:secret: objectStorage: type: aws region: "CODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_REGION_PLACEHOLDER" bucket: "CODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_BUCKET_PLACEHOLDER"with
secret: objectStorage: type: aws existingSecretName: "STORAGE_SECRET_NAME_PLACEHOLDER"Replace
STORAGE_SECRET_NAME_PLACEHOLDERwith the name of the secret that will be created. For example,codecanvas-objectstorage-secret-ext.Create an
object-storage-secret.yamlfile and copy the snippet below to it.apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret type: Opaque metadata: name: "STORAGE_SECRET_NAME_PLACEHOLDER" namespace: "NAMESPACE_PLACEHOLDER" stringData: CODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_ACCESS_KEY: "CODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_ACCESS_KEY_PLACEHOLDER" CODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_SECRET_KEY: "CODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_SECRET_KEY_PLACEHOLDER" CODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_BUCKET: "CODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_BUCKET_PLACEHOLDER" CODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_REGION: "CODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_REGION_PLACEHOLDER"Replace the following placeholders:
STORAGE_SECRET_NAME_PLACEHOLDERwith the name of the secret that will be created. It should match the name incustom.values.yamlyou've specified earlier. For example,codecanvas-objectstorage-secret-extNAMESPACE_PLACEHOLDERwith your Kubernetes namespaceCODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_ACCESS_KEY_PLACEHOLDERwith the AWS access keyCODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_SECRET_KEY_PLACEHOLDERwith the AWS secret keyCODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_BUCKET_PLACEHOLDERwith the name of the S3 bucket created for CodeCanvasCODECANVAS_OBJECT_STORAGE_REGION_PLACEHOLDERwith the AWS region where the bucket is located (e.g.,eu-west-1)
Run:
kubectl apply -f object-storage-secret.yamlYou can now delete the
object-storage-secret.yamlfile or keep it based on your organization's secret management policies.
7. Create a master secret
The CodeCanvas application keeps user secrets (e.g., credentials to external services) in the database in an encrypted form. The master secret is used to encrypt and decrypt these data.
The master secret can be any Base64-encoded string. For example, you can generate a random string using openssl.
Generate the master secret by running
openssl rand -base64 32In
custom.values.yaml, replaceMASTER_SECRET_PLACEHOLDERwith the generated value.
8. Configure the system administrator account
The system administrator account will be used for logging in to and configuring CodeCanvas after the installation. You can either provide credentials manually or let the system generate them automatically.
To manually set up the administrator account, in
custom.values.yaml, replace:ADMIN_USERNAME_PLACEHOLDERandADMIN_PASSWORD_PLACEHOLDERwith desired administrator credentials.ADMIN_EMAIL_PLACEHOLDERwith an email address for receiving administrator notifications from CodeCanvas.
Alternatively, you can remove the localAdministrator.username and localAdministrator.password sections from custom.values.yaml. In this case, the default username will be admin and a random password will be generated during installation (shown after the chart is deployed). Note that you still have to specify an email instead of ADMIN_EMAIL_PLACEHOLDER.
9. Specify the Ingress class
In custom.values.yaml, replace INGRESS_CLASS_PLACEHOLDER with the Ingress class used for the CodeCanvas application cluster.
10. (Optional) Specify the Kubernetes service account for the CodeCanvas pod
Suppose you've set up a Service account in the application cluster and prefer the service account name to be independent of the Helm release name. In that case, you may want to specify a particular name for the Kubernetes service account that the CodeCanvas Helm chart will create. To do this:
Add the following parameter to the corresponding section of
custom.values.yaml:application: serviceAccount: name: "CODECANVAS_KSA_NAME"Replace
CODECANVAS_KSA_NAMEwith the desired name of the service account.
11. (Optional) Configure Sysbox container runtime
By default, CodeCanvas runs worker containers in the --privileged mode (the containers have root privileges on the host node). If you want to avoid this due to security reasons, install Sysbox Container Runtime as described here.
12. Accept the license agreement
In custom.values.yaml, replace ACCEPTANCE_PLACEHOLDER with true to explicitly accept the CodeCanvas license agreement.
13. Install the CodeCanvas chart
Run:
Here:
NAMESPACE_PLACEHOLDERis your Kubernetes namespacecodecanvasis the Helm release name. You can change it if needed.
III. Verify the installation
After you install your CodeCanvas instance, verify the installation.
1. Verify the state of CodeCanvas pods
Run:
All pods must be in the Running state. On average, it takes about 2 minutes after deployment for a pod to become active.
If the pods are not Running, try finding the cause by running:
and
2. Verify domain name resolution
The domain name must resolve to the Ingress load balancer. You can check this by running:
The output must not contain any errors.
3. Check the CodeCanvas application
Open your CodeCanvas instance in a browser. When logging in to CodeCanvas, use the administrator credentials provided during the installation.
IV. Activate CodeCanvas
Follow the instructions on how to activate your CodeCanvas instance.
V. Configure a computing platform
A computing platform in CodeCanvas is a configuration entity that represents the infrastructure responsible for running dev environments. It consists of a dev environment cluster managed by a Kubernetes operator, a Relay server, and a Jump server. Learn more about the CodeCanvas architecture.
1. Prepare a dev environment cluster
Note that your CodeCanvas installation can use multiple dev environment clusters, e.g., distributed across different regions. The requirements for all dev environment clusters are the same.
Amazon EKS cluster
Set up a Kubernetes cluster for dev environments. Make sure the cluster meets the requirements from the table below. Depending on your needs, you can create multiple dev environment clusters (the requirements are the same for all clusters). To reduce latency for end users, we recommend deploying the dev environment cluster in the same region as the potential dev environment users.
Requirement
Description
Helm
Version 3.8.0 or later
Kubernetes
Version 1.29 or later
Cluster nodes
Sufficient nodes to run dev environments, each with Linux OS (Ubuntu, x86_64), recommended min resources: 4 CPU cores and 8GB memory. See our recommendations below
- Key recommendations on nodes
General node requirements
Linux OS (Ubuntu, x86_64), recommended minimum resources: 4 vCPUs and 8GB memory.
Configure autoscaling
Use autoscaling to adjust the number of nodes based on the load. Start with a minimum number of nodes that is enough to cover normal usage and allow autoscaling to add more nodes during peak usage. See our recommendations on autoscaling
Estimate the resources
Estimate normal and peak concurrent usage – the average and max number of concurrent environments. For example, if during peak activity, 20 developers use 2–3 dev environments each, your peak demand is 60 active environments.
Calculate total resource requirements: For example, if your typical dev environment is 4 vCPUs and 16GB memory, for 60 dev environments you will need 240 vCPUs and 960GB memory.
Important: Kubernetes requires a part of each node's resources for system tasks, such as
kubelet,aws-node, and others. You should reserve approximately 0.2 vCPU and 1–2GB memory per node for the Kubernetes system tasks. The exact values depend on the installation. To view the actual node resource usage, runkubectl describe node <node-name>Choose a node allocation strategy
One Node – One Dev Environment
A single node (AWS instance) hosts only one dev environment (worker pod). In our example, you would need 60 separate nodes for 60 dev environments, for instance,
m5.xlargeinstances (each with 4 vCPUs and 16GB memory).(+) No overprovisioning: Each node is fully utilized by a single dev environment.
(+) Fault tolerance: Only one dev environment is affected if a node fails.
(-) Higher overhead: Kubernetes requires a part of each node's resources for system tasks. So, in our example, each dev environment will have 4 vCPUs and 16GB memory, but a developer will get only 3.8 vCPUs and 14–15GB memory. The rest (0.2 vCPU and 1–2GB memory) will be used by the Kubernetes system tasks with the resulting overhead of 60 * (0.2 vCPUs and 1–2GB) = 12 vCPUs and 60–120GB. You can solve this by using larger instances.
(-) Slower start times: The autoscaler must provision a new node for each new dev environment.
One Node – Multiple Dev Environments
A single node (AWS instance) hosts multiple dev environments (worker pods). In our example with 60 dev environments (240 vCPUs and 960GB memory in total), you could divide this load into 4–6 nodes, such as
m5.16xlarge(64 vCPUs, 256GB memory) orm5.12xlarge(48 vCPUs, 192GB memory).(-) Overprovisioning: Resources are wasted if fewer dev environments are running than a node can accommodate.
(-) Fault tolerance: If a node fails, multiple dev environments are affected.
(+) Lower overhead: Multiple dev environments share the same node, reducing the overhead from Kubernetes system tasks (0.2 vCPU and 1–2GB memory per node). In our example, with 4–6 nodes, the resulting overhead is 4–6 * (0.2 vCPUs and 1–2GB) = 0.8–1.2 vCPUs and 4–12GB memory. Compare it to the 12 vCPUs and 60–120GB overhead in the One Node – One Dev Environment strategy.
(+) Faster start times: If a node has available resources, new worker pods can start immediately without waiting for a new node to be provisioned.
(+) Potential cost savings: Using fewer, larger instances can be more cost-effective (times cheaper) than using many smaller instances. However, this depends on how well you can predict resource usage and how efficiently you can pack dev environments onto nodes.
Choose Amazon instance types
To compare and choose AWS instance types, use the official AWS documentation.
Avoid
t-series instances (e.g.,t3,t4g), as these burstable types aren't designed for sustained performance. Instead, consider using instances with a fixed performance level, such asmorcseries.
CSI driver
Install the
ebs.csi.aws.comCSI driver in the cluster. For installation instructions, refer to the AWS documentation. Learn more about CSI in CodeCanvasCSI snapshot controller
Install the CSI snapshot controller in the cluster to enable Kubernetes snapshot manipulation. You can install it using the AWS-managed add-on or manually.
Storage class
Create a Kubernetes
StorageClassfor provisioning persistent volumes used by dev environments. You can use the recommended configuration below or define your own based on performance or cost preferences. The recommended configuration guarantees dev environment performance: it uses AWSgp3volumes with 16,000 IOPS and 750 MB/s throughput.Your dev environment cluster can have multiple storage classes. When creating an instance type, you can choose from the available storage classes.
Create a
storage-class.yamlfile and copy the snippet below to it.apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: StorageClass metadata: name: codecanvas-storage # You can change this name mountOptions: - debug parameters: type: gp3 iops: "16000" throughput: "750" provisioner: ebs.csi.aws.com allowVolumeExpansion: true reclaimPolicy: Delete volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumerApply the configuration to the cluster:
kubectl apply -f storage-class.yaml
Volume snapshot class
Create a Kubernetes
VolumeSnapshotClassto enable snapshot support for persistent volumes used in dev environments. You can use our recommended volume snapshot class configuration below.Your dev environment cluster can have multiple volume snapshot classes. When creating an instance type, you can choose from the available classes.
Create a
snapshot-class.yamlfile and copy the snippet below to it.apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: VolumeSnapshotClass metadata: name: codecanvas-volume-snapshot # You can change this name driver: ebs.csi.aws.com deletionPolicy: DeleteApply the configuration to the cluster:
kubectl apply -f snapshot-class.yaml
CSI snapshot validation webhook
Install an add-on to the CSI driver that implements Kubernetes snapshot validation. For the instructions, refer to the Kubernetes documentation. Tested with v6.2.2.
2. (Optional) Install a Relay server
If you plan to use JetBrains IDEs in your CodeCanvas instance, you should configure at least one Relay server. It enables connections between the JetBrains client on a local machine and the remote IDE backend.
For the best user experience, the Relay server should be deployed closer to the dev environment cluster to minimize latency (e.g., in the dev environment cluster itself or in the same region).
Follow the instructions on how to install a Relay server.
3. (Optional) Install a Jump server
If you want users to connect to dev environments via SSH (e.g., using VS Code/Cursor remote development or terminal access), you need to set up a Jump server. Otherwise, this step is optional.
For the best user experience, the Jump server should be deployed closer to the dev environment cluster to minimize latency (e.g., in the dev environment cluster itself or in the same region).
Follow the instructions on how to install a Jump server.
4. Connect the dev environment cluster
Select Administration in the header navigation, then in the sidebar menu, select Computing Platforms.
Click New connection.
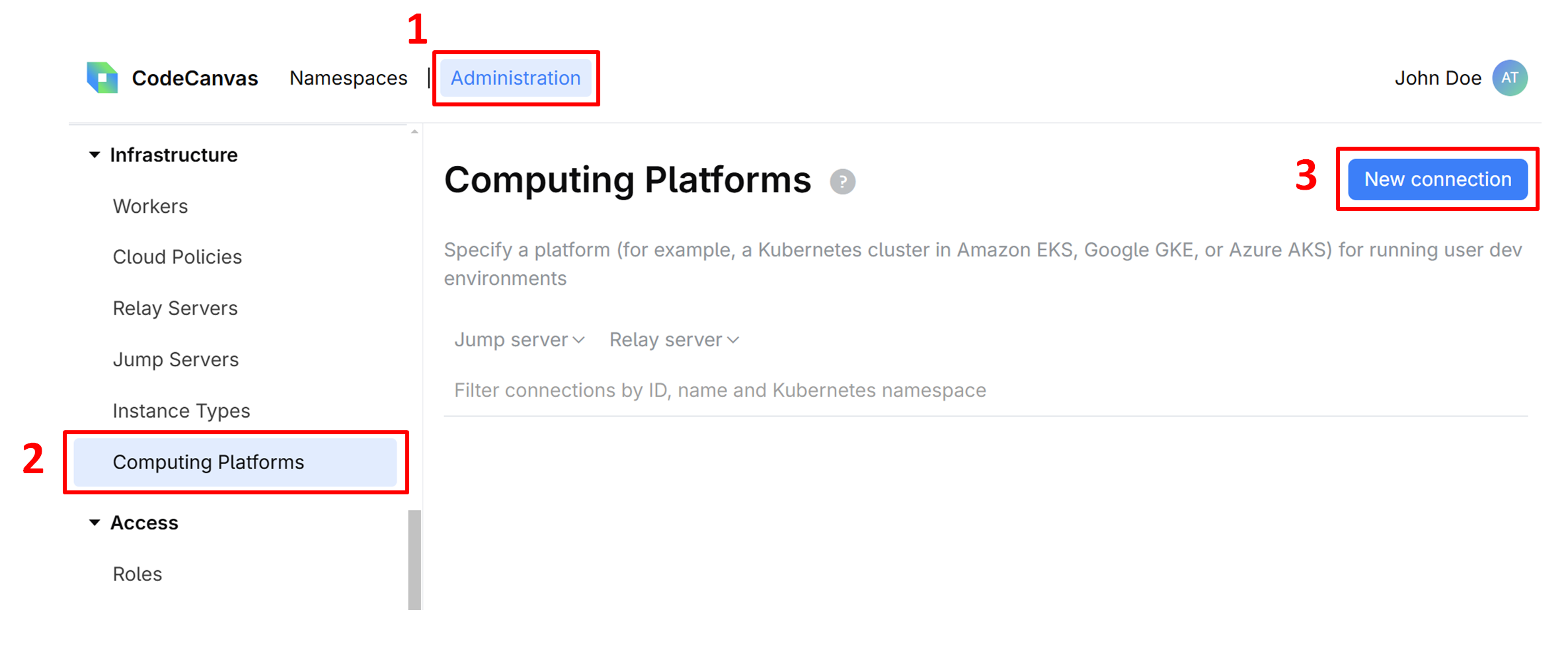
Give this connection a Name, specify other settings:
Kubernetes namespace – the Kubernetes namespace where the dev environments are running. The namespace may already exist, otherwise, it will be created during the connection.
Relay server and Jump server – the servers that you've created in the previous steps.
Here you can also modify the pod YAML template according to your needs. Learn more about this and other computing platform settings
Click Save to add the connection to the list. Note that the connection is not yet active.
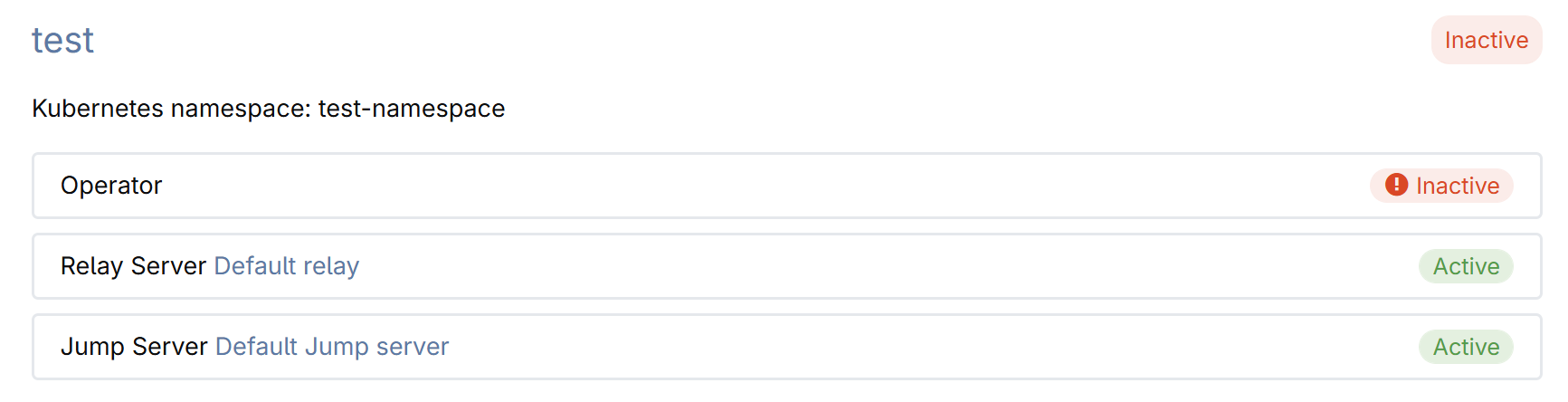
Click the connection name to open its details.
The connection details page provides the snippet that you should use to install the CodeCanvas operator in the dev environment cluster. The operator communicates with the CodeCanvas application and starts/stops worker pods in the dev environment cluster.
To communicate with each other, the CodeCanvas application and the operator require a key pair. The public key is stored in CodeCanvas, and the private key is used by the operator.
To generate a key pair, click Generate keys. The private key will be automatically added to the snippet.
(Optional) Modify default network policies by updating the snippet. By default, all inbound traffic to dev environments is blocked (including traffic between them), and all outbound traffic is allowed. Learn how to change the network policies
Copy the snippet to the clipboard.
Run the snippet to apply it to the dev environment cluster. The snippet configures the cluster and installs the operator.
Click Test connection and ensure that all checks are successful.

VI. Post-installation steps
After successfully verifying the installation and connecting the computing platform, you can proceed to configuration of your CodeCanvas instance: creating dev environment instance types, adding users, namespaces, and so on.