Release notes
This section lists functionality added to DataGrip in the current release. To view release notes for other DataGrip versions, click the version switcher on the help site and select the version that you need.
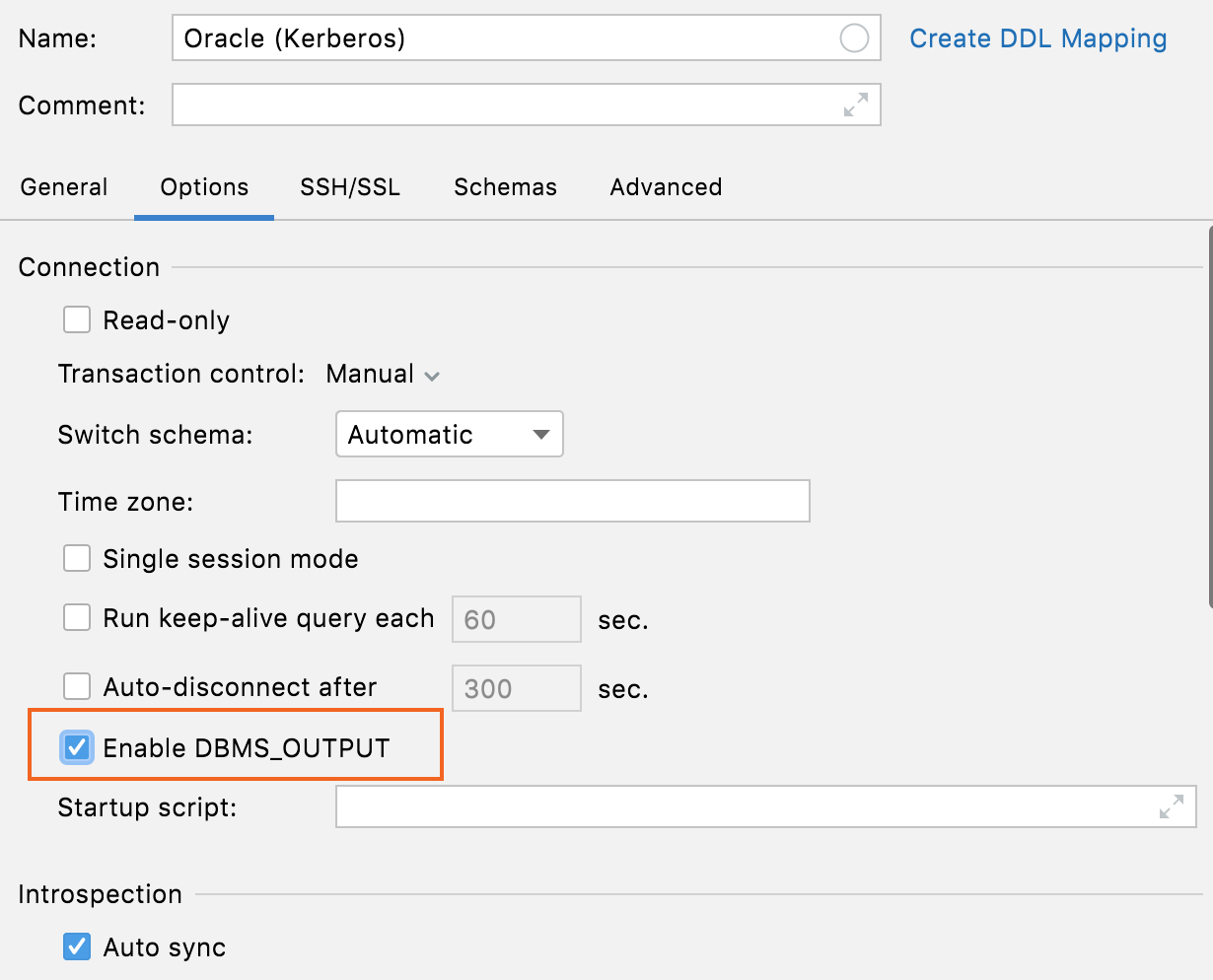
Connectivity: enable DBMS_OUTPUT for Oracle and IBM Db2 LUW
The Enable DBMSOUTPUT option on the Options tab lets you enable DBMS_OUTPUT by default for new sessions.
Connectivity: expert options
The Advanced tab includes the Expert options list where you can enable some workarounds for different databases. Use these workarounds as temporary solutions.
All databases: Introspect using JDBC metadata.
Oracle: Disable incremental introspection, Fetch LONG values, Introspect server objects.
Microsoft SQL Server: Disable incremental introspection.
PostgreSQL (and similar) : Disable incremental introspection, Do not use xmin in queries to pgdatabase.
SQLite: Register REGEXP function.
MySQL: Use SHOW CREATE for source code.
ClickHouse: Automatically assign sessionid.
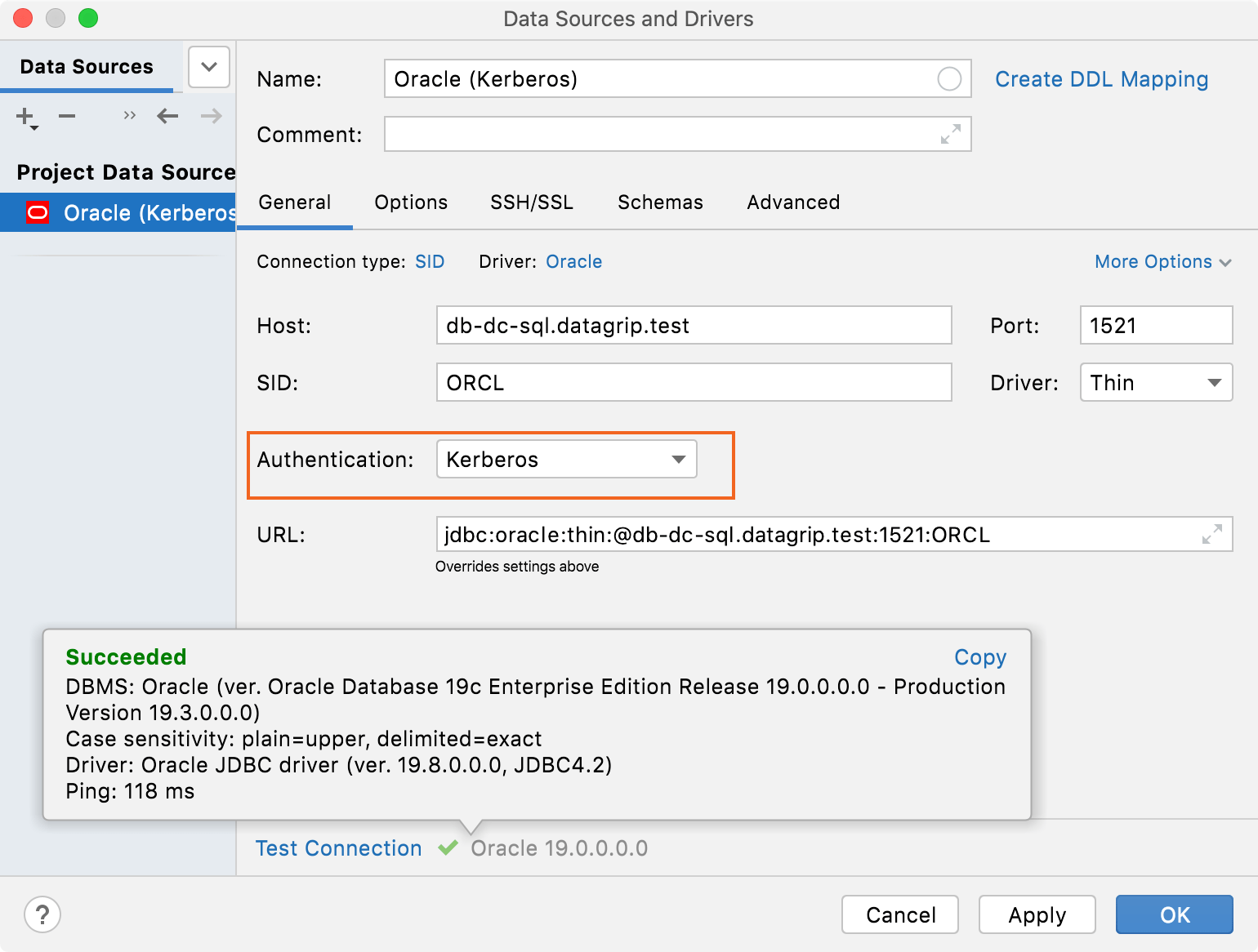
Connectivity: Kerberos authentication for Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server
You can select Kerberos authentication in Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server data sources. For more information about connecting to Oracle with Kerberos by using a thin driver, see Connect to Oracle by using Kerberos (JDBC Thin Driver).
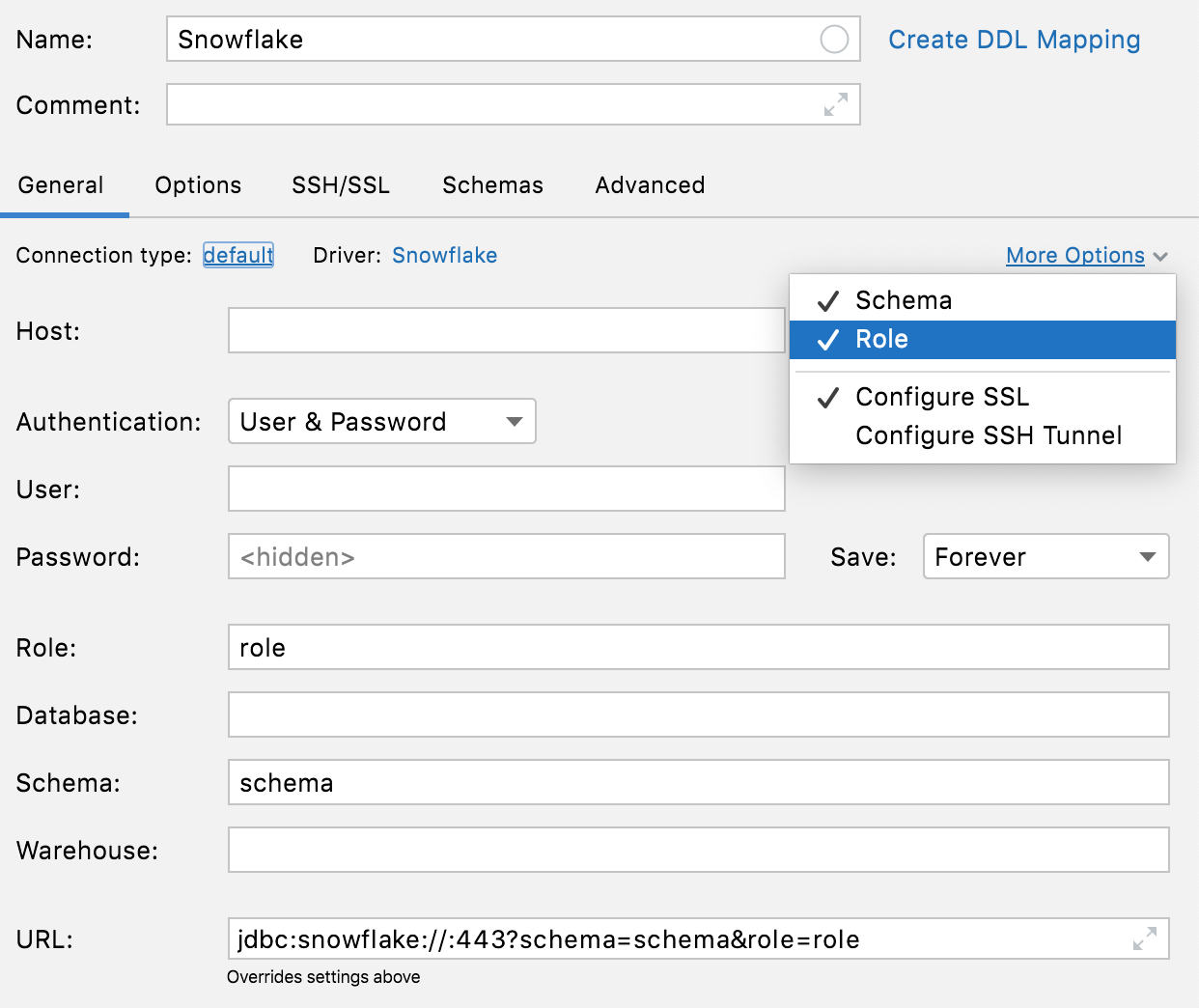
Connectivity: the More options button
Use the More Options link to add Schema and Role fields for Snowflake connections. Also, you can use Configure SSL and Configure SSH Tunnel menu items to configure SSH and SSL.
Connectivity: warning about accidental spaces
If any value except User or Password has leading or trailing spaces, DataGrip will warn you about them when you click Test Connection.

Data sources: DDL data sources
DDL data sources received UI updates that can help you to dump, synchronize, and store your database state.
Database Explorer: distributed tables in ClickHouse
Distributed tables are now placed under a dedicated node in the Database Explorer.
Database Explorer: table view for tree nodes
Press F4 on any schema node to see the table view of the node’s contents.

Differences viewer: a new database diff window
The new database diff window is still a work in progress, but you can already try it. For more information about the differences viewer, see Differences viewer for database objects.

Editing: aggregates
By using aggregates, you can select values of multiple cells and get a single summary value.
To see the aggregate view, right-click a cell and select Show Aggregate View. Select a range of cells for which you want to receive an aggregate value.

Editing: automatic column types in CSV files
DataGrip automatically detects column types in CSV files. The main benefit of this is that you can sort data by numeric values. Before, they were treated as text.
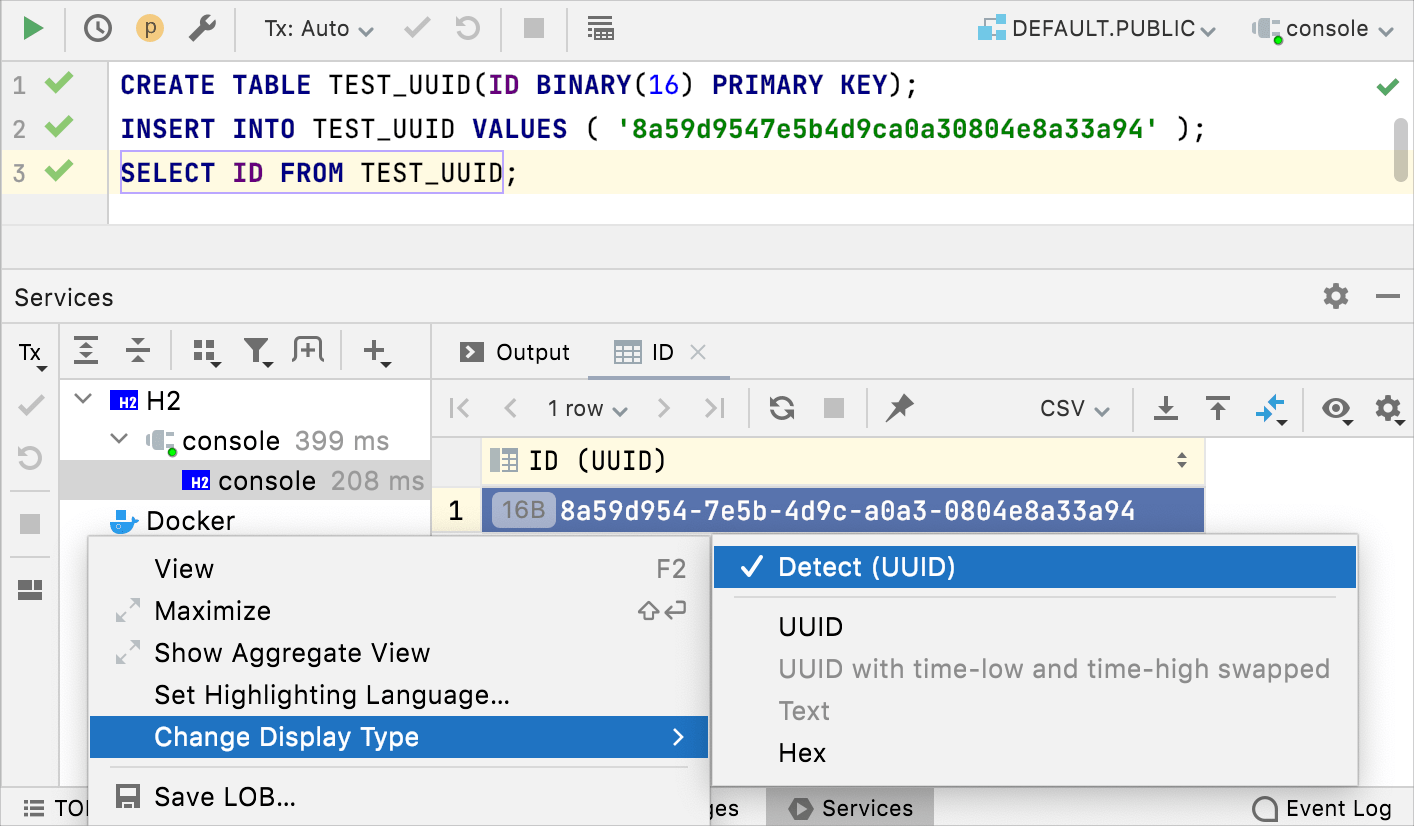
Editing: display mode for binary data
16-byte data is now displayed as UUID by default. You can also customize how binary data is displayed in the column.
Editing: independent split
If you split the editor and open the same table, the data editors will now be completely independent. You can set different filtering and ordering options for them. Previously, filtering and ordering were synchronized.

Editing: setting for default sorting
You can define which sorting method to use as the default for tables. You can select between Sort via ORDER BY or client-side. The client-side sorting does not run any new queries and sorts only the current page.
To configure the settings, open settings by pressing Ctrl+Alt+S and navigate to .
In the Sorting section, select or clear the Sort via ORDER BY checkbox. When this option is on, data for the whole table is sorted according to the corresponding database system.
Import and export: automatic detection of the first row as a header
When you open or import a CSV file, DataGrip automatically detects that the first row is the header and contains the names of the columns.

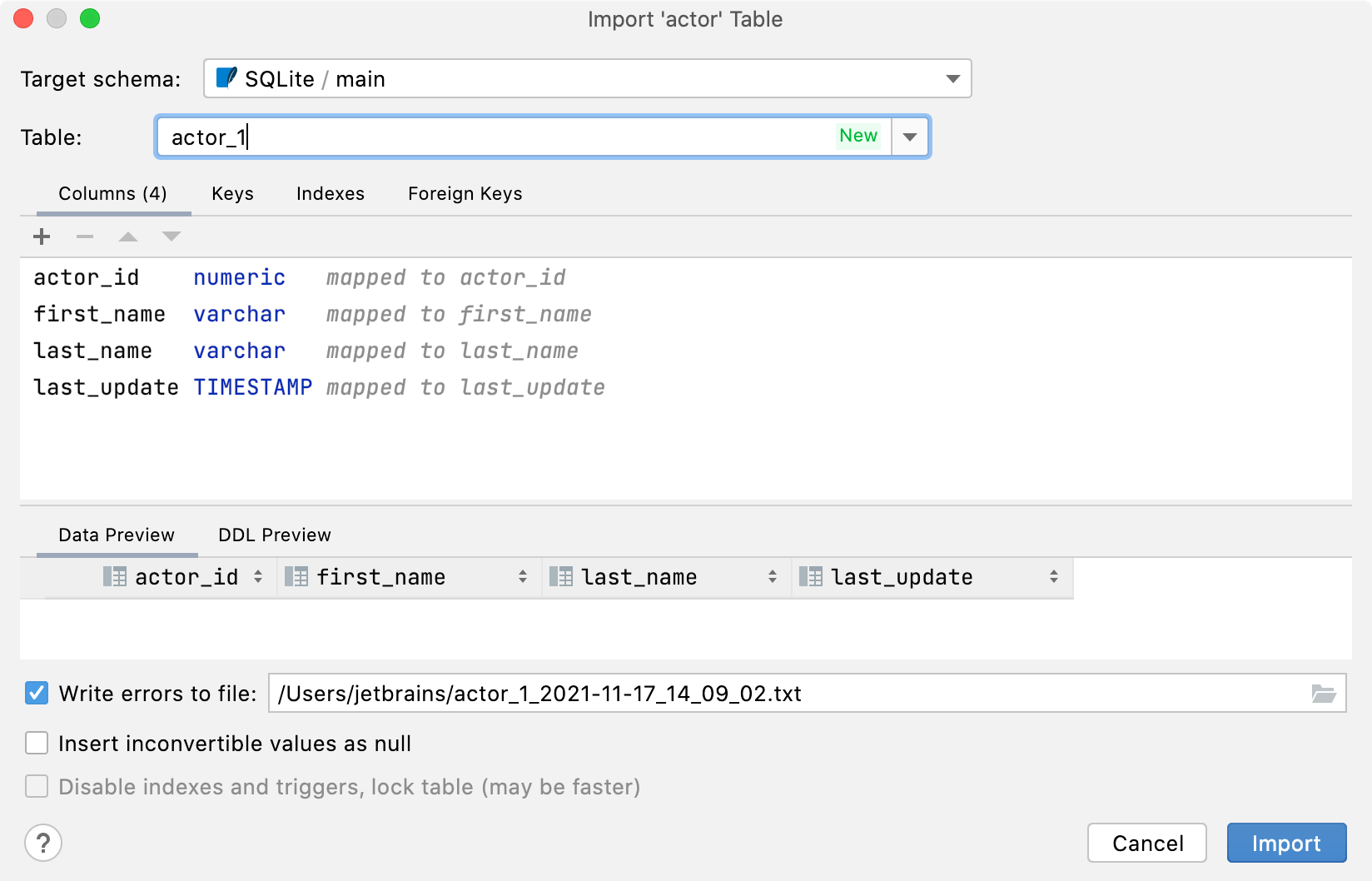
Import: new UI for importing data
The import dialog received the following improvements:
You can choose an existing table or create a new one.
You can change the target schema in the import dialog. The dedicated dialog for the target will not appear if you copy the table or the result set.
The target is saved as default per schema. So, if you are constantly copying from one particular schema to another, there will be no need to choose the target each time.
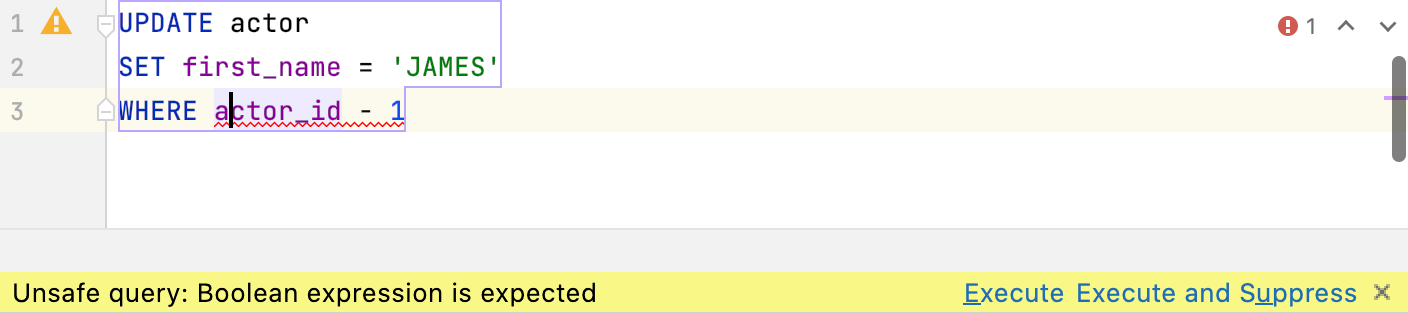
Inspections: check for boolean expressions
The inspection checks for boolean expressions in WHERE and HAVING clauses.
If the expression doesn’t seem to be explicitly boolean, we highlight it in yellow and warn you before you run such a query. It works for ClickHouse, Couchbase Query, IBM Db2 LUW, H2, Apache Hive, MySQL, MariaDB, Amazon Redshift, SQLite, and Vertica. In all other databases, this will be highlighted as an error.
Introspection: introspection levels for Oracle
We introduced three levels of introspection for Oracle databases.
Level 1: Names of all supported objects and their signatures, except names of index columns and names of private package variables.
Level 2: Everything except source code.
Level 3: Everything.
For more information about introspection levels, see .
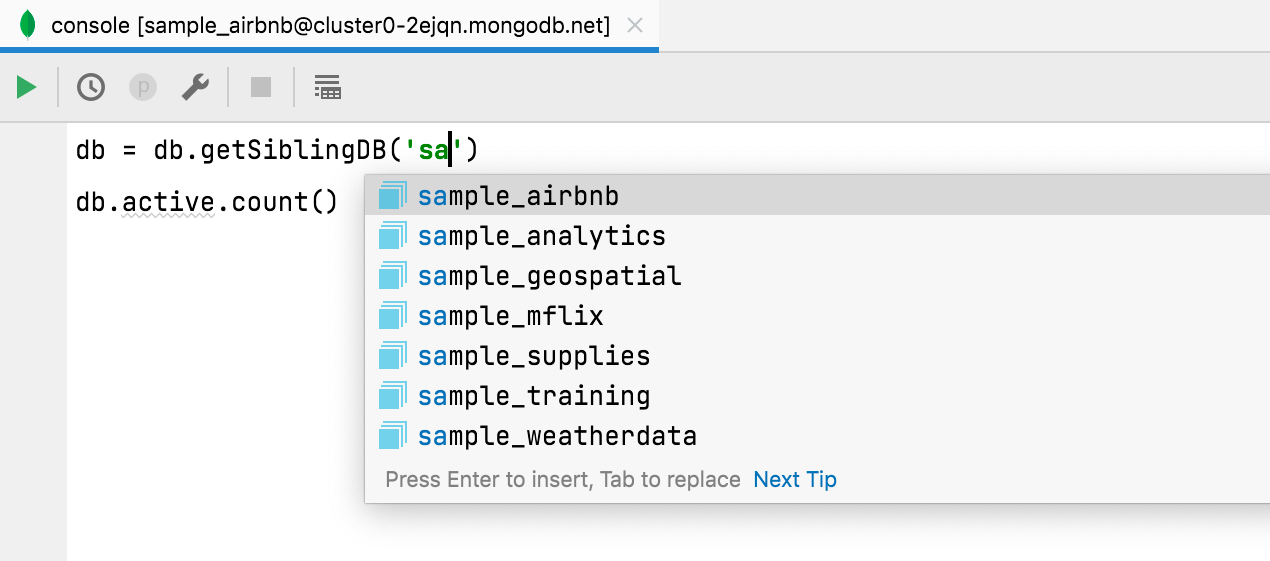
MongoDB: code completion for database names
Database names are completed when using getSiblingDB, and collection names are completed when using getCollection.
Additionally, field names are completed and resolved if used from a collection that was defined through code completion.
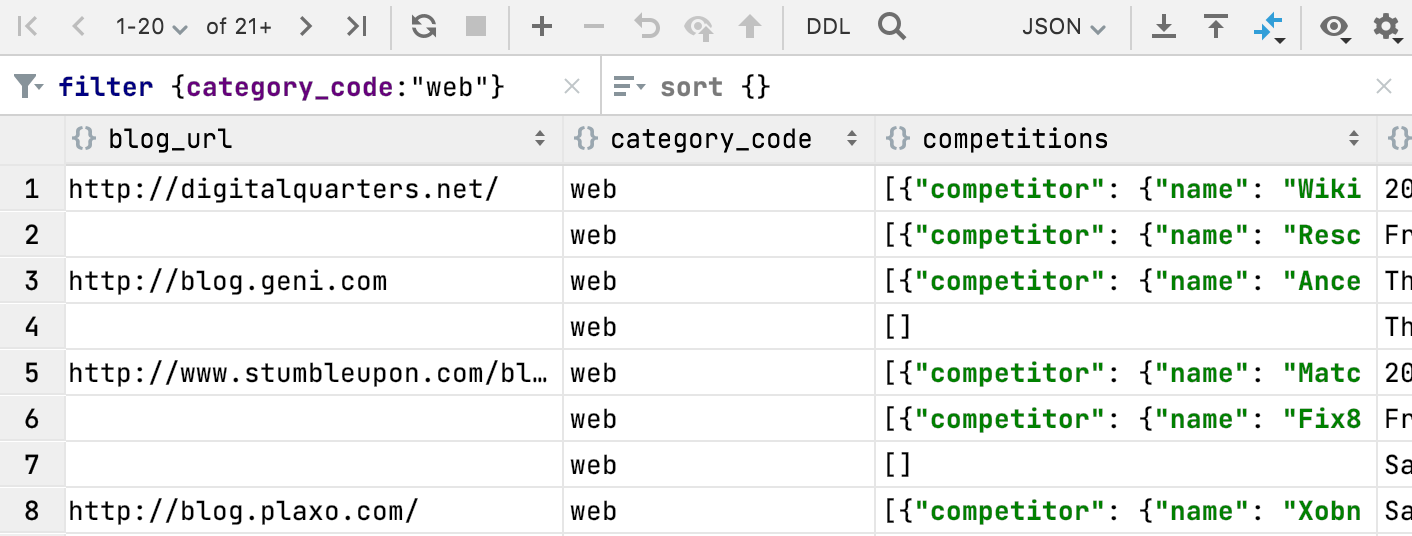
MongoDB: Completion for filter {} and sort {}
Code completion now works when you filter data in MongoDB collections.
Navigation: foreign key navigation by several values
In the data editor, you can now select several values and navigate to the related data.

Query console: timestamps in output hidden by default
Timestamps are no longer shown for query output by default. If you want to return to the previous behavior, open settings by pressing Ctrl+Alt+S and navigate to , select Show timestamp for query output.
Enabled | Disabled |
|---|---|
 |  |
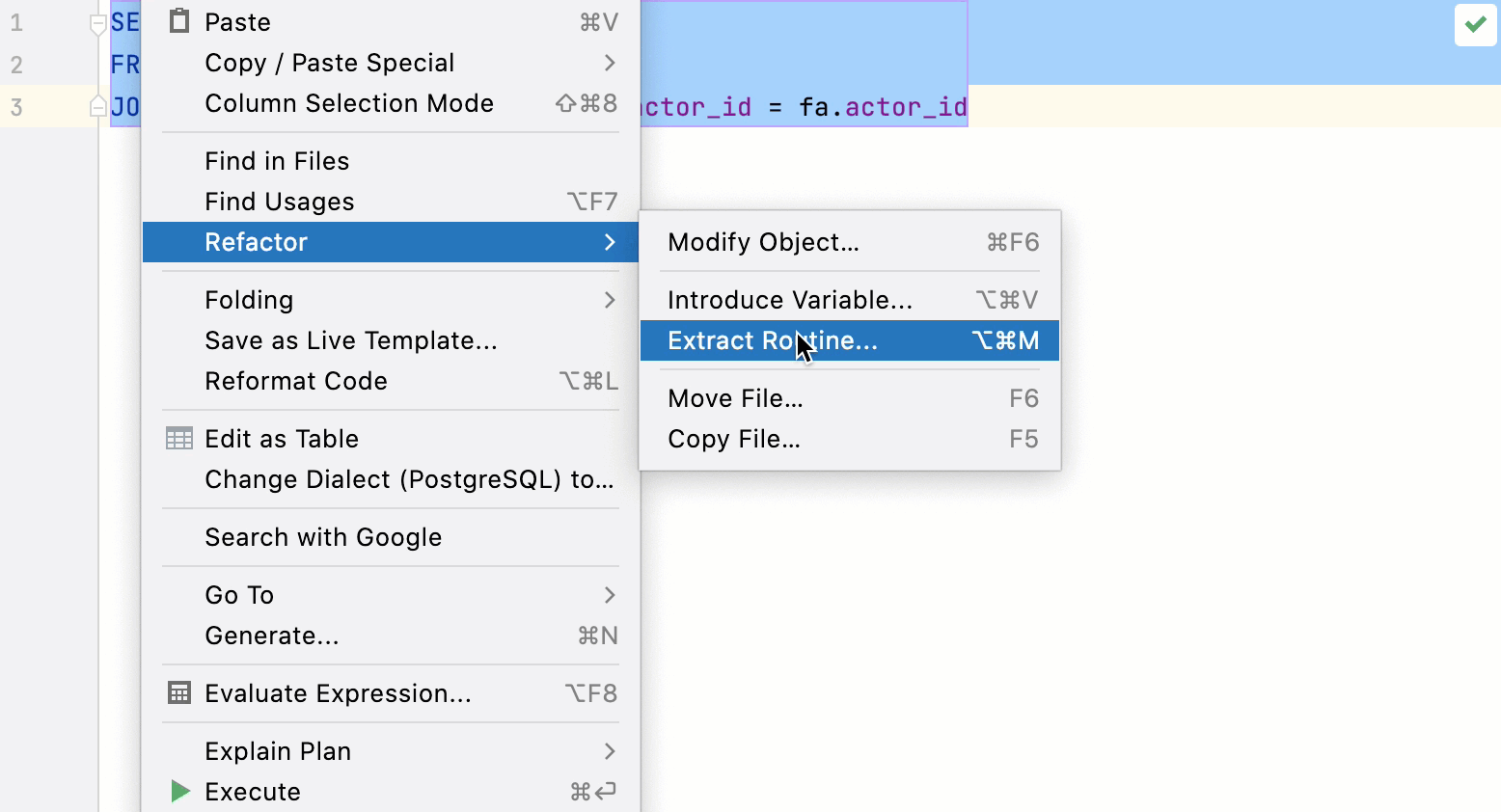
Refactorings: extract function for queries
You can extract queries as a table function. To do this, right-click a query and navigate to .
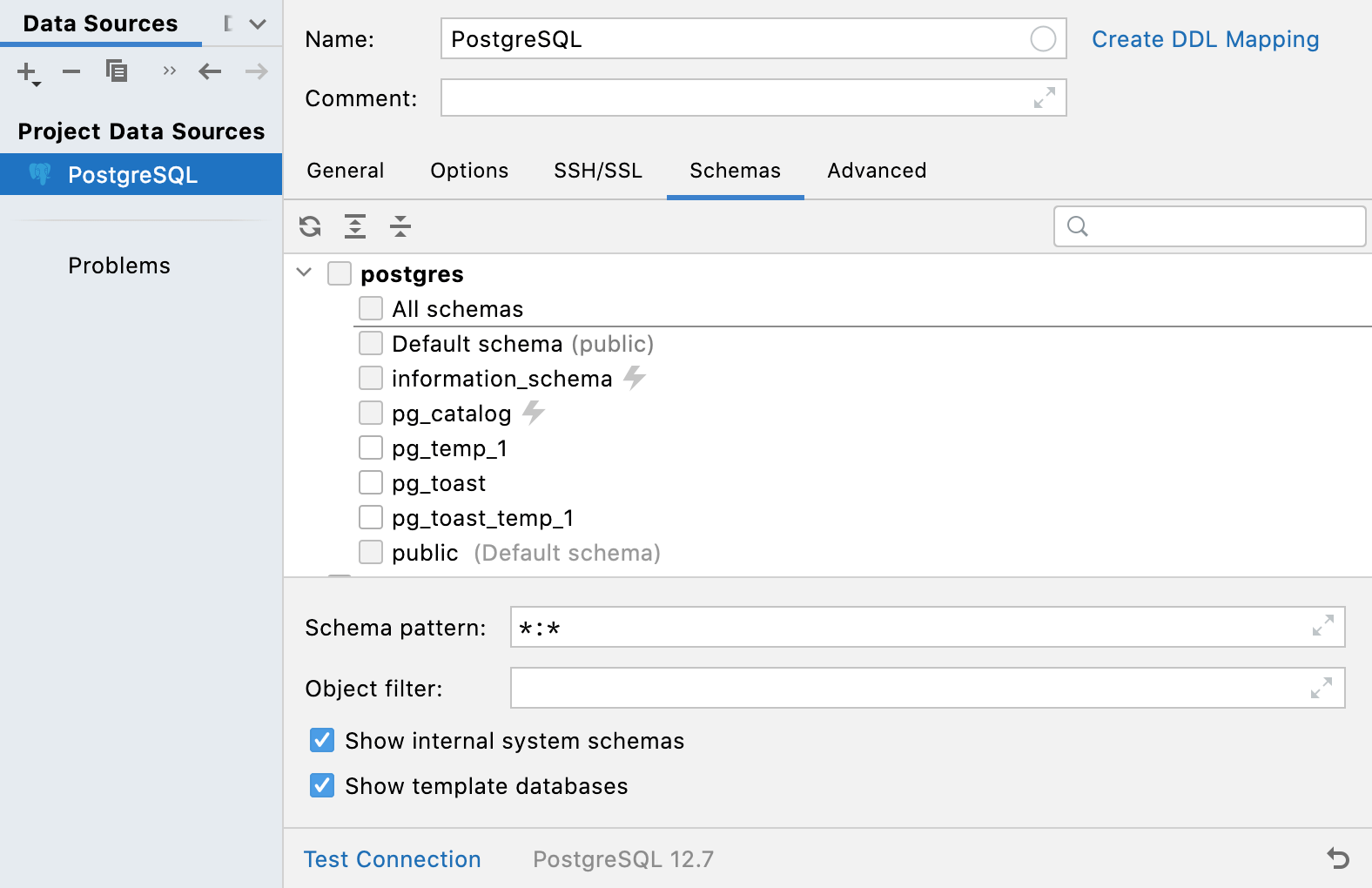
Schemas: ability to hide system schemas and template databases (PostgreSQL only)
Internal system schemas (like pg_toast or pg_temp) and template databases used to be hidden from the schemas list. It’s now possible to display them with the help of Show internal system schemas and Show template databases options on the Schemas tab. Options are available in PostgreSQL only.
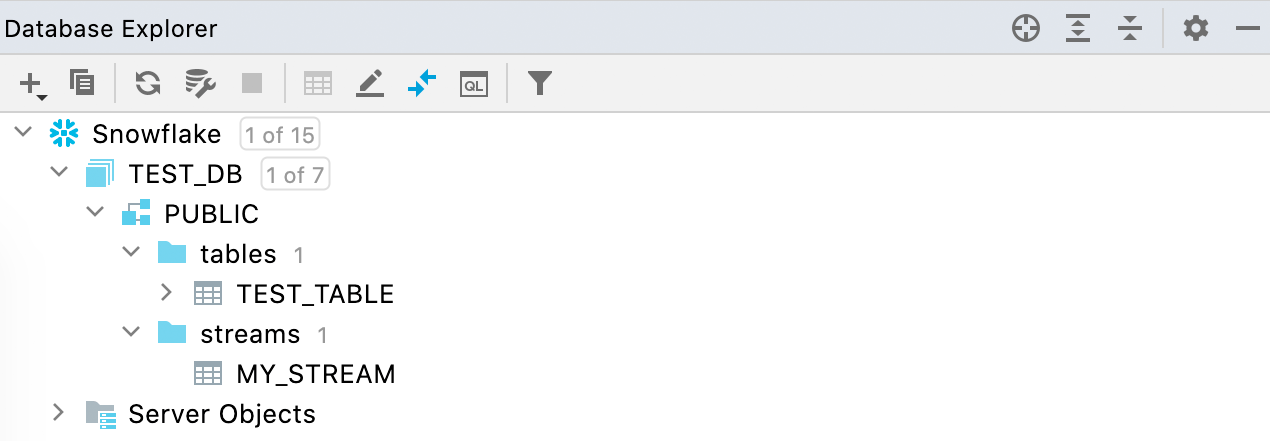
Snowflake: support for streams
Streams are displayed in the database explorer as well as tables and views.