Getting started with Rust
This tutorial helps you get started with Rust development in JetBrains Fleet. It covers installation, project setup, and working with Rust code.
Prerequisites
Download and install JetBrains Toolbox
Download and install JetBrains Toolbox.
For macOS, you can also download the installer that matches your processor type: Apple Silicon or Intel. Ensure you select the correct option based on your system's processor.
Download and install JetBrains Fleet
In JetBrains Toolbox, click Install next to the JetBrains Fleet icon.
Rust environment
Use instructions on the official Rust site to install and configure Rust.
Set up a workspace
A workspace is the directory that contains your project. It includes both project files and settings. You can either open an existing project or start a new one by opening an empty directory.
Open a workspace
Press ⌘ O or select File | Open from the main menu.
In the file browser, navigate to the folder containing your code and click Open.
Set up a workspace
A workspace is the directory that contains your project. It includes both project files and settings. You can either open an existing project or start a new one by opening an empty directory.
In this tutorial we will walk through project setup from scratch.
Open a workspace
Press ⌘ O or select File | Open from the main menu.
In the file browser, navigate to an empty folder where you want to store your code, then click Open.
When you open a directory, it becomes the root of a workspace. You can view its contents in the Files view.
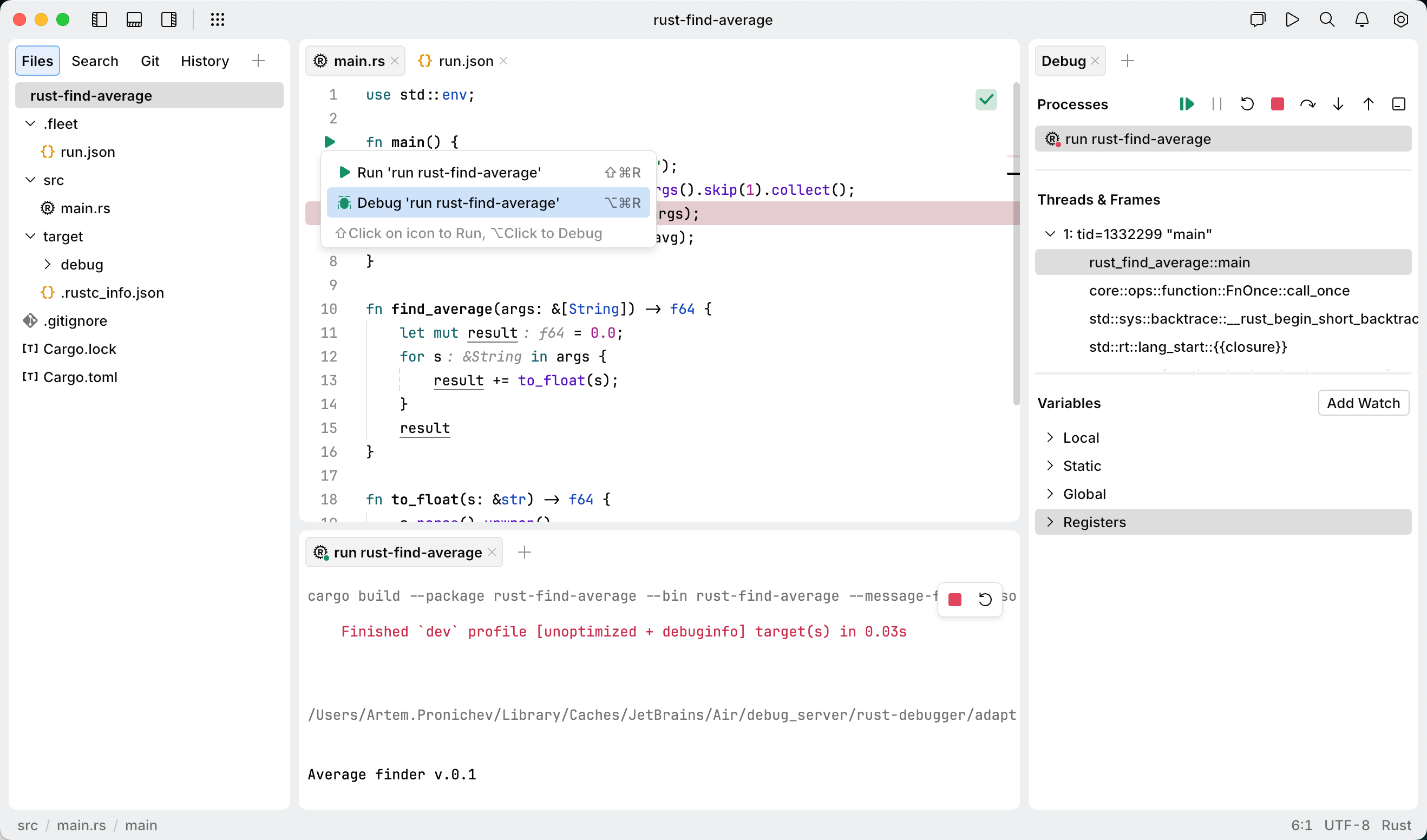
To start coding, create a project by using Cargo. Cargo is the build system and package manager for the Rust programming language. It provides a way to manage Rust projects, including building, testing, and managing dependencies.
Create project files
With your current workspace opened, click .
Run the following command in the command line:
cargo new find_averageNavigate to the main.rs file in find_average | src.
Open main.rs and replace code in the file with the following code:
use std::env; fn main() { println!("Average finder v.0.1"); let args: Vec<String> = env::args().skip(1).collect(); let avg = find_average(&args); println!("The average is {}", avg); } fn find_average(args: &[String]) -> f64 { let mut result = 0.0; for s in args { result += to_float(s); } result } fn to_float(s: &str) -> f64 { s.parse().unwrap() }
Smart Mode
You can use JetBrains Fleet as a smart text editor, rather than a full-fledged code editor. However, if you need code intelligence features, you can enable them by turning Smart Mode on.
Enable Smart Mode
In the top-right corner of the window, click Smart Mode, then Enable.
After you click the Enable button, you may have to wait for some time, while the backend is being prepared.
Running your code
With Smart Mode enabled and a configured Rust interpreter, you can run your project. You can use the gutter icon in the editor or create a run configuration to fine-tune how your application is executed.
Run from the editor
Navigate to the entry point of your application and click the run icon in the gutter. Select Run `configuration-name`.
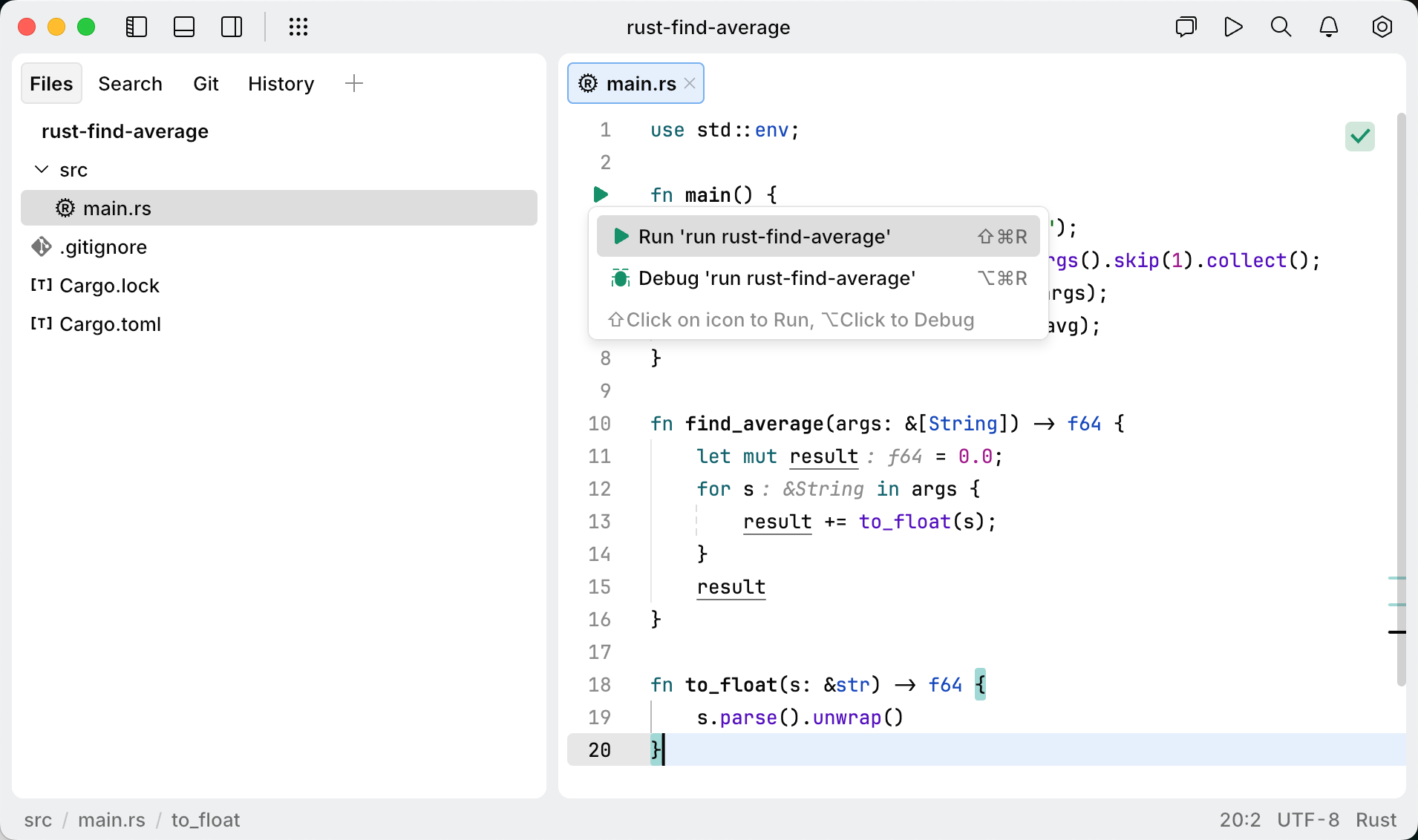
If you are going to pass parameters to your program or otherwise customize the startup of your program, use a run/debug configuration.
A run configuration defines the parameters for running your application. It can include commands, executable paths, environment variables, arguments, and other required context.
Creating run configurations
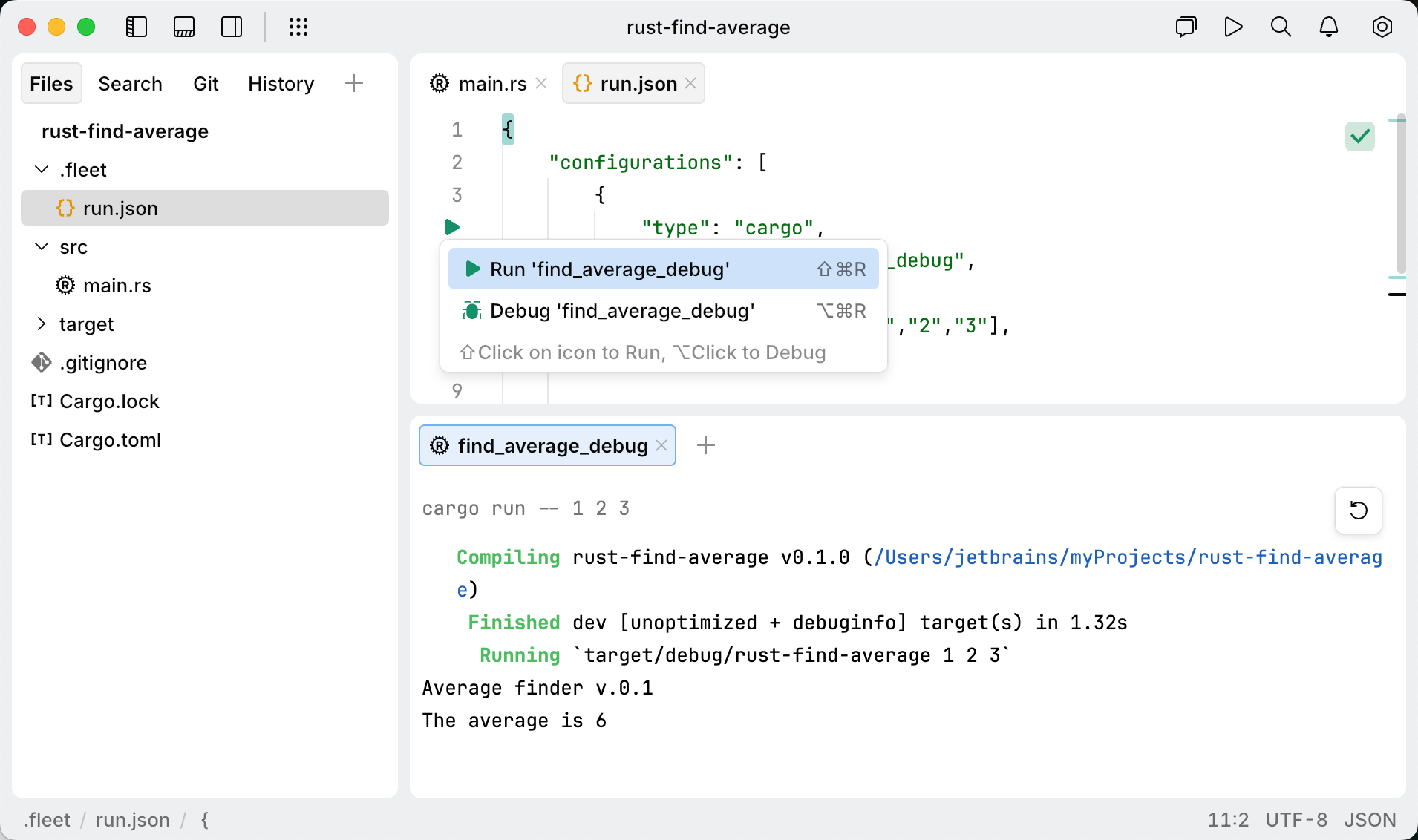
Click the Run icon (⌘ R) and select Create Run Configurations in run.json.
In the run.json file that opens, define running or debugging parameters. If the file is empty, press ⌥ ⏎ or click the file template link.
Alternatively, paste and edit the following code:
{ "configurations": [ { "type": "cargo", "name": "Rust configuration", "cargoArgs": ["run"], "executableArgs": ["1","2","3"], } ] }Modify the configuration properties according to your environment.
For more information about Rust run configurations in JetBrains Fleet, refer to Rust run configurations.
Press ⌘ R or select from the main menu. Select the configuration you want to run or debug.
Debugging your code
Broadly, debugging is the process of detecting and correcting errors in a program. You can run the debugging from the gutter of the editor or by using run.json. For a tutorial on debugging, refer to Debug Rust code.
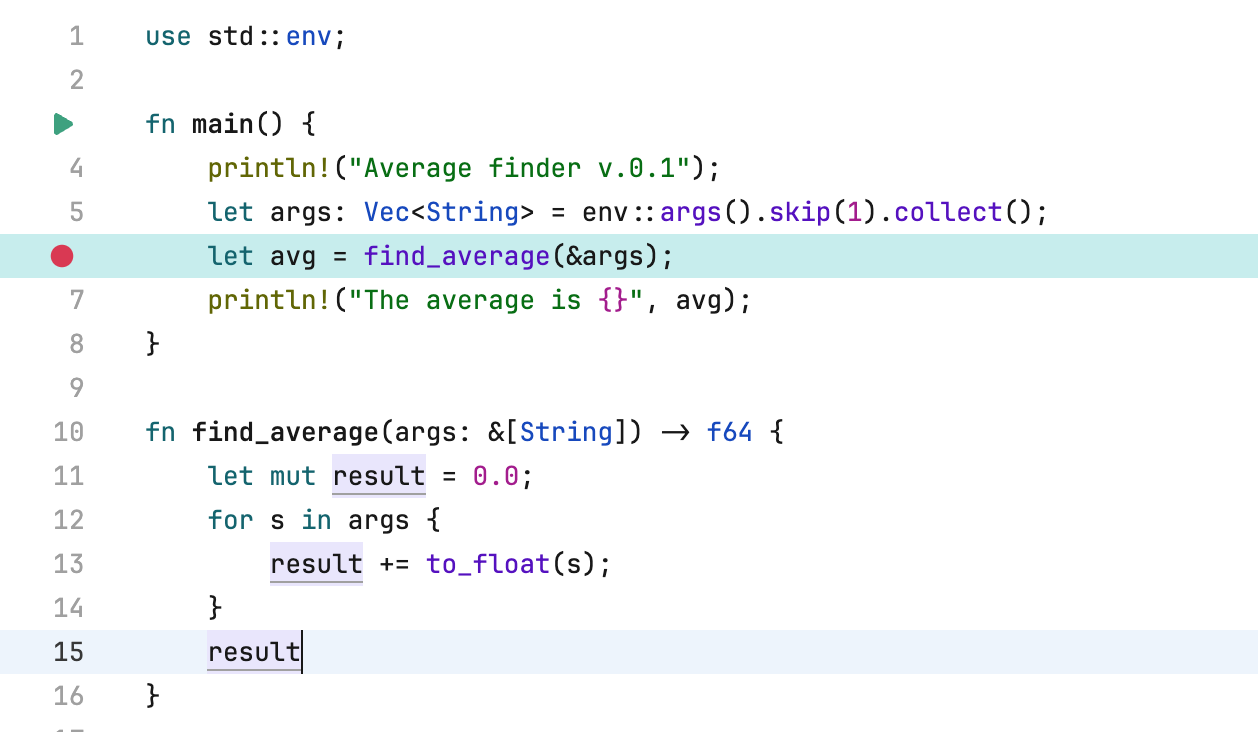
Each debugging process starts with setting a breakpoint.
Set a breakpoint
Click the gutter next to the line where you want to create a breakpoint.
Now we can proceed with debugging. As it was said, you can use the gutter icon or a run configuration.
Starting a debug session from the gutter
Click the Run icon on the gutter.
Select Debug `run find_average`.