Launch JetBrains Fleet from CLI
Some workflows require launching JetBrains Fleet from the command line. To support these scenarios, JetBrains Fleet provides several commands that you can use in a shell script or terminal.
Generate scripts
In JetBrains Toolbox, click Tool actions and select Settings.
Expand the Tools node.
Enable the Generate shell scripts option.
In the Shell scripts location field, specify a folder that is accessible via the
PATHenvironment variable.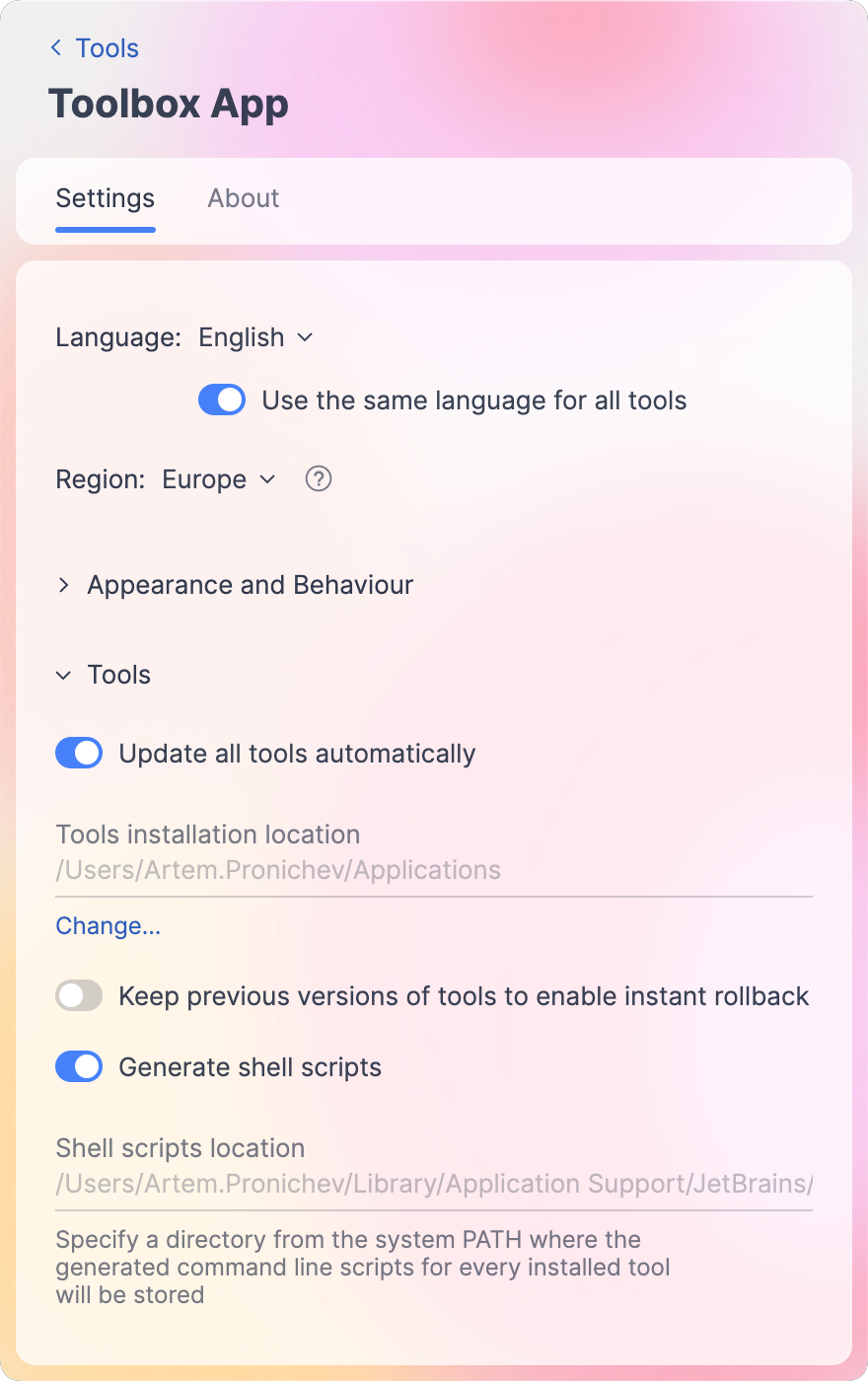
Configure a command name
In JetBrains Toolbox, click Tool actions and select Settings.
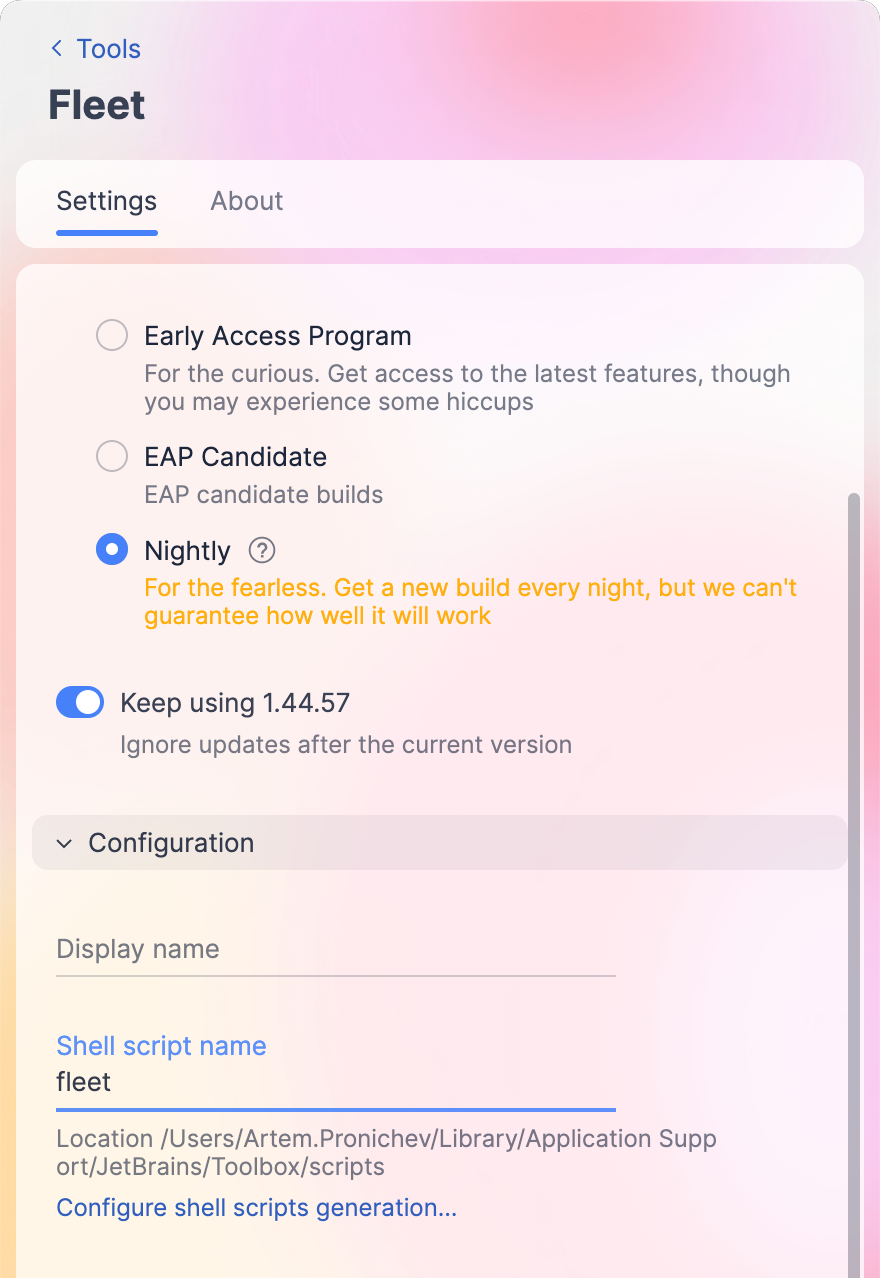
Expand the Configuration node.
Under Shell script name, specify the name for the command that launches JetBrains Fleet.
Launch JetBrains Fleet
The following commands launch a local instance of JetBrains Fleet.
fleet– launches JetBrains Fleet in its last saved state.fleet <dir-name>– opens the specified directory in JetBrains Fleet as a new workspace.fleet <file-name>– attaches the specified file to the open workspace. If no workspace is available, JetBrains Fleet creates a new one.fleet --goto=<file-name>:line[:column]– opens the specified file on a certain line and column.Examples:
fleet://fleet.ssh/<hostname>?<query_params>: connect to SSH using a URI handler. For more information, refer to Connecting to SSH with JetBrains Fleet URI handler.fleet my/dir --goto=my/file:10: opens ./my/dir and ./my/file on line 10.fleet -- --goto=my/file:10: opens .my/file on line 10.fleet -- --goto=my/file:10:5: opens .my/file on line 10 and column 5.fleet -- --goto=my/file:10 --goto=my/file2:5:2: opens .my/file on line 10 and ./my/file2 on line 5 and column 2.fleet my/file/without/col/line:5 --goto=my/file:10: opens ./my/file/without/col/line:5 on line 5 and column 1 and .my/file on line 10.
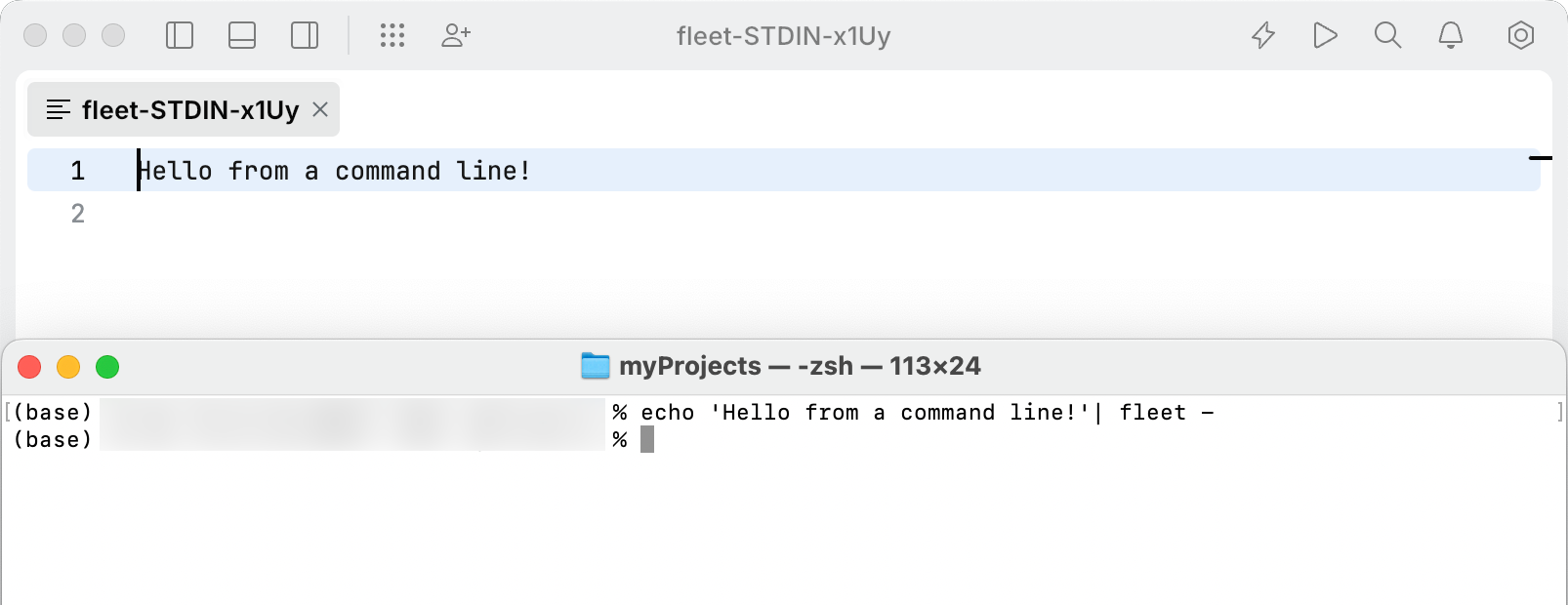
Direct the standard output (stdout) of a command line into JetBrains Fleet
Run a command in your terminal and append
| fleet -to the command. For example:echo 'Hello from a command line!'| fleet - dir | fleet - ./test_script.sh | fleet -Fleet will create a new scratch document to display the output. The document will have an automatically generated filename.
Options
The table below provides the summary for the options that you can use with the fleet command.
-d | Enables logging of debug messages in the launcher. For logging of debug messages in JetBrains Fleet itself, use the |
-h | Provides the reference for the available options and flags. |
--wait | Continues execution in the command line until the specified task (for example, starting a server or editing a file) is finished. 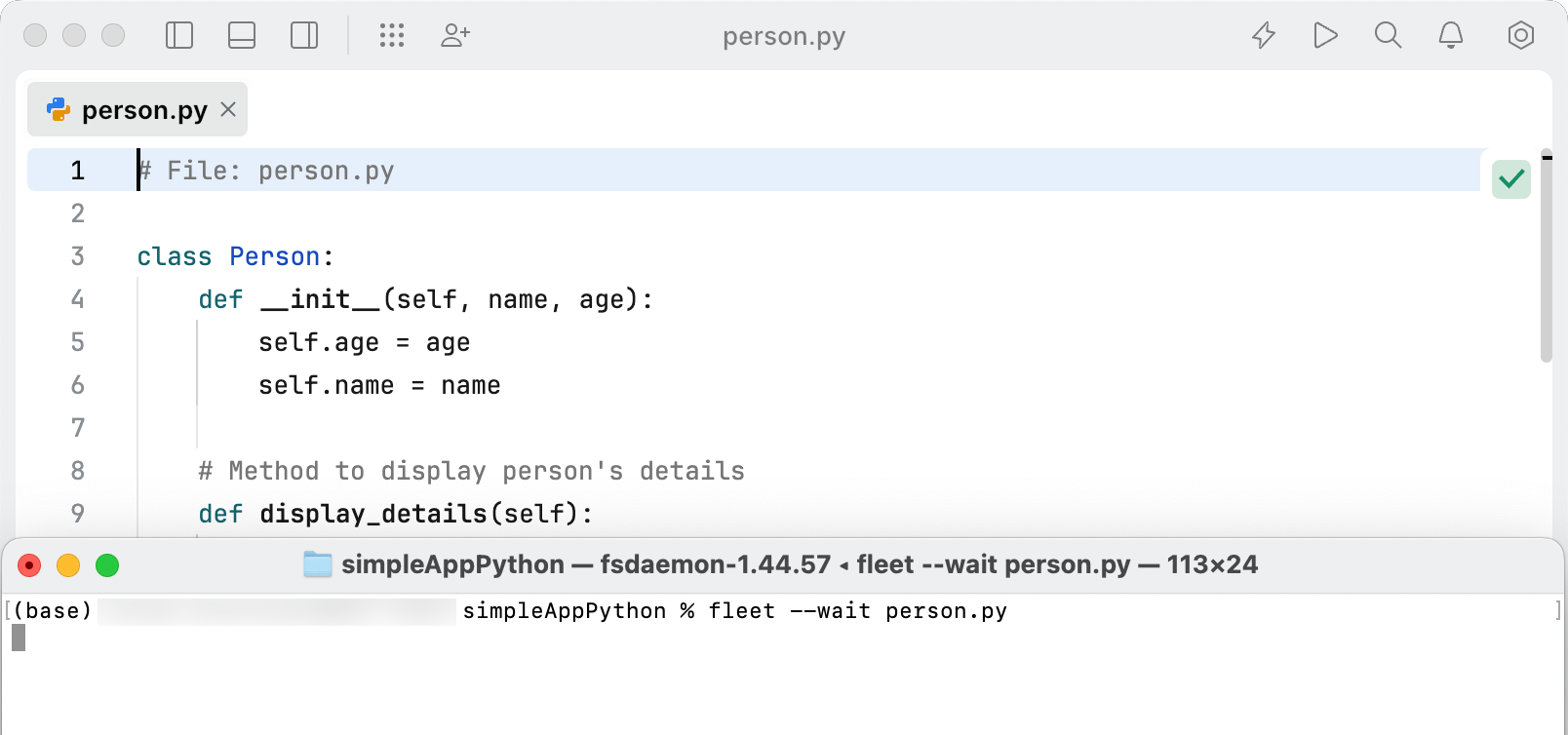 |
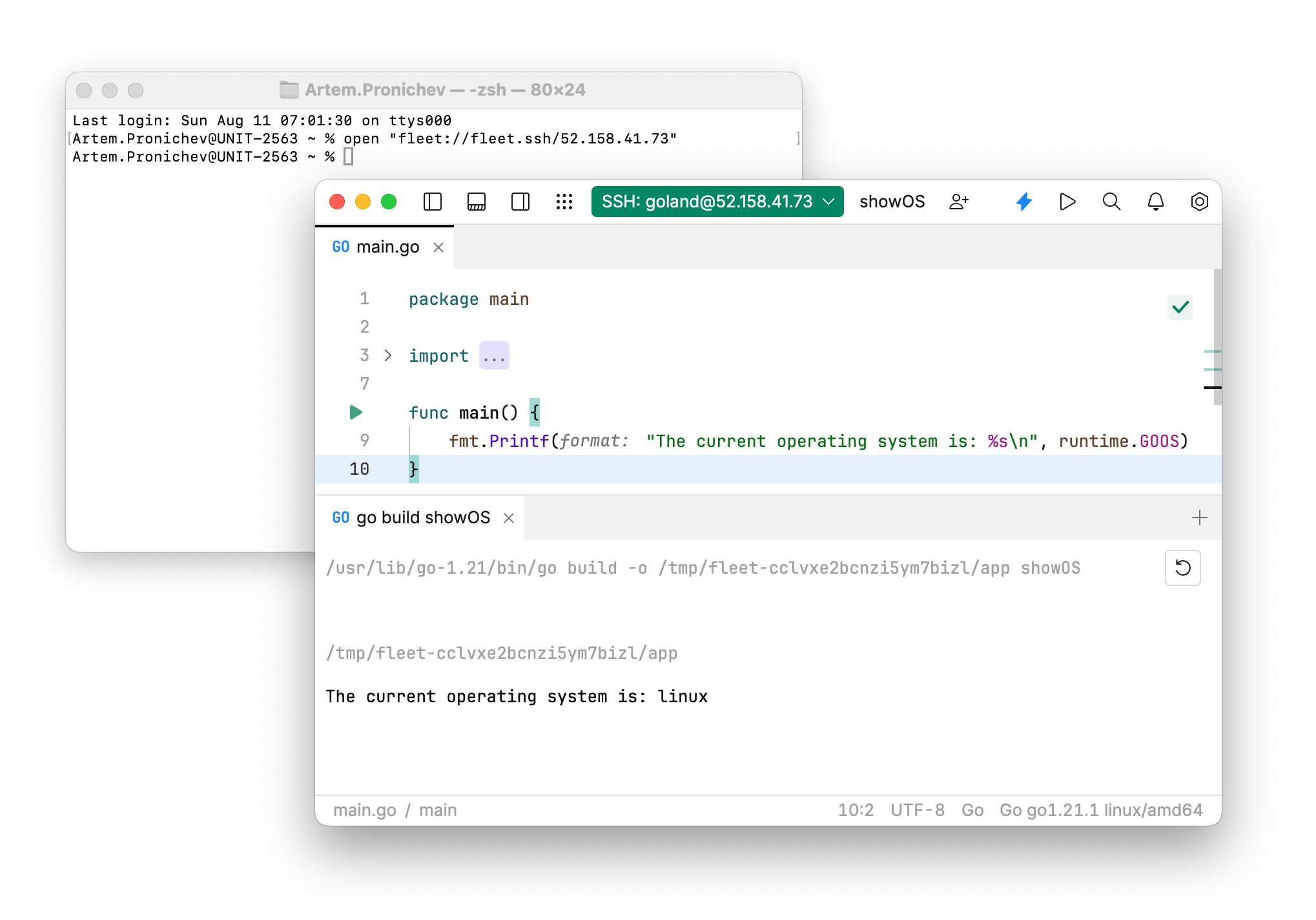
Connecting to SSH with JetBrains Fleet URI handler
JetBrains Fleet supports direct connections to SSH using a URI handler. This allows you to connect to remote hosts from the command line using a streamlined URI format.
The URI format for connecting to SSH with JetBrains Fleet is:
On macOS, the format is the following:
Parameters
You can use the following parameters within the URI to customize your connection:
hostname(required): The address of the remote host you wish to connect to.username(optional): The username for the SSH connection. You can also specify this as part of the hostname using the SSH URI syntax:<username>@<hostname>.port(optional): The port number for the SSH connection. You can also specify this alongside the hostname using the SSH URI syntax:<hostname>:<port>.pwd(optional): The working directory to open on the remote host. If not specified, JetBrains Fleet will open an empty workspace on the host.forceNewHost(optional): A boolean value (trueorfalse). The default isfalse. Setting this totruewill force JetBrains Fleet to ignore previous known hosts and establish a new connection each time.
SSH URI syntax
You can specify the username and port using the common SSH URI syntax directly in the hostname section of the URI. For example:
On macOS, the format is the following:
Default behavior
If some parameters are not specified, JetBrains Fleet will attempt to use the closest known match from previous connections or revert to default values. The .ssh/config file is considered when connecting.
If you do not specify pwd, JetBrains Fleet will open an empty workspace on the host.
Examples
Below are examples demonstrating how to use the JetBrains Fleet URI handler to connect to SSH hosts:
Connecting with a username and working directory:
fleet://fleet.ssh/example.org?username=foo&pwd=/home/foo/my_test_projectThis example connects to
example.orgwith the usernamefooand opens the/home/foo/my_test_projectdirectory.Connecting with a username in the hostname:
fleet://fleet.ssh/foo@example.org?pwd=/home/foo/my_test_projectThis connects to
example.orgwith the usernamefooand sets the working directory to/home/foo/my_test_project.
Additional notes
Only the
hostnameparameter is required. Other parameters are optional but can enhance the connection experience by pre-configuring specific settings.Always ensure that URIs are properly formatted to prevent connection issues.
When using
forceNewHost=true, note that this will override any existing known host configurations, forcing a fresh connection setup each time.