Connection to a database
Enable the Database Tools and SQL plugin
This functionality relies on the Database Tools and SQL plugin, which is bundled and enabled in IntelliJ IDEA by default. If the relevant features are not available, make sure that you did not disable the plugin.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Open the Installed tab, find the Database Tools and SQL plugin, and select the checkbox next to the plugin name.
This topic gives you an overview of how the connection to a database works in IntelliJ IDEA. For more information about features and concepts, refer to the dedicated topics.
Data source
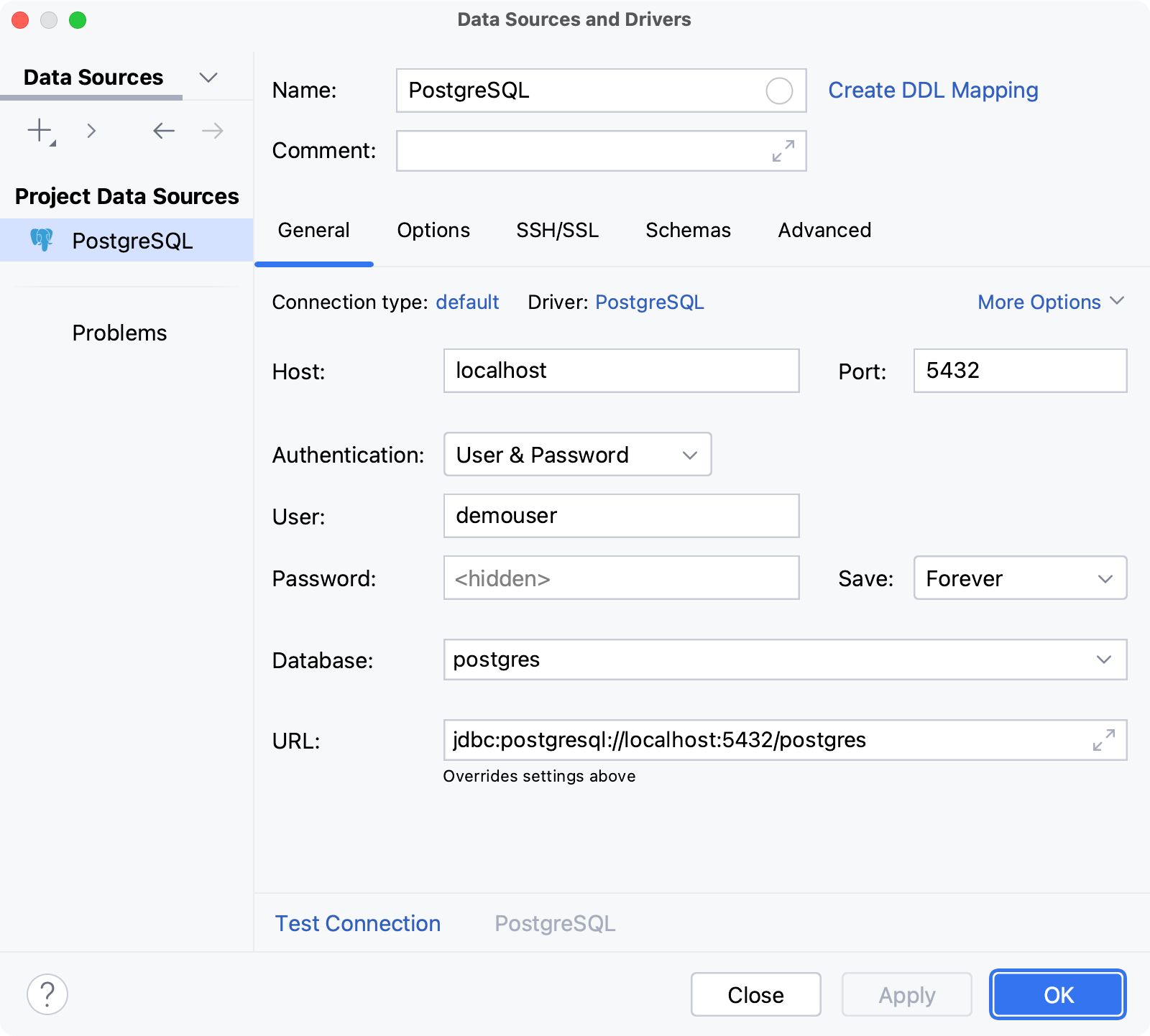
To connect to a database, IntelliJ IDEA requires connection details (for example, host, port, password, SSH configuration settings, and so on). For every database, the connection details are stored in a dedicated connection configuration — data source.
Below is an example of the PostgreSQL data source settings in the Data Sources and Drivers dialog ( Shift+Enter) . For information about dialog fields, refer to the dialog reference topic and data source creation instructions.
Session
For a data source, connections to the database are established in special wrappers – sessions. Each session is a wrapper over a single connection, and it stores the connection's information (for example, whether it is active or not, transaction control mode, and other settings).
Sessions can have clients – files, whose queries are sent by using the connection that the session holds. Data editor can also be a client for a session.
Depending on the way you create a new session, it can be connected either automatically or after a certain action. The green dot in the corner of a session's icon indicates the connected status.
You can create a new session by doing either of the following:
Open a query console, view database object's data in data editor, or attach an SQL file to a data source.
As a result, under the data source node in the Services tool window, the new session node appears with a client node under it.
For a query console, the session will be connected once you perform an action that requires interaction with the database. For example, once you run a query.
For a table, the session is connected automatically, as IntelliJ IDEA requires an active connection to request the table data from the database, receive it, and display it in the data editor.
For an SQL file, the session is connected automatically. To run queries against either of the data source databases or schemas, you have to attach your file to them by selecting them in the <schema> list.
Perform an action that requires interaction with the database. For example, run a stored procedure or run a script by using run configurations.
As a result, the new connected session node appears under the data source node in the Services tool window.